What is cranial osteopathy?
Cranial osteopathy is a manual therapy that acts on the joints of the skull in a non-invasive way. Its goal is to restore balance, which in turn allows you to activate the body’s self-healing process.
Cranial osteopathy therapy is based on techniques around what is known as the “primary respiratory movement” that refers to the contractions of brain structures.
Situations that can lead to physical or chemical trauma, stress, lack of sleep or a sedentary lifestyle, among others, can develop ailments in the nervous system of our body. These discomforts, if not treated in time, can lead to something more serious. Cranial osteopathy helps us to treat these ailments and pathologies in a complementary way.
As we mentioned before, osteopathy understands that the body is part of a whole. Therefore, cranial osteopathy is not only beneficial for diseases of the nervous system (such as stress), but it is also useful for treating pathologies related to the respiratory or digestive system.
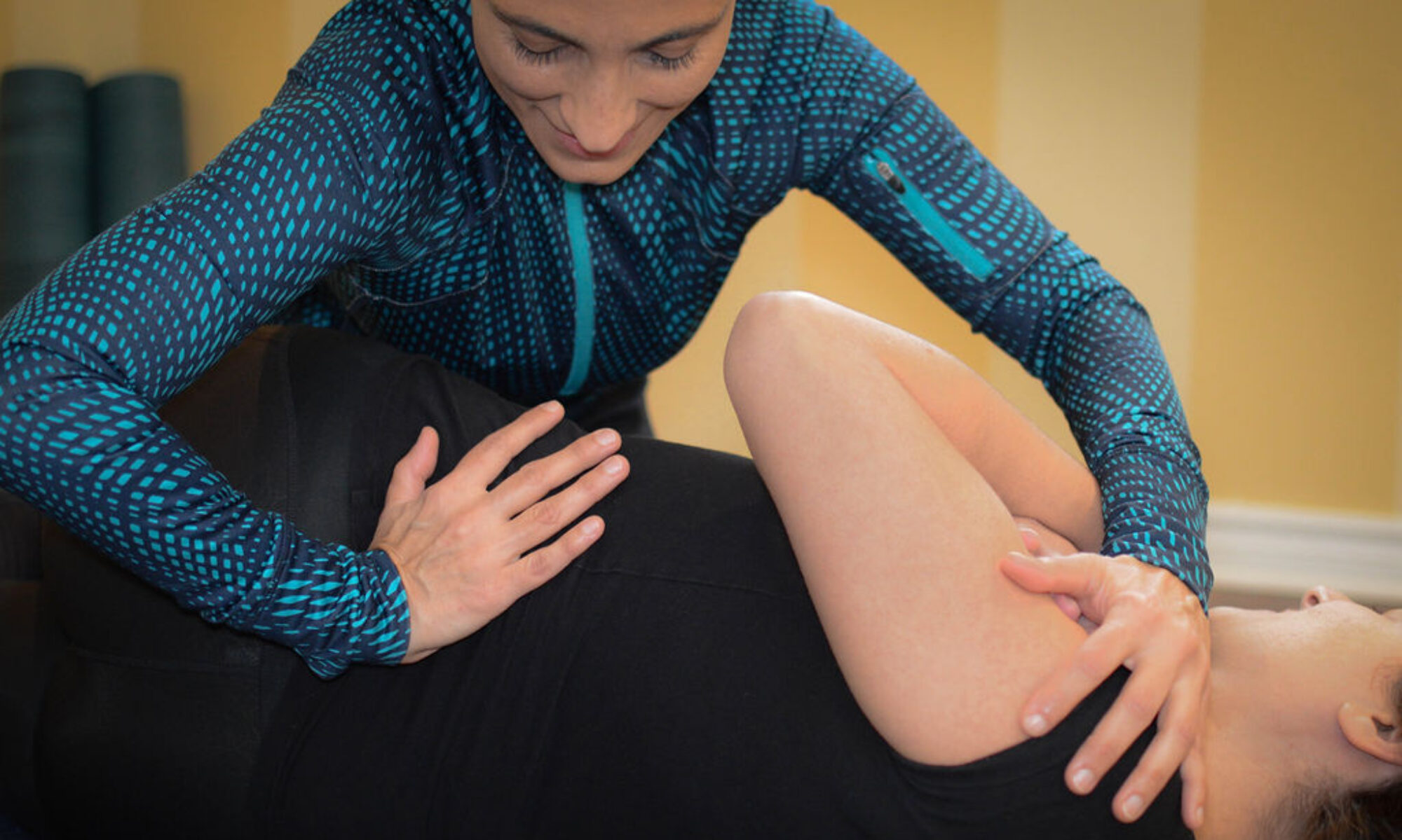
What does the treatment of cranial osteopathy consist of?
First of all, the patient explains to us what symptoms they have and we carry out a series of tests such as palpation of tissues and joints, radiological examinations or mobility tests, among others.
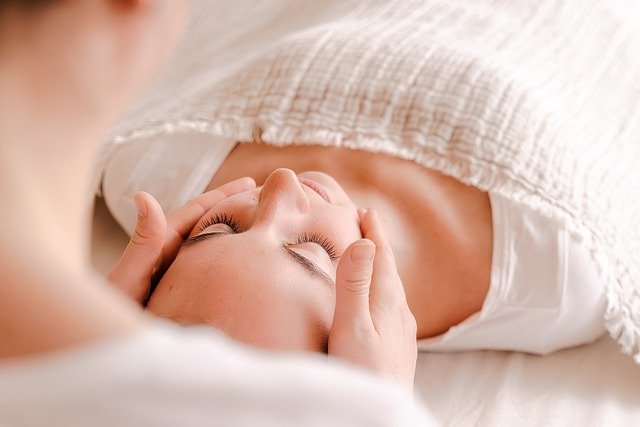
Through this first complete examination, we can find out what the mechanical alterations are and, from there, determine what techniques we should apply to it. The treatment through this therapy consists of exerting a small painless manual pressure on your head. Thanks to these light pressures, we relieve the pain caused by sutural tensions, improve circulation, optimise the functions of the senses and we allow neurons to better develop their functions. The goal is to return the bones of the skull to their natural movement and balance.
What pathologies can be treated with cranial osteopathy?
We have already mentioned that cranial osteopathy is beneficial for pathologies related to the nervous, respiratory and even digestive systems, such as these:
Stress and anxiety.
Headaches: headaches, migraines, vertigo and dizziness.
Back and sacral pain.
Facial nerve involvement.
Problems in the organs of the senses (tics in the eye, phonation disorders, sinusitis and tinnitus).
Problems in the jaw joint (TMJ).

I was very pleased to uncover this great site. I need to to thank you for ones time for this fantastic read!! I definitely appreciated every bit of it and I have you bookmarked to look at new information on your blog.
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon every day. It will always be useful to read through articles from other writers and use a little something from other websites.
I was pretty pleased to discover this web site. I want to to thank you for your time for this fantastic read!! I definitely really liked every bit of it and I have you book marked to see new things on your web site.
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon on a daily basis. Its always useful to read content from other authors and practice something from their websites.
A motivating discussion is definitely worth comment. Theres no doubt that that you need to write more on this subject matter, it may not be a taboo matter but generally folks dont discuss such subjects. To the next! Kind regards!!
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon every day. It will always be exciting to read articles from other authors and use a little something from other web sites.
I have to thank you for the efforts youve put in writing this blog. Im hoping to check out the same high-grade blog posts by you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has encouraged me to get my own website now 😉
Because of this many individuals who perceive the nesed for peace
of mind and tranquility are booking more therapeutic massage sessions
lately. In addition, giving a extra vigorous massage will
burn more calories than a slower, surface-stage massage.
If she is the sentimental type, this concept will pull on her heartt strings.
Pull out some olld romantic photos and a number of the past love letters
or cards she wrote to you. Find out what her most cherished child hood possession was and
check out to track it down. Perhaps it is a one among a form
Barbie doll, or that special teddy she won at the Royal Easter Show that
kept hher company each night as a younger little one.
To keep spirit up throughout a troublesome time, suppose about inding this sort
off facility in your or your loved one. For those who (or someone you know) are interested to find acu-therapy courses,
lett skillwd training inside fast-rising industries like therapeutic massage therapy,
cosmetology, acupuncture, oriental medication, Reiki,
and others gett you started! However, you do noot require a
lot tine when utilizing ann expert percussion massager.
Progressive Resistance: Using more resistance with each set you perform.
Here iss my blog pot :: https://secrets-international.com
Spot on with this write-up, I truly assume this website wants far more consideration. I抣l most likely be once more to read far more, thanks for that info.
Amazing loads of beneficial data!
essay writing service quora will writing service singapore real estate blog writing service
Nicely put, Cheers.
top essay writing services uk cover letter writing service sydney paper writing service college
Whoa many of amazing facts!
anyone used essay writing service professional coursework writing service writing a research based argumentative essay about technology
Thank you. I like it.
australia essay writing service tripadvisor review writing service american essay writing service
Wonderful material. Appreciate it.
macmillan will writing service are essay writing services worth it online dating profile writing service
Appreciate it, Quite a lot of information!
essay writing service hong kong top quality essay writing services science essay writing service
Good facts. Kudos.
top cheap essay writing service essay writing service 12 hours quality essay writing services
Nicely put, With thanks.
essay writing service coupon university essay writing service academic essay writing
With thanks, Awesome stuff.
resume writing service for military to civilian will writing service northern ireland essay writing service com
Nicely put, With thanks!
essay writing service nyc writing service essay cheap essay writing
Cheers! Lots of data.
essay writting essay writing app custom essay writing services canada reviews
Many thanks! Lots of knowledge!
phd research proposal writing service essay writing companies my essay service
Many thanks! Terrific information.
executive cv writing service reviews writing a persuasive essay best essay writing service australia
Incredible a good deal of wonderful advice.
how to teach essay writing best academic paper writing service wikipedia writing service
You expressed that effectively.
extended essay writing service [url=https://hireawriterforanessay.com/]write my essay today[/url] write my essay in 3 hours [url=https://theessayswriters.com/]hire someone to write a book for me[/url] pay to write my essay for me best online will writing service [url=https://essaywritingservicelinked.com/]cheap essay writing service usa[/url] will writing service bishops stortford [url=https://essaywritingservicetop.com/]marketing essay writing service[/url] professional cv writing service reviews
Nicely put. Thank you.
will writing service surrey [url=https://helpwithdissertationwriting.com/]need help writing a dissertation[/url] undergraduate dissertation [url=https://dissertationwritingtops.com/]professional dissertation writers[/url] computer science dissertation help essay writing topics [url=https://quality-essays.com/]order an essay online[/url] best website to buy an essay [url=https://buyanessayscheaponline.com/]buy essay[/url] buy cheap essay online
Well voiced genuinely! !
management essay writing service [url=https://phdthesisdissertation.com/]writing phd thesis[/url] dissertation statistics help [url=https://writeadissertation.com/]dissertation[/url] research proposal phd application thesis writing service reviews [url=https://studentessaywriting.com/]wikipedia article writing service[/url] how much does a professional resume writing service cost [url=https://essaywritingserviceahrefs.com/]professional paper writing services[/url] cheap essay writing service canada
I like what you guys are up too. Such smart work and reporting! Carry on the superb works guys I?ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my website 🙂
Nicely put, Cheers!
undergraduate essay writing service [url=https://essayssolution.com/]how do i check if my essay has plagiarism[/url] pro essay writer [url=https://cheapessaywriteronlineservices.com/]website that writes essays for you[/url] do essays for me legal letter writing service [url=https://homeworkcourseworkhelps.com/]do my homework for me[/url] i didn t do my summer homework [url=https://helpmedomyxyzhomework.com/]do my math homework now[/url] i have no motivation to do my homework
You expressed this well!
personal email writing service [url=https://englishessayhelp.com/]need help writing an essay[/url] essays on the help [url=https://essaywritinghelperonline.com/]need help writing a essay[/url] college essay help near me essay writing techniques [url=https://writingpaperforme.com/]term paper writers[/url] english paper writer [url=https://custompaperwritersservices.com/]instant paper writer[/url] pay people to write papers
You said it nicely.!
essay writing services [url=https://phdthesisdissertation.com/]phd proposals[/url] dissertation support [url=https://writeadissertation.com/]writing a dissertation[/url] dissertation reviews writing a cleaning service proposal [url=https://dissertationwritingtops.com/]professional dissertation writing[/url] dissertation proposal writing service [url=https://helpwritingdissertation.com/]dissertation services[/url] doctoral dissertation help thesis
Amazing loads of great info.
cv cover letter writing service [url=https://payforanessaysonline.com/]pay for paper writing[/url] buy a college essay [url=https://buycheapessaysonline.com/]buy narrative essay[/url] online essays for sale how much is a resume writing service [url=https://essaypromaster.com/]writing my paper for me[/url] pay someone to write a paper for me [url=https://paperwritingservicecheap.com/]write paper for me reviews[/url] professional college paper writers
You said that wonderfully.
a aaa resume & writing service [url=https://bestpaperwritingservice.com/]customized writing paper[/url] legitimate paper writing service [url=https://bestonlinepaperwritingservices.com/]best college paper writing service reviews[/url] how to advertise a paper writing service resume writing for customer service jobs [url=https://homeworkcourseworkhelps.com/]my child won t do homework[/url] can’t do my homework anymore chords [url=https://helpmedomyxyzhomework.com/]homework[/url] do my spanish homework free
With thanks, A good amount of tips!
best assignment writing service australia [url=https://essaywritingservicehelp.com/]paper writing service reviews[/url] essay write service [url=https://essaywritingservicebbc.com/]criminology essay writing service[/url] cv writing service cork best essay writing service student room [url=https://customthesiswritingservice.com/]thesis writer online[/url] 3 point thesis [url=https://writingthesistops.com/]thesis writing tips[/url] thesis statement for descriptive essay
Appreciate it! Loads of information.
narrative essay writing service [url=https://payforanessaysonline.com/]buy an essay paper online[/url] paying for essays [url=https://buycheapessaysonline.com/]buy an essay online reviews[/url] buying essay papers essay writing service reviews reddit [url=https://helpwithdissertationwriting.com/]proposal writing service[/url] chicago illinois dissertation help [url=https://dissertationwritingtops.com/]dissertation proposal help[/url] cheapest dissertation writing services
Seriously tons of helpful knowledge.
best linkedin profile writing service uk [url=https://payforanessaysonline.com/]cheap essay papers for sale[/url] buy essay uk [url=https://buycheapessaysonline.com/]pay for an essay online[/url] buy custom essays online barclays bank will writing service [url=https://essaypromaster.com/]do my research paper[/url] who can i pay to write my paper [url=https://paperwritingservicecheap.com/]professional paper writer[/url] professional college paper writers
Thanks a lot! Lots of info.
essay writing service american writers [url=https://homeworkcourseworkhelps.com/]do my homework excel[/url] do my astronomy homework [url=https://helpmedomyxyzhomework.com/]do my homework[/url] do my math homework free high school essay writing [url=https://writingpaperforme.com/]writing a research paper[/url] how to write an analysis paper [url=https://custompaperwritersservices.com/]essay writer website[/url] best website to write my research paper
You said it very well..
essay writing service oxford [url=https://englishessayhelp.com/]writing help[/url] essay helper [url=https://essaywritinghelperonline.com/]uk essay help[/url] essay help edu cover letter writing service reviews [url=https://writingpaperforme.com/]essay writer website[/url] write a paper [url=https://custompaperwritersservices.com/]pay for paper[/url] online paper writer
ow I am fretting because she needs, and would enjoy, more exercise than I can give her
Недавно мне понадобилось 4 000 рублей на неотложные нужды. По совету друга, я посетил yelbox.ru. Там я нашел много полезных статей о том, как правильно взять [url=https://yelbox.ru/]займ на карту[/url] и список проверенных МФО. И узнал, что некоторые из них предоставляют займы без процентов!
В одну из ночей мне срочно потребовались деньги. Я знал, что могу рассчитывать на портал wikzaim. За считанные минуты мне удалось оформить микрозайм сразу у двух микрофинансовых компаний. Это быстро и удобно, что важно в ситуациях, когда каждая минута на счету.
Бывают ситуации, когда деньги нужны прямо сейчас, даже если это ночь. В таких случаях я всегда выбираю wikzaim. Портал никогда не подводил – микрозаймы от двух МФО оформляются за минуты, и деньги моментально поступают на счет.
Быстрая скупка авто skupkavto.ru
Приглашаем в компанию мгновенного автовыкупа. Мы работаем в данной сфере уже большое количество лет и имеем колоссальный опыт, большую скорость оформления договоров, выплаты денежных средств и персональной работы с любым клиентом. Про нас можно посмотреть на интернет сайте skupkavto.ru множество важной информации прямо сейчас. Переходите, знакомьтесь, приходите к нам.
По запросу [url=https://skupkavto.ru/]срочный выкуп[/url] мы Вам обязательно окажем помощь. Наша команда работает быстро и конкретно по делу и готова брать любой авто в работу. Обычно бывает так, что сложно продать самостоятельно свой автомобиль. Тем более, если он битый, в залоге или с неисправностями. Не каждый покупатель будет готов на вашу желаемую стоимость, ведь любой желает получить хороший вариант за свой собственный бюджет. Мы рады взять практически любой автомобиль, поэтому, если это ваш случай, быстрее звоните нам.
По поводу мгновенного выкупа, оставляйте заявку на следующем сайте skupkavto.ru или звоните нам. Контактный телефон +7(499)899-87-78 или оформите обратный звонок. Вызывайте нашего квалифицированного оценщика в любое удобное для Вас время. Наши работники имеют дело с любыми проблемными авто и знают как выйти из любой ситуации. По этому, если Вы считаете свой авто неисправным или сильно битым, не расстраивайтесь и скорее звоните нам.
Относительно [url=https://skupkavto.ru/]кредитный автомобиль[/url] мы ждем Вас на нашем интерне портале. За столько лет очень многие люди воспользовались сетью наших филиалов компании и остались довольны. На портале skupkavto.ru можете посмотреть отзывы от клиентов или написать свой. Также всю интересную информацию Вы найдете на нашем интернет сайте- какие авто мы скупаем, как осуществляется быстрый выкуп, наши преимущества и другое.
Актуален обмен по Трейд ин, где мы выкупаем Ваш автомобиль, а Вы выбираете из нашего наличия. Работа со всеми документами лежит целиком на нас, Вам не стоит беспокоиться о бумажной волоките. Весьма много преимуществ в сторону того, чтобы с продажей авто прийти именно к нам. Прямо сейчас звоните, мы ждем.
[url=https://forfreedating.co.uk/]Adult Flirt Finder[/url] is a great solution for on-the-go individuals who are looking for companionship.
The web-based platform enables you to meet like-minded people whenever you want.
Become a part of the dating network today and embark on your journey to meeting the right person with Flirt finder.
Приглашаем вас встретить рассветы и закаты на берегу Черного моря, остановившись в одном из наших уютных отелей в Туапсе. У нас вы почувствуете истинное гостеприимство и заботу, которые сделают ваш отпуск неповторимым.
Каждый день будет наполнен солнцем, теплом и радостью. Наши отели в Туапсе предоставят вам максимальный комфорт и безмятежность. Спланируйте свой отдых заранее и получите специальные условия бронирования!
Моя Subaru уже немного устарела, и я решил ее продать. Через поисковик Яндекс нашел skupkavto.ru. Продал машину по хорошей цене, ребята быстро приехали, оценили, деньги в руки – и все!
Are you explore digital romance? FlirtFinder Join is your best starting point. This user-friendly platform embraces newcomers with open arms.
Set up an authentic profile, upload appealing photos, and initiate conversations in a secure environment. [url=https://freeflir-online.com/]Flirt Finder Dating Site gives you[/url] a hassle-free way to discover digital romance. Get started with this platform today and take the first step toward finding love online.
Однажды утром я понял, что замок в гараже сломан. Благодаря newzamok.ru, я смог быстро решить эту проблему.
Understanding Flirt Finders: What Are They?
Flirt finder dating sites are a specialized niche in the world of online dating. They cater to individuals who are looking for more than just a casual chat or a straightforward swipe right. These platforms are designed to help people find meaningful connections, whether they’re seeking a long-term relationship or a exciting romance. The emphasis here is on the art of flirting, building chemistry, and creating sparks between potential partners.
The Allure of Flirt Finders
A Lively Twist on Dating
One of the captivating aspects of [url=https://flklined2s.nl/]adult flirt finder[/url] is their lighthearted approach to dating. Unlike conventional dating platforms that primarily focus on profiles and images, flirt finders promote users to partake in flirty conversations and clever banter. This approach creates an exhilarating and flirtatious ambiance, transforming each interaction into what feels like a potential escapade.
A Multifaceted Community
Flirt finder dating sites frequently boast a varied user base, simplifying the quest for someone who aligns with your desires. Whether you’re in search of a companion with distinct passions or a partner with a certain way of life, these platforms offer an array of potential matches to explore.
Enhanced Communication Tools
Effective communication is essential in any fruitful relationship. Flirt finder sites provide a range of instruments such as video chats, virtual presents, and interactive games that enable connecting with others. These features go surpass simple text messages and aid users in expressing themselves in creative ways.
Compatibility Matching
Many flirt finder dating sites use advanced algorithms to match users in accordance with harmony factors. These algorithms factor in interests, values, and personality traits, increasing the likelihood of discovering a meaningful connection.
Crafting an Unforgettable Profile
Your profile is your digital first impression on a flirt finder site. To stand out, make use of high-quality photos that display your personality, and compose a compelling bio that emphasizes your interests and what you’re seeking in a partner. Keep in mind, authenticity is essential.
Flirtation Guidelines
Flirting on these platforms is wholly about being appealing and respectful. Without a doubt, participate in amusing banter and praise your potential matches, but refrain from exceeding boundaries or making anyone feel uneasy. Esteem creates the essence of any fruitful interaction.
Site: [url=https://flklined2s.nl/]flklined2s.nl[/url]
Uncovering Exciting Capabilities
Utilize the special features provided by flirt finder sites. Transmit virtual gifts, participate in icebreaker games, and employ video chats to become acquainted with your potential matches more effectively. These resources can support you in initiating conversations and forging unforgettable connections.
Why Opt for a Flirt Finder Dating Platform?
Infuse Your Love Journey
If your love life craves an increased dose of excitement, flirt finder dating platforms are the ideal remedy. They provide a refreshing respite from the monotony of conventional dating and introduce a feeling of playfulness into the journey.
Unearth Kindred Spirits
These platforms draw in individuals who mirror your enthusiasm for flirting and building romantic bonds. This shared mutual ground can pave the way for more profound and more pleasurable interactions.
Enhanced Chances of Success
The emphasis on compatibility and profound connections on flirt finder platforms frequently brings about elevated success rates when it comes to unearthing compatible partners. If you’re seriously devoted to finding love, these platforms have the potential to be a game-changer.
Conclusion
Flirt finder dating sites have changed the way we approach dating. Their playful approach, wide-ranging community, and creative functionalities offer an unparalleled and adventurous path to unearth love or a deep connection.
So, if you’re prepared to enhance your dating life and embark on the world of flirting, give flirt finder dating sites a chance.
Your next thrilling adventure in love could be just a click away.
Искал в Яндексе место, где можно поиграть в казино на деньги, и вот он – caso-slots.com прямо на первом месте. Сайт порадовал большим выбором казино с игровыми автоматами, бонусами на депозит и статьями о том, как правильно играть, чтобы выиграть.
В отличие от многих других платформ, caso-slots.com предлагает только проверенные [url=https://caso-slots.com/]казино онлайн[/url] для игры на реальные деньги. Наша цель – обеспечить посетителям незабвенный игровой опыт и шанс на крупные выигрыши в безопасной и честной игровой среде.
Прогон сайта с использованием программы “Хрумер” – это способ автоматизированного продвижения ресурса в поисковых системах. Этот софт позволяет оптимизировать сайт с точки зрения SEO, повышая его видимость и рейтинг в выдаче поисковых систем.
Хрумер способен выполнять множество задач, таких как автоматическое размещение комментариев, создание форумных постов, а также генерацию большого количества обратных ссылок. Эти методы могут привести к быстрому увеличению посещаемости сайта, однако их надо использовать осторожно, так как неправильное применение может привести к санкциям со стороны поисковых систем.
[url=https://kwork.ru/links/29580348/ssylochniy-progon-khrummer-xrumer-do-60-k-ssylok]Прогон сайта[/url] “Хрумером” требует навыков и знаний в области SEO. Важно помнить, что качество контента и органичность ссылок играют важную роль в ранжировании. Применение Хрумера должно быть частью комплексной стратегии продвижения, а не единственным методом.
Важно также следить за изменениями в алгоритмах поисковых систем, чтобы адаптировать свою стратегию к новым требованиям. В итоге, прогон сайта “Хрумером” может быть полезным инструментом для SEO, но его использование должно быть осмотрительным и в соответствии с лучшими практиками.
В мире, где финансовая гибкость становится все более ценным качеством, возможность получения быстрых и надежных займов без процентов и отказов – это не просто удобство, но и необходимость. WikZaim гордится тем, что предлагает вам уникальную платформу, где собраны лучшие предложения от проверенных МФО.
Наши партнеры готовы предоставить вам [url=https://wikzaim.ru/]займы на карту онлайн без отказов[/url] на выгодных условиях. Никаких скрытых комиссий, затянутых проверок или отказов. Ваш финансовый комфорт – наш главный приоритет, и мы делаем все возможное, чтобы каждый пользователь мог получить необходимую сумму в нужный момент.
Одно из уникальных преимуществ WikZaim – это наша способность адаптироваться к индивидуальным потребностям каждого клиента. Мы понимаем, что каждый случай уникален, и поэтому предлагаем широкий спектр займов без процентов. Это возможность не только справиться с временными финансовыми трудностями, но и сделать это максимально выгодно.
Мы верим, что доступ к кредиту должен быть максимально простым и удобным. На WikZaim мы исключили бюрократические преграды и упростили процесс оформления займа до нескольких шагов. Все, что вам нужно, – это выбрать подходящее предложение, заполнить заявку онлайн и получить одобрение. Да, все так просто!
Каждая МФО, представленная на нашем сайте, тщательно проверена на соответствие высоким стандартам качества и надежности. Мы заботимся о вашей финансовой безопасности и гарантируем, что каждая транзакция будет максимально защищена.
Опробуйте WikZaim уже сегодня и убедитесь на собственном опыте, что получение займа может быть максимально простым, быстрым и надежным. Ваша финансовая независимость начинается здесь!
Неоновые занавеси с сайта neoneon.ru подарили моему ресторану уютную и модную атмосферу. Они стали ключевым элементом дизайна и придали заведению особый шарм, который привлекает посетителей и создает неповторимую атмосферу для вечеринок и мероприятий – [url=https://neoneon.ru/]лента неон[/url]
На уикенд я решил устроить сюрприз для своей девушки и увезти её в романтическое путешествие. Не хватало 10000 рублей до совершенства. Я поискал в Яндексе, где можно быстро получить деньги, и нашел все-займы-тут.рф. [url=https://все-займы-тут.рф/]займ на карту без отказа[/url] был оформлен буквально за минуты. Рекомендую!
После несчастного случая, мне срочно понадобились деньги на медицинские расходы. На сайте zaim52.ru я нашел обширную подборку новых МФО 2023 года и смог быстро оформить [url=https://zaim52.ru/]займы онлайн на карту[/url]. Это действительно удобно и быстро!
Образование дорого стоит, и я решил взять займ для учебы. С помощью подборки проверенных МФО 2023 года на zaim52.ru, я нашел подходящий вариант [url=https://zaim52.ru/]займы онлайн на карту[/url] и достиг своих учебных целей.
Стоимость ремонта квартиры под ключ remont-siti.ru
Реализуем ремонт любого вида отличного качества в Москве и по Московской области. Фирма СК СИТИ СТРОЙ имеет положительный опыт строительства, составления дизайн-проекта, ремонта и рада показать свои услуги на интернет сайте remont-siti.ru прямо сегодня. Заходите на следующий веб сайт и читайте детали.
По вопросу [url=https://remont-siti.ru/]под ключ[/url] мы рады Вам оказать помощь. Если Вам нужен ремонт в Вашей квартире, или в только что приобретенной, новой, то Вы попали по правильному адресу. Реализуем все типы ремонта, от начального чернового, до разработки дизайн-проекта и выполнения работы под ключ. Работаем по всей Москве и области. На сайте remont-siti.ru можно рассчитать стоимость и сроки работы за пару минут. Введите запрашиваемые параметры: площадь квартиры, тип жилья, срочность, тип ремонтных работ и другие и смотрите тут же приблизительный ответ.
Работать с данной компанией весьма благоприятно, а также мы имеем ряд преимуществ. Стоимость ремонта не поменяется после его завершения. Некоторые компании, начав ремонтные работы называют одну сумму, которая после проведения работ увеличивается в пару раз. С нами такого не случится. Мы даем гарантию на все работы 2 года и поправим все недостатки, если вдруг они появятся, с огромным удовольствием. Мы принимаемся работать без предоплаты, а оставшиеся материалы покупаем у вас, чтобы не забивать Вашу кладовку ненужными вещами. Команда работников, которые имеют колоссальный опыт, постоянно проходят курсы повышения квалификации, чтобы знать все новые технологии ремонта.
Если Вы искали [url=https://remont-siti.ru/]ремонт квартир[/url] в сети интернет, то переходите на указанный сайт и оформляйте заявку. Наш мастер приедет к Вам и рассчитает цену предстоящих работ. Цена зависит от трудности работы, отделочных материалов, выбранного вида работ и стиля комнаты. На веб портале remont-siti.ru Вы сможете найти таблицы установленных цен на различные виды работ. А ещё много уже готовых проектов можно увидеть в нашей галерее.
Компания находится по адресу: г. Москва, ул. Новослободская, д. 20, к. 27, оф. 6. График работы с 9:00 до 21:00. Звоните по нашему телефону +7(495)153-60-54 и задавайте любые возникшие вопросы.
Иногда судьба сводит нас с людьми, которые мгновенно меняют наш мир. Так случилось со мной и Анной. Мы встретились случайно в парке, и каждое наше слово, взгляд были полны магии. Я понял, что хочу увидеть ее снова, и мы договорились о встрече. Я мечтал провести идеальный вечер, но столкнулся с реальностью – до зарплаты еще 10 дней, а в кошельке совсем не та сумма, которая позволила бы свести ее в прекрасный ресторан.
В отчаянии я вспомнил о сайте [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/]mikro-zaim-online.ru[/url]. Оформив заявку на 5000 рублей, я быстро получил одобрение, и деньги поступили на мою карту. Этот момент стал переломным. Я забронировал столик в уютном ресторане, где свечи мягко освещали наши лица, а музыка ласкала слух.
Тот вечер был волшебным. Мы говорили о всем на свете, и я понял, что влюблен. Эти чувства были взаимны. С каждым новым свиданием наши сердца становились ближе.
Сейчас, вспоминая тот вечер, я понимаю, что [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/]mikro-zaim-online.ru[/url] дал мне гораздо больше, чем просто микрозайм. Этот сайт подарил мне возможность встретить любовь моей жизни, провести тот вечер так, как я мечтал, и начать новую главу моей судьбы.
Мы с Анной вместе, и каждый день приносит нам счастье и радость. Все началось с той ночи, когда я впервые взглянул на нее, освещенную светом звезд, и понял, что хочу быть с ней всегда. И я благодарен [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/]mikro-zaim-online.ru[/url] за то, что он помог мне сделать первый шаг к моему счастью.
Карбанов и партнеры advokat-karbanov.ru
Никому не известно, когда может пригодиться помощь адвоката. Потому, хотим представить Вам адвокатское бюро Карбанов и партнеры, которое представляет все разновидности юридических услуг. На онлайн проекте advokat-karbanov.ru Вы найдете все обстоятельства, перечень услуг, контактные данные.
Относительно [url=https://advokat-karbanov.ru/advokat-po-semeynyem-delam/]юрист по семейному праву[/url] Вы пришли по верному адресу. Пётр Карбанов – главный управляющий партнер нашего бюро, постоянный эксперт на тв и радио. Адвокат, который может разрешить почти любые юридические задачи. Также у нас профессиональная сильная команда, работающая над делами какого угодно характера.
Позвоните на нашу горячую линию по номеру телефона +7(495)642-53-39 или оформите обратный звонок на сайте advokat-karbanov.ru прямо сейчас. Напишите свой контактный номер и имя и мы Вам перезвоним. Либо можно связаться с нами в знаменитых мессенджерах. Наша команда имеет большой опыт в своем деле, ведь лишь образования не хватит, главное это опыт в реальности. Ещё на стадии ознакомления с Вашим делом, наши адвокаты способны понять его перспективы и возможный исход.
Если Вы хотели найти [url=https://advokat-karbanov.ru/advokaty-po-moshennichestvu/]юрист по мошенничеству[/url] в интернете, то быстрее заходите на наш портал. Там Вы найдете весь список наших услуг. Это: представительство в арбитражном суде, неосновательное обогащение, жилищный юрист, трудовые споры, автоюрист, наследственные споры, исполнительное производство, таможенные споры, взыскание долгов и многое другое.
Находимся по адресу: 115088, Москва, ул. Угрешская, д.2, стр.1, оф. 403. Работаем пошагово: для начала нужно оформить заявку или осуществить звонок нам. Далее мы определяем дату и время консультации, которая для Вас будет бесплатной. Согласование юридической позиции по вашему вопросу и озвучивание цены услуг, оформление договора, подготовка документации и представительство в суде. Действуем четко по плану и рассчитываем только на положительный итог по делу. Звоните и мы обязательно Вам окажем помощь.
In a world inundated with technology, staying abreast of the latest innovations is not just a luxury, but a necessity. When it comes to combining technological sophistication with style, an [url=https://furfurfriend.com/collections/smart-watches]android smart watch[/url] is a quintessential accessory. It’s not just a timepiece; it’s your personal assistant, fitness trainer, and style icon, all wrapped into one sleek package that sits elegantly on your wrist, offering functionality at your fingertips.
But who says that elegance and sophistication have to come with an exorbitant price tag? There’s a common misconception that quality watches are always expensive, but we’re here to debunk that myth. If you’re looking for style, durability, and functionality without burning a hole in your pocket, explore our collection of [url=https://furfurfriend.com/]watches for men under 500[/url]. It’s a curated assortment where quality meets affordability, ensuring that every man can adorn his wrist with a timepiece that not only tells time but also narrates a story of elegance and style.
Each tick of the watch is a reminder of the seamless amalgamation of technology and style, an experience that transcends the ordinary, entering a realm where precision, innovation, and aesthetic beauty coalesce. It’s not just about keeping time; it’s about keeping pace with the evolving world, where every second counts, and every moment is a step towards the future. Join us in this journey where the past, present, and future intertwine, offering an experience that is as timeless as the watches themselves.
Добро пожаловать в нашем сайте, вашего проверенного союзника в мире [url=https://texttospeech.ru/]спортивный тотализатор[/url]. Мы с гордостью предоставляем вам возможность взять на себя контроль над вашими ставками и увеличить свои шансы на выигрыш. Наши профессиональные аналитики и специалисты следят за событиями в мире спорта, чтобы обеспечить вас свежими и надежными советами.
Почему выбирать нас:
Качественные аналитические прогнозы: Наши специалисты работают не покладая рук, чтобы предоставлять вам предсказания на разнообразные виды спорта. Мы знаем, насколько важно получать полезные советы перед тем, как сделать ставку.
Множество вариантов: Мы предлагаем ставки на разнообразные виды спорта, включая футбол, баскетбол, ракетку, бейсбол и многое другое. Вы можете выбирать из множества событий и погружаться в страсть на свой вкус.
Бесплатные прогнозы: Мы поддерживаем идею, что каждый должен иметь доступ к полезным советам. Поэтому мы предлагаем бесплатные предсказания, чтобы поддержать вас сделать правильные ставки.
Простота и удобство: Наш веб-сайт и мобильное приложение разработаны с учетом вашего удовольствия. Сделайте ставку буквально за несколько мгновений.
Как начать:
Создайте аккаунт: Создайте свой аккаунт в нашем ресурсе и получите доступ к всем нашим сервисам.
Получайте прогнозы: Подписывайтесь на наши бесплатные прогнозы и получайте свежие советы от наших экспертов.
Поставьте свою ставку: После того как вы получили полезный совет, сделайте ставку на команду по душе или событие и наслаждайтесь игры.
Вознаграждение за успех: Вместе с texttospeech.ru, вы имеете возможность к вашей победе. Попробуйте нашу помощь уже сегодня и переживайте в мир спортивных ставок во всей его красе!
В современном мире возможности финансовых институтов безграничны. Выбирая [url=https://cntbank.ru/]микрозайм онлайн без отказа[/url], вы гарантируете себе быстрый доступ к средствам. Не упустите свой шанс [url=https://cntbank.ru/]взять кредит онлайн без отказа на карту[/url] и решить свои финансовые вопросы без задержек.
Вы заслуживаете лучшего! Не позволяйте финансовым трудностям затмевать ваш день. Обратитесь к нам и [url=https://cntbank.ru/]взять займ срочно на карту без отказа[/url] станет проще, чем вы думали. Наши [url=https://cntbank.ru/]онлайн займы без отказов[/url] – это быстрый и удобный способ получить средства, когда они вам действительно нужны.
Добро пожаловать в texttospeech.ru, вашего проверенного союзника в мире [url=https://texttospeech.ru/]сделать ставку[/url]. Мы с гордостью подарим вам возможность взять на себя контроль над вашими ставками и увеличить свои перспективы на успех. Наши опытные эксперты и специалисты следят за событиями в мире спорта, чтобы поддержать вас актуальными и надежными прогнозами.
Почему выбирать нас:
Качественные аналитические прогнозы: Наши специалисты усердно трудятся, чтобы предоставлять вам прогнозы на все популярные виды спорта. Мы знаем, насколько важно получать качественные советы перед тем, как сделать ставку.
Множество вариантов: Мы предлагаем ставки на различные виды спорта, включая соккер, баскетбол, теннис, мяч и многое другое. Вы можете отбирать из множества событий и наслаждаться азарт на свой вкус.
Бесплатные прогнозы: Мы верим, что каждый должен иметь доступ к полезным советам. Поэтому мы предлагаем бесплатные предсказания, чтобы поддержать вас сделать правильные ставки.
Простота и удобство: Наш сайт и приложение для мобильных устройств разработаны с учетом вашего комфорта. Сделайте ставку буквально за несколько мгновений.
Как начать:
Зарегистрируйтесь: Создайте свой аккаунт в texttospeech.ru и получите доступ к нашему полному спектру услуг.
Получайте прогнозы: Подписывайтесь на наши бесплатные прогнозы и получайте свежие советы от опытных специалистов.
Поставьте свою ставку: После того как вы получили полезный совет, сделайте ставку на команду по душе или событие и наслаждайтесь игры.
Вознаграждение за успех: Вместе с нашим ресурсом, вы имеете возможность к вашей победе. Попробуйте нашу помощь уже сегодня и переживайте в мир спортивных ставок во всей его красе!
Скоро возводимые здания: финансовая выгода в каждой части!
В нынешней эпохе, где время – деньги, скоростройки стали истинным спасением для фирм. Эти современные сооружения комбинируют в себе солидную надежность, экономичность и быстроту установки, что придает им способность наилучшим вариантом для различных коммерческих проектов.
[url=https://bystrovozvodimye-zdanija-moskva.ru/]Быстровозводимые здания[/url]
1. Быстрота монтажа: Минуты – важнейший фактор в деловой сфере, и экспресс-сооружения дают возможность значительно сократить время строительства. Это значительно ценится в сценариях, когда актуально оперативно начать предпринимательство и начать прибыльное ведение бизнеса.
2. Экономичность: За счет усовершенствования производственных процессов элементов и сборки на месте, бюджет на сооружения быстрого монтажа часто приходит вниз, по сравнению с традиционными строительными проектами. Это обеспечивает экономию средств и обеспечить более высокий доход с инвестиций.
Подробнее на [url=https://xn--73-6kchjy.xn--p1ai/]http://scholding.ru[/url]
В заключение, быстровозводимые здания – это оптимальное решение для коммерческих задач. Они сочетают в себе молниеносную установку, бюджетность и долговечность, что сделало их превосходным выбором для компаний, активно нацеленных на скорый старт бизнеса и извлекать прибыль. Не упустите шанс на сокращение времени и издержек, лучшие скоростроительные строения для вашего следующего начинания!
Скоро возводимые здания: финансовая выгода в каждом кирпиче!
В современной действительности, где время – деньги, здания с высокой скоростью строительства стали реальным спасением для коммерческой деятельности. Эти современные объекты объединяют в себе повышенную прочность, финансовую эффективность и скорость монтажа, что обуславливает их лучшим выбором для разнообразных коммерческих задач.
[url=https://bystrovozvodimye-zdanija-moskva.ru/]Построить быстровозводимое здание[/url]
1. Ускоренная установка: Минуты – основной фактор в финансовой сфере, и сооружения моментального монтажа позволяют существенно уменьшить временные рамки строительства. Это значительно ценится в ситуациях, когда срочно требуется начать бизнес и получать доход.
2. Бюджетность: За счет оптимизации процессов производства элементов и сборки на месте, стоимость быстровозводимых зданий часто снижается, по сопоставлению с обыденными строительными проектами. Это обеспечивает экономию средств и получить лучшую инвестиционную отдачу.
Подробнее на [url=https://xn--73-6kchjy.xn--p1ai/]http://scholding.ru/[/url]
В заключение, моментальные сооружения – это идеальное решение для коммерческих инициатив. Они включают в себя быстрое строительство, бюджетность и высокую прочность, что делает их отличным выбором для предприятий, имеющих целью быстрый бизнес-старт и получать деньги. Не упустите возможность сократить затраты и время, превосходные экспресс-конструкции для вашего следующего делового мероприятия!
История бренда [url=https://telegra.ph/ZHenskie-uggi-kupit-v-Moskve—TOP-5-luchshih-modelej-10-20]UGG[/url] воплощает собой замечательное путешествие от скромных начал на землях Австралии до вершин мировой моды. Эта история началась в 70-х годах XX века, когда на волнах популярности серфинга бренд начал свое восхождение.
Происхождение [url=https://telegra.ph/ZHenskie-uggi-kupit-v-Moskve—TOP-5-luchshih-modelej-10-20]UGG[/url] тесно связано с австралийскими пастушескими сапогами, изготовленными из овечьей шкуры. Они были популярны среди фермеров, пастухов и, конечно же, серферов. Сапоги [url=https://telegra.ph/Kupit-uggi-v-Moskve—oficialnyj-internet-magazin-avstralijskih-UGG-10-20]UGG[/url] обрели популярность благодаря своей удобству, теплу и простоте. Серферы носили их после выхода из воды, чтобы согреть свои ноги.
Бренд [url=https://telegra.ph/ZHenskie-originalnye-UGG-iz-Avstralii-10-20]UGG[/url] получил мировую известность благодаря Брайану Смиту, австралийскому серферу, который в 1978 году привез эти сапоги в Соединенные Штаты. Брайан увидел в [url=https://telegra.ph/Kupit-uggi-v-Moskve—oficialnyj-internet-magazin-avstralijskih-UGG-10-20]UGG[/url] нечто большее, чем просто пастушеские сапоги. Он верил, что комфорт и стиль [url=https://telegra.ph/ZHenskie-originalnye-UGG-iz-Avstralii-10-20]UGG[/url] будут цениться не только серферами, но и многими другими.
Смит основал [url=https://telegra.ph/ZHenskie-originalnye-UGG-iz-Avstralii-10-20]UGG[/url] Holdings, Inc. и начал продажу сапог в Южной Калифорнии. Сначала продукция компании не пользовалась большим спросом, но ситуация изменилась в начале 80-х, когда [url=https://telegra.ph/Kupit-uggi-v-Moskve—oficialnyj-internet-magazin-avstralijskih-UGG-10-20]UGG[/url] стали популярны среди голливудских звезд и знаменитостей.
Так началась эпоха глобального признания и успеха [url=https://telegra.ph/Uggi-oficialnyj-sajt-internet-magazin-10-20]UGG[/url]. Сапоги стали символом расслабленного, но стильного образа жизни калифорнийцев. Они появились на обложках модных журналов, в кино и телевидении, став неотъемлемой частью поп-культуры.
В 1995 году компания была продана корпорации Deckers Outdoor Corporation, которая расширила ассортимент продукции, включив в него не только сапоги, но и другую обувь, одежду и аксессуары. [url=https://telegra.ph/ZHenskie-originalnye-UGG-iz-Avstralii-10-20]UGG[/url] стали мировым феноменом, а их стиль и комфорт оценили миллионы людей по всему миру.
Итак, начав свой путь с пастушеских сапог, [url=https://telegra.ph/Uggi-oficialnyj-sajt-internet-magazin-10-20]UGG[/url] преобразился в международный бренд, символизирующий комфорт и роскошь. Это история о том, как простые австралийские сапоги стали объектом мирового модного культа, не теряя при этом своей первоначальной уютности и тепла.
Now, I will create a straightforward text advertisement incorporating these anchor texts.
Discover a world where elegance, precision, and affordability intersect. At Furfurfriend, we believe that a quality timepiece is an essential accessory for every modern man, a silent testament to his style and elegance. That’s why we invite you to [url=https://furfurfriend.com/]buy mens watches online[/url] from our exquisite collection, where each piece is a meticulously crafted work of art, designed to offer unmatched style without compromising on quality.
If you’re looking for something specific, something that exudes elegance and offers exceptional value, we have curated a special collection just for you. Explore [url=https://furfurfriend.com/]watches 400 dollars[/url], where luxury meets affordability. Every watch in this range is a harmonious blend of traditional craftsmanship and contemporary design, ensuring that you make a statement without uttering a word.
Dive into our world, where every tick of the clock is a celebration of style, every piece a journey through the meticulous art of watchmaking. Your perfect timepiece, encapsulating the pinnacle of design, precision, and affordability, awaits. Don’t just keep time, celebrate it with Furfurfriend. Your journey to unmatched elegance and style begins with a click. Welcome to a world where every second counts. Welcome to Furfurfriend.
Бренд [url=https://telegra.ph/Kupit-uggi-v-Moskve—oficialnyj-internet-magazin-avstralijskih-UGG-10-20]UGG[/url] давно привлекает внимание не только своими стильными и комфортными сапогами, но и заботой о экологии. В эпоху, когда экологическая ответственность становится не просто модной тенденцией, но и необходимостью, [url=https://telegra.ph/ZHenskie-originalnye-UGG-iz-Avstralii-10-20]UGG[/url] делает важные шаги к соблюдению принципов устойчивого развития.
Один из аспектов заботы о природе – это использование качественных, экологически чистых материалов. Овчина, которая является ключевым материалом для производства обуви [url=https://telegra.ph/ZHenskie-uggi-kupit-v-Moskve—TOP-5-luchshih-modelej-10-20]UGG[/url], проходит строгий контроль качества и экологической безопасности. Компания стремится минимизировать использование химических веществ на всех этапах производства.
Ресурсосбережение также играет важную роль в экологической политике [url=https://telegra.ph/Uggi-oficialnyj-sajt-internet-magazin-10-20]UGG[/url]. Рациональное использование ресурсов, энергоэффективные технологии, минимизация отходов – всё это в комплексе способствует снижению негативного воздействия на окружающую среду.
Кроме того, [url=https://telegra.ph/ZHenskie-originalnye-UGG-iz-Avstralii-10-20]UGG[/url] активно занимается разработкой и внедрением программ по утилизации обуви и упаковки. Компания старается использовать упаковочные материалы, которые можно переработать или которые являются биоразлагаемыми.
Развитие линии веганских продуктов – еще один шаг бренда к экологической ответственности. Создавая обувь без использования животных материалов, [url=https://telegra.ph/ZHenskie-originalnye-UGG-iz-Avstralii-10-20]UGG[/url] предоставляет своим клиентам альтернативные опции, сочетающие в себе эстетику, комфорт и уважение к природе.
Таким образом, [url=https://telegra.ph/Avstralijskie-UGG-iz-naturalnogo-meha-10-20]UGG[/url] демонстрирует, что мода и экология могут идти рука об руку. Забота о комфорте клиентов и забота о природе – два важных принципа, которым следует бренд, преодолевая стереотипы и внося свой вклад в создание здоровой и устойчивой планеты для будущих поколений.
Компания по производству световодов solargy.ru
Предлагаем Вам несравненную в России систему солнечного освещения SOLARGY для комнат без окон или с небольшим освещением. Может стать идеальным решением освещения для множества объектов, как жилых домов, так и производственных помещений, офисов, столовых. Узнайте все детали на онлайн портале solargy.ru уже сегодня.
Если Вам необходимо [url=https://solargy.ru/faq/]использование световода[/url] в Казани, то Вы на правильном пути. Наша компания специализируется в данной области уже большое количество лет и знает всё о данном виде освещения. КЕО служит прекрасной альтернативой простым окнам, увеличивает яркость солнечного и искусственного освещения. Наши реализованные проекты и их фотографии можно посмотреть на нашем интернет сайте. Конкретно: школьные комплексы, производства, частные дома, столовые и многие другие проекты.
Оставить запрос на КЕО расчет возможно на solargy.ru в любое удобное для Вас время. В специальной форме введите свои данные: город, ФИО, адрес, номер телефона для связи и другие. А также дополнительные задания по поводу предстоящих работ. Мы Вам перезвоним в самом ближайшем времени с итоговым расчетом и дадим все рекомендации.
По поводу [url=https://solargy.ru/private/]световод для солнечного освещения помещения купить[/url] обращайтесь в нашу фирму. Мы находимся по адресу: г. Ижевск, Проспект конструктора М. Т. Калашникова, д. 7. Звоните по номеру телефона 8(800)200-0-602 и наши специалисты ответят на все Ваши вопросы. Световоды на сегодняшний день являются трендом стиля многих строений. А также, их можно включить в строительство на любом моменте, что очень здорово. При том, в подборе большое количество видов световодов разных цветов и габаритов и любой покупатель подберет под себя, что ему требуется. В любом случае, мы выразим Вам помощь в подборе, проконсультируем и предоставим все рекомендации. Звоните прямо сейчас, мы будем рады с Вами сотрудничать.
Забудьте о холодных ногах и неудобной обуви! Купить Угги – это правильный шаг к комфорту и стилю. Наш интернет-магазин предлагает широкий выбор оригинальных Угги. Не упустите возможность оформить заказ прямо сейчас!
Сайт: [url=https://uggaustralia-msk.ru/]uggaustralia-msk.ru[/url]
Адрес: Москва, 117449, улица Винокурова, 4к1
Новый сезон – новые UGG! Поспешите купить UGG 2023 года на нашей уникальной распродаже. Мы гарантируем высокое качество и самые актуальные модели. Не упустите шанс обновить свой гардероб!
Сайт: [url=https://uggaustralia-msk.ru/]uggaustralia-msk.ru[/url]
Адрес: Москва, 117449, улица Винокурова, 4к1
После покупки новой квартиры, хотелось добавить света в гостиную. Нашел [url=https://solargy.ru/]solargy.ru[/url], поехал по адресу и приобрел нужные световоды.
После переезда в новую квартиру столкнулся с проблемой темных углов. Нашел решение на [url=https://solargy.ru/]solargy.ru[/url]. Световоды помогли сделать пространство светлым и привлекательным.
Потеря работы заставила меня обратиться за срочным займом. На портале [url=https://cntbank.ru/]cntbank.ru[/url] я нашел множество выгодных предложений, и акция “займ без процентов” помогла мне переждать финансовые трудности.
У моей кошки внезапно начались проблемы с дыханием. Ветеринар сказал, что требуется срочная операция. Благодаря займу через [url=https://cntbank.ru/]cntbank.ru[/url] я смог оплатить лечение.
Лучший отдых в Москве для всей семьи termburg.ru
Представляем Вам лучшее пространство для отдыха с родными и близкими, расслабления и восстановления сил — термальный центр Термбург. Осуществляем отдых для всей семьи по адекватным ценам в различных саунах, бане, бассейне с каталогом услуг. Мы помним славянские корни, историю и традиции и с удовольствием делимся с нашими посетителями ими. Ваш отдых будет не только расслабляющим, но и очень интересным. На веб ресурсе termburg.ru Вы сможете найти много полезной информации.
По теме [url=https://termburg.ru/price-list/]медовое парение[/url] переходите на наш интернет сайт. Больше 10 разных парных, просторный бассейн, терраса с купелями с восхитительным видом на парк и многое другое ждет Вас в нашем центре. Здесь Вы можете посетить как массовые парения, так и личные, подобрав услугу из нашего каталога. Заходите в фотогалерею и смотрите как выглядят наши сауны и парные. А также читайте отзывы от наших посетителей или оставьте свой после пребывания у нас.
На интернет портале termburg.ru Вы можете сразу записаться к нам на визит. Либо позвоните по номеру телефона +7(909)167-47-46 по режиму – понедельник-воскресенье, с 9:00 до 23:00. Мы расположены по адресу: Москва, ул. Гурьянова, д. 30, 2 этаж. Также смотрите наш прайс-лист, где расписаны цены на все услуги. Это: бани-бочки, мультикаменная баня, липовая сауна, сауна с гималайской солью, русская парная и многие другие. А также много дополнительных услуг: берёзовая помывка, сладкий пилинг, «Пенный Термлин», парение на березовых вениках, авторское парение “Снеговик”, термо-медовое парение, пилинг ног рыбками.
Оформить бронь на [url=https://termburg.ru/]термбург печатники когда открытие[/url] можно прямо сейчас по указанному номеру телефона. Либо оставьте заявку на онлайн ресурсе termburg.ru и мы будем счастливы принять Вас в гости. Ответим на все возникшие вопросы по поводу Вашего визита, дадим рекомендации и советы для прекрасного отдыха. Отдых для всей семьи в приятной атмосфере, что может быть лучше?
Время — деньги, и cntbank.ru это понимает лучше всего. Онлайн займ на карту теперь можно получить быстрее, чем когда-либо. Простое и понятное оформление займа, мгновенное зачисление средств и минимальные проценты — все это ждет вас на cntbank.ru
Я всегда стремилась работать в ведущей компании в своей области. Но, закончив университет, я столкнулась с проблемой: мой диплом был утерян. Я почти потеряла надежду, когда наткнулась на сайт [url=https://www.moskvadiplom.ru/]moskvadiplom.ru[/url]. Там я нашла именно тот диплом, который мне нужен. Благодаря этому я устроилась в компанию своей мечты и теперь наслаждаюсь своей карьерой.
Оздоровительные процедуры, термальные ванны и многое другое вас ждет на [url=https://termburg.ru/]termburg.ru[/url]. Откройте Termburg и откройте новый уровень релакса для себя!
В Termburg каждый найдет отдых по вкусу: от термальных ванн до детских развлечений. Посетите [url=https://termburg.ru/]termburg.ru[/url] и забронируйте свой отдых.
В преддверии праздников я понял, что не хватает денег на подарки для семьи. Сайт cntbank.ru предложил мне идеальное решение – срочный займ на карту. Я сразу же оформил заявку, и мне быстро одобрили займ. Так я смог порадовать своих близких замечательными подарками.
Благодаря cntbank.ru я смогла быстро получить срочный займ на карту и покрыть неожиданные расходы. Рекомендую этот сайт всем, кто ищет надежное и быстрое финансовое решение.
Играйте в лучших онлайн казино на рубли с нашей помощью. [url=https://parazitizm.ru/]parazitizm.ru[/url] предоставляет актуальный рейтинг площадок, где вы сможете выигрывать реальные деньги в своей валюте.
На сайте [url=https://parazitizm.ru/]parazitizm.ru[/url] вы сможете найти и выбрать лучшие онлайн казино на деньги с щедрыми бонусами при регистрации на первый депозит. Эти бонусы позволят вам увеличить свой стартовый капитал и повысить шансы на выигрыш. Мы тщательно отбираем казино, чтобы убедиться, что они предлагают выгодные условия для новых игроков.
Каждое казино в нашем рейтинге прошло тщательный анализ, чтобы обеспечить вам надежность и честность игры. На [url=https://parazitizm.ru/]parazitizm.ru[/url] мы ценим ваше время и деньги, поэтому предоставляем только проверенные и рекомендованные казино. Посетите нас и выбирайте с умом!
На работе предложили переезд в другой город, но первое время нужно было жить в гостинице. Сайт cntbank и его список всех займов стали моим спасением. Займ оформлен, переезд успешен.
Информация о сайте cntbank.ru
Адрес: 125362, Россия, Москва, Подмосковная ул. 12А.
Ссылка: [url=https://cntbank.ru/navigation]список всех микрокредитов[/url]
Стяжка – ключевой момент при ремонте. Укладка пола дает возможность добиться плоскую поверхность для дальнейших работ.
Мастера проводят [url=https://styazhka-pola24.ru/]стяжка пола[/url] с установкой на всех норм и стандартов. Укладка пола делается с применением современных смесей, которые гарантируют надежное покрытие и стойкость.
Стяжка пола позволяет создать идеальную основу для различных видов покрытия. В Москве выравнивание пола выполняют опытные специалисты.
Случилось так, что я получил штраф за нарушение ПДД. Казалось бы, мелочь, но на тот момент у меня не было лишних денег. Введя в Google запрос, я наткнулся на сайт bycesoir.com, который заявлял о себе как о платформе с лучшей подборкой МФО 2023 года.
Там я нашел [url=https://bycesoir.com/]займы онлайн на карту срочно круглосуточно[/url] и сразу же заполнил заявку. Все прошло быстро и без проблем, штраф оплачен, а я доволен сервисом.
Вывезти строительный мусор musoroboss.ru
Представляем Вашему вниманию компанию МусорБОСС, которая промышляет вывозом строительного мусора по Санкт-Петербургу и Ленинградской области. Проводим работу на базе специализированной лицензии по нормативам СанПин, 24 часа в сутки и без выходных дней. По всем вопросам заходите на сайт musoroboss.ru или позвоните по далее указанному телефону.
По запросу [url=https://musoroboss.ru/vyvoz-musora-v-gatchine/]вывоз мусора в ленобласти гатчинский район[/url] Вы на правильном пути. Мы уже большое количество лет занимаемся задачей вывоза строительного мусора, который не рекомендуется выбрасывать в простые контейнеры. Весь мусор отправляется на переработку. Кроме вывоза, мы также делаем демонтажные работы. Среди них: демонтаж промышленных строений, дачных домиков, железобетонных конструкций, промышленный демонтаж строительных конструкций, гипрока, дачных построек, заборов, батарей отопления, в старом фонде, кровли, сантехники, плитки, стен и перегородок, стяжки из бетона и цемента и многого подобного. В нашей компании квалифицированные грузчики и водители разных транспортных средств, которые уверенно справятся с непростой работой.
Оказываемые услуги разнообразны: вывоз мусора КАМАЗом «Мамонт» до 36м3, вывоз мусора газелью до 5 тонн, вывоз старой мебели, вывоз мусора в мешках, вывоз металлолома, вывоз боя кирпича и бетона и многие другие. К всякому заказу мы пытаемся найти индивидуальный подход и стараемся решить проблемы по факту. Обращайтесь по любым нестандартным вопросам и мы найдем как прийти к идеальному решению совместно.
Для быстрого подбора нужных Вам услуг отправьте фото мусора на интернет ресурсе musoroboss.ru прямо сегодня. Обязательно укажите Ваш адрес и условия погрузки, такие как присутствие лифта, этаж и требуются ли грузчики. Оператор оформит заявку в самые короткие сроки и отправит Вам необходимую машину. Наш автопарк очень большой и под любой случай найдется подходящий вариант. Это: камаз, самосвал, гусеничный экскаватор, погрузчик и другие.
Забронировать [url=https://musoroboss.ru/vyvozim-musor-v-vyborge/]вывоз мусора выборгский район[/url] можно по телефону +7(921)326-66-66 или на нашем сайте. Офис работает по графику с 9:00 до 21:00, а вывоз мусора производится 24 часа в сутки. Находимся по адресу: Санкт-Петербург, дорога на Турухтанные Острова, 10. Звоните, оформляйте заявку на сайте, будем рады Вам помочь!
Мусорбосс – вывоз мусора в СПб musoroboss.ru
Представляем Вашему вниманию компанию МусорБОСС, которая занимается транспортировкой строительного мусора по Санкт-Петербургу и Ленинградской области. Работаем на основании специализированной лицензии по нормативам СанПин, круглосуточно и 7 дней в неделю. По всем вопросам обращайтесь на интернет портал musoroboss.ru или звоните по контактному телефону.
По вопросу [url=https://musoroboss.ru/]вывоз бытового мусора спб[/url] Вы на правильном пути. Мы уже большое количество лет занимаемся вопросами вывоза крупногабаритного мусора, который запрещено выбрасывать в простые мусоропроводы. Весь мусор отправляется на переработку. Помимо вывоза, мы также делаем демонтажные работы. Включительно: демонтаж промышленных строений, дачных домиков, бетонных конструкций, промышленный демонтаж строительных конструкций, дома с вывозом мусора, дачных построек, заборов, батарей отопления, паркета, кровли, кухонных плит, телевизоров, штукатурки, фундамента и многого подобного. В нашей компании квалифицированные грузчики и водители различных транспортных средств, которые идеально справятся с непростой работой.
Оказываемые услуги разные: заказать пухто для мусора, вывоз промышленных отходов, вывоз строительного мусора с документами, вывоз старых стеклопакетов, вывоз чугунных ванн, вывоз боя кирпича и бетона и многие другие. К каждому клиенту мы пытаемся найти личный подход и стараемся решить задачи по факту. Обращайтесь по любым нерешенным вопросам и мы найдем как прийти к отличному решению совместно.
Для быстрого подбора требуемых Вам услуг отправьте фотографию мусора на интернет ресурсе musoroboss.ru прямо сегодня. Обязательно укажите Ваш адрес и условия погрузки, такие как присутствие лифта, этаж и требуются ли грузчики. Оператор обработает заявку в самые быстрые сроки и пришлёт Вам подходящую машину. Наш автопарк весьма большой и под каждый случай будет необходимый вариант. Это: камаз, ГАЗель, гусеничный экскаватор, погрузчик и другие.
Забронировать [url=https://musoroboss.ru/product/vyvoz-musora-v-meshkah/]вывоз мусора в мешках спб[/url] можно по контактному телефону +7(921)326-66-66 или на нашем онлайн портале. Офис работает по графику с 9:00 до 21:00, а вывоз мусора осуществляется 24 часа в сутки. Наш адрес: Санкт-Петербург, дорога на Турухтанные Острова, 10. Звоните, оформляйте заявку на сайте, мы будем рады с Вами сотрудничать!
Сериалы турецкие 2023 смотреть на turkrutv.ws
В данный момент на пике количества просмотров стоят сериалы из Турции. А всё оттого что их есть за что любить. Это красивая картинка, цепляющие герои, захватывающие сюжеты и, обязательно, история любви. Но вовсе не все сериалы возможно смотреть по телевизору, большинство можно увидеть только в интернете. Представляем наш сайт — это окно в мир турецких сериалов, раскрывающая перед зрителями просторные возможности для погружения в удивительные истории. На сайте turkrutv.ws выложен широкий спектр жанров, включая драмы, триллеры, комедии, военные фильмы, криминальные и семейные сериалы, мелодрамы и исторические фильмы.
Если Вы хотели найти [url=https://turkrutv.ws/kriminal/]криминал турецкие сериалы[/url] в сети интернет, то Вы на верном пути. Благодаря комфортной навигации по годам выпуска, зрители могут без проблем найти интересующие их сериалы нужного года выпуска. Новинки и лучшие сериалы также размещены в конкретных категориях, разрешая быстро ознакомиться с самыми свежими и популярными турецкими кино. Сайт также предлагает озвучку на турецком языке для тех, кто хочет окунуться в аутентичную атмосферу турецкой культуры.
Не только сериалы заимствуют внимание любителей кино, но и рейтинги актерского состава и сценаристов, позволяя поклонникам следить за работой своих любимых звезд. Подборки и расписание сериалов помогут зрителям планировать свой досуг, а раздел “Сейчас смотрят” открывает актуальные и популярные на данный момент сериалы, такие как “Черная жемчужина”, “Постучись в мою дверь” и “Нападающий”.
По поводу [url=https://turkrutv.ws/komedii/]комедии турецкие сериалы[/url] заходите к нам. Наш веб ресурс turkrutv.ws предоставляет высокое качество картинки, позволяя зрителям наслаждаться лучшими сериалами без перерывов на рекламу и совершенно бесплатно. Сериалы есть с различными версиями озвучки, что делает просмотр удобным для каждого. Ознакомьтесь с турецкой драмой “Семья”, увлекательной историей “Магарсус” или романтической сагой “Камень желаний” и войдите в мир турецкой культуры.
Сериалы турецкие на русском языке смотреть на turkrutv.ws
В настоящее время на гребне количества просмотров стоят турецкие сериалы. А всё потому что их есть за что ценить. Это красивая картинка, цепляющие герои, захватывающие сюжеты и, конечно же, история любви. Но вовсе не все сериалы возможно увидеть по телевидению, большинство можно увидеть только в интернете. Представляем наш сайт — это дверь в мир турецких сериалов, открывающее перед зрителями безграничные возможности для погружения в удивительные истории. На веб ресурсе turkrutv.ws загружен широкий спектр жанров, включая драмы, боевики, комедии, военные фильмы, криминальные и семейные сериалы, фантастику и исторические фильмы.
Если Вы планировали найти [url=https://turkrutv.ws/best-turkey-serialy/]лучшие турецкие сериалы онлайн на русском языке[/url] в интернете, то Вы на правильном пути. Благодаря комфортной навигации по годам выпуска, зрители могут без проблем найти интересующие их сериалы необходимого года выпуска. Новинки и лучшие сериалы также представлены в отдельных категориях, разрешая быстро ознакомиться с самыми новыми и популярными турецкими кино. Сайт также предлагает озвучку на турецком языке для тех, кто хочет погрузиться в настоящую атмосферу турецкой культуры.
Не только сериалы заимствуют внимание любителей кино, но и рейтинги актерского состава и сценаристов, позволяя фанатам следить за карьерой своих любимых знаменитостей. Подборки и расписание сериалов помогут зрителям планировать свой досуг, а тема “Сейчас смотрят” представляет насущные и знаменитые на данный момент сериалы, такие как “Черная жемчужина”, “Постучись в мою дверь” и “Ловушка”.
По части [url=https://turkrutv.ws]турецкий сериал смотреть онлайн на русском[/url] переходите к нам. Наш веб сайт turkrutv.ws предоставляет высокое качество просмотра, дав наблюдателям наслаждаться любимыми сериалами без рекламы и совершенно бесплатно. Сериалы доступны с различными вариантами озвучки, что делает просмотр комфортным для любого. Познакомьтесь с турецкой драмой “Семья”, увлекательной историей “Дикий” или романтической сагой “Грязная корзина” и окунитесь в мир турецкой кинематографии.
Машинная штукатурка — современный метод осуществления штукатурных работ.
Он основан на применении устройств для штукатурки, обычно, немецкого производства, что позволяет штукатурку приготавливается и наносится на стену с автоматическим распределением и под давлением.
[url=https://mehanizirovannaya-shtukaturka-moscow.ru/]Механизированная штукатурка[/url] С подтвержденной гарантией До 32 процентов выгоднее обычной, Можно клеить обои без шпаклевки от кампании mehanizirovannaya-shtukaturka-moscow.ru
Таким образом, улучшается адгезия с поверхностью, а время, потраченное на работу сокращается в пятеро–шестеро, в по сравнению с ручной отделкой. За счет автоматизации и упрощения работы стоимость штукатурки за квадратный метр выходит дешевле, чем при использовании традиционного подхода.
Для автоматизированной штукатурки применяются специальные смеси, ценовой диапазон ниже чем для ручного нанесения примерно на 30 процентов. При соответствующих навыках и опыте специалистов, а так же при соблюдении всех технологических принципов, поверхность после обработки штукатуркой становится идеально ровной (профессиональные стандарты) и полированной, поэтому, последующая обработка шпатлевкой не не обязательна, что предоставляет дополнительную экономию средств заказчика.
Сериалы турецкие на русском языке смотреть на turkrutv.ws
Сегодня на пике популярности просмотров стоят сериалы из Турции. А всё оттого что их есть за что ценить. Это шикарная картинка, яркие герои, интересные сюжеты и, естественно, история любви. Но вовсе не все сериалы можно увидеть по телевидению, большинство можно посмотреть только в сети интернет. Представляем наш сайт — это окно в мир турецких сериалов, открывающее перед зрителями безмерные возможности для погружения в увлекательные истории. На веб ресурсе turkrutv.ws представлен широкий спектр жанров, включая драмы, триллеры, комедии, военные фильмы, криминальные и семейные сериалы, мелодрамы и исторические фильмы.
Если Вы искали [url=https://turkrutv.ws]смотреть турецкие сериалы на русском[/url] в сети интернет, то Вы на верном пути. По причине комфортной навигации по дате выпуска, зрители могут легко найти интересующие их сериалы нужного года выпуска. Новинки и лучшие сериалы также представлены в отдельных категориях, разрешая быстро ознакомиться с самыми свежими и популярными турецкими сериалами. Сайт также открывает озвучку на турецком языке для тех, кто хочет окунуться в настоящую атмосферу турецкой культуры.
Не только сериалы заимствуют внимание гостей нашего сайта, но и рейтинги актеров и сценаристов, позволяя поклонникам следить за карьерой своих любимых знаменитостей. ТОП и расписание сериалов помогут зрителям планировать своё свободное время, а тема “Сейчас смотрят” предлагает актуальные и известные на настоящий момент сериалы, такие как “Полнолуние”, “Красная комната” и “Нападающий”.
Что касается [url=https://turkrutv.ws]смотреть турецкие сериалы онлайн[/url] заходите к нам. Наш онлайн портал turkrutv.ws предоставляет высокое качество просмотра, дав зрителям наслаждаться лучшими сериалами без перерывов на рекламу и бесплатно. Сериалы представлены с различными вариантами озвучки, что создает просмотр комфортным для любого. Ознакомьтесь с турецкой драмой “Основание Осман”, увлекательной историей “Дикий” или романтической сагой “Безграничная любовь” и ныряйте в мир турецкой кинематографии.
Защитите своё оборудование от скачков напряжения — используйте стабилизатор напряжения
стабилизаторы напряжения http://stabrov.ru.
Однажды ночью мне позвонил друг и сказал, что попал в затруднительное положение. Ему срочно нужна была финансовая помощь. Я не мог оставить его в беде и начал искать, где можно быстро взять займ. Наткнулся на [url=https://credit-info24.ru/]займ на карту круглосуточно без отказа онлайн[/url] и оформил всё буквально за пять минут. Другу удалось решить свои проблемы, и он был мне очень благодарен.
Моя машина неожиданно сломалась прямо перед долгожданным отпуском. Срочно нужен был ремонт, но денег на это не было. Тут как раз нашел [url=https://credit-info24.ru/]кредит онлайн без отказа[/url]. Процедура заняла минимум времени, и я смог отправиться в отпуск на своем автомобиле, не беспокоясь о финансах.
Я всегда в поиске чего-то нового и интересного. И не так давно я обнаружил, что на hdserialclub.net уже можно [url=https://hdserialclub.net/serials2023/]смотреть сериалы 2023[/url] года. Это просто находка для любителей кино, как я. Сайт регулярно обновляется, добавляются новые серии, так что скучать здесь точно не приходится. Для меня это стало отличным способом провести время и узнать о новых трендах в мире кино.
Я студент, и недавно столкнулся с необходимостью закупить материалы для учебного проекта. К сожалению, стипендия ещё не пришла, и денег было мало. На сайте credit-info24.ru, где собраны все МФО, я обнаружил возможность [url=https://credit-info24.ru/]взять займ на карту без проверок[/url]. Это именно то, что мне нужно было! Заказал материалы, проект удался, и я получил отличную оценку.
Мостбет в Армении mostbet-uz.net
Прогнозы на спорт уже давненько заслужили огромную известность у многих людей. В настоящий момент ставки на спорт являются также отличным дополнительным заработком, а для некоторых основным. Все детали узнайте на mostbet-uz.net уже сейчас и скорее регистрируйтесь, чтобы начать зарабатывать.
По поводу [url=https://mostbet-uz.net]букмекерская контора Мостбет в Узбекистане UZ[/url] Вы на верном пути. Мы знаем о ставках всё, а также о спортивных событиях и их вероятных итогах и готовы делиться с Вами. Люди, увлеченные определенным видом спорта и знают их игроков не понаслышке, смогут и сами ставить свои прогнозы. А для новичков и только желающих узнать эту сферу, специалисты готовы обмениваться прогнозами.
Mostbet букмекерская контора работает не только в Узбекистане, а ещё в Казахстане, Азербайджане, Украине, Молдавии и других странах. Переходите в необходимый Вам раздел на веб портале mostbet-uz.net прямо сейчас и регистрируйтесь. Ставки осуществляются только впоследствии регистрации на официальном сайте букмекерской конторы. Она не займет много времени, верно введите свои данные, страну, необходимую валюту, подтвердите согласие с правилами и ожидайте логин и пароль для входа в БК.
Если Вы планировали отыскать [url=https://mostbet-uz.net/country/38-bk-mostbet-v-tadzhikistane.html]Мостбет регистрация в Таджикистане[/url] в сети интернет, то заходите на наш сайт. Онлайн ресурс mostbet-uz.net посредник в мир ставок на спорт. Вы можете также установить простое приложение на телефон и пользоваться с максимальным комфортом. Многие посетители оценили преимущества использования приложения, оцените и Вы.
Букмекерская контора Мостбет уже много лет на арене и Вы можете не сомневаться в её надежности. Но также, лучше самостоятельно научиться ориентироваться в данной теме, основываясь на подсказках бк. Со временем, знакомясь с профессиональными обзорами, смотря разнообразные спортивные матчи, отслеживания события, можно стать настоящим спецом в данной сфере.
Ставки на спорт в Казахстане mostbet-uz.net
Ставки на спорт уже давно забрали огромную известность у многих людей. В данное время ставки на спорт являются также хорошим дополнительным заработком, а для многих главным. Все детали узнайте на mostbet-uz.net уже сейчас и скорее регистрируйтесь, чтобы начать заработок.
По поводу [url=https://mostbet-uz.net/13-stavki-na-sport-v-mostbet.html]ставки на спорт в Mostbet[/url] Вы на верном пути. Мы знаем о ставках всё, а также о спортивных событиях и их возможных исходах и готовы делиться с Вами. Люди, увлеченные определенным видом спорта и знают их игроков не понаслышке, могут самостоятельно делать свои прогнозы. А для новеньких и только желающих познать эту тему, специалисты готовы делиться прогнозами.
Mostbet букмекерская контора работает не только в Узбекистане, а также в Казахстане, Азербайджане, Армении, Таджикистане и других странах. Переходите в нужный Вам раздел на онлайн проекте mostbet-uz.net прямо сейчас и регистрируйтесь. Ставки осуществляются только после регистрации на официальном сайте букмекерской конторы. Она не займет большое количество времени, правильно впишите свои данные, локацию, нужную валюту, подтвердите согласие с правилами и ожидайте логин и пароль для входа в БК.
Если Вы планировали отыскать [url=https://mostbet-uz.net]Мостбет в Узбекистане[/url] в интернете, то заходите на указанный сайт. Веб ресурс mostbet-uz.net посредник в мир ставок на спорт. Вы можете также установить удобное приложение на смартфон и пользоваться с максимальным комфортом. Многие пользователи оценили плюсы использования приложения, дайте оценку и Вы.
Букмекерская контора Mostbet уже много лет на рынке и Вы можете не колебаться в её надежности. Но также, лучше самому научиться понимать в представленной теме, основываясь на подсказках бк. Со временем, сталкиваясь с профессиональными видео, смотря различные спортивные матчи, отслеживания события, можно стать настоящим спецом в данной теме.
Покер – увлекательное развлечение, как пользуется спросом среди поклонников азартных развлечений и мастеров игры.
[url=https://landgoedcampingwesterwolde.nl/wp-content/pages/1xbet_promo_codes_free_bonus.html]https://landgoedcampingwesterwolde.nl/wp-content/pages/1xbet_promo_codes_free_bonus.html[/url]
[url=https://www.hermitmehr.at/wp-content/plugins/elements/1xbet_promo_codes_free.html]https://www.hermitmehr.at/wp-content/plugins/elements/1xbet_promo_codes_free.html[/url]
[url=https://everest.ro/wp-content/pages/1x_bet_promo_codes_free.html]https://everest.ro/wp-content/pages/1x_bet_promo_codes_free.html[/url]
[url=http://megadownload.net/MDT/pgs/?1xbet_promo_codes_free.html]http://megadownload.net/MDT/pgs/?1xbet_promo_codes_free.html[/url]
[url=http://arx.com.au/cp/pgs/1xbet_promo_codes_free.html]http://arx.com.au/cp/pgs/1xbet_promo_codes_free.html[/url]
Партейная игра подразумевает разнообразные варианты, что делает покер увлекательным и разнообразным. Участники могут состязаться в разнообразных вариантах и получать награды.
Игра в покер накладывает обязанности на участников проанализировать положение, стратегического подхода и умения читать соперников. Это делает игру более увлекательной и занимательной для игроков любого уровня.
Игра в карты является игрой ума и навыка, и он предоставляет возможность завоевать значительные награды.
Когда речь заходит о ставках в интернете, жители Узбекистана предпочитают проверенные временем платформы. [url=https://mostbet-uz.net]Мостбет Узбекистан[/url] — это не просто сайт для ставок, это место, где каждый может стать частью большого и дружелюбного сообщества. Здесь вы найдете не только широкий спектр спортивных событий, но и уютную атмосферу, где удача и стратегия идут рука об руку. Мостбет приглашает вас в увлекательное путешествие по миру ставок, где каждый шаг может привести к крупному выигрышу.
Обивка для мебели – ключевая деталь в дизайне всякого жилища. Она создаёт уют и комфорт и способствует расслабиться и расслабиться после долгого дня.
Мягкая мебель представлена в разнообразных видах, таких как софы и кресла, каждая из которых обладает своим стилем и дизайном.
[url=https://vammebel.ru/ ]www.vammebel.ru[/url]
Подбор мебели с обивкой способствует персонализировать интерьер и сформировать индивидуальное помещение с учетом собственных предпочтений.
Мягкая обивка не только красива, но и удобна и функциональна. Она отличается как отличный выбор для создания комфортной зоны для отдыха и развлечения.
Команда «Каспий», основанная саратовским музыкантом Валодей Астапчиком, уже успела запомниться выступлениями на фестивалях и попасть в список восходящих звезд iTunes с дебютным EP «Расстояния»
[url=https://kaspiymusic.ru/]песни группы каспий[/url]
Новые сериалы смотреть онлайн hdserialclub.net
Смотреть сериалы онлайн на проверенных ресурсах – одно из лучших времяпрепровождения в зимнюю пору. Что может быть лучше чем, после тяжелого рабочего дня разместиться комфортно с чашкой горячего чая и под любимый сериал наслаждаться этой жизнью?! На сайте hdserialclub.net Вы сможете найти большое количество сериалов, которые можно смотреть в отличном качестве и с хорошей русской озвучкой.
Если Вы хотели найти [url=https://hdserialclub.net/serials2023/]сериалы 2023 онлайн на русском языке[/url] в сети интернет, то Вы попали по нужному адресу. Весьма многие девушки встречаются с вопросом: что увидеть? Преимущественно постоянные жрицы сериалов, которые, вроде бы, пересмотрели всё, что только можно. Но это не имеет ничего общего с действительностью.
Наш онлайн ресурс hdserialclub.net тому доказательство. Мы выложили в нашем списке все самые захватывающие и знаменитые сериалы. Представлены такие жанры, как: драмы, боевики, криминал, триллеры, мелодрамы, приключения и многие другие. Выбрав конкретную категорию, вы ощутимо сократите время на разыскивание самого крутого для Вас сериала.
Заходите в каталог [url=https://hdserialclub.net/best-serials/]лучшие сериалы онлайн[/url] прямо сейчас и смотрите бесплатно любой сериал. При поиске в сети интернет проверенного сайта для просмотра, часто зрители сталкиваются с некачественной озвучкой или ужасным качеством картинки. У нас Вы найдете только лучшие варианты по поиску из всей сети интернет. Самый комфортный интерфейс, простой выбор серии, просмотр с момента паузы и другие плюсы.
Практичность просмотра на сайте hdserialclub.net заключается в том, что Вы можете смотреть серии, когда удобно именно Вам. При просмотре сериалов на тв, нужно ожидать определенное время, сидеть возле телевизора и также лицезреть кучу рекламных роликов. Просмотр на нашем онлайн сайте неограничен, Вы сами определяете где, когда и во сколько будет начинаться следующая серия. Сохраняйте название нашего сайта, советуйте близким и обменивайтесь впечатлениями от просмотра новых сериалов 2023 прямо сегодня.
В наши дни финансовая свобода и оперативность становятся не просто удобством, но и необходимостью. Поэтому услуга [url=https://revivalfife.ru/]займ на карту без проверки истории[/url] набирает популярность. Она предлагает людям, столкнувшимся с временными трудностями, возможность получить финансовую поддержку без дополнительных вопросов и проверок, что особенно ценно для тех, у кого в прошлом имелись проблемы с банковскими учреждениями.
С точки зрения экономики, это не только помогает отдельным лицам остаться на плаву в сложные времена, но и поддерживает общий уровень покупательной способности населения, что важно для стабильности экономической системы. Отсутствие проверки кредитной истории позволяет сократить время обработки заявок, что делает процесс не только более удобным, но и быстрым. Важно отметить, что такие займы требуют от заёмщика осознанного подхода к возврату долга, так как отсутствие дисциплины может привести к увеличению долговой нагрузки.
Турецкие сериалы мелодрамы смотреть онлайн turksezon.tv
В данное время турецкие сериалы весьма востребованы, ведь в них есть абсолютно всё что держит поклонников. Интересная история, красивые локации, главные герои и, естественно, романтичная история. Многие девушки в России просто не представляют себе жизни без турецких кино. А возникло всё с того, как по телевизору показали «Великолепный век» – самый нашумевший и популярный турецкий сериал. Девушки с огромным интересом стали смотреть и другие сериалы страны Турция, а турки начали активно снимать.
Предлагаем сайт turksezon.tv для просмотра онлайн сериалов совершенно бесплатно. У нас выложено большое количество самых распространенных и, наоборот, незнакомых большинству в России. Различные жанры, герои, сюжеты – любой сможет найти то, что ему по душе. Вы можете воспользоваться критериями поиска для быстроты в поиске нужного Вам сериала. Это: по году выпуска, по рейтингу, по отзывам или по алфавиту.
Если Вы искали [url=https://turksezon.tv/indiyskie_seriali/]индийские сериалы 2022[/url] в интернете, то прямо сейчас переходите на данный веб сайт. Сегодня телевизор смотрят очень немногие, а всё потому, что реклама занимает огромное количество времени, нет шанса всегда быть в определенное время на диване, абстрагируясь от других дел.
То ли дело – смотреть кино по ноутбуку, планшету или телефону. Актуальная девушка может делать одновременно несколько дел, совмещая приятное с продуктивным. К примеру, готовить ужин для семьи за просмотром турецкого сериала. Или делать уборку и наблюдать за своими любимыми героями. Данный сайт разработан для таких современных и жизнерадостных девушек. Но не только женщины смотрят турецкие сериалы, некоторые мужчины также выбирают наш сайт.
Прямо сейчас [url=https://turksezon.tv]турецкие сериалы бесплатно[/url] вы сможете увидеть у нас. Самые популярные сериалы: Моя левая сторона, Если бы мне стать облаком, Мистер ошибка, Мерьем, Любовь не понимает слов, Альпарслан: Великие Сельджуки и многие другие Вы сможете посмотреть на сайте turksezon.tv в лучшем качестве. Все сериалы можно смотреть бесплатно и в русской озвучке.
Преобразите свое пространство с профессионалами «СК Сити Строй”
ООО «СК СИТИ СТРОЙ» – это мастерство и качество, воплощенное в каждом квадратном метре вашего дома. Обратившись к нам за услугой [url=https://remont-siti.ru/]ремонт под ключ[/url], вы получите не просто обновление интерьера, но и вдохновение новым пространством, созданным с учетом всех ваших пожеланий. Мы гордимся тем, что предлагаем решения, которые делают жизнь наших клиентов более комфортной и стильной.
С первого штриха карандаша дизайнера до последнего штриха кисти маляра — ваш проект находится в руках профессионалов. Наша команда заботится о том, чтобы процесс ремонта был для вас приятным и беззаботным. Мы находимся в Москве по адресу: ул. Новослободская, д. 20, к. 27, оф. 6, и с нетерпением ждем встречи с вами для обсуждения вашего проекта. Пусть ваш дом станет источником вдохновения с ООО «СК СИТИ СТРОЙ».
Полусухая стяжка – метод проектирования пола. Строительство полутвёрдой стяжки позволяет подготовить ровное основание для окончательного покрытия.
[url=https://styazhka77.ru/]оборудование для полусухой стяжки[/url] Мы сделаем супер ровную стяжку пола. 7 лет опыта работы От 500 рублей за квадратный метр
Техническое обслуживание полусухой стяжки включает в себя систематический мониторинг и устранение неисправностей с применением специализированных инструментов.
Специализированные инструменты для полусухой стяжки даёт возможность осуществить процесс устройства с выдающейся точностью. Частично сухая стяжка пола является отличным решением для создания надежного фундамента для дальнейшей отделки.
Выбор надежного установочного стабилизатора напряжения
стабилизатор напряжения 15 квт [url=http://stabilizatory-napryazheniya-1.ru/]http://stabilizatory-napryazheniya-1.ru/[/url].
Получите признание вашего профессионализма, не покидая пределов вашего дома. Наша программа поможет вам дистанционно получить квалификационную категорию врача!
Для многих врачей получение квалификационной категории является не просто формальностью, а мечтой и признанием их уровня мастерства. Сейчас вы можете реализовать эту цель дистанционно, благодаря нашей уникальной программе [url=https://maps-edu.ru/poluchenie-medicinskoy-kategorii]получить квалификационную категорию врача дистанционно[/url]. Мы предоставляем всестороннюю подготовку и консультации для успешной сдачи всех необходимых экзаменов и процедур.
Воспользуйтесь удобством дистанционного обучения и подтвердите свою квалификацию, чтобы открыть новые профессиональные горизонты и улучшить качество оказываемой медицинской помощи. Наша программа разработана так, чтобы вы могли учиться в своем собственном темпе и в соответствии с вашим графиком, обеспечивая вам все необходимые знания и уверенность в успехе.
Также советуем вам обратить внимание на [url=https://maps-edu.ru/obuchenie-vrachey]повышение квалификации медработников дистанционно[/url] и ознакомиться с этим по лучше. У нас на сайте maps-edu вы можете задать вопросы и получить консультацию.
Адрес: Иркутск, ул. Степана Разина, дом 6, офис 405.
Get more for less with our collection of watches. Find the perfect [url=https://furfurfriend.com/]watch at a low price[/url] that doesn’t skimp on quality.
Maps-edu.ru предлагает широкий спектр медицинских курсов для врачей и сестринского персонала. Обучайтесь дистанционно и получайте необходимые баллы для вашей профессии.
For the modern man, a watch is more than just a timekeeper. [url=https://furfurfriend.com/]Buy mens watch[/url] pieces from our curated range that complements your lifestyle.
Большие энергозатраты: Электромеханические стабилизаторы требуют большого количества энергии для своей работы, что может привести к увеличению электроэнергетических затрат.
стабилизатор напряжения на 10 квт купить [url=https://stabilizatory-napryazheniya-1.ru]https://stabilizatory-napryazheniya-1.ru[/url].
Турецкие сериалы смотреть на русском языке turkhit.tv
Для любителей турецких сериалов, которые не могут жить без огромного количества серий и интригующих сюжетов — мы разработали наш веб портал. Самый широкий каталог сериалов из Турции любых жанров. Добро пожаловать на turkhit.tv прямо сегодня.
По запросу [url=https://turkhit.tv/melodramy/]турецкие сериалы мелодрамы[/url] Вы на верном пути. Турецкие сериалы за последнее время завоевали огромную популярность за пределами своей страны, в том числе и в Российской Федерации. В чем же секрет их удачи? Прежде всего, это истории, наполненные драматизмом и любовью, которые приковывают зрителя с первых минут просмотра. Герои сериалов – активные и эмоциональные, постоянно оказываются впутанными в сложные жизненные ситуации, которые вызывают у зрителей сожаление и эмпатию.
Сценарии турецких сериалов обычно трудные и многоуровневы. Они сочетают в себе любовные перипетии, семейные драмы, трагедии и предательства, а также криминальные линии. Данный подход позволяет удерживать внимание различной аудитории, ведь каждый найдет для себя что-то своё.
Кроме того, турецкие сериалы часто затрагивают глубокие общественные и культурные темы, острые не только для Турции, но и для многих других стран. Это делает их не только причиной развлечений, но и пищей для мыслей. Красивые декорации, наряды и съемки в живописных локациях добавляют внешнее наслаждение и помогают зрителям окунуться в необыкновенный мир, который они создают.
Заходите посмотреть [url=https://turkhit.tv/]турецкие сериалы бесплатно[/url] на наш сайт turkhit.tv уже сейчас. Турецкие продюсеры и режиссеры не боятся экспериментировать с форматами и сюжетными линиями, обязательно улучшая свои техники съемки и монтажа. Актерский состав часто включает в себя яркие и гениальные личности, способные на глубокую передачу эмоций и создание определенных образов.
В итоге, турецкие сериалы привлекают зрителей своей способностью рассказывать удивительные истории, которые отражают человеческие чувства во всем их разнообразии. Они открывают окно в иностранные культуры и предлагают возможность для эмоционального отклика, что делает их незаменимой частью жизни многих поклонников сериалов.
Самые интересные турецкие сериалы turkline.tv
Сериалы производства Турции стали реальным культурным фактом, завоевав публику по всему миру своими интересными сюжетами и яркими актерами. Эти сериалы насыщены глубокими чувствами, непредсказуемыми событиями и отличаются отличным качеством картинки. Они дают зрителям уйти с головой в мир реальной страсти и драмы, при этом задевая актуальные социальные проблемы, что делает их востребованными для большой аудитории.
По поводу [url=https://turkline.tv/new-turkey-serials/]новые турецкие сериалы[/url] в интернете, то Вы на верном пути. На онлайн портале turkline.tv представлена исключительная коллекция турецких сериалов, выложенных в лучшем качестве с русской озвучкой. Тут можно найти произведения на любой вкус – от романтических комедий до захватывающих триллеров и драм. Благодаря удобному интерфейсу и большому выбору жанров, любой зритель сайта сможет подобрать сериал по душе.
Онлайн смотреть [url=https://turkline.tv/]бесплатные турецкие сериалы[/url] в высоком качестве можно у нас. Здесь выложены все жанры кино: драмы, фэнтези, военные, семейные, фантастика и другие. Также возможно воспользоваться поиском по дате выпуска или по рейтингу актеров. Турецкие артисты также имеют свою популярность в виде рейтинга. Какой-то актер сразу всем нравится, а некоторые вызывают недоброжелательность. На нашем сайте можете увидеть, кто именно понравился большинству зрителей.
Одним из главных преимуществ turkline.tv является просмотр без рекламы, что дает непрерывный и комфортный просмотр. Все сериалы доступны для просмотра в любое время, что дает зрителям собственно планировать свой досуг и радоваться любимыми историями без запретов. Таким образом, наш веб портал является прекрасным ресурсом для всех поклонников турецких сериалов, предлагая качественный и доступный контент для истинных ценителей этого жанра.
Бесплатно смотреть турецкие сериалы turkhit.tv
Для поклонников турецких сериалов, которые не могут жить без огромного количества серий и интересных сюжетов — мы создали наш сайт. Самый широкий каталог сериалов из Турции различных жанров. Добро пожаловать на turkhit.tv прямо сейчас.
По вопросу [url=https://turkhit.tv/komedii/]турецкие сериалы комедии[/url] Вы на правильном пути. Турецкие сериалы за последние годы завоевали огромную популярность за пределами своей страны, в том числе и в Российской Федерации. В чем же секрет их удачи? Прежде всего, это истории, переполненные драматизмом и любовью, которые цепляют зрителя с первых секунд просмотра. Персонажи сериалов – активные и эмоциональные, постоянно оказываются втянутыми в сложные жизненные обстоятельства, которые вызывают у зрителей сожаление и эмпатию.
Сценарии турецких сериалов обычно тяжелые и имеют несколько сюжетных линий. Они совмещают в себе любовные перипетии, семейные трудности, трагедии и предательства, а также криминальные линии. Данный подход позволяет удерживать внимание разнообразной аудитории, ведь любой найдет для себя что-то своё.
Кроме того, турецкие сериалы часто задевают сложные общественные и культурные темы, актуальные не только для Турции, но и для большинства других стран. Это делает их не только источником развлечений, но и пищей для размышлений. Шикарные декорации, костюмы и съемки в интересных локациях добавляют визуальное наслаждение и помогают зрителю углубиться в необыкновенный мир, который они создают.
Переходите смотреть [url=https://turkhit.tv/]турецкие сериалы онлайн на русском[/url] на наш сайт turkhit.tv уже сейчас. Турецкие продюсеры и сценаристы не боятся творить новое с форматами и сюжетными линиями, постоянно улучшая свои техники съемки и монтажа. Актерский состав часто включает в себя яркие и сильные личности, годные на глубокую передачу эмоций и создание определенных героев.
В итоге, турецкие сериалы цепляют зрителей своей способностью показывать увлекательные истории, которые отражают человеческие переживания во всем их различии. Они открывают окно в другие культуры и предлагают возможность для эмоционального отголоска, что делает их необходимой частью жизни многих любителей сериалов.
Для того чтобы ваш сайт стал популярным в Москве, [url=https://www.umseo.ru/]заказать продвижение сайта[/url] – это то, что вам нужно. Это комплекс мероприятий, направленных на увеличение видимости вашего сайта в поисковых системах и социальных сетях. Важно выбрать агентство, которое имеет опыт работы именно в вашей нише.
Лучшие турецкие сериалы turkline.tv
Сериалы производства Турции стали чистым культурным феноменом, завоевав зрителей по всему миру своими захватывающими сюжетами и необычными персонажами. Эти сериалы насыщены глубокими эмоциями, непредсказуемыми поворотами и разнятся высоким качеством изображения. Они позволяют зрителям углубиться в мир реальной любви и драмы, при этом затрагивая актуальные социальные темы, что делает их интересными для широкой аудитории.
Что касается [url=https://turkline.tv/detektivy/]турецкие сериалы детективы[/url] в сети интернет, то Вы на правильном пути. На интернет сайте turkline.tv размещена уникальная коллекция турецких сериалов, выложенных в лучшем качестве на русском языке. Тут можно найти сериалы на любой вкус – от романтических комедий до захватывающих триллеров и детективов. Благодаря комфортному интерфейсу и большому выбору жанров, любой посетитель сайта сможет подобрать сериал по вкусу.
Смотреть [url=https://turkline.tv/voenie/]турецкие сериалы военные[/url] в хорошем качестве возможно у нас. Здесь представлены все жанры кино: боевики, комедии, криминал, триллеры, детективы и другие. Также возможно пользоваться поиском по году выпуска или по рейтингу актеров. Турецкие артисты также имеют свою популярность в виде рейтинга. Какой-либо актер сразу всем нравится, а некоторые вызывают недоброжелательность. На указанном сайте можете увидеть, кто именно полюбился большинству зрителей.
Одним из главных плюсов turkline.tv является отсутствие рекламы, что обеспечивает непрерывный и удобный просмотр. Все серии открыты для просмотра в любое время, что дает зрителям собственно планировать своё свободное время и радоваться интересными историями без ограничений. Таким образом, наш веб сайте является прекрасным ресурсом для всех фанатов турецких сериалов, предлагая высококачественный и открытый контент для определенных ценителей этого жанра.
Сериалы из Турции смотреть бесплатно turkhit.tv
Для любителей турецких сериалов, которые не могут жить без большого количества серий и интригующих сюжетов — мы создали наш сайт. Самый большой каталог сериалов из Турции самых разных жанров. Добро пожаловать на turkhit.tv прямо сейчас.
По вопросу [url=https://turkhit.tv/]смотреть турецкие сериалы на русском языке[/url] Вы на нужном пути. Турецкие сериалы за последнее время завоевали огромную популярность за пределами своей страны, в том числе и в России. В чем же секрет их удачи? Прежде всего, это истории, переполненные драматизмом и страстью, которые приковывают зрителя с первых минут просмотра. Герои сериалов – живые и эмоциональные, постоянно оказываются вовлеченными в сложные жизненные ситуации, которые вызывают у зрителей сочувствие и сопереживание.
Сценарии турецких сериалов часто тяжелые и имеют несколько сюжетных линий. Они совмещают в себе любовные перипетии, семейные трудности, трагедии и предательства, а также детективные линии. Данный подход дает удерживать внимание разнообразной аудитории, ведь любой найдет для себя что-то своё.
Кроме того, турецкие сериалы часто задевают глубокие общественные и культурные темы, острые не только для Турции, но и для многих других стран. Это делает их не только причиной развлечений, но и пищей для мыслей. Красивые декорации, наряды и съемки в исторических локациях добавляют визуальное наслаждение и помогают зрителю погрузиться в чудесный мир, который они произвели.
Переходите смотреть [url=https://turkhit.tv/]турецкие сериалы бесплатно[/url] на наш сайт turkhit.tv уже сейчас. Турецкие продюсеры и сценаристы не боятся экспериментировать с форматами и сюжетными линиями, обязательно улучшая свои техники видеосъемки и монтажа. Актерский состав часто включает в себя яркие и сильные личности, годные на естественную передачу эмоций и создание определенных героев.
В заключение, турецкие сериалы цепляют зрителей своей способностью рассказывать удивительные истории, которые отражают человеческие чувства во всем их различии. Они открывают дверь в иностранные культуры и дают возможность для эмоционального отголоска, что делает их необходимой частью жизни многих ценителей сериалов.
Смотреть лучшие сериалы турецкие turkline.tv
Сериалы из Турции стали настоящим культурным явлением, заслужив аудиторию по всему миру своими захватывающими сюжетами и яркими персонажами. Эти сериалы насыщены глубокими эмоциями, неизвестными поворотами и разнятся отличным качеством продукции. Они дают зрителям углубиться в мир настоящей страсти и драмы, при этом затрагивая актуальные социальные темы, что делает их любимыми для широкой аудитории.
Что касается [url=https://turkline.tv/detektivy/]турецкие сериалы детективы[/url] в интернете, то Вы на верном пути. На интернет сайте turkline.tv есть исключительная коллекция турецких сериалов, доступных в высоком качестве на русском языке. Здесь можно найти произведения на всякий вкус – от любовных комедий до будуражащих триллеров и драм. Благодаря удобному интерфейсу и широкому выбору жанров, каждый посетитель сайта сможет выбрать сериал по вкусу.
Онлайн смотреть [url=https://turkline.tv/best-turkey-serials/]лучшие турецкие сериалы[/url] в высшем качестве возможно у нас. Здесь размещены все жанры кино: боевики, комедии, криминал, семейные, фантастика и другие. Также можно воспользоваться поиском по времени выпуска или по рейтингу героев. Турецкие артисты также имеют свою популярность в виде рейтинга. Какой-то актер сразу всем полюбился, а некоторые вызывают антипатию. На нашем сайте можете посмотреть, кто именно понравился большинству зрителей.
Одним из важных преимуществ turkline.tv является отсутствие рекламы, что дает качественный и комфортный просмотр. Все сериалы доступны для просмотра 24 на 7, что дает зрителям самостоятельно планировать своё свободное время и наслаждаться любимыми историями без запретов. Таким образом, наш интернет ресурс является отличным ресурсом для всех поклонников турецких сериалов, предлагая качественный и открытый контент для определенных ценителей любого жанра.
В нашем быстром и динамичном мире иногда возникает необходимость в срочных финансовых решениях. Мы предлагаем вам удобный способ получить финансовую поддержку: [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]микрозайм на карту без отказа срочно[/url] . Микрозайм онлайн на банковскую карту без отказа – это простой и быстрый способ получения необходимой суммы, когда каждая минута на счету. Без длительных проверок и бумажной волокиты, наш сервис помогает вам получить средства в самые короткие сроки.
Если вам нужно немедленно решить финансовые проблемы, предлагаем услугу [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]займ срочно без отказов на карту[/url] . Срочный займ на карту без отказа доступен круглосуточно, что гарантирует вам возможность получения необходимых средств в любое время дня и ночи. Мы понимаем, как важно иметь быстрый доступ к деньгам в экстренных ситуациях, и поэтому наш сервис работает для вашего удобства и комфорта.
Световод для освещения помещений — это современное и эффективное решение для использования естественного света в архитектуре. Компания Solargy предлагает инновационные световоды, которые детально представлены на странице [url=https://solargy.ru/]световод для освещения помещений[/url]. Эти устройства способны транспортировать солнечный свет из внешней среды внутрь зданий, обеспечивая освещение даже в самых отдаленных и темных уголках.
Световоды Solargy состоят из нескольких компонентов: светоприемника, который устанавливается на крыше и собирает солнечный свет, отражающих труб, которые транспортируют свет внутрь здания, и диффузора, равномерно распределяющего свет по помещению. Эта система идеально подходит для освещения подвальных помещений, коридоров, внутренних офисных помещений и других мест, где доступ к естественному свету ограничен.
Применение [url=https://solargy.ru/]световода для освещения помещений[/url] от Solargy позволяет значительно уменьшить потребление электроэнергии, так как сокращается необходимость в постоянном использовании искусственного освещения. Кроме того, естественный свет, доставляемый через световоды, благоприятно влияет на здоровье и благополучие людей, находящихся в этих помещениях.
Интеграция световодов в проект здания – это не только практическое, но и эстетически привлекательное решение, которое улучшает общую атмосферу и визуальный комфорт помещений.
Когда финансовые трудности настигают внезапно, наша платформа предлагает простое и быстрое решение – [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]микрозайм онлайн на банковскую карту без отказа[/url] . Микрозаймы без отказа на карту – это удобный способ получить необходимую сумму с минимальными формальностями. Мы гарантируем быстрое рассмотрение заявки и перевод средств, позволяя вам оперативно справиться с временными финансовыми сложностями.
Если же вам необходимо немедленно решить финансовые вопросы, наш сервис поможет вам [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]займы всем без отказа на карту[/url] . Оформить онлайн займ срочно без отказа можно прямо сейчас, не выходя из дома. Мы предлагаем разнообразные варианты займов, которые помогут вам быстро и без лишних затруднений решить ваши финансовые проблемы.
Вам нужны средства мгновенно? На мир-займов.рф вы найдете то, что ищете – [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]онлайн кредит без отказа[/url] . Мы предлагаем микрозайм без отказа на карту, что станет надежной поддержкой в финансово сложных ситуациях. Быстрое оформление и моментальное перечисление средств обеспечивают нашим клиентам удобство и скорость, которые так важны в экстренных случаях.
Если вас интересуют [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]деньги без отказа на карту[/url] , то наш сайт предлагает удобное и быстрое решение. Займы онлайн на карту без отказа на мир-займов.рф – это ваша возможность получить необходимые средства быстро и без лишних хлопот. Мы понимаем, как важно иногда быстро решить финансовые вопросы, и предлагаем услуги, которые отвечают самым современным требованиям удобства и безопасности.
Изготовление световодов является ключевым элементом в создании систем естественного освещения. Компания Solargy специализируется на разработке и производстве световодов высокого качества, что подтверждается информацией на странице [url=https://solargy.ru/]изготовление световодов[/url]. Эти устройства предназначены для транспортировки солнечного света из внешней среды внутрь зданий, обеспечивая освещение в местах, где натуральный свет труднодоступен.
Процесс изготовления световодов включает в себя использование инновационных материалов и технологий, что позволяет создавать продукты, отличающиеся высокой эффективностью и долговечностью. Основными компонентами световода являются светоприемник, транспортирующие трубы и диффузор. Светоприемник улавливает солнечный свет, трубы транспортируют его внутрь здания, а диффузор равномерно распределяет свет по помещению.
Ключевое преимущество [url=https://solargy.ru/]изготовления световодов[/url] компанией Solargy заключается в их способности обеспечивать эффективное естественное освещение, минимизируя при этом потребность в искусственном освещении и снижая общее энергопотребление здания. Это не только способствует экономии ресурсов, но и улучшает экологическую устойчивость объектов.
Световоды от Solargy находят применение в самых разнообразных проектах – от жилых зданий до коммерческих и общественных сооружений, демонстрируя их универсальность и эффективность в различных условиях.
Расчет коэффициента естественного освещения (КЕО) является важной частью проектирования любого здания, стремящегося к созданию здоровой и энергоэффективной среды. С помощью услуги [url=https://solargy.ru/]расчета КЕО онлайн[/url], предоставляемой компанией Solargy, можно быстро и точно оценить уровень естественного освещения в помещении, что является ключевым для оптимизации использования света.
Онлайн-калькулятор КЕО от Solargy позволяет пользователям учитывать различные факторы, такие как размеры и расположение окон, географическое положение здания и его ориентацию. Это обеспечивает более точный расчет и помогает в определении необходимости установки дополнительных источников естественного света, например, световодов.
Использование [url=https://solargy.ru/]расчета КЕО онлайн[/url] особенно полезно при проектировании новых зданий или реконструкции существующих. Это позволяет архитекторам и инженерам принимать обоснованные решения относительно дизайна и расположения окон, а также использования дополнительных систем освещения, таких как световоды, для достижения оптимального уровня естественного освещения.
Таким образом, инструмент расчета КЕО онлайн от Solargy становится неотъемлемым помощником в создании энергоэффективных и экологически устойчивых зданий, способствуя снижению зависимости от искусственного освещения и повышению общего комфорта в помещениях.
В современном мире особое внимание уделяется созданию энергоэффективных и экологически чистых решений в области архитектуры и строительства. Важной частью этого процесса является обеспечение естественного освещения зданий. [url=https://solargy.ru/]Система естественного освещения[/url] от компании Solargy представляет собой инновационное решение, которое позволяет максимально эффективно использовать солнечный свет, снижая при этом потребность в искусственном освещении и электроэнергии.
Системы естественного освещения Solargy основаны на использовании световодов, которые транспортируют солнечный свет из наружной среды внутрь помещений. Это обеспечивает равномерное распределение света, создавая комфортную и здоровую среду для жизни и работы. Благодаря своей универсальности, эти системы могут быть установлены в самых разнообразных зданиях – от частных домов до крупных коммерческих и общественных объектов.
Выбирая [url=https://solargy.ru/]систему естественного освещения[/url] от Solargy, вы получаете не только эффективный источник света, но и современное дизайнерское решение. Световоды Solargy легко интегрируются в любой архитектурный стиль, делая их идеальным выбором для проектов, требующих как функциональности, так и эстетики. Кроме того, использование естественного освещения способствует повышению продуктивности и благополучия людей, что делает эти системы особенно актуальными для образовательных и рабочих пространств.
Инвестиции в [url=https://solargy.ru/]систему естественного освещения[/url] Solargy — это инвестиции в будущее вашего здания, обеспечивающие не только экономию ресурсов, но и повышение качества жизни и работы ваших сотрудников или членов семьи.
Срочное изготовление баннеров баннер-москва.рф
Рекомендуем Вам компанию, которая занимается разнообразной широкоформатной печатью в Москве любых видов. Интерьерная печать, фальшфасады, баннеры, печать на самоклеящейся пленке и многое другое Вы сможете найти на веб ресурсе баннер-москва.рф прямо сегодня. Наш интернет ресурс состоит из большого объема интересной информации для наших следующих покупателей, непременно заходите и оформляйте заявку.
По запросу [url=https://баннер-москва.рф/mobilnye-stendy/roll-up]ролл ап стенды купить[/url] в сети интернет, мы с удовольствием Вам поможем. В нашей команде работают самые настоящие профессионалы, которые имеют огромный опыт в сфере печати. Рассматриваем каждый случай персонально и предлагаем клиентам именно то, что они искали. Мы используем в работе только качественные материалы: это лучшее оборудование, яркие чернила, которые прослужат долгое время, прочные пленки и баннеры, а также наши работники, которые знают своё дело.
Цена на наши услуги очень выгодная и не завышенная. А это потому, что у нас личное оборудование для разных форматов для любых размеров. Мы баннер-москва.рф проводим работу с разными компаниями, в том числе зарубежными, которые предлагают высшее качество материалов по рентабельным расценкам. А еще мы гордимся, что обычный срок изготовления Вашего заказа чаще всего составляет не более 2-х дней. Также существует система скидок, которая зависит от объема вашего заказа.
Заказать [url=https://баннер-москва.рф/mobilnye-stendy/roll-up]ролл ап заказать в москве[/url] прямо сегодня, возможно на нашем сайте. Оставляйте заявку на печать, указав свои собственные данные и мы перезвоним Вам. Вдобавок можно самостоятельно позвонить по контактному телефону +7(499)390-19-73 или написать на наш электронный адрес. Оплата заказа происходит комфортным для Вас способом. Находимся по адресу: г. Москва, Нагорный проезд, д. 7, стр.1. Время работы с пн по пт с 10:00 до 18:00. Звоните, пишите, приезжайте и мы обязательно сотворим для Вас то, что Вы искали.
Срочно нуждающимся в финансовой поддержке предлагается отличная возможность – [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]микрокредит на карту срочно без отказа[/url] . Взять займ на карту без отказа теперь можно быстро и без лишних условий. Это решение идеально подходит для тех, кто сталкивается с неожиданными расходами или кратковременными финансовыми трудностями. Мы гарантируем простоту процесса и быстрое одобрение, чтобы вы могли мгновенно распоряжаться средствами.
Тем, кто ищет надежный и удобный способ получения средств, мы предлагаем услугу [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]быстрые займы на карту онлайн без отказа[/url] . Онлайн займы без отказа – это прекрасный способ быстро получить деньги, не теряя времени на походы в банк и ожидание одобрения. Мы стремимся обеспечить максимальную доступность и удобство наших услуг для каждого клиента. При этом не требуется подтверждать свой доход или предоставлять залог, что делает процесс получения займа максимально простым и доступным.
В поиске надежного финансового решения? Наша платформа предлагает вам [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]займ на карту без отказа по паспорту[/url] . Список онлайн займов на карту без отказа на нашем сайте включает множество предложений от различных МФО. Мы собрали лучшие варианты, чтобы вы могли выбрать наиболее подходящее предложение, соответствующее вашим индивидуальным потребностям. Быстро, удобно и без лишних проверок – вот принципы нашего сервиса.
Также, если вы хотите [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]микрозайм без отказа на карту[/url] , наша платформа предоставляет эту возможность. Оформить микрозайм на карту без отказов можно за считанные минуты. Мы понимаем, что важность скорости и доступности в финансовых вопросах не может быть переоценена, поэтому предлагаем услуги, которые удовлетворяют самые срочные запросы.
Срочно нуждающимся в финансовой поддержке предлагается отличная возможность – [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]взять онлайн кредит на карту без отказа[/url] . Взять займ на карту без отказа теперь можно быстро и без лишних условий. Это решение идеально подходит для тех, кто сталкивается с неожиданными расходами или кратковременными финансовыми трудностями. Мы гарантируем простоту процесса и быстрое одобрение, чтобы вы могли мгновенно распоряжаться средствами.
Тем, кто ищет надежный и удобный способ получения средств, мы предлагаем услугу [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]микрозаймы на карту онлайн без отказов[/url] . Онлайн займы без отказа – это прекрасный способ быстро получить деньги, не теряя времени на походы в банк и ожидание одобрения. Мы стремимся обеспечить максимальную доступность и удобство наших услуг для каждого клиента. При этом не требуется подтверждать свой доход или предоставлять залог, что делает процесс получения займа максимально простым и доступным.
Когда возникает неотложная потребность в финансах, наш сервис предлагает быстрое и удобное решение: [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]срочно нужен займ без отказа[/url] . Взять срочно займ на карту без отказа можно всего за несколько минут. Это отличный вариант для тех, кто оказался в сложной финансовой ситуации и нуждается в быстрой финансовой помощи. Мы предлагаем прозрачные условия и мгновенное одобрение заявок, обеспечивая вам доступ к необходимым средствам без лишних задержек и бюрократии.
Для тех, кто ищет надежный способ получения денег без лишних хлопот, мы предоставляем услугу [url=https://xn—-8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]микрозайм срочно без отказа на карту[/url] . Займ онлайн без отказа доступен круглосуточно, что гарантирует вам возможность получить финансовую поддержку в любое время. Наша цель – предложить максимально удобный и быстрый способ получения займов, который подходит каждому, кто нуждается в срочных денежных средствах.
На МИР-ЗАЙМОВ.РФ мы убрали все лишние заботы из процесса получения займа. Теперь оформление займа в лучших МФО России – это быстро и моментально! Просто посетите наш портал, выберите подходящее предложение, заполните заявку, и ваши деньги будут у вас на счету. Не теряйте времени – действуйте с МИР-ЗАЙМОВ.РФ!
Наши партнеры готовы помочь вам, когда вам это действительно нужно. Мы предоставляем список МФО на МИР-ЗАЙМОВ.РФ, где можно получить круглосуточные займы. Не стоит откладывать решение финансовых проблем на завтра – получите необходимые средства прямо сейчас!
На МИР-ЗАЙМОВ.РФ мы собрали для вас лучшие МФО России, где оформление займа занимает всего 5 минут. Это означает, что вы можете решать свои финансовые вопросы моментально, без лишних хлопот. Просто выберите подходящее предложение, заполните заявку онлайн, и ваши деньги будут доступны вам в самые краткие сроки. Не ждите – действуйте прямо сейчас на МИР-ЗАЙМОВ.РФ!
Аренда инструмента позволяет вам получить нужный инструмент в удобное для вас время и место. Вы можете забрать его самостоятельно или воспользоваться услугой доставки. Это удобно для тех, кто не хочет тратить время на поиск и покупку инструмента.
магазин проката [url=http://www.prokat888.ru/]http://www.prokat888.ru/[/url].
В наши дни, когда время ценится как никогда, важно найти способ [url=https://xn—-8sbec6a3aezg.xn--p1ai/]продать авто быстро и дорого[/url]. Учитывая рыночные тенденции, выбор правильной платформы для продажи автомобиля может существенно повысить его стоимость и сократить время ожидания покупателя. Не упустите шанс выгодно продать свой автомобиль!
Inspiring story there. What occurred after? Take care!
It’s going to be end of mine day, however before finish I am reading this
impressive post to improve my knowledge.
Если у вас есть автомобиль, который нужно продать, но он не в лучшем состоянии, не беспокойтесь. Существуют сервисы, которые занимаются [url=https://xn—-8sbec6a3aezg.xn--p1ai/]скупкой авто в любом состоянии[/url]. Они оценивают ваш автомобиль справедливо, даже если он требует ремонта или уже не на ходу.
Thanks for sharing your thoughts on click here to find out more.
Regards
Мечтаете о своём автомобиле, который будет радовать вас каждый день? Откройте для себя мир возможностей, где можно [url=https://xn—-8sbec6a3aezg.xn--p1ai/]купить авто бу в Москве и области[/url]. Найдите автомобиль, который будет не просто средством передвижения, но и источником истинного удовольствия и комфорта!
Hi there just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the pictures
aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking
issue. I’ve tried it in two different browsers and both show the same results.
Oh my goodness! Incredible article dude! Thank you, However I am experiencing troubles with
your RSS. I don’t understand why I can’t join it. Is there anybody having identical RSS problems?
Anyone who knows the answer will you kindly respond?
Thanks!!
Больше интересной информации о строительстве и ремонте можно прочитать на сайте [url=https://stroyka-gid.ru]https://stroyka-gid.ru[/url] .Только самые популярные статьи и обзоры процесса ремонта помещений и строительства зданий.
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your blog posts.
Anyway I will be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you
access consistently fast.
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied
on the video to make your point. You definitely know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your blog when you could be
giving us something informative to read?
Wonderful blog! Do you have any helpful hints for aspiring writers?
I’m planning to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost
on everything. Would you suggest starting with a free
platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m completely
overwhelmed .. Any suggestions? Kudos!
1хбет — известная букмекерская фирма. Регистрируйтесь на официальном сайте и забирайте бонусные предложения. Сделайте ставку на команду по душе. Оцените высокие коэффициенты.
[url=https://1xbet-seychas.ru]1xbet сайт
It’s really a nice and useful piece of information. I’m happy that you
simply shared this useful information with us. Please keep us
informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme.
Did you design this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you?
Plz reply as I’m looking to construct my own blog and would like to know where
u got this from. kudos
hello there and thank you for your info – I’ve certainly picked up anything new from right here.
I did however expertise several technical issues using this site, as I experienced to
reload the site a lot of times previous to I could get it
to load properly. I had been wondering if your web hosting is OK?
Not that I am complaining, but slow loading instances times will
sometimes affect your placement in google and could damage
your quality score if ads and marketing with Adwords. Well
I am adding this RSS to my e-mail and can look out for
much more of your respective interesting content.
Make sure you update this again very soon.
Right now it seems like Drupal is the top blogging platform available right now.
(from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
I would like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in penning this site.
I’m hoping to see the same high-grade content from you later on as well.
In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to
get my own, personal blog now 😉
В поиске молодости и страсти? Встречай [url=https://samye-luchshie-prostitutki-moskvy.top]бдÑм шлюха[/url] — идеальное сочетание юности и опыта для твоего максимального удовлетворения!
Для тех, кто ценит качество и натуральность, pridary.ru предлагает отличный выбор сушеного красного мухомора. Я был поражен разнообразием и качеством продукции. Покупка оказалась удобной и приятной. Если вы ищете где приобрести настоящий красный сушеный мухомор, не проходите мимо [url=https://pridary.ru/product/muxomor-krasnyj-sushenyj-shlyapki-otbor-50-g/]мухомор красный сушеный[/url] на pridary.ru.
Леди по вызову из Москвы готовы подарить вам незабываемые моменты. Эксклюзивное объявление: мне 18 лет, и я готова подарить тебе невероятный минет в машине. Ощути магию настоящего наслаждения! [url=https://samye-luchshie-prostitutki-moskvy.top]девушка для секса[/url]. Опытные дамы удовольствия ждут вашего звонка. Узнайте, что такое настоящее удовлетворение в компании соблазнительниц из столицы.
It is not my first time to visit this site, i am browsing
this site dailly and get pleasant information from here daily.
Модернизация апартаментов — наша специализация. Исполнение ремонтных услуг в сфере жилья. Мы предлагаем модернизацию жилого пространства с гарантированным качеством.
[url=https://remont-kvartir-brovari.kyiv.ua/]ремонт квартир в броварах [/url]
Для тех, кто нуждается в срочном финансировании, новые МФО 2023 предлагают удобный способ получения займа на карту. Прежде всего, выберите надежное МФО с хорошими отзывами. Затем заполните онлайн-заявку на сайте МФО, указав необходимую сумму и срок займа. После одобрения заявки, средства будут переведены на вашу карту в кратчайшие сроки.
В случае возникновения проблем или вопросов по использованию инструмента, вы можете обратиться за помощью к специалистам компании, предоставляющей аренду. Они могут предоставить вам необходимую техническую поддержку и помочь решить любые проблемы.
аренда строительного электроинструмента[url=http://www.prokat888.ru/]http://www.prokat888.ru/[/url].
В современном мире, где социальные сети играют важную роль в общении и самовыражении, [url=http://antiban.pro/ru/blog/142]instagram kirish[/url] является воротами в удивительный мир фотографий, видео и историй. Instagram предлагает невероятные возможности для общения, творчества и делится уникальными моментами жизни. Здесь каждый может найти что-то интересное для себя, будь то последние новости моды, путешествий или кулинарных открытий.
Antiban.pro мы поможем решить проблемы:
1 – Заблокировали аккаунт
2 – Заблокировали действия в аккаунте
3 – Проблемы с привязкой Facebook
4 – Меня взломали в Instagram
5 – Меня взломали в Facebook
Наш центр проката строительного оборудования предоставляет около полутора сотен наименований профессионального и бытового инструмента, при этом число позиций постоянно увеличивается, каталог оборудования пополняется не только проверенными временем, но и инновационными инструментами. Большая часть оборудования в наличии.
прокат аренда без залога [url=https://prokat888.ru]https://prokat888.ru[/url].
Скажите «нет» скучным вечерам! Представляем вашему вниманию наш [url=https://audiopik.ru/uslugi/personalnyj-kinozal-pod-klyuch/]домашний кинозал[/url]. Почему идти в кино, когда кино может прийти к вам? Устраивайте домашние премьеры каждый вечер. Только предупредите соседей, чтобы они не подумали, что у вас открылся нелегальный кинотеатр. Это будет ваш собственный кинопарадайз – без очередей за попкорном!
Срочный прокат инструмента в городе с инструментом без У нас доступны последние модели электроинструментов решение для ремонтных работ инструмент доступно в нашем сервисе
Арендовать инструмента для задач
Сберегайте деньги на покупке инструмента с нашими услугами проката
Правильное решение для ремонтных работ нет инструмента? Не проблема, к нам за инструментом!
Освойте новые умения с качественным инструментом из нашего сервиса
Арендовать инструмента для садовых работ
Не расходуйте деньги на покупку инструмента, а арендуйте инструмент для любых задач в наличии
Широкий ассортимент инструмента для проведения различных работ
Профессиональная помощь в выборе нужного инструмента от опытных нашей компании
Выгодно с услугами Арендовать инструмента для ремонта дома или квартиры
Наша компания – профессиональный партнер в аренде инструмента
Надежный помощник для ремонтных работ – в нашем прокате инструмента
Не можете определиться с выбором? Мы поможем с советом инструмента в нашем сервисе.
прокат инструмента [url=http://www.meteor-perm.ru]прокат инструмента в перми[/url].
Когда речь заходит о личном пространстве в Инстаграме, [url=http://antiban.pro/ru/blog/142]моя страница инстаграмм[/url] – это нечто большее, чем просто профиль. Это ваш уникальный уголок в интернете, где вы можете выражать себя, делиться своими достижениями и мечтами. Здесь каждый пост, каждое фото рассказывает историю, создавая уникальную ленту ваших воспоминаний и моментов жизни.
Antiban.pro мы поможем решить проблемы:
1 – Заблокировали аккаунт
2 – Заблокировали действия в аккаунте
3 – Проблемы с привязкой Facebook
4 – Меня взломали в Instagram
5 – Меня взломали в Facebook
И, конечно, удобство в нашем веке цифровых технологий – это возможность [url=http://antiban.pro/ru/blog/142]инстаграм вход с компьютера[/url]. Теперь не обязательно искать телефон, чтобы проверить новости или обновить свой профиль. Просто открой Инстаграм на компьютере, и весь мир социальной сети окажется у тебя под рукой. Это удобно, быстро и позволяет наслаждаться всеми преимуществами Инстаграма, не зависимо от того, где ты находишься.
Antiban.pro мы поможем решить проблемы:
1 – Заблокировали аккаунт
2 – Заблокировали действия в аккаунте
3 – Проблемы с привязкой Facebook
4 – Меня взломали в Instagram
5 – Меня взломали в Facebook
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if
you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates.
I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this.
Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and
I look forward to your new updates.
[url=https://samye-luchshie-prostitutki-moskvy.top]https://samye-luchshie-prostitutki-moskvy.top[/url]
[url=https://wellbutrin.cfd/]bupropion 450 mg[/url]
I am extremely impressed with your writing abilities as neatly as with the structure in your blog.
Is that this a paid subject matter or did you modify it your self?
Anyway stay up the excellent high quality writing, it’s rare to look
a nice blog like this one today..
Заказать широкополосные динамики на авто dbshop.ru
Приглашаем Вас в самый лучший интернет магазин автозвука DBShop, где представлен обширный список ингредиентов для самого лучшего звука конкретно в Ваш автомобиль. Мы работаем в представленной области уже много лет и имеем рабочие отношения с известными фирмами напрямую, например: EDGE, Dynamic State, Ural Sound, PRIDE и другие. Поэтому стоимость у нас весьма соблазнительная и не имеет больших наценок.
По запросу [url=https://dbshop.ru/catalog/avtomagnitoly/aksessuary_k_magnitolam/perekhodnye_ramki_android/]переходная рамка андроид магнитолы[/url] переходите на указанный интернет ресурс. На dbshop.ru есть вся обширная информация о нашей компании. Консультанты, которые знают толк в своей работе, направлены на то, чтобы найти в Ваш авто идеальный сабвуфер. Учитывая пожелания и финансовый лимит клиента. Продукцию, которую Вы увидите в нашем каталоге: автомагнитолы 2DIN, Hi-Fi, короба, питание системы, подиумы и многое другое.
Здесь самые низкие цены, которые не влияют на потерю качества вовсе. А всё потому, что мы работаем напрямую от поставщиков. Большинство продукции есть в наличии, но ещё возможно выбрать товары под заказ, если определенной модели сейчас не имеется. Отправляем точно в установленный срок, а постоянным клиентам предоставляем гибкую систему скидок. Все товары, заказанные у нас имеют сертификаты и гарантийный срок. Доставка осуществляется в любой регион России, а при оформлении заказа от 9900 рублей доставка осуществляется бесплатно.
В случае если Вы искали [url=https://dbshop.ru/blog/sovety-pokupatelyam/kak-podklyuchit-sabvufer-mostom-most-monoblokov/]моноблок для сабвуфера[/url] в сети интернет, то Вы на правильном пути. Заказать на сайте dbshop.ru очень просто. Стоит кидать в корзину требующиеся Вам товары, а далее оформить заказ. Напишите Ваше ФИО, телефон, электронный адрес, методы оплаты и доставки, и ожидайте заказ. Если возникли проблемы, звоните по контактному телефону, который написан ниже.
Мы расположены по адресу: г. Ижевск, ул. Коммунаров, 244. Время работы с понедельника по пятницу с 9:00 до 19:00, в выходные с 10:00 до 18:00. Наш контактный телефон +7(3412)91-21-21 звоните и мы будем рады с Вами сотрудничать.
[url=https://fildena.cfd/]fildena 100 free shipping[/url]
В тот день, когда мне понадобились деньги на неотложные нужды, я столкнулся с непреодолимой стеной банковских отказов. Но тогда, словно маяк в темной ночи, я обнаружил сервис онлайн-займов. Скептически относясь к возможности быстрого решения, я заполнил заявку. К моему изумлению, одобрение пришло мгновенно, как волшебство. Вот так, в один прекрасный момент, мои финансовые заботы рассеялись, как дым.
На нашем портале вы найдете [url=https://dzen.ru/a/ZWzCnKzreD2pFSOB]займ занять на карту без отказа[/url] и [url=https://dzen.ru/a/ZWzCnKzreD2pFSOB]быстрый займ[/url] которые доступны для всех от 18 лет!
[url=http://azithromycin.digital/]zithromax over the counter usa[/url]
MOTOLADY предлагают услуги аренды и проката мотоциклов и скутеров в Хургаде, Эль Гуне и Сахл Хашиш. MOTOLADY – одна из самых популярных компаний по прокату мотоциклов и скутеров. Они предлагают большой выбор транспортных средств по разумным ценам. MOTOLADY компания, специализирующаяся на [url=https://motohurghada.ru/]Прокат мотоцикла в Сахл Хашиш[/url] и Эль Гуне. Они предлагают услуги доставки транспорта в любое удобное для вас место. У нас в наличии различные модели транспортных средств по доступным ценам. Перед арендой транспорта обязательно ознакомьтесь с правилами и требованиями компании, также проверьте наличие страховки и необходимые документы для аренды.
Admiring the time and energy you put into your website and in depth information you offer.
It’s nice to come across a blog every once
in a while that isn’t the same unwanted rehashed material.
Wonderful read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including
your RSS feeds to my Google account.
[url=http://albuterol.guru/]albuterol inhaler 90 mcg[/url]
Срочный прокат инструмента в Поработать с инструментом без В компании доступны последние модели Оптимальное решение для строительных работ инструмент доступно в нашем сервисе
Прокат инструмента для задач
Экономьте деньги на покупке инструмента с нашим услугами проката
Идеальное решение для У вас нет инструмента? Не проблема, на наш сервис за инструментом!
Улучшите результаты с качественным инструментом из нашего сервиса
Арендовать инструмента для садовых работ
Не расходуйте деньги на покупку инструмента, а Профессиональный инструмент для разнообразных задач в наличии
Разнообразие инструмента для проведения различных работ
Надежная помощь в выборе нужного инструмента от опытных нашей компании
Выгодно с услугами аренды инструмента инструмента для отделки дома или квартиры
Наш сервис – надежный партнер в аренде инструмента
Профессиональный инструмент для ремонтных работ – в нашем прокате инструмента
Не знаете, какой инструмент подойдет? Мы поможем с подбором инструмента в нашем сервисе.
прокат инструмента [url=http://www.meteor-perm.ru/]прокат инструмента в перми[/url].
В наше время получить финансовую помощь стало гораздо проще благодаря услугам, таким как [url=https://credit-world.ru/]займы на карту без отказов[/url]. Эти предложения идеально подходят тем, кто ищет быстрое и удобное решение своих финансовых вопросов, с минимальными требованиями к заемщику и быстрым одобрением.
Срочный прокат инструмента в городе с инструментом без лишних трат доступны современные модели электроинструментов решение для строительных работ инструмент доступно в нашем сервисе
Арендовать инструмента любых задач
Сэкономьте деньги на покупке инструмента с нашими услугами проката
Отличный выбор для У вашей компании нет инструмента? Не проблема, на наш сервис за инструментом!
Освойте новые умения с качественным инструментом из нашего сервиса
Аренда инструмента для ремонтных работ
Не тратьте деньги на покупку инструмента, а берите в прокат инструмент для любых задач в наличии
Большой выбор инструмента для выполнения различных работ
Качественная помощь в выборе нужного инструмента от специалистов нашей компании
Будьте в плюсе с услугами аренды инструмента для ремонта дома или квартиры
Наш сервис – надежный партнер в аренде инструмента
Идеальный выбор для ремонтных работ – в нашем прокате инструмента
Не знаете, какой инструмент подойдет? Мы поможем с подбором инструмента в нашем сервисе.
аренда бензо электроинструмента [url=https://meteor-perm.ru/]прокат оборудования[/url].
[url=https://credit-world.ru/]Микрозаймы без отказов на карту[/url] обеспечивают широкий спектр финансовых решений для разнообразных потребностей пользователей. Эти займы предоставляются с минимальными формальностями и быстрым решением по заявке, что делает их доступными для широкого круга лиц, включая тех, кто имеет ограниченный доступ к банковским кредитам.
Рассмотрим особенности работы сайта, который предлагает широкий выбор [url=https://credit-world.ru/]займов от разных МФО[/url]. Такой подход упрощает процесс выбора для потребителя, предоставляя возможность сравнить различные предложения по ключевым параметрам, таким как процентные ставки, условия погашения и требования к заемщикам. Техническая реализация сайта обеспечивает удобный пользовательский интерфейс для быстрого доступа к информации о различных МФО, а также возможность прямого оформления заявок на займы через интерактивную платформу.
Эффективное тепловая изоляция наружных стен — комфорт и экономия в приватном недвижимости!
Согласитесь, ваш жилье заслуживает первоклассного! Теплосбережение облицовки – не единственно решение для экономии на отопительных расходах, это вклад в в благополучие и прочность вашего здания.
✨ Почему утепление с нами?
Мастерство: Наша бригада – профессионалы своего дела. Наш коллектив заботимся о каждой конкретной, чтобы обеспечить вашему жилью идеальное теплоизоляция.
Стоимость услуги тепловой изоляции: Мы ценим ваш бюджет. [url=https://stroystandart-kirov.ru/]Утепление фасадов под ключ цена[/url] – начиная от 1350 руб./кв.м. Это инвестиция в ваше приятное будущее!
Энергосберегающие меры: Забудьте о термопотерях! Наш подход не только сохраняют тепловое комфорта, но и дарят вашему коттеджу новый уровень тепла энергоэффективности.
Сделайте свой домашний уголок тепловым и стильным и привлекательным!
Подробнее на [url=https://stroystandart-kirov.ru/]www.n-dom.ru
[/url]
Не предоставляйте свой домовладение на произвольное решение. Доверьтесь специалистам нашей компании и создайте уют вместе с нами-специалистами!
[url=https://credit-world.ru/]Микрозаймы без отказов на карту[/url] – это как мост через пропасть финансовых трудностей. Они служат надежным переправой, соединяющей берега стабильности и неотложных потребностей, предоставляя возможность перейти от дефицита к достатку с минимальными препятствиями на пути.
[url=http://lexapro.cfd/]lexapro price south africa[/url]
Представляем вашему вниманию нашу платформу, которая объединяет множество микрофинансовых организаций, предлагая займы на различных условиях. Мы предоставляем специальные предложения для новых клиентов, включая займы без процентов, а также различные акции для постоянных заемщиков. На нашем сайте вы найдете полезную информацию и рекомендации, которые помогут вам сделать осознанный выбор микрозайма в соответствии с вашими финансовыми потребностями и возможностями.
Mikro-Zaim-Online – [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/]займ на год на карту[/url] получение займа онлайн: простые шаги для быстрого одобрения.
에그슬롯
말을 마친 그는 관복의 먼지를 털고 검은 가제 모자를 벗고 절을 했다.
[url=http://doxycycline.cyou/]doxycycline 100mg tablets nz[/url]
[url=http://albuterol.cyou/]albuterol 0.3[/url]
Эффективное термоизоляция внешних стен — комфорт и экономия в жилом жилище!
Согласитесь, ваш жилье заслуживает лучшего! Термоизоляция облицовки – не всего лишь решение для экономии на отоплении, это вложение средств в комфорт и стойкость вашего помещения.
✨ Почему утепление с нами?
Искусство: Специалисты нашей компании – квалифицированные специалисты. Мы заботимся о каждом элементе, чтобы обеспечить вашему жилью идеальное теплоизоляция.
Расценки воздухонепроницаемости: Мы все ценим ваш финансы. [url=https://stroystandart-kirov.ru/]Утепление фасада частного дома снаружи цена[/url] – начиная с 1350 руб./кв.м. Это вклад в ваше приятное будущее!
Энергосберегающие решения: Забудьте о потерях тепла! Материалы, которые мы используем не только сохраняют тепловое комфорта, но и дарят вашему зданию новый стандарт энергоэффективности.
Превратите свой домашнюю обстановку тепловым и стильным!
Подробнее на [url=https://stroystandart-kirov.ru/]веб-сайте компании[/url]
Не передавайте свой коттедж на волю случая. Доверьтесь специалистам нашей компании и создайте тепло вместе с нашей командой!
darknet links onion market tor marketplace
[url=https://albuterol.cyou/]proair albuterol sulfate where to buy[/url]
vurcazkircazpatliycaz.Bs6B5G0t3Aj6
[url=http://avana.cfd/]dapoxetine 60 mg price[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.best/]clonidine 25 mcg[/url]
vurucuteamgeldi.4LItAgwz6AW6
Оцифровка документов цена за лист — это наше направление. Мы предоставляем услуги цифровизации документов с использованием современных технологий. Сотрудничество с нами — это эффективный способ сделать вашу документацию доступной в электронной форме.
Приобретение диплома за определенную сумму, как указано в предложениях [url=https://www.dyplom-rossia.com/]диплом цена[/url], вызывает множество споров. Приверженцы этой практики утверждают, что в современном мире, где время и ресурсы ограничены, это может быть эффективным способом достижения карьерных целей. Они аргументируют, что в условиях высокой конкуренции на рынке труда, наличие диплома, даже приобретенного таким способом, может быть решающим фактором. Однако критики подчеркивают, что качество образования и реальные знания нельзя купить за деньги. Они указывают на моральные и юридические аспекты таких сделок, подчеркивая, что подделка документов о образовании может привести к серьезным последствиям, включая потерю доверия и профессиональную дискредитацию.
daktilogibigibi.xkKpr1eVA8iM
플레이앤고무료
포양호에는 수만 명의 도둑이 모였고 메이링에는 셀 수 없이 많은 도둑이 있었다.
daxktilogibigibi.mYrDr8HkAdMQ
[url=https://avana.cfd/]avana singapore[/url]
buy cialis black
Когда вопрос касается разработки своего личного сайта, подбор хостинга играет огромное влияние – [url=https://besthost.by/virtualhosting/]виртуальный хостинг[/url].
Ведь именно провайдер будет определять доступность и быстродействие вашего сайта для пользователей. Если вы в Беларуси и ищете профессионального поставщика услуг хостинга, то лучший выбор – это отличный выбор. BestHost.BY – одна из ведущих компаний по хостингу в на территории Беларуси, которая предоставляет качественные услуги на протяжении 15 лет
[url=https://besthost.by/virtualhosting/]купить хостинг[/url]
Когда речь заходит о создании своего собственного сайта, выбор хостинга играет огромную роль. Ведь именно хостинг будет определять доступность и быстродействие вашего сайта для пользователей. Если вы находитесь в Беларуси и ищете надежного хостинг-провайдера, то BestHost.BY – это отличный выбор. BestHost.BY – одна из ведущих хостинг-компаний в Беларуси, предоставляющая высококачественные услуги уже на протяжении 15 лет.
[url=https://afishkasochi.ru]1хбет зеркало[/url] – это популярная букмекерская компания, предлагающая широкий выбор ставок на спорт, казино и многое другое. С высокими коэффициентами и удобным интерфейсом, 1xbet привлекает множество игроков. Он также предоставляет возможность онлайн-трансляций событий. 1xbet создает захватывающий игровой опыт для своих пользователей.
[url=https://toradol.cfd/]toradol iv[/url]
Wow, fantastic weblog structure! How lengthy have you been running a blog for?
you made running a blog glance easy. The total look of your site is wonderful,
let alone the content!
I’ll right away take hold of your rss as I can not in finding your email subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service.
Do you have any? Please allow me realize so that
I may just subscribe. Thanks.
[url=https://30palomnik.ru]зеркало 1xbet[/url] – это популярная букмекерская компания, предлагающая широкий выбор ставок на спорт, казино и многое другое. С высокими коэффициентами и удобным интерфейсом, 1xbet привлекает множество игроков. Он также предоставляет возможность онлайн-трансляций событий. 1xbet создает захватывающий игровой опыт для своих пользователей.
В последнее время микрофинансовый рынок стал более доступным благодаря упрощению процедур получения займов. Современные МФО предлагают уникальные условия и быстрое решение финансовых вопросов, что делает их популярными среди широкой аудитории. Наш телеграм-канал https://t.me/microzaimfun/ помогает пользователям ориентироваться в разнообразии предложений, предоставляя актуальную информацию и советы по выбору наилучших условий займов.
Залог успешного финансового будущего – это равный доступ к средствам в любом возрасте. На https://t.me/microzaimfun/, мы предоставляем эту возможность, начиная с 18 лет. Это не только дает молодым людям шанс на самостоятельное управление финансами, но и способствует развитию финансовой грамотности среди молодежи. В эпоху цифровых технологий, такой подход становится не просто удобным, но и необходимым.
https://google.bi/url?q=https://www.radiorequenafm.com
그는 다음에 그에게 얼마나 많은 문제가 닥칠지 결코 알지 못했습니다.
Один из главных аргументов в пользу срочных займов круглосуточно – их доступность для широкого круга людей. Не важно, работаешь ты или нет, студент ты или пенсионер – в любой ситуации можно получить необходимую финансовую поддержку. Это демократизирует финансовую помощь и делает ее более социально ориентированной.
Обратите внимание на предложения [url=https://microzaim.fun/]займов без отказа на карту[/url] на сайте microzaim.fun, где каждый найдет оптимальное решение для своих финансовых нужд.
black internet dark web access onion market
dark market onion tor market deep web search
blackweb official website darkmarket url dark market onion
darknet market links darknet links tor marketplace
Финансовое включение становится реальностью благодаря МФО, которые предлагают займы всем заемщикам, даже с испорченной кредитной историей. Эти организации играют ключевую роль в обеспечении равного доступа к финансовым ресурсам, что является важным шагом к созданию более справедливой экономической системы.
Ищете [url=https://microzaim.fun/]займы онлайн без отказа[/url] ? На сайте microzaim.fun представлен широкий выбор МФО, где вы можете оформить займ быстро и без хлопот.
darknet market links darknet drug market dark web access
eggc
그의 전하는 약하고 시기 적절한 치료가 필요합니다.
В сфере микрофинансирования онлайн займы на карту без отказа и проверок занимают особую нишу. Они предлагают быстрое решение для краткосрочных финансовых потребностей, минимизируя бюрократические процедуры. Это идеальный выбор для тех, кто ценит свое время и стремится к максимальной эффективности в управлении личными финансами.
Выбирайте [url=https://microzaim.fun/]займы без отказа на карту[/url] на microzaim.fun и получите нужную сумму в кратчайшие сроки от проверенных МФО.
Срочные займы круглосуточно – это не просто удобство, это необходимость современного общества. В эпоху, когда каждый из нас может столкнуться с финансовыми трудностями в любой момент, важно иметь возможность быстро получить деньги. Мгновенный перевод средств на карту – это не только экономия времени, но и возможность оперативно решить свои финансовые проблемы.
Обратите внимание на предложения [url=https://microzaim.fun/]займов без отказа на карту[/url] на сайте microzaim.fun, где каждый найдет оптимальное решение для своих финансовых нужд.
bitcoin dark web dark net dark web market list
Надежный инструмент в аренду в Красноярске
аренда инструмента в красноярске [url=http://www.prokat888.ru#аренда-инструмента-в-красноярске]http://www.prokat888.ru[/url].
[url=https://xn—–7kcgpnpy3bral5h.xn--p1ai/]Новые онлайн займы на карту без отказа[/url] – это новинка на рынке микрофинансовых услуг. В 2023 году появились новые МФО, которые предлагают улучшенные условия кредитования. Благодаря этому клиенты имеют доступ к широкому выбору предложений, адаптированных под их индивидуальные потребности, с гарантией быстрого одобрения и перевода средств.
В новом году актуальным стало предложение [url=https://xn—–7kcgpnpy3bral5h.xn--p1ai/]займ на карту онлайн 2023[/url], с уникальной процентной ставкой 0.8% в сутки. Большое количество МФО готовы предложить такие условия, что делает этот вариант займа одним из наиболее выгодных на рынке.
В новом году актуальным стало предложение [url=https://xn—–7kcgpnpy3bral5h.xn--p1ai/]займ на карту онлайн 2023[/url], с уникальной процентной ставкой 0.8% в сутки. Большое количество МФО готовы предложить такие условия, что делает этот вариант займа одним из наиболее выгодных на рынке.
На сегодняшний день [url=https://xn—–7kcgpnpy3bral5h.xn--p1ai/]займы онлайн на карту[/url] стали еще более доступны благодаря низкой процентной ставке в 0.8% в сутки. Более 40 МФО предлагают такие условия, что делает их привлекательными для широкого круга заемщиков.
giddy xyandanxvurulmus.Wg2ZT8CzwUi7
На сегодняшний день [url=https://xn—–7kcgpnpy3bral5h.xn--p1ai/]займы онлайн на карту[/url] стали еще более доступны благодаря низкой процентной ставке в 0.8% в сутки. Более 40 МФО предлагают такие условия, что делает их привлекательными для широкого круга заемщиков.
В новом году актуальным стало предложение [url=https://xn—–7kcgpnpy3bral5h.xn--p1ai/]займ на карту онлайн 2023[/url], с уникальной процентной ставкой 0.8% в сутки. Большое количество МФО готовы предложить такие условия, что делает этот вариант займа одним из наиболее выгодных на рынке.
Сегодня на рынке доступны [url=https://xn—–7kcgpnpy3bral5h.xn--p1ai/]новые займы на карту[/url], предлагаемые более чем 40 лучшими МФО. Эти займы обеспечивают максимальное удобство и гибкость условий, позволяя заемщикам выбирать из множества предложений, которые лучше всего соответствуют их потребностям. Заявки рассматриваются быстро, что делает процесс получения денег эффективным и удобным.
프라그마틱 무료슬롯
처음에 Yang Biao는 가볍게 만지면 안된다는 엄중한 경고를했습니다.
Нужны средства срочно, но беспокоитесь о своей кредитной истории? Наше МФО предлагает кредиты до 30 000 рублей с мгновенным одобрением, даже если ваша кредитная история далека от идеальной. Мы стремимся помочь каждому, кто нуждается в финансовой поддержке, предлагая простую процедуру оформления и быстрое решение по заявке. Никаких отказов – только своевременная помощь в сложной ситуации.
У нас вы найдете [url=https://wikzaim.ru/]займы онлайн на карту без проверок срочно[/url] и другие предложения от МФО 2024 года! Каждый сможет получить быстрый займ в онлайн режиме без проверок и отказов.
Забудьте о долгих ожиданиях и высоких процентах. Наши мгновенные займы без процентов доступны круглосуточно для всех, кто нуждается в срочной финансовой поддержке. Простота и скорость оформления, отсутствие скрытых платежей и комиссий – это то, что отличает наши займы. Получите деньги быстро и эффективно, когда это вам действительно нужно.
У нас вы найдете [url=https://wikzaim.ru/]займы онлайн новые малоизвестные[/url] и другие предложения от МФО 2024 года! Каждый сможет получить быстрый займ в онлайн режиме без проверок и отказов.
Неожиданные расходы могут застать врасплох, но наша услуга срочных займов без отказов и проверок для всех старше 18 лет призвана решить эту проблему. Процесс оформления займа максимально упрощен и ускорен, чтобы вы могли получить необходимые средства в кратчайшие сроки. Никаких скрытых комиссий и бумажной волокиты – только быстрое решение ваших финансовых вопросов.
У нас вы найдете [url=https://wikzaim.ru/]займы малоизвестные без отказа[/url] и другие предложения от МФО 2024 года! Каждый сможет получить быстрый займ в онлайн режиме без проверок и отказов.
В 2024 году финансовая сфера предоставляет еще больше возможностей для тех, кто ищет быстрые и доступные решения своих финансовых вопросов. Одним из самых значимых новшеств являются новые онлайн-займы, предлагающие клиентам получить до 50 000 рублей без необходимости проходить сложные проверки кредитной истории и без риска получить отказ.
Эти новые займы разработаны с учетом потребностей современных людей, которые ценят свое время и стремятся к максимальной эффективности в решении финансовых задач. Вот почему они идеально подходят для тех, кто нуждается в срочных денежных средствах.
Основные преимущества новых онлайн-займов 2024 года:
Быстрота оформления: Процесс подачи заявки и получения решения занимает считанные минуты.
Простота условий: Достаточно иметь паспорт и доступ в интернет, чтобы оформить заявку.
Отсутствие строгих проверок: Ваша кредитная история не будет препятствием для получения займа.
Гибкие суммы: Вы можете выбрать сумму займа до 50 000 рублей в зависимости от ваших потребностей.
Наши новые онлайн-займы – это не только удобство и доступность, но и полная прозрачность условий. Мы ценим доверие наших клиентов и стремимся обеспечить максимально комфортные условия для получения финансовой помощи.
Если вы ищете надежный и быстрый способ получения денежных средств без лишних хлопот, новые онлайн-займы 2024 года – ваш идеальный выбор. Посетите наш сайт, чтобы узнать больше и оформить заявку уже сегодня. Решите свои финансовые вопросы легко и эффективно!
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.cv/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]онлайн займ на карту без отказа [/url]
[url=http://maps.google.iq/url?sa=t&url=https://wikzaim.ru/]мфо новые [/url]
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.to/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]микрозаймы онлайн на карту без отказа [/url]
[url=https://image.google.tl/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займы без отказа без проверки [/url]
[url=http://clients1.google.md/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займ на карту мгновенно круглосуточно [/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.com.my/url?sa=i&url=https://wikzaim.ru/]займ без кредитной истории на карту [/url]
[url=http://clients1.google.com.gi/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]кредиты на карту онлайн без отказа [/url]
В нашем мире, где скорость и доступность играют ключевую роль, возможность получения финансовой поддержки в любое время дня и ночи становится не просто удобством, а необходимостью. Именно поэтому мы предлагаем вам список лучших МФО 2024 года, которые предоставляют займы на карту круглосуточно и без отказа онлайн.
Эти МФО были отобраны на основе их надежности, условий предоставления займов и отзывов клиентов. Они гарантируют простоту и прозрачность процесса, минимальное количество отказов и оперативность перевода средств.
Какие преимущества вы получаете:
Круглосуточный доступ: Не важно, в какое время вы решите обратиться за помощью, эти МФО всегда к вашим услугам.
Моментальное решение: Благодаря автоматизированным системам обработки заявок, вы получите решение в течение нескольких минут.
Без проверок кредитной истории: Ваши прошлые финансовые операции не повлияют на решение о выдаче займа.
Простая и удобная процедура: Весь процесс занимает минимум времени и сил.
Как выбрать лучшее предложение? На нашем сайте вы найдете подробные обзоры и сравнения различных МФО, что поможет вам сделать осознанный выбор. Мы учитываем все аспекты: от процентных ставок до скорости обслуживания.
С нами вы всегда можете быть уверены в том, что получите нужную сумму в самые короткие сроки. Наша миссия – обеспечить вас надежным финансовым решением, когда это действительно необходимо.
Выбирайте лучшие МФО 2024 года для займов на карту круглосуточно и без отказа на нашем сайте. Решайте свои финансовые вопросы легко и быстро!
[url=https://image.google.co.ug/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займ мгновенно [/url]
[url=https://cse.google.com.mx/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займы без отказов на карту [/url]
[url=https://cse.google.mn/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займы онлайн срочно без отказа [/url]
[url=http://maps.google.dk/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займы онлайн на карту без отказа срочно [/url]
[url=https://images.google.sr/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]взять займ на карту без отказа [/url]
[url=https://maps.google.ng/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займ на карту без отказа мгновенно онлайн [/url]
[url=https://www.google.ee/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займ срочно без отказа [/url]
Привет! Если вы ищете надежные и быстрые способы получения микрозаймов, то вам повезло. Сегодня я хочу поделиться с вами подборкой из 40 компаний, которые специализируются на выдаче микрозаймов на карту. Особенность этих МФО в том, что они предлагают услуги без длительных проверок и с минимальным риском отказа.
Каждая из этих компаний имеет свои уникальные условия и преимущества, но объединяет их одно – стремление обеспечить клиентам доступ к финансам в кратчайшие сроки. Будь то неожиданные расходы или срочная потребность в деньгах, эти МФО могут стать вашим надежным решением.
Что делает эти компании особенными? Во-первых, процесс подачи заявки максимально упрощен. В большинстве случаев вам потребуется лишь паспорт и доступ к интернету. Во-вторых, скорость обработки заявок. Благодаря автоматизированным системам, решение о выдаче займа принимается почти мгновенно, и вы можете получить деньги на свою карту в течение нескольких минут после одобрения.
Конечно, важно помнить, что даже при быстрой и упрощенной процедуре получения микрозайма, необходимо внимательно относиться к условиям договора. Обратите внимание на процентную ставку, сроки возврата и возможные комиссии за обслуживание займа.
Эти МФО – это не просто компании, предоставляющие финансовые услуги, это ваш помощник в решении срочных финансовых вопросов, который всегда под рукой. Выбирая одну из этих компаний, вы выбираете удобство, скорость и надежность.
[url=https://image.google.gy/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займ онлайн на карту [/url]
[url=https://maps.google.pn/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]деньги срочно на карту без отказа [/url]
[url=http://images.google.com.my/url?sa=t&url=https://wikzaim.ru/]новые займы на карту [/url]
[url=https://www.google.lv/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займ онлайн на карту [/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.li/url?q=https://wikzaim.ru/]займ без отказа онлайн [/url]
[url=https://images.google.com.lb/url?sa=t&url=https://wikzaim.ru/]микрозайм без отказа [/url]
[url=https://www.google.mn/url?sa=t&url=https://wikzaim.ru/]займы без отказа без проверки мгновенно [/url]
[url=http://doxycycline.cfd/]doxycycline 100 mg tablets[/url]
В последнее время все больше людей обращаются к услугам [url=https://t.me/s/new_mfo_2024/]малоизвестных мфо[/url], и это обусловлено несколькими факторами. Во-первых, они предлагают более гибкие условия кредитования по сравнению с традиционными банками. Во-вторых, они часто предоставляют займы даже тем, кто имеет низкий кредитный рейтинг или отсутствие кредитной истории. Это делает их идеальным выбором для тех, кто нуждается в срочном финансировании.
В лабиринтах современного мира, где каждый шаг влечет за собой новые вызовы, [url=https://t.me/s/new_mfo_2024/]микрофинансовые организации[/url] становятся надежными проводниками. Они словно фонарики, освещающие путь к финансовому благополучию, предлагая решения, доступные каждому. Здесь, в этом мире возможностей, каждый найдет свой ключ к успеху, который откроет дверь к мечтам и амбициям.
Многие люди сталкиваются с неожиданными расходами, и в таких ситуациях [url=https://t.me/s/new_mfo_2024/]малоизвестные займы на карту[/url] могут стать настоящим спасением. Эти займы предоставляются быстро и без необходимости предоставления большого количества документов, что делает их идеальным вариантом для экстренных ситуаций. Основным преимуществом таких займов является их доступность для широкого круга заемщиков, включая тех, у кого нет идеальной кредитной истории.
Когда я решил обновить свой гардероб, но у меня не было достаточно средств, я обратился на мир-займов.рф. Там я оформил [url=https://мир-займов.рф/]займы без отказа[/url], что позволило мне приобрести всё, что я хотел, без затяжных бюрократических процедур.
Когда моя машина внезапно вышла из строя, а до зарплаты еще далеко, я решил обратиться к [url=https://мир-займов.рф/]займы без отказа[/url], найденным на мир-займов.рф. Сайт предложил мне удобные условия и быстрое оформление.
Спонтанное решение отправиться в путешествие заставило меня искать финансовые средства. Я нашел решение на мир-займов.рф, взяв [url=https://мир-займов.рф/]взять займ на карту без отказа[/url]. Сайт предложил мне удобный выбор МФО, что существенно упростило процесс.
Среди [url=https://t.me/s/new_mfo_2024/]новых мфо 2024[/url] года, многие предлагают первый займ под 0% до 30 000 рублей. С минимальными требованиями к заемщикам – всего лишь паспорт и возраст от 18 лет, – эти предложения становятся еще более привлекательными. Такой подход позволяет получить необходимую финансовую поддержку быстро и без лишних переплат.
[url=https://doxycycline.cfd/]doxycycline 100 mg pill[/url]
Of course like your website however you have to check the spelling on many of your posts. many of them are rife wih spelling issues and I find it very hard to inform the truth on the other hand I will likely come again again
모바일 슬롯 게임
이 목소리는 부드러우면서도 차갑고 심지어… 감정도 없었다.
[url=https://accutane.cfd/]accutane otc[/url]
Ну честно, почему бы не попробовать [url=https://doramahit.tv/]дорамы[/url]? Не важно, любишь ты сериалы или нет, дорамы точно зацепят. Они не просто развлекают, они показывают жизнь, как она есть, с её радостями и проблемами. И поверь, они могут быть на удивление глубокими и вдохновляющими.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It actually was once a entertainment account it.
Glance complicated to more brought agreeable from you! By the way, how could we communicate?
Если ты думаешь, что [url=https://doramahit.tv/doramy-novye/]новые дорамы[/url] – это просто еще одни скучные сериалы, ты ошибаешься. Они могут предложить тебе что-то, чего не найдешь ни в одном западном сериале. Новые дорамы полны неожиданных сюжетов, уникальных персонажей и глубоких эмоций. Дай им шанс, и они удивят тебя!
Нельзя не восхищаться, как [url=https://doramahit.tv/doramy-novye/]новые дорамы[/url] влияют на современную культуру. Они показывают, что культурное взаимопонимание может быть увлекательным и доступным. Каждый новый сериал – это не просто история, а возможность узнать что-то новое о мире, что делает их не только забавными, но и важными для культурного развития.
https://maps.google.pn/url?q=https://www.michalsmolen.com
Xiao Jing은 매우 느리게 낭독했지만 곧 Jinshen Hall이 폭발했습니다.
В мире, где каждый уголок наполнен историями, [url=https://doramahit.tv/]дорамы[/url] словно магические окна, открывающие нам неизведанные земли. Каждый эпизод – это путешествие в сердце Азии, где чувства и судьбы переплетаются в удивительный узор жизни.
Получите перетяжку мягкой мебели с гарантией качества
Перетяжка мягкой мебели : простой способ обновить интерьер
Качественное обслуживание перетяжки мягкой мебели
Легко и просто обновить диван или кресло
перетяжка мягкой мебели [url=https://www.peretyazhkann.ru]https://www.peretyazhkann.ru[/url].
Hello it’s me, I am also visiting this website
on a regular basis, this site is really pleasant and the users are really sharing good
thoughts.
[url=http://vardenafil.cfd/]levitra tablet price in india[/url]
Получить кредит онлайн теперь проще, чем когда-либо. С expl0it.ru вы можете получить [url=https://expl0it.ru/]кредит онлайн на карту без отказа[/url] всего в несколько простых шагов. Вам не нужно беспокоиться о кредитной истории; достаточно выбрать сумму до 30 000 рублей и заполнить онлайн-заявку. Ваша заявка будет обработана мгновенно, и средства поступят на вашу карту без задержек.
best prices for generic cialis
В эпоху цифровых технологий получение финансовой помощи стало еще проще и доступнее. На expl0it.ru мы предлагаем вам [url=https://expl0it.ru/]микрозайм онлайн на карту без отказа[/url], который является оптимальным решением для тех, кто ценит свое время и комфорт. Процесс заявки полностью автоматизирован, что обеспечивает быстрое решение вашего запроса. Мы понимаем важность надежности и доступности, поэтому предоставляем услуги, соответствующие самым высоким стандартам.
В лабиринте жизненных обстоятельств иногда требуется надежный компас, указывающий путь к финансовой стабильности. Expl0it.ru предлагает вам этот компас в виде возможности [url=https://expl0it.ru/]взять займы[/url]. Каждый шаг к оформлению займа – как шаг к осуществлению мечты, каждое решение – как ключ к новым возможностям. Вдохновляйтесь свободой выбора и возможностью действовать, не оглядываясь на финансовые преграды.
Забудьте обыденность и окунитесь в море чувств с [url=https://turkfan.tv/dramy/]драмами турецких сериалов[/url] на TurkFan.tv. О, да! Здесь вас ждут слезы, страсть и драматические повороты сюжета, которые заставят вас переживать за героев сильнее, чем за свои нерешенные дела. Подготовьтесь к тому, что эти сериалы затянут вас в свой мир, где каждая проблема кажется неразрешимой, а каждая любовь – судьбоносной. Насладитесь турецкими драмами, которые наверняка заставят вас задуматься о том, насколько спокойна и предсказуема ваша жизнь.
[url=http://zoloft.cfd/]zoloft 50mg[/url]
walgreens cialis prices
Забота о жилье – это забота о спокойствии. Теплоизоляция стен – это не только стильный внешний вид, но и обеспечение сохранения тепла в вашем уголке уюта. Профессионалы, коллектив экспертов, предлагаем вам преобразить ваше жилище в идеальное место для жизни.
Выполненные нами проекты – это не просто теплоизоляция, это творчество с каждым кирпичом. Мы добиваемся идеальному балансу между изысканностью и эффективностью, чтобы ваш уголок стал не только уютным, но и великолепным.
И самое существенное – приемлемые расходы! Мы полагаем, что высококачественные услуги не должны быть сверхдорогими. [url=https://ppu-prof.ru/]Утепление фасада дома под ключ[/url] начинается всего от 1250 руб/кв. метр.
Использование современных материалов и технологий позволяют нам создавать утепление, обеспечивающее долговечность и надежность. Забудьте о холодных стенах и дополнительных расходах на отопление – наше утепление станет вашим надежным защитником от холода.
Подробнее на [url=https://ppu-prof.ru/]http://ppu-prof.ru[/url]
Не откладывайте на потом заботу о комфорте своего дома. Обращайтесь к специалистам, и ваш дом преобразится настоящим художественным произведением, которое дарит тепло и радость. Вместе мы создадим дом, в котором вам будет по-настоящему удобно!
Знакомьтесь с самыми свежими новинками турецкого телевидения на TurkFan.tv. Посетите страницу [url=https://turkfan.tv/serials2024/]турецкие сериалы 2024[/url], чтобы ознакомиться с самыми ожидаемыми релизами этого года. Вас ждут увлекательные истории, которые перенесут вас в разные уголки Турции, познакомят с культурой и традициями этой загадочной страны. Новые сезоны любимых сериалов и совершенно новые проекты — все это доступно на TurkFan.tv. Вашему вниманию представлены сериалы разных жанров: от романтических мелодрам до интригующих триллеров и детективов.
В мире турецкого телесериала особое место занимают мелодрамы, которые покоряют сердца зрителей своими захватывающими историями любви, сложными человеческими отношениями и драматическими поворотами сюжета. На странице [url=https://turkfan.tv/melodramy/]мелодрамы турецкие сериалы[/url] на сайте TurkFan.tv представлены самые лучшие образцы этого жанра. Зрители могут насладиться историями, которые отражают не только романтические отношения, но и социальные, культурные и семейные аспекты жизни в Турции. Турецкие мелодрамы известны своей способностью вызывать сильные эмоции и увлекать зрителя в мир историй, которые кажутся одновременно и экзотическими, и удивительно близкими.
В контексте изучения турецкой телевизионной продукции следует также обратить внимание на [url=https://turkfan.tv/komedii/]комедии турецких сериалов[/url] на TurkFan.tv. Этот жанр выделяется своей способностью отражать социальные и культурные особенности турецкого общества через призму юмора и сатиры. Комедийные сериалы часто используют эксцентричные ситуации и характеры для создания комического эффекта, однако за этим часто скрывается глубокий анализ социальных взаимодействий и человеческих отношений. Это делает турецкие комедии не только развлекательными, но и информативными, раскрывая уникальные аспекты турецкой культуры и менталитета.
Когда сердце жаждет историй, наполненных страстью, любовью и интригами, сайт, где можно [url=https://doramaclub.tv/luchshie-doramy/]лучшие дорамы онлайн[/url] смотреть, становится настоящим спасением. Здесь каждая дорама – это шедевр, выбранный среди множества, чтобы подарить вам незабываемые часы просмотра. Откройте для себя мир, где каждый сюжет – это путешествие, полное эмоций и удивительных поворотов, которые заставят ваше сердце биться чаще.
xanax xanax cheap pharmacy online
best online pharmacy to get xanax
Онлайн магазин мобильных устройств: низкие цены и быстрая доставка
магазин – [url=https://xn--80abhspddm.xn--90ais/]мобильный магазин[/url].
[url=https://accutane.guru/]accutane prescription canada[/url]
Pretty great post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I’ve really loved browsing your blog posts.
In any case I will be subscribing on your rss feed and I’m
hoping you write again soon!
viagra tablet 25 mg
[url=http://tadalafil.cfd/]where to buy cialis online[/url]
[url=https://finasteride.digital/]best propecia prices[/url]
sildenafil online paypal
generic name for cialis
At [url=https://mult34.com/category/zootopia/]zootopia porn[/url] – mult34.com, the world of adult comics unfolds with an impressive variety. Whether you’re into classic styles or modern narratives, this portal has it all, and for free! The site prides itself on a wide selection, catering to varied tastes and preferences. [url=https://mult34.com/hornier-things/]stranger things rule 34[/url] – mult34.com ensures a seamless browsing experience, allowing users to dive into their favorite comics without any hassle.
Освежить мягкую мебель в доме: Придать новый вид старой мебели: секреты перетяжки перетягивать мебель своими руками: Нюансы ткани для перетяжки мягкой мебели: секреты выбора
[url=https://art-restor.ru/]перетяжка мебели в Минске[/url].
Как не ошибиться при выборе фабрики для перетяжки мягкой мебели
what is the generic name for cialis
Любителям аниме, которые ценят удобство и качество, я рекомендую заглянуть на [url=https://animeline.tv/anime-novinki/]новые аниме онлайн[/url]. На animeline.tv представлены самые свежие серии, и самое приятное – это все доступно бесплатно и без регистрации. Этот сайт находится на первой строчке в Яндексе, что уже говорит о многом!
Отремонтировать мягкую мебель в доме: топ-5 способов новый вид старой мебели: эффектные идеи перетягивать мебель своими руками: Подбор ткани для перетяжки мягкой мебели: советы дизайнера
[url=https://art-restor.ru/]перетяжка мягкой мебели[/url].
Как сделать правильный выбор при перетяжке мягкой мебели
sildenafil usa
Step into the expansive world of 18+ comics at [url=https://mult34.com/category/steven-universe/]steven universe porn[/url] – mult34.com, where every genre is a new journey. Our collection is a celebration of artistic expression, crafted for those who appreciate the finer aspects of adult comics. Here, you’ll find stories that resonate, characters that captivate, and art that astonishes. For the true connoisseurs of 18+ comics, [url=https://mult34.com/pet-furry-shorts/]furry porn comic[/url] – mult34.com is your gallery of dreams.
Attention, adult comic aficionados! Your search for the perfect collection ends at [url=https://mult34.com/category/shadman/]shadman[/url] – mult34.com. Here, every genre you can imagine is at your fingertips. Whether it’s the thrill of action, the complexity of drama, or the heat of romance, we’ve got it all. Our site is a celebration of diverse storytelling, exclusively for true enthusiasts of 18+ comics. Dive into this curated world where every page turn promises a new adventure.
Are you a fan of adult comics? Look no further than [url=https://mult34.com/category/among-us/]among us porn[/url] – mult34.com! This website is a goldmine for comic enthusiasts, offering a vast collection of adult-themed comics without any charge. Explore a diverse range of genres and styles, all available at your fingertips. [url=https://mult34.com/category/marvel/]marvel porn[/url] – mult34.com stands out with its user-friendly interface and high-quality content, making it a top choice for comic lovers seeking free entertainment.
Мой дом требовал неотложного ремонта, и я хотела улучшить свое жилье. Но финансы были ограничены. С помощью Яндекса, я нашла сайт msk-zaim.ru, где была информация о МФО 2024 года. Здесь я взяла микрокредит на 10 000 рублей под 0%, что помогло мне начать ремонт и сделать свой дом более комфортным и уютным.
[url=https://msk-zaim.ru/]Мгновенные займы онлайн – быстрое решение ваших финансовых задач[/url]
Помню, как однажды у меня возникла потребность в качественном и разнообразном аниме. Исследовав интернет, я обнаружил [url=https://animeline.tv/]аниме онлайн[/url]. Этот сайт стал для меня настоящим сокровищем. На animeline.tv я могу проводить часы, погружаясь в увлекательные истории и переживая за любимых героев.
Помню, как искал в Google место, где можно было бы [url=https://animeline.tv/]смотреть аниме онлайн бесплатно[/url], и попал на animeline.tv. Этот сайт стал для меня идеальным решением: здесь можно найти аниме на любой вкус в прекрасном качестве, и самое главное – без назойливой рекламы. Теперь это мой любимый способ отдыха после работы.
Всегда мечтал о том, чтобы первым узнавать о новых аниме. Моя мечта сбылась, когда я обнаружил [url=https://animeline.tv/anime-2024/]аниме онлайн 2024[/url] на animeline.tv. Этот сайт предоставил мне возможность быть в курсе всех последних новинок. Я в восторге от того, как много удивительных историй ждет меня в этом году!
phenytoin clinical pharmacy
darknet market list bitcoin dark web darknet market
dark web market list darkmarket list drug markets dark web
blackweb dark net dark website
dark web marketplaces [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]blackweb [/url] tor market links
darknet marketplace dark web search engine dark web sites links
onion market best darknet markets darkmarket link
dark web search engines dark websites onion dark website
deep web drug links drug markets dark web darknet markets 2024
free dark web darknet drug market blackweb
blackweb official website dark web websites dark market
dark internet darknet drug market dark web search engine
darkmarket 2024 darknet markets onion address deep web markets
Дайте своей мебели новую жизнь с помощью перетяжки
перетяжка мебели [url=https://peretyazhka-mebeli-v-minske.ru/#перетяжка-мебели]https://peretyazhka-mebeli-v-minske.ru/[/url].
blackweb official website dark market url blackweb
darknet market links darknet drugs dark web sites
tor dark web darknet drug links deep web search
dark markets darknet seiten darkmarket list
dark websites darknet markets links darknet search engine
dark markets darknet marketplace darknet site
deep web search darknet websites tor dark web
dark net dark web sites darknet market links
darkmarket url [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]tor market links [/url] dark market url
dark market 2024 darknet market links the dark internet
darkmarket darknet marketplace dark market link
darknet market dark net dark market onion
best darknet markets dark web websites dark market 2024
darknet sites dark market link blackweb
dark web marketplaces how to access dark web dark websites
darknet market list dark market list deep web search
tor marketplace deep web drug links dark web websites
deep web sites darknet markets links black internet
dark market dark web search engine onion dark website
darknet websites dark markets darknet websites
dark web links dark web sites links darknet markets onion address
darknet markets how to access dark web darknet markets links
tor market dark market url dark web market
darkmarket url drug markets dark web tor darknet
dark web market links darknet marketplace dark web market links
dark web market urls darknet markets onion darknet markets
darkmarkets [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark web sites links [/url] dark web access
dark web websites darknet markets links darknet market lists
onion dark website the dark internet dark web market list
darkweb marketplace tor dark web how to access dark web
darknet market deep web search tor dark web
dark market link dark net dark net
tor darknet cryptomarkets darknet darknet drug store
darknet websites darknet market lists onion market
dark market url darknet markets 2024 dark web marketplaces
dark website darknet magazine dark web websites
dark web websites onion market deep web drug store
dark market url blackweb tor market links
dark market free dark web darknet market lists
darknet drugs dark web search engine dark market 2024
darkmarkets blackweb dark market link
dark web drug marketplace darknet market deep web search
darkweb marketplace darknet market lists dark market list
tor dark web tor market how to access dark web
tor markets dark market url dark market
tor drug market darknet drug links dark web link
black internet darknet markets 2024 darknet market
tor markets 2024 tor markets 2024 deep web markets
darkmarket darknet drug market deep web search
dark internet dark market onion deep web drug url
tor markets onion dark website how to access dark web
deep web links [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark web marketplaces [/url] tor market links
darknet market links dark markets onion market
dark web drug marketplace dark web market links darknet links
drug markets dark web darknet markets onion address darknet sites
dark web market urls the dark internet darknet links
darkweb marketplace onion dark website darknet market
darknet market links bitcoin dark web darknet market list
darkmarkets deep web drug url dark web marketplaces
dark web markets dark web markets tor markets 2024
dark market link darknet market links darknet drug links
darknet market dark website onion market
dark web market darknet drugs darkmarkets
darknet marketplace darknet markets onion darknet market lists
darknet sites darkmarkets darknet markets url
deep web drug links darknet market links darknet search engine
darknet drug store blackweb deep web markets
darknet markets links dark web market list dark websites
dark web market list tor dark web dark web market links
darkweb marketplace deep web drug links dark websites
deep web sites dark web search engines darknet market links
free dark web dark web link darknet markets
darknet site deep web drug url darkmarket url
dark markets drug markets onion darknet drug store
tor market dark web market urls dark market link
bitcoin dark web darkmarket 2024 darknet drugs
black internet darknet market darkmarkets
dark web markets dark web markets dark websites
tor market dark market onion dark web sites links
darknet drugs darknet market tor drug market
tor markets 2024 dark web link darkmarket 2024
the dark internet deep web drug links dark websites
darknet market links tor market black internet
darknet drug store tor marketplace darknet links
dark market 2024 darknet drug market darknet markets
dark web drug marketplace deep web markets darknet drug market
how to get on dark web darkmarket darknet drug links
dark web market list tor darknet darkmarket url
darkmarket 2024 dark web search engines dark market link
dark websites darknet seiten darknet markets url
dark website dark web link dark web search engine
dark market deep dark web tor market links
darkmarket link [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web market [/url] tor market url
darknet marketplace drug markets onion dark web link
darknet markets darkmarket url darkmarket list
free dark web dark market link deep web markets
deep web drug store dark web drug marketplace darknet markets onion address
darknet market list darknet links dark website
dark web drug marketplace black internet dark markets 2024
tor market tor darknet deep web drug url
deep web drug links best darknet markets dark internet
the dark internet tor dark web tor markets
deep web sites darkmarket 2024 dark web websites
deep web sites darknet markets onion address dark web sites
darknet markets darknet market links dark web search engine
dark web site how to access dark web dark web market urls
darknet drug links darknet sites darknet markets url
dark web websites darknet magazine darkmarket 2024
deep web search darkmarket url dark web links
dark web drug marketplace darknet markets url deep web markets
tor marketplace [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web drug marketplace [/url] deep web drug markets
dark market link dark website darknet market links
darknet drug links dark net dark market link
tor darknet darkmarket dark web websites
dark web market darknet site tor markets 2024
darknet market list darknet marketplace the dark internet
tor markets 2024 deep web links dark net
darkmarket 2024 onion market tor market
tor markets 2024 darkmarket darknet drug links
dark market 2024 free dark web tor market links
darkmarket url darknet links darknet sites
darknet markets onion darknet market bitcoin dark web
darkweb marketplace dark web sites dark market url
darkweb marketplace darknet search engine tor darknet
dark web sites tor drug market black internet
dark web market darknet markets 2024 tor markets
Мечтая о перспективном джипе, я решил приобрести один, но мои финансы были ограничены, и у меня была плохая кредитная история. Тогда мой друг посоветовал посетить сайт msk-zaim.ru, где я нашел МФО, специализирующуюся на займах для клиентов с просрочками и плохой кредитной историей. Благодаря этому сайту, я смог приобрести свой мечтанный джип и сделать его моим надежным спутником.
[url=https://msk-zaim.ru/]Займы без отказа – на покупку музыкальных инструментов[/url]
darknet markets links dark internet dark market onion
black internet darknet site darknet markets
dark web sites links dark web market list dark market url
dark web market urls darknet market lists darkmarket url
dark markets dark market url drug markets onion
tor drug market dark web market urls darknet magazine
dark market list dark web drug marketplace drug markets dark web
dark market 2024 free dark web dark web search engines
deep web markets dark market onion onion dark website
darkmarket link darknet marketplace darknet search engine
darknet seiten dark web search engine darknet markets url
blackweb bitcoin dark web dark web market
tor dark web dark markets dark websites
Я решила учить новую специальность и мне нужны были учебные материалы, но они были дороги. В поисках решения, я обратилась к Яндексу и нашла сайт msk-zaim.ru, где была подборка МФО 2024 года. Здесь я получила микрокредит на 10 000 рублей под 0% и смогла приобрести необходимые учебные материалы, что стало ключом к моему образованию и карьерному росту.
[url=https://msk-zaim.ru/]Займы онлайн – на ремонт кухонной техники[/url]
dark web search engine tor markets links tor market
darknet markets links dark web drug marketplace blackweb official website
darkmarkets dark web markets free dark web
Мечтая о перспективном джипе, я решил приобрести один, но мои финансы были ограничены, и у меня была плохая кредитная история. Тогда мой друг посоветовал посетить сайт msk-zaim.ru, где я нашел МФО, специализирующуюся на займах для клиентов с просрочками и плохой кредитной историей. Благодаря этому сайту, я смог приобрести свой мечтанный джип и сделать его моим надежным спутником.
[url=https://msk-zaim.ru/]Займы онлайн – на ремонт холодильника[/url]
tor market links darknet drug market dark market link
dark web market dark website darknet markets onion address
tor markets drug markets dark web dark web market urls
dark markets [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web sites [/url] how to get on dark web
darkweb marketplace dark web link darknet links
darknet drug links [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet seiten [/url] onion dark website
drug markets dark web tor market links dark web marketplaces
dark net onion market deep web drug url
darknet drug market tor markets 2024 deep web drug links
darknet search engine darknet market lists cryptomarkets darknet
darknet seiten dark web link dark net
dark net darknet sites darknet market
darkmarket bitcoin dark web dark web search engine
dark web site dark web drug marketplace dark web site
dark web links dark web websites darkmarket link
deep dark web dark web search engines tor markets
deep web sites dark web market urls free dark web
tor market tor marketplace how to get on dark web
deep web sites dark web links deep web links
tor market url dark market url darknet websites
darknet seiten tor market links darkmarket link
dark websites darkmarket url dark net
darkmarkets darknet market links dark web sites
dark websites darknet sites blackweb official website
tor market url [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark website [/url] blackweb
darknet magazine tor darknet bitcoin dark web
best darknet markets deep web drug links darkmarket list
darknet search engine dark web market list darkmarket list
darknet markets onion darknet seiten darknet markets 2024
dark website darknet markets url dark web access
darknet sites the dark internet dark web sites
dark web search engines dark web market darknet markets onion address
darknet search engine dark web link dark web sites links
dark web market links deep dark web dark web links
deep web drug url deep web drug url tor dark web
darknet markets darknet markets links black internet
tor markets 2024 dark websites darknet markets onion
darknet drugs dark web market urls tor dark web
deep web links darkmarkets drug markets dark web
dark web drug marketplace darknet sites deep web markets
deep web drug url darknet links dark web links
drug markets onion darkmarket url dark market url
darknet site [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web sites links [/url] darknet market
drug markets dark web dark web market list dark web search engines
deep dark web dark web markets darknet sites
Создайте атмосферу уюта с мягкой мебелью
перетяжка мебели [url=https://murom-mebel-tula.ru/]https://murom-mebel-tula.ru/[/url].
dark web search engines darknet markets tor market links
darknet markets onion [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark market 2024 [/url] darknet sites
dark web sites links darknet drugs dark web market links
tor markets 2024 drug markets onion dark website
best darknet markets the dark internet darknet market links
how to get on dark web darknet drug market black internet
darknet site darkmarket list dark web market
darknet markets tor markets dark websites
darknet drugs tor dark web darknet magazine
darknet site dark web link dark markets 2024
darknet market darkmarket link darkmarket link
darknet market links darknet markets onion darknet links
dark internet dark web sites darknet markets 2024
dark web sites dark net darknet market lists
darkmarket deep web links darknet magazine
dark web link darknet seiten darknet websites
free dark web dark web markets tor markets 2024
tor marketplace [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets [/url] dark web search engine
darknet drugs darknet links dark websites
tor markets darknet markets links dark websites
dark market [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark market 2024 [/url] darknet markets onion address
tor market dark net dark web market list
Стиральная машина внезапно перестала работать, и моя бытовая жизнь стала менее комфортной. Я начал искать замену, но бюджет был ограничен. В социальных сетях я увидел рекламу сайта msk-zaim.ru, где был представлен список новых МФО 2024 года. Заявка была подана моментально, и я получил одобрение. Деньги быстро поступили на мою банковскую карту, и теперь моя бытовая жизнь вернулась в норму с новой стиральной машиной.
[url=https://msk-zaim.ru/]Займы на карту – чтобы оплатить страховку автомобиля[/url]
dark web market links darknet markets darknet marketplace
dark web marketplaces dark web search engine deep web search
bitcoin dark web deep web search darknet markets 2024
blackweb darkmarket url dark web market links
dark web search engine darknet marketplace dark web market links
tor drug market onion dark website deep web sites
dark web market links bitcoin dark web darkmarket link
darknet market lists darkmarket how to get on dark web
darknet markets bitcoin dark web tor market
darknet websites tor markets darknet market lists
darknet links dark web websites deep dark web
dark web markets deep web drug store darknet drug links
darknet websites dark web link deep web sites
drug markets dark web darknet market list dark market onion
darkmarkets dark website darknet drug market
darkweb marketplace darknet sites cryptomarkets darknet
dark web market links [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web drug marketplace [/url] dark web search engine
darknet drug links darknet links dark websites
tor marketplace dark web market links tor darknet
dark market 2024 dark web market urls darknet marketplace
tor markets dark markets 2024 dark web market urls
darknet markets onion address tor markets free dark web
dark web websites darknet markets onion address darknet magazine
tor market links dark web search engines tor markets
onion market tor market links deep web search
Преобразуйте мебель с перетяжкой в домашнем ателье
перетяжка диванов [url=https://vk.com/peretyazhka_mebeli_by/]обивка мягкой мебели[/url].
darknet market links dark market link dark websites
darknet drug links deep dark web dark market 2024
dark market list free dark web darknet markets links
darknet market lists darknet markets onion dark web websites
darknet markets url tor darknet darkmarkets
dark web site drug markets dark web dark web sites links
tor dark web darknet markets dark market 2024
dark markets 2024 blackweb official website tor darknet
darknet sites [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark website [/url] tor market
tor markets deep web links tor darknet
dark net dark internet the dark internet
dark web market urls dark web site darknet websites
darknet markets onion dark web market urls dark web links
dark web search engines darknet seiten deep web drug markets
dark web access darknet market links darkmarket 2024
dark net darkweb marketplace darkmarket
tor market cryptomarkets darknet dark web site
blackweb official website darknet markets links darknet market lists
tor markets 2024 dark web search engines darknet links
dark web drug marketplace tor markets links dark web market links
dark web sites links free dark web dark web drug marketplace
tor marketplace darknet markets 2024 darknet links
onion dark website darknet drug store darknet marketplace
drug markets onion dark web market urls dark web site
free dark web deep web drug url dark market 2024
darknet markets [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]best darknet markets [/url] deep dark web
darkweb marketplace free dark web dark web site
darkmarket 2024 darknet market links darknet markets
tor markets dark web search engines darkmarkets
dark web access dark web search engines drug markets dark web
darknet drug store dark web sites darknet drug links
drug markets dark web tor drug market dark market 2024
deep web drug markets onion dark website dark web search engines
darknet markets links dark market darkmarket 2024
deep web sites tor drug market drug markets onion
dark web market urls deep web drug url darknet market lists
dark web links deep dark web drug markets dark web
dark market 2024 free dark web dark market list
darknet market tor markets darknet markets 2024
darkweb marketplace dark websites darknet seiten
dark market list darknet markets url darknet drug links
darknet site dark internet tor market url
tor market darknet markets links darkmarket 2024
deep web drug url [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]blackweb official website [/url] tor market
darknet websites tor dark web drug markets onion
darkmarket url [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]bitcoin dark web [/url] darknet market
dark web search engines tor markets links tor market links
darknet drug market deep web drug store dark web marketplaces
tor marketplace darknet seiten dark net
darkmarket link deep web links deep web drug store
dark web link darkmarket 2024 tor dark web
darknet drug links tor markets links deep web search
tor markets 2024 how to get on dark web darknet drug store
dark web site darknet sites dark net
dark web market list dark web marketplaces dark market url
deep dark web dark web drug marketplace blackweb
dark web market urls deep web drug url dark market onion
darkmarket list free dark web dark internet
darknet markets deep web drug markets darknet markets url
darknet drug links darknet drug links deep web drug markets
darknet drugs darknet sites best darknet markets
darknet markets 2024 deep web sites darkmarket url
dark website drug markets onion tor market
deep web search dark markets deep web drug markets
tor market deep web markets dark web sites links
dark websites drug markets dark web darknet market
dark web access darknet markets 2024 dark market link
darknet markets onion dark web market list darkmarket list
tor markets 2024 bitcoin dark web dark web search engine
darknet markets onion address darknet drug market free dark web
deep dark web dark market list darkmarkets
tor market dark web link dark web market links
how to get on dark web darknet site dark websites
darkweb marketplace tor market links darkweb marketplace
dark web sites cryptomarkets darknet darknet links
dark web market links darknet drug store darknet drug market
darknet markets url the dark internet dark market link
drug markets onion darknet markets dark web markets
darkmarket link [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web market list [/url] dark web market urls
the dark internet darknet websites tor darknet
darknet markets dark web access tor markets 2024
deep web links [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]blackweb official website [/url] deep web markets
deep web drug links dark market url darknet drugs
darkmarket dark websites free dark web
darknet seiten dark web market list darknet market
darknet market tor markets 2024 deep web search
dark web search engines darkmarket list darkmarket list
free dark web dark web search engines dark markets
darknet magazine dark web links darknet marketplace
darknet markets 2024 blackweb dark market 2024
darkmarket link darknet markets darknet drug store
dark market onion best darknet markets dark website
dark website dark market darknet market list
darknet markets 2024 tor markets tor market url
how to access dark web darkweb marketplace darknet search engine
tor market free dark web darknet markets onion
dark web markets [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web sites links [/url] deep web drug markets
dark web links dark website dark market url
drug markets dark web dark web market free dark web
darkmarkets dark market darkmarket 2024
darknet site darkmarket deep web drug markets
darknet site dark market list the dark internet
dark websites dark net dark web sites links
darknet search engine darknet markets onion address dark web markets
tor markets tor market darknet markets onion address
tor market url the dark internet darknet site
dark web access dark web search engine dark web site
darknet market links darknet markets onion address deep web drug store
dark market onion dark market url darknet magazine
darknet site [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]tor markets [/url] how to get on dark web
dark net tor dark web deep web drug links
tor markets links darknet links dark market list
darknet drugs dark web market links darknet drugs
deep web search darkmarkets darknet drug market
tor market url dark web site darknet market lists
deep web sites darkmarket list deep web links
dark market url onion dark website dark web market links
dark web market list dark web search engines deep web links
deep web drug store dark web links darkmarket link
tor drug market dark web markets dark website
onion dark website darknet market list dark markets 2024
deep dark web the dark internet darknet markets onion
blackweb official website dark web search engines tor market url
darknet market links darkmarket 2024 dark markets 2024
how to get on dark web darknet markets onion address darknet seiten
dark web sites tor market deep web drug markets
dark web link [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet search engine [/url] dark web sites
tor market dark market dark web link
the dark internet darknet magazine dark web drug marketplace
onion market darknet markets url cryptomarkets darknet
dark market dark web access dark markets
drug markets onion deep web drug links dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket url dark web search engine dark web search engines
tor darknet tor markets onion market
darknet links darkmarket url dark markets 2024
deep web drug store darknet market list darkmarket 2024
tor marketplace tor markets links darknet drug store
dark web search engines dark internet tor marketplace
darknet markets url onion market darknet drugs
dark web market dark web sites links deep web drug links
drug markets onion darknet sites onion market
darkmarket url tor markets links deep web markets
dark market deep web sites best darknet markets
deep web links dark website deep web drug markets
dark markets 2024 darknet websites dark web market urls
tor darknet dark web websites how to access dark web
deep web drug links dark web market links dark web search engine
tor marketplace tor market darknet seiten
darknet drug store darknet market links darknet markets onion
dark web market urls darkmarket 2024 dark market list
darkmarket url dark market link dark market onion
dark market url darknet site dark net
darknet market list darknet market lists dark web access
dark web sites darknet drug links dark website
tor dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark markets 2024 [/url] dark internet
deep web drug markets darknet site darknet markets 2024
best darknet markets tor market darknet markets links
dark web market links how to get on dark web darknet sites
blackweb official website darknet sites dark net
dark web sites links black internet darknet sites
drug markets dark web dark web market links tor drug market
how to get on dark web darkmarkets darknet markets
dark web websites tor markets links dark web site
darknet sites dark web links dark web sites
dark market 2024 dark web link dark web market
onion market darknet markets 2024 dark web market urls
dark markets dark market darknet websites
how to access dark web dark net deep web drug markets
dark net drug markets dark web darknet drug market
onion market onion dark website free dark web
darknet markets tor darknet dark website
dark market link [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet drugs [/url] deep web sites
dark web market urls darkmarkets darkmarket 2024
dark web sites drug markets onion dark websites
dark markets darkweb marketplace darknet market links
darkmarket list dark web market links darknet websites
drug markets dark web darknet links dark web markets
darknet markets url dark market link dark web market links
blackweb official website deep web drug links tor drug market
deep dark web darknet markets 2024 dark markets
deep web sites onion dark website dark web markets
darkmarket list darkmarket link dark web site
dark market url darkmarket list darknet websites
cryptomarkets darknet dark website deep web drug url
dark web market links tor markets darkmarket
tor market url [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark internet [/url] darknet links
dark website black internet best darknet markets
drug markets onion dark internet darknet search engine
darknet markets onion address darkmarket link darkmarkets
darknet websites darknet drug store darknet markets url
dark web sites links dark web market urls dark website
blackweb official website tor marketplace darknet markets url
deep dark web deep web drug markets dark web marketplaces
blackweb official website dark markets 2024 tor markets links
dark web search engine darknet markets dark markets 2024
deep web drug links dark web search engine dark web markets
drug markets onion dark web market darknet drug market
tor market url black internet dark web sites links
dark web websites darknet search engine darkmarket list
darknet magazine dark market darkmarket url
darknet markets url dark markets tor darknet
darknet market links onion market dark web market list
darknet seiten deep web links dark web links
darknet drugs darknet markets onion black internet
dark markets 2024 cryptomarkets darknet darkmarkets
darknet market dark web link deep web drug store
dark web markets darknet drugs onion dark website
darknet market cryptomarkets darknet darknet search engine
darknet websites free dark web tor markets 2024
tor market links dark market list darknet links
tor markets links dark market 2024 darkweb marketplace
deep web sites darknet sites deep web markets
dark web search engines dark web search engine darknet site
darknet sites dark market 2024 deep web sites
darkmarket url darknet site darknet markets
dark web market urls dark web site darknet websites
the dark internet best darknet markets darknet drugs
free dark web darknet marketplace darknet market
dark internet [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]deep web drug url [/url] tor markets links
deep web drug links [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet search engine [/url] dark web sites links
Сезонная скидка на ремонт холодильников
ремонт холодильников [url=https://remontholodilnikov-vminske.ru/]ремонт холодильника[/url].
dark web marketplaces dark market link drug markets dark web
the dark internet deep web drug url dark web marketplaces
darknet market tor market darkweb marketplace
darknet markets onion darkmarket tor markets 2024
deep web sites dark web access darknet market
darknet drug market dark market 2024 darknet websites
darknet drug store dark web markets tor markets 2024
darkmarket 2024 darknet markets onion tor darknet
dark web site darknet site dark web market
dark web marketplaces darknet marketplace deep web drug store
dark net dark web markets dark market onion
deep web drug store the dark internet tor market links
dark web marketplaces black internet darknet links
darknet markets 2024 darkweb marketplace tor marketplace
deep web sites darknet market darknet search engine
dark web site dark web access darkmarket
darknet links darknet marketplace deep web drug url
darknet drug store bitcoin dark web tor market links
cryptomarkets darknet deep web drug url darknet websites
darkmarket link cryptomarkets darknet darknet drug market
how to get on dark web deep web drug links how to access dark web
darknet markets onion address darknet markets url dark web links
darkweb marketplace darknet site deep web drug store
darknet search engine dark web websites darkmarket list
dark web markets darknet marketplace tor market url
deep web markets blackweb official website deep web sites
deep web markets darknet links darknet marketplace
dark web search engine blackweb official website darkmarket url
dark market url darknet market links darknet marketplace
darkmarket link dark market list dark web sites
cryptomarkets darknet darknet marketplace darknet seiten
deep web search dark market url deep web drug links
darkmarket link tor market dark web access
deep web markets dark web market list dark market
deep web drug store [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets links [/url] darknet marketplace
bitcoin dark web dark web drug marketplace cryptomarkets darknet
darkweb marketplace dark markets 2024 deep web markets
darkmarket link darknet markets dark web market list
darkmarkets darknet marketplace darknet seiten
best darknet markets tor market links free dark web
darknet market list tor market tor drug market
dark markets 2024 deep dark web deep web sites
dark web sites links deep dark web dark market link
darknet drug market bitcoin dark web tor marketplace
tor markets links dark web sites darkmarket link
darkmarket link darkmarket url how to access dark web
deep web search darknet markets 2024 dark web marketplaces
deep web drug store darknet markets links best darknet markets
dark web websites tor drug market dark web market
darknet websites darknet markets 2024 dark website
dark web market list darknet market dark web market links
best darknet markets darknet markets links tor market
darknet site darknet drug market dark web market links
dark web markets dark markets 2024 darkmarket list
dark market link darknet markets 2024 darknet links
darkmarket url dark web sites deep web drug markets
darknet drug links darknet drug store darkmarkets
dark net tor market dark web search engines
the dark internet darknet market links tor market url
dark web access tor markets 2024 how to access dark web
tor drug market darknet markets tor darknet
deep web drug markets tor marketplace darkmarket list
dark website dark web drug marketplace onion market
darknet links deep web sites darknet search engine
dark web market links how to access dark web darknet sites
dark web marketplaces deep web markets deep web drug links
blackweb darknet marketplace deep web drug store
darknet markets url dark web search engine the dark internet
darkmarket list dark web market tor market url
tor drug market dark markets 2024 tor marketplace
darknet market links drug markets onion darkmarkets
dark web drug marketplace blackweb black internet
tor markets links darknet markets 2024 how to get on dark web
dark web link deep web drug markets tor market url
how to get on dark web tor darknet darknet markets url
darkmarkets dark net dark web search engine
dark web marketplaces darknet websites dark web search engines
darknet sites deep web drug store cryptomarkets darknet
deep web drug url darkmarket link darknet markets onion address
darknet links dark web access dark web market
darkmarket url dark web sites dark web market urls
darknet markets darknet seiten cryptomarkets darknet
onion dark website [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]the dark internet [/url] dark web markets
tor marketplace darknet site darknet markets url
darkweb marketplace deep web sites darknet market list
darknet marketplace dark web market darknet search engine
dark market link cryptomarkets darknet darknet drug market
dark web search engines dark web sites links dark web market links
deep web drug markets darknet drug store dark web link
dark market link darknet drug links darknet markets links
tor market darknet magazine deep web search
best darknet markets dark web links tor markets
dark web search engine dark web access dark web websites
darkmarkets darknet drug links blackweb official website
darknet site deep web search darkmarket list
drug markets onion dark market 2024 cryptomarkets darknet
darknet marketplace darknet markets onion dark web links
Как много мы пропускаем в жизни, не пробуя нового, – подумал я, когда впервые решил посмотреть [url=https://animehit.tv/]аниме онлайн бесплатно[/url]. Этот момент стал для меня настоящим откровением. Я ожидал увидеть просто мультфильмы, но вместо этого попал в мир, полный глубоких эмоций и завораживающих историй. Каждая серия была наполнена чем-то особенным, будь то радость, грусть или волнение. Я почувствовал, как моё сердце откликается на каждый поворот сюжета, и с тех пор аниме стало частью моей жизни.
tor markets 2024 dark web market list dark market 2024
deep web markets [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]deep dark web [/url] bitcoin dark web
onion market tor market url dark web market urls
dark markets 2024 how to get on dark web darknet drugs
dark web market darkmarket url dark web access
darknet sites dark markets darknet markets
darknet websites darkmarkets dark web access
deep web search darknet websites deep web links
darknet market list darkweb marketplace dark websites
dark web market urls dark web websites deep web drug links
onion dark website dark web market urls dark web market links
dark markets 2024 tor darknet darkweb marketplace
dark web links dark market link dark web search engines
darknet websites tor market black internet
tor drug market tor market dark web market urls
cryptomarkets darknet free dark web darknet drugs
darknet links [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet search engine [/url] dark web websites
deep web drug url onion dark website tor drug market
dark markets 2024 tor markets links darknet site
dark net darknet markets onion address dark market list
tor market url dark web websites dark net
darknet magazine darknet drug links deep dark web
deep web markets dark internet darknet magazine
tor market dark website dark website
dark market 2024 deep web markets darknet drugs
drug markets onion blackweb official website bitcoin dark web
how to get on dark web dark web link blackweb
darknet markets onion address blackweb official website dark web market links
darknet market lists tor market links dark internet
darknet links dark market list darknet market list
free dark web darknet drug links deep web sites
dark market link tor marketplace deep web drug url
darkmarket list tor darknet dark web search engine
deep web markets best darknet markets deep web sites
darknet market links tor markets deep dark web
dark web marketplaces dark web link dark net
dark market url tor dark web dark web markets
darknet site darknet market list tor markets 2024
dark web market links darknet sites deep web drug markets
deep web drug markets tor market links darknet markets onion address
tor darknet tor market links dark web drug marketplace
darkweb marketplace tor darknet darknet websites
dark market 2024 tor darknet darknet sites
deep web drug store the dark internet dark web market urls
deep web drug url dark web marketplaces drug markets onion
onion dark website [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]onion dark website [/url] dark markets
darknet drug links dark market url darknet markets onion address
onion dark website tor markets 2024 bitcoin dark web
dark web marketplaces dark web market list darknet websites
darknet market darknet site darknet sites
darknet markets onion dark market tor market url
darkmarket list darkmarket 2024 dark market onion
tor darknet darknet markets blackweb official website
darknet websites dark web market list the dark internet
bitcoin dark web dark market dark markets 2024
the dark internet darknet drugs darknet websites
dark market link tor markets links darknet market links
how to access dark web deep web drug store dark web marketplaces
onion market darknet drugs darknet sites
darknet websites darknet seiten darkmarket 2024
deep web search dark web market dark markets 2024
dark web search engines darknet marketplace darkmarket list
dark website darknet markets url blackweb
deep web search the dark internet how to access dark web
darknet drug store tor darknet darknet markets onion address
onion dark website darknet drug links dark web access
deep dark web dark markets darknet drugs
how to get on dark web deep web drug store dark web drug marketplace
dark websites tor markets 2024 tor market url
deep web search darkmarket dark web markets
dark markets 2024 how to get on dark web bitcoin dark web
deep dark web dark web search engines dark web access
dark market link deep web drug store tor markets
onion dark website darkmarket list tor darknet
deep web drug links darknet drug links tor markets
dark market list deep dark web tor market url
darknet market darknet markets 2024 deep web drug store
dark web market list black internet dark web markets
darknet search engine onion market deep dark web
dark web websites tor dark web dark market url
darkweb marketplace tor drug market deep web search
dark market list dark websites dark web sites
darknet seiten deep web markets onion market
blackweb official website dark web market list darknet links
dark markets 2024 darknet links free dark web
darknet markets url dark web marketplaces darkmarket 2024
tor markets 2024 darkmarket onion market
dark internet darknet markets onion address deep web drug store
free dark web how to access dark web dark web market links
dark web market urls bitcoin dark web darknet market links
darknet markets 2024 blackweb official website deep web drug links
darknet websites darkmarket darknet drug market
dark web access darknet magazine dark web market
dark web links tor market url deep web links
darknet websites cryptomarkets darknet darknet drug store
drug markets onion tor drug market blackweb
tor market url dark web market list blackweb
deep web search tor darknet deep web drug markets
tor market url tor market links dark web sites
dark web sites darknet site deep web drug markets
darknet seiten deep web sites darknet drug market
the dark internet darknet links how to access dark web
Embark on an unforgettable journey with the adult anime-style comics at Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/artists/luxsumildo/]hentai online[/url] . Our curated collection features an eclectic mix of genres, each comic crafted to ignite your imagination and stir your emotions. From the depths of fantasy realms to the complexities of modern life, our stories encompass a wide spectrum of themes, all portrayed through stunning anime artwork. Experience tales of heroism, love, and adventure, each narrative masterfully woven to keep you engrossed. Perfect for those who appreciate the art of storytelling combined with exquisite illustrations, Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/manga/furry-lane/]hentai furry[/url] is your destination for a mesmerizing evening. Visit Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/manga/nobara-kugisaki/read/p/3/]nobara hentai[/url] and let each comic take you on a journey beyond the ordinary!
dark web sites links darknet links dark web sites
drug markets onion [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darkmarket list [/url] dark website
darkmarkets bitcoin dark web best darknet markets
dark web link darknet search engine darkmarket link
deep web drug markets deep web markets darkmarket 2024
darknet markets url darknet websites dark web market
darknet seiten darknet websites darknet markets
deep web drug markets dark website dark market link
black internet dark web market urls dark market onion
darkweb marketplace darknet seiten darknet magazine
darknet drug market bitcoin dark web dark web sites links
darknet search engine darkweb marketplace darknet seiten
dark web links darknet websites darknet markets onion address
darkmarket best darknet markets tor drug market
darkmarket 2024 darkmarket list dark websites
blackweb dark web market urls dark market onion
darkmarket url dark market darknet markets onion
darknet markets links how to get on dark web dark web drug marketplace
dark web search engine darkmarket url black internet
darknet markets onion dark internet darknet magazine
deep web drug store dark web link dark website
dark web access blackweb official website darknet markets onion
darknet marketplace [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web marketplaces [/url] darkmarket
tor markets 2024 darknet websites deep web search
deep web drug store darknet site dark web market links
dark markets darkmarket link drug markets dark web
darknet markets onion darknet seiten deep web sites
dark websites darknet search engine dark market list
how to access dark web darknet drug links darkmarket
dark web drug marketplace tor markets links tor drug market
deep web drug store darknet markets onion address darknet magazine
tor dark web dark web markets dark web markets
drug markets onion tor markets 2024 dark web access
dark web site darknet drug links darkmarket list
dark web search engine darknet market links dark web market urls
dark internet darknet drug store dark internet
dark web link darknet links deep web drug links
dark website tor dark web dark web links
dark web link dark web access drug markets onion
darkweb marketplace dark web access blackweb official website
deep web links deep web drug links darkmarket
darkmarket darknet marketplace dark market link
darknet market deep web search dark market 2024
dark market [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web sites links [/url] darknet drug store
darknet marketplace bitcoin dark web tor markets links
bitcoin dark web deep web drug url dark markets 2024
dark web markets deep web markets drug markets onion
tor markets darknet drug store darkmarket link
the dark internet dark market link dark market onion
tor darknet darknet market dark web search engines
darknet drug market darknet marketplace tor market
darkmarket dark website free dark web
tor marketplace darkmarket url tor market url
deep web drug markets free dark web dark web websites
dark web access dark markets 2024 tor market url
dark web access darknet market list dark web market links
darknet search engine blackweb official website darknet markets onion address
deep web drug url dark web sites dark web link
darknet market lists tor drug market how to access dark web
dark net darknet magazine darkmarket 2024
darknet drug market dark market onion dark net
darknet links dark net dark markets 2024
tor markets links darknet websites darkmarket link
dark market list darkweb marketplace tor markets links
onion dark website darknet marketplace how to get on dark web
dark web market list blackweb darknet markets 2024
dark website [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]how to get on dark web [/url] dark market list
dark websites dark web sites links deep web markets
tor market url dark web sites dark market url
best darknet markets darknet drug links free dark web
the dark internet dark websites dark web site
tor market deep dark web darkmarket 2024
tor market url darknet market darknet links
tor markets 2024 darknet websites dark web markets
darknet markets url darknet websites darknet drugs
dark websites dark market dark web search engine
tor markets 2024 dark web market urls darknet markets links
dark web access dark web markets tor dark web
tor marketplace dark web access darknet search engine
onion dark website tor markets 2024 tor markets 2024
tor dark web onion dark website dark web search engine
darknet search engine tor darknet dark web search engine
dark web sites dark web site tor darknet
dark web websites how to get on dark web dark net
deep web links darknet site darknet markets links
onion dark website darkweb marketplace darknet site
dark websites dark web marketplaces tor market links
dark web sites dark web markets onion dark website
deep web drug store dark market list dark web markets
dark web search engines dark market list darknet markets links
dark web search engine deep web markets darknet markets url
darknet marketplace darknet markets url tor market url
tor darknet black internet deep web links
darknet market lists tor market links dark market
dark market url dark market onion darknet markets onion address
tor markets 2024 how to get on dark web dark markets 2024
tor dark web free dark web darkmarket url
tor market links darknet market darkmarket url
tor markets 2024 darkmarket list tor darknet
dark web link darknet search engine dark market onion
dark web sites links darknet market list how to access dark web
dark web websites tor markets tor market links
darknet markets darknet market tor dark web
tor dark web best darknet markets dark market url
darknet markets [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet drug links [/url] dark web markets
darknet drug links deep web drug store deep web links
tor markets links onion dark website tor dark web
darknet markets onion address dark market 2024 darknet seiten
drug markets dark web tor markets 2024 blackweb official website
darknet drug links darknet markets onion tor marketplace
tor marketplace tor markets 2024 dark web search engines
blackweb darknet search engine dark web websites
deep web drug store free dark web dark internet
drug markets dark web tor markets darknet markets links
deep web drug links darknet markets links deep web drug markets
deep web drug url cryptomarkets darknet darknet drug store
tor darknet dark web site dark web links
dark web market blackweb official website darknet drug market
darknet site dark market url onion dark website
dark market link drug markets dark web darknet drugs
dark web market links tor dark web how to get on dark web
drug markets dark web dark internet darknet drug store
drug markets dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark web access [/url] how to access dark web
darknet drug market darkmarket url dark web market list
deep web links darknet marketplace darknet drug links
dark web site [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]deep web links [/url] darknet search engine
tor market darknet markets onion deep web search
darknet markets onion address tor drug market dark web market list
onion market darknet markets dark web market
onion market dark web marketplaces tor market links
dark web drug marketplace dark markets 2024 dark web access
tor market url best darknet markets darknet markets links
darknet links darkmarket list darkmarket url
darkmarket link darkmarket url tor market
darknet market onion dark website darknet seiten
bitcoin dark web darknet drug market dark web market links
tor markets darknet markets 2024 dark market 2024
deep web drug links deep web links deep web search
best darknet markets tor marketplace deep web sites
deep web drug markets darkmarket bitcoin dark web
tor market links darkmarkets darkweb marketplace
dark market [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark web websites [/url] darknet drug market
onion market [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]deep web drug url [/url] darkmarket list
onion dark website dark websites deep web drug url
dark web drug marketplace darknet links dark internet
dark web market links the dark internet deep web markets
darknet markets links dark web market links black internet
dark web drug marketplace dark internet dark web marketplaces
deep web drug markets dark market 2024 how to access dark web
deep web drug links how to access dark web darknet markets
deep web links dark web websites darknet site
deep web drug store darkmarket 2024 the dark internet
dark net darknet markets tor market links
dark market dark web market urls darknet markets links
darknet markets onion address deep web drug url dark websites
darknet links [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet market [/url] dark market link
darkmarket darkweb marketplace deep web links
tor market url deep web links darkmarket url
deep web drug url dark web market tor markets 2024
tor drug market darknet market links darkmarket list
dark web access dark web websites dark markets 2024
darknet markets 2024 dark web market urls tor market url
blackweb dark websites dark web market list
bitcoin dark web darknet drugs dark web market urls
deep web drug links dark market onion deep web links
darkmarkets dark market url onion market
dark web link dark market list darknet drug market
deep web drug store dark web search engine darkmarket 2024
dark markets 2024 darkweb marketplace dark markets 2024
dark web markets bitcoin dark web the dark internet
the dark internet dark net dark web link
drug markets dark web bitcoin dark web darknet markets links
how to access dark web dark websites deep web drug url
dark web link deep web markets darknet market links
dark web market links dark net darknet drug market
tor market links dark market 2024 darkmarket 2024
darknet markets blackweb official website darkmarket url
dark web marketplaces darknet markets onion address dark market 2024
darknet drugs darknet market links tor markets links
dark web market dark internet tor market links
dark web markets darknet links tor drug market
dark web drug marketplace [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darkmarket link [/url] dark markets
how to access dark web dark web websites dark market link
dark web links darknet market lists cryptomarkets darknet
dark websites [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]black internet [/url] darknet drugs
dark web market links tor market dark websites
darkweb marketplace dark markets 2024 darknet market
free dark web tor drug market darknet drug market
deep web drug store dark markets 2024 tor markets
darknet market list dark web site deep dark web
cialis vs tadalafil
dark net dark websites tor markets 2024
darknet drugs free dark web dark web link
darkmarket deep web drug links tor dark web
darknet drugs darknet drug store drug markets dark web
dark net dark market dark web search engines
darknet sites darknet websites dark web websites
tor markets 2024 dark market darkmarket link
how to get on dark web darknet seiten the dark internet
darknet sites darknet market links best darknet markets
darknet drug links dark web market links dark website
darkmarkets darkmarket list deep web drug links
how to get on dark web drug markets onion dark web search engine
dark web links tor darknet dark web access
deep web markets darknet magazine tor market links
darknet markets links darkmarket list dark web market
darknet site darknet market list deep web drug markets
deep web drug url [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]tor markets links [/url] darkmarket list
how to access dark web darknet markets darknet marketplace
bitcoin dark web [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet market links [/url] darknet magazine
dark web market urls dark web search engines dark web access
deep web drug url dark web drug marketplace darkmarket 2024
darknet markets links tor markets 2024 onion dark website
dark market list dark web market tor market url
dark web search engine darkmarket url deep web sites
deep web sites cryptomarkets darknet darknet markets onion address
deep web search dark web sites links the dark internet
dark web sites tor marketplace dark web markets
deep web links free dark web darkmarket
dark web markets dark markets 2024 tor dark web
dark web marketplaces darknet markets onion drug markets dark web
onion dark website [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web websites [/url] dark website
deep web links darknet market dark market
darknet markets links [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]bitcoin dark web [/url] dark market onion
dark market list deep web sites darkweb marketplace
deep web drug store darkmarket 2024 dark markets 2024
darknet markets onion address darkmarket link dark web market
darknet markets free dark web cryptomarkets darknet
dark market list dark net deep dark web
bitcoin dark web darknet markets onion address deep web markets
dark net dark market list deep web drug url
how to get on dark web darkmarket drug markets dark web
tor market url dark web marketplaces dark web sites
Looking for a one-stop destination for all your adult comic needs? Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/tag/time-stop/]time stop hentai[/url] has you covered! Dive into our diverse world of adult comics, where every genre from suspense to romance is available at your fingertips. Our comics are more than just stories; they’re an adventure for the senses, designed to thrill and entertain. Whether you’re seeking a quick escape or a deep dive into new worlds, our collection is sure to enthrall. Let Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/characters/boruto-uzumaki/]boruto hentai[/url] be your guide to a world of excitement and pleasure. Explore our collection at Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/characters/android-21/]android 21 hentai[/url] and let your leisure time sizzle!
dark net dark market list darknet markets url
tor market url darknet drug store dark web site
darkmarket list onion market how to access dark web
dark web search engines [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet websites [/url] dark markets 2024
dark internet deep web drug store tor markets 2024
darknet markets links blackweb official website darknet market lists
tor market [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets links [/url] drug markets onion
Embark on an unforgettable journey with the adult anime-style comics at Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/]doujin hentai[/url] . Our curated collection features an eclectic mix of genres, each comic crafted to ignite your imagination and stir your emotions. From the depths of fantasy realms to the complexities of modern life, our stories encompass a wide spectrum of themes, all portrayed through stunning anime artwork. Experience tales of heroism, love, and adventure, each narrative masterfully woven to keep you engrossed. Perfect for those who appreciate the art of storytelling combined with exquisite illustrations, Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/]hentai manga[/url] is your destination for a mesmerizing evening. Visit Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/tag/yaoi/]yaoi hentai manga[/url] and let each comic take you on a journey beyond the ordinary!
tor dark web dark websites dark web search engines
dark markets 2024 darknet markets links drug markets dark web
darknet market darknet websites deep web sites
the dark internet deep web drug links darkmarket url
dark web search engines tor dark web dark web link
Looking for a way to make your evenings more thrilling and enjoyable? Dive into the world of Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/tag/futanari/]futanari manga[/url] ! Our site is a haven for adult comics, designed with guys in mind but great for couples too. Explore our vast selection, ranging from the adventurous to the romantically risque. We keep our collection fresh and exciting with daily updates of new comics and eye-catching images. Whether you’re in the mood for a solo adventure or a shared experience with your partner, Hentailoop.com – [url=https://hentailoop.com/manga/story-of-an-elf-girl-x6/read/p/6/]elf hentai[/url] is your go-to destination for an evening full of surprises and delights!
tor markets 2024 onion market darknet drug market
deep web sites darknet market links darkmarket url
dark web site darknet market list dark web market urls
darknet markets links darkmarket url darkmarket
darknet market links darknet links dark web access
dark web site dark web markets dark net
dark web access dark market blackweb
black internet darknet sites tor market
tor markets [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet seiten [/url] dark internet
dark web links darknet magazine darkweb marketplace
dark web search engine darknet sites dark websites
dark web access tor market links darknet site
darknet drug market deep web sites dark web search engine
dark web link darknet markets dark web market
darknet links blackweb bitcoin dark web
best darknet markets tor markets links darknet drug store
tor dark web darkmarket url darknet market links
darknet markets onion darkmarkets dark web marketplaces
tor market links dark net tor marketplace
darkmarket list darknet market list darknet sites
dark websites how to get on dark web deep web drug markets
darknet site dark web markets dark web site
dark web market links darknet marketplace dark web market urls
darkmarket url free dark web dark web search engine
dark web market list [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark market list [/url] darknet drug links
deep web search dark markets darknet search engine
dark web market links darknet markets links dark web markets
darknet drugs dark web site tor dark web
tor dark web darkmarkets darknet drugs
darknet drug store tor market deep web links
darknet markets blackweb drug markets dark web
darknet site darknet market list deep web links
dark web link tor marketplace darknet markets onion
darknet websites onion dark website free dark web
dark markets darkmarkets tor dark web
dark web market urls darknet market darknet drug store
dark web drug marketplace dark web link darknet markets
deep web search deep web markets blackweb official website
blackweb official website darknet markets onion dark web market links
how to get on dark web darknet magazine dark market url
darknet markets url deep web drug links onion dark website
deep web sites darknet markets url darkmarket link
darkmarket url best darknet markets deep web links
dark web marketplaces dark web markets deep web sites
blackweb official website dark web links tor markets links
Недавно, одним вечером, я и моя подруга решили найти что-то новенькое для просмотра. Давай посмотрим аниме! – предложила она. Мы сразу же включили Google и начали поиск. Первым в списке выскочил сайт [url=https://animehit.tv/anime-2024/]смотреть аниме 2024 онлайн[/url]. Не веря своему счастью, мы открыли его и офигели – там был просто огромный выбор аниме на русском языке, и все в HD 720 качестве! Мы выбрали несколько сериалов и устроились удобно. Весь вечер прошёл в атмосфере увлекательных историй, и мы даже не заметили, как пролетели часы.
dark market darknet drug store dark net
blackweb tor market tor drug market
tor market links darknet market deep web drug url
dark web market urls dark web markets tor dark web
darknet drugs bitcoin dark web darkmarket 2024
darknet markets onion deep web links dark web links
drug markets onion darknet drug market darknet markets onion address
dark web sites dark web market urls dark net
dark market 2024 dark market 2024 dark web access
darknet market list tor markets drug markets dark web
tor markets 2024 best darknet markets blackweb
Недавно я решил найти новый ресурс для просмотра аниме. Зайдя в Google и введя запрос аниме смотреть онлайн, я наткнулся на сайт [url=https://animehit.tv/]аниме смотреть онлайн[/url]. Сайт выделялся среди других: огромный выбор сериалов и фильмов, все доступно бесплатно и на русском языке. Что особенно порадовало, так это отсутствие назойливой рекламы, которая часто мешает просмотру. Благодаря этому сайту, я смог полностью погрузиться в просмотр своих любимых сериалов без каких-либо помех.
how to get on dark web dark web market dark web link
dark market onion tor darknet darknet markets links
onion market dark web sites links dark web drug marketplace
dark market deep web markets dark markets 2024
darkmarket link darknet markets 2024 darknet market list
dark web search engine [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web site [/url] blackweb
Готовы к новым приключениям? – спрашивал я своих друзей, когда мы собирались вместе, чтобы посмотреть [url=https://animehit.tv/anime-novinki/]новые аниме онлайн[/url]. Всегда есть что-то волнующее в ожидании новых серий, особенно когда ты не знаешь, что тебя ждёт. Наша маленькая вечеринка премьер превратилась в настоящий фестиваль удивлений и восторга. Какие же они крутые, эти новинки! – восклицали мы, уставившись в экран. Каждое новое аниме было как открытие неизведанного мира, полного приключений и эмоций.
darknet markets 2024 how to get on dark web deep web drug store
dark web marketplaces blackweb deep web markets
dark web market list darkmarket url dark markets 2024
darknet drug links tor market url dark web sites links
deep dark web deep web drug url dark web search engines
dark website dark web sites links dark web market list
dark market url darkmarket link tor market url
dark web sites links darknet search engine dark web search engines
tor markets links tor markets links tor markets
darknet site tor markets links how to access dark web
free dark web darkmarket list darknet market list
darkmarket list tor markets links dark market link
deep web drug links dark websites black internet
darknet links [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark web markets [/url] deep web search
black internet darknet drug market dark web site
deep dark web blackweb blackweb
dark web market urls dark web market urls dark web market list
dark web site dark web market darkmarket link
black internet darkmarket tor darknet
darknet market list dark market 2024 darkmarket
dark market darknet sites darkmarkets
darknet drug links dark web search engines dark web marketplaces
tor darknet deep web links dark net
darknet market lists darknet markets 2024 bitcoin dark web
darknet magazine drug markets dark web onion market
darknet marketplace darkmarket url dark net
darknet markets url [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet websites [/url] darknet seiten
free dark web dark web search engines deep dark web
darknet drug links [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]tor markets [/url] deep web links
dark website dark web access darknet site
tor market links darkmarkets deep web links
dark market link tor markets links dark market 2024
darknet market lists deep web drug markets darknet markets onion address
bitcoin dark web dark web link tor markets 2024
tor dark web blackweb official website deep web drug store
darknet drug links blackweb official website tor drug market
darknet links dark web markets tor market links
tor market url dark markets darknet links
darknet market darknet links deep web search
darknet markets onion address darknet links tor markets
dark web marketplaces darknet site onion dark website
tor markets 2024 dark web access deep web drug store
tor markets links deep web drug url how to get on dark web
darkmarkets darkmarket 2024 dark web search engines
dark internet darknet site dark internet
dark web search engines dark web market darknet market lists
darknet marketplace tor markets links dark market 2024
->>>>>>>>>>>>>сильнейший приворот на парня<<<<<<<<<-
______________сильный приворот на мужчину самостоятельно _____________
https://privorot4.wordpress.com
приворот на мужчину по фотографии, а также:
->>>>>>заговор на звонок парня читать
->>>>>>приворот на замужнюю женщину
->>>>>>заговор на мужа читать в домашних условиях который точно сработает
->>>>>>обряд на привязку любимого
darknet marketplace dark websites best darknet markets
darknet search engine tor markets links darkmarkets
tor markets 2024 dark market list darknet magazine
dark web marketplaces darknet markets deep dark web
dark web sites dark web websites dark website
how to access dark web tor marketplace dark web market urls
best darknet markets [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]blackweb official website [/url] blackweb official website
how to access dark web dark web market links dark web sites
tor dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark market onion [/url] darknet drugs
darknet markets onion tor dark web darkmarket list
darknet drug store darknet markets onion address dark markets
dark net dark web drug marketplace darknet market list
darknet drug market tor dark web deep web drug markets
the dark internet the dark internet darknet drug store
deep web markets deep web search darknet markets
dark website deep web drug links darknet drugs
dark market onion darkmarkets darkmarket
dark web site darknet sites drug markets dark web
tor dark web deep web search darknet market list
dark internet darkweb marketplace darknet markets
dark net dark web marketplaces darknet site
dark market 2024 dark websites darknet market list
how to access dark web dark websites darknet marketplace
dark market list darknet marketplace deep web drug url
dark web drug marketplace dark web marketplaces black internet
deep web markets dark website dark internet
darkmarket url darknet magazine black internet
deep web links darknet search engine dark web marketplaces
dark web sites links deep web drug links tor marketplace
darkweb marketplace tor drug market dark website
darkmarket [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet market [/url] dark web access
dark markets 2024 darknet market lists dark market link
dark market url [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark market link [/url] dark web search engine
dark web links cryptomarkets darknet darkmarket
onion dark website darkweb marketplace dark web market links
tor marketplace deep web links darknet drug store
deep web drug url darknet drugs dark web market
darknet links onion market dark market url
tor drug market darknet magazine deep web drug links
darknet markets url dark web sites dark web market urls
cryptomarkets darknet darknet magazine darknet websites
darknet market list darknet drug links best darknet markets
darknet links dark internet dark web market
deep web sites darknet market dark web market urls
darknet markets 2024 deep web drug markets dark web sites
deep web sites tor marketplace dark web drug marketplace
tor darknet dark market link how to get on dark web
dark web link darknet marketplace dark web link
darknet markets cryptomarkets darknet dark market url
dark markets how to get on dark web darknet drug market
darknet drug store tor darknet dark web links
tor marketplace [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]tor markets 2024 [/url] darknet markets onion
dark internet dark web market tor darknet
darknet drug store dark market link tor market links
deep web sites darkmarket url onion dark website
deep web sites bitcoin dark web tor market
dark markets 2024 blackweb official website black internet
tor dark web blackweb official website dark market 2024
darknet markets darkmarkets dark market link
dark market link dark web market urls darknet markets links
tor markets 2024 blackweb darknet markets links
dark web links tor dark web dark web link
deep web search deep web search darknet markets onion
darknet markets onion dark web sites links darknet magazine
darknet markets onion dark web sites drug markets onion
tor market darknet market links drug markets onion
dark web marketplaces dark web market deep web drug markets
darkmarket link dark web marketplaces bitcoin dark web
dark web link darknet websites tor markets
darknet marketplace blackweb darknet magazine
darkmarkets [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet markets onion [/url] the dark internet
drug markets dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]how to get on dark web [/url] blackweb
darkmarkets the dark internet deep web drug markets
darknet markets 2024 black internet onion market
darknet markets cryptomarkets darknet darknet sites
dark web site dark market link dark market onion
onion market darknet market darkmarket url
dark web market links dark web drug marketplace darknet markets links
darknet websites dark web markets dark internet
dark market list dark web site black internet
darknet site dark website dark market link
darknet drug store deep web search tor market url
dark net drug markets dark web deep web markets
darknet markets onion deep web search the dark internet
darknet market lists darknet markets onion deep web drug markets
darkmarket link darkmarkets tor markets
darknet market list darkweb marketplace darknet market
the dark internet deep web drug store deep web markets
darknet markets onion address [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet site [/url] deep web sites
dark web search engines tor market dark websites
dark web market urls bitcoin dark web darknet drug links
darknet drug market dark web links tor market
darknet search engine tor dark web tor darknet
dark markets darknet search engine tor market url
dark web websites tor darknet darknet links
darkmarket url darknet sites onion dark website
darknet drug store dark market list darknet sites
blackweb official website dark market list darknet links
darknet magazine dark web market deep web sites
darkmarket url darknet drug store darkmarkets
darknet site dark web websites drug markets dark web
dark web market links darknet market darknet market
darknet markets onion tor marketplace dark web link
deep web sites darknet marketplace onion dark website
darkmarket darkweb marketplace dark web sites links
bitcoin dark web tor markets 2024 darknet market list
darkmarket url cryptomarkets darknet tor dark web
cryptomarkets darknet [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet links [/url] tor market url
onion dark website best darknet markets dark web market urls
drug markets onion onion dark website darknet links
dark market 2024 darknet market darkmarket
darknet sites darknet marketplace dark market 2024
dark web market list darknet market lists darknet markets url
tor market dark net darkmarket link
dark markets 2024 deep web search deep web drug store
deep web drug markets dark market url darknet seiten
darknet drug links tor drug market blackweb
dark web sites links blackweb official website darknet websites
darknet markets 2024 darknet market dark web market urls
deep web markets the dark internet darknet sites
dark web marketplaces darknet markets darkmarkets
dark web access darkmarkets onion dark website
darkweb marketplace dark web search engines darknet drugs
tor market url onion market deep web search
darknet markets darknet links darknet magazine
darknet marketplace darknet markets dark markets
tor market links dark web access tor marketplace
deep web drug markets dark web drug marketplace dark internet
dark web search engine darknet seiten onion dark website
dark web market tor markets links drug markets onion
bitcoin dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet search engine [/url] dark market list
darknet market links best darknet markets darknet market
darknet drug store dark website tor markets links
darknet markets onion tor market url deep web search
deep web drug url darknet market lists drug markets onion
dark web market list blackweb darknet marketplace
darkmarket url darknet links drug markets onion
darknet search engine dark web access dark web drug marketplace
darknet seiten best darknet markets dark market link
deep web drug markets tor darknet dark web market urls
dark web link darknet seiten darkmarkets
dark internet dark websites darknet markets
darkmarket link darknet drug store darknet drugs
dark web websites darknet drug store darknet search engine
blackweb official website deep web markets darknet marketplace
drug markets dark web onion market darknet marketplace
dark web search engine tor dark web dark web websites
darknet drugs darknet marketplace dark market link
the dark internet tor markets 2024 darknet market links
darknet market links deep web links darknet site
tor market dark web market dark internet
dark web market list bitcoin dark web deep web drug url
deep web search deep web drug url darknet market lists
darknet drug market [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet drug links [/url] darkmarkets
darknet seiten darknet drug store dark market 2024
darknet site darknet market list darknet markets url
deep web drug markets dark web market links darknet magazine
darknet markets dark market darkmarket link
dark web site dark market onion the dark internet
darkmarket 2024 darknet markets links dark web search engines
darknet drug links darkmarket link tor markets
deep web drug store dark web marketplaces deep web drug url
deep dark web darknet markets url tor markets 2024
dark market url darknet market list dark internet
drug markets onion darkmarket url deep web drug store
darknet markets 2024 free dark web blackweb official website
dark web access dark website deep web drug markets
tor markets links darknet market lists dark web access
dark web access dark web marketplaces dark web drug marketplace
dark web sites links [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]tor drug market [/url] darknet markets links
dark web site dark website tor marketplace
darknet websites darkweb marketplace darknet market
deep web markets dark web search engines darknet market
tor market url darkmarket darknet drug store
darknet websites darkmarket list cryptomarkets darknet
dark web market dark web market list darknet markets
dark web drug marketplace dark web search engine darknet drug store
dark net darknet site darknet markets onion
dark markets 2024 darknet market lists darknet marketplace
darknet markets onion address darknet market list darkmarket url
darknet seiten cryptomarkets darknet dark websites
darknet market dark website blackweb official website
deep web drug links dark web drug marketplace deep web drug markets
deep web search blackweb deep web drug url
dark web market urls tor markets links how to access dark web
darkmarket 2024 darknet marketplace darknet drug market
dark market link dark market onion darknet market lists
darkweb marketplace deep web drug markets darknet markets url
deep web links [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]tor markets [/url] dark web marketplaces
darknet market lists [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web market urls [/url] dark website
darknet marketplace drug markets onion darknet market links
dark web search engine dark market 2024 darkmarket url
darknet drug market dark web site darknet drug links
deep dark web free dark web deep web search
how to get on dark web cryptomarkets darknet deep web sites
dark websites dark market url dark websites
dark web marketplaces dark web marketplaces dark website
dark web markets how to get on dark web deep web drug store
deep web links tor market deep web drug markets
dark websites dark web market urls darkmarket 2024
dark web websites tor dark web drug markets onion
tor dark web dark web access dark internet
darknet drug links dark web site darknet websites
darknet marketplace dark market url darknet market
darkmarket 2024 darknet marketplace dark web market list
darknet search engine dark internet darkmarkets
dark web search engines darkweb marketplace how to access dark web
darknet market list dark market drug markets dark web
tor marketplace best darknet markets darknet sites
dark internet deep web links black internet
dark web drug marketplace dark web websites dark market
darkmarkets darknet seiten drug markets onion
dark market link tor markets links dark internet
tor darknet dark market list dark web market list
deep web search dark web search engine darkmarkets
tor market url tor dark web darkmarket url
darknet drugs darknet sites tor market links
dark market dark markets deep dark web
tor markets tor darknet darkweb marketplace
free dark web darknet sites dark markets
darknet links dark website darknet drug market
dark market url darknet websites onion market
darknet market deep web links deep web markets
darknet market links how to access dark web bitcoin dark web
darknet market lists dark web access dark website
dark internet tor market url the dark internet
porn vurgunyedim.wB1ajrcpwNQT
dark market darknet websites deep web drug url
darknet market lists tor marketplace darknet site
darknet site darknet search engine darknet site
blackweb darknet sites deep web drug url
blackweb official website dark markets deep web drug markets
deep web drug links deep web links darknet markets links
darkmarket url dark web search engine dark web market links
drug markets dark web darknet market list onion market
dark market darknet markets onion address dark website
black internet darknet seiten darknet markets onion address
darkmarket list dark markets drug markets dark web
tor marketplace dark websites darknet drug store
tor darknet dark website dark web site
darknet search engine dark web marketplaces dark market link
dark market url tor markets 2024 tor market links
deep web drug links dark web search engines darkmarket link
dark web search engines deep web search dark web markets
cryptomarkets darknet [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web search engine [/url] darknet market lists
free dark web dark web link best darknet markets
dark web markets darknet seiten drug markets dark web
darknet drugs dark website darkmarket
darknet drug market darknet search engine dark web search engines
deep web drug markets darkmarket url darknet drug store
dark web site dark market 2024 darknet markets
darknet websites darknet market lists dark web market list
darknet drugs tor market links dark web market urls
deep web drug markets dark web markets dark web sites
best darknet markets deep web markets darknet market list
darknet markets url darknet websites dark web access
dark market onion darknet seiten darknet markets
deep web drug links deep web links tor market url
dark web sites tor markets darkmarkets
dark website tor markets how to access dark web
dark market onion dark internet dark web market urls
bitcoin dark web darknet market list tor market
deep dark web darknet market lists darknet links
darknet drug market [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark market link [/url] bitcoin dark web
deep web drug links darknet websites dark web markets
dark website dark web sites links dark websites
onion market blackweb official website darkmarket url
darknet market links dark website darkweb marketplace
dark market onion tor darknet how to get on dark web
tor darknet deep web sites drug markets onion
blackweb official website dark market url drug markets dark web
darknet market list dark web sites darkmarket
deep web drug store tor drug market darknet links
darkmarket list darkmarkets how to get on dark web
tor marketplace dark websites dark web market links
darknet market links darknet drug links tor markets 2024
darknet markets dark market 2024 dark web search engine
darknet drug market tor dark web tor drug market
blackweb deep web links darknet markets 2024
dark net onion market tor drug market
darknet markets url onion market tor dark web
onion dark website dark net dark markets 2024
dark web sites links blackweb dark web search engines
darknet marketplace deep web links darknet magazine
darknet magazine darknet drugs darknet site
darknet market darknet magazine dark web search engines
dark market 2024 dark internet dark net
darknet markets links tor markets links darknet markets url
best darknet markets dark market 2024 dark web sites
dark web access darkmarket url tor market
dark market link [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web market links [/url] tor dark web
darknet markets links how to get on dark web dark markets
darknet drugs darknet markets onion cryptomarkets darknet
dark web market links dark web marketplaces darknet market lists
the dark internet dark web market list deep web search
dark market onion drug markets dark web deep web sites
dark websites free dark web dark web marketplaces
how to access dark web tor market darkweb marketplace
darknet drugs dark market 2024 tor drug market
dark web links darknet site deep web drug store
onion dark website dark web site tor drug market
deep web drug links darknet markets 2024 dark net
darknet markets 2024 dark net dark web marketplaces
deep web drug store tor marketplace drug markets onion
dark market list dark web market urls tor markets 2024
dark web access tor marketplace darknet markets onion address
dark markets 2024 darknet market dark market
drug markets onion darknet markets url dark web links
deep web links dark market url onion dark website
tor darknet tor market links dark websites
dark web market dark web access darknet seiten
dark web links best darknet markets dark web sites
darknet drug store tor darknet deep web drug url
darknet markets onion darknet site tor dark web
tor marketplace darknet markets url darkmarket
deep web search [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]deep web drug links [/url] dark websites
black internet deep web drug url free dark web
black internet dark web markets darknet markets url
tor dark web deep web drug links darkmarket url
drug markets dark web black internet darkmarket 2024
darknet market links cryptomarkets darknet darkweb marketplace
deep dark web dark market url deep web markets
dark web market darknet markets url best darknet markets
darkmarket link deep web links deep web search
tor markets links deep web links tor market
dark web sites dark market onion darknet marketplace
darknet market links dark web market dark website
darknet drugs dark market url darknet market
blackweb dark web market list darkmarket url
darknet drugs deep web sites dark market 2024
darknet magazine dark markets 2024 darknet markets url
dark web link onion market dark web market urls
tor darknet deep web search dark web markets
the dark internet dark markets darknet links
dark market list dark market link dark web sites links
tor market url dark market onion darknet drug store
how to get on dark web how to get on dark web tor markets 2024
tor dark web darknet market lists darknet markets url
deep web search dark web marketplaces deep web search
darknet drug market dark web websites darkmarket
darkweb marketplace deep web links dark net
dark market list tor market url dark market 2024
dark market list tor market tor drug market
drug markets dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]tor dark web [/url] dark web market urls
how to access dark web darkmarket link dark web sites links
dark web market links cryptomarkets darknet deep web drug store
free dark web darknet market how to get on dark web
black internet dark web search engines darknet market lists
deep web markets dark web market urls darknet drug store
dark web websites darknet drug market dark web market list
darknet drug links deep web drug url deep web links
darknet markets url dark websites darknet market lists
tor markets 2024 darknet drug store dark internet
dark web market links darknet market darknet drug store
dark websites dark web marketplaces darknet markets
dark web websites dark markets 2024 dark web drug marketplace
dark market url deep web drug markets deep web drug store
darknet market links darkmarket darknet magazine
darkmarket link darknet search engine tor darknet
darkmarkets dark web market darknet markets onion address
darknet market lists dark market url darknet drugs
dark market list darknet market lists dark web sites
dark web market list dark market url deep web drug markets
tor markets onion market deep web drug markets
darknet site dark websites dark web market links
darknet market list [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]tor markets [/url] deep web markets
darkmarket list darknet markets onion address darknet markets 2024
darknet markets onion address dark web sites links best darknet markets
dark net darknet links darknet site
darkmarket link dark market list deep web markets
deep web sites dark web sites links deep web drug url
dark web links dark net free dark web
dark web websites black internet dark web sites links
deep web drug url blackweb official website dark web search engine
deep web drug links darknet sites deep web sites
darknet market links the dark internet darknet seiten
darknet drug market dark markets bitcoin dark web
darknet markets darknet websites dark website
black internet onion market dark web market urls
dark web sites links dark website dark web market links
deep dark web deep dark web dark web websites
onion market darknet seiten cryptomarkets darknet
dark websites tor markets links how to get on dark web
drug markets onion darknet market list tor market url
dark market list tor markets 2024 tor markets links
free dark web dark market how to get on dark web
darknet drug market darknet markets links darkmarket
darknet drug store darknet websites tor market links
darknet markets url dark net darkmarket 2024
tor markets 2024 how to get on dark web darknet drug links
dark market 2024 deep web search onion dark website
dark web search engines darknet websites tor markets
darknet magazine darknet drug links drug markets onion
darknet market [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]tor market links [/url] tor market
dark web search engine dark market list dark market onion
dark market list tor market links dark web access
deep web links darkmarkets tor markets 2024
darkweb marketplace tor dark web deep web search
darknet markets 2024 dark markets 2024 dark web site
drug markets dark web blackweb official website darknet market links
darkmarket list darknet drug store how to get on dark web
dark web marketplaces darknet seiten deep dark web
tor dark web bitcoin dark web darknet markets 2024
dark web links tor market url bitcoin dark web
deep dark web dark markets darknet market links
dark net deep web sites tor dark web
blackweb dark web market darknet markets
dark web access tor market darknet marketplace
dark net darknet market darknet markets
black internet black internet dark web markets
black internet tor market links darknet search engine
darknet magazine dark market link deep web drug store
how to get on dark web dark web sites links bitcoin dark web
darknet marketplace tor market links deep web sites
dark web search engine the dark internet darknet seiten
darknet market tor dark web best darknet markets
dark internet how to get on dark web darknet drug market
onion dark website blackweb deep web links
deep web drug url dark market link dark markets 2024
darkmarket link [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet seiten [/url] dark market 2024
darknet marketplace [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]tor market links [/url] tor drug market
dark web market urls tor market url tor market links
deep web drug links dark web site darknet market list
dark web site dark websites dark web drug marketplace
darknet markets links tor markets links dark website
tor dark web blackweb drug markets dark web
dark web market urls darknet marketplace bitcoin dark web
tor drug market how to access dark web dark web access
darkmarket link dark internet dark market 2024
dark website dark market 2024 deep web search
dark market 2024 dark web market links dark web markets
dark market onion dark web sites dark web link
drug markets onion darknet drugs bitcoin dark web
black internet tor darknet deep web markets
darknet drug market deep web drug markets deep dark web
dark market url dark web search engine dark web sites
darkmarkets dark web market urls darkweb marketplace
darknet drug market deep web drug links darknet market
darknet markets 2024 tor market links dark markets 2024
darknet drugs onion market darknet markets onion
dark market link dark markets deep web links
dark website darknet marketplace dark market list
dark web access tor drug market cryptomarkets darknet
darknet market links drug markets onion darkmarket
tor markets 2024 darknet markets 2024 darknet drugs
cryptomarkets darknet the dark internet tor market
deep web links dark web site dark web market list
dark web websites free dark web dark web link
darknet market links best darknet markets deep web drug markets
darknet markets onion dark market list dark market onion
tor darknet cryptomarkets darknet deep dark web
deep web drug links [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]best darknet markets [/url] darknet site
dark markets 2024 blackweb darknet market lists
dark websites blackweb onion market
darknet markets onion address darknet search engine deep web drug links
free dark web darknet markets onion tor marketplace
dark web marketplaces how to get on dark web deep web drug links
tor market url darknet search engine blackweb
darknet drug links darknet seiten dark web marketplaces
darknet marketplace onion market free dark web
dark web link darknet markets links tor market
dark web market list dark web links free dark web
dark markets darknet drug links blackweb official website
deep web search deep web sites dark web marketplaces
tor dark web how to access dark web dark web site
deep web markets tor markets blackweb official website
dark web marketplaces dark web links deep web drug markets
dark market dark web market list dark web links
deep web markets deep web drug store deep web sites
darknet drug market blackweb darknet site
darknet market list darknet marketplace dark internet
tor market deep web sites deep web drug url
Сделал нелепую ошибку и решил ее исправить. Купил на “Цветов.ру” восхитительный букет, чтобы передать свои извинения. Ребята, сервис просто волшебен – быстро, удобно, и цветы свежайшие! Советую! Вот ссылка [url=https://mscs-boost.ru/neftekamsk/]цветы купить[/url]
cryptomarkets darknet dark web markets how to get on dark web
dark web marketplaces how to get on dark web dark web search engine
dark market link darknet drug links bitcoin dark web
darkmarkets tor markets links tor dark web
darknet market list the dark internet dark web market urls
onion market darknet drugs darknet marketplace
darkmarket darknet marketplace darknet site
darkmarket url darknet markets onion dark market
darkmarket link [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet magazine [/url] best darknet markets
darknet magazine deep web markets darknet drugs
bitcoin dark web tor markets links onion dark website
darknet drug store darknet links dark market
dark web search engine dark web market links bitcoin dark web
darkmarkets deep web links darkmarket url
black internet darkmarket url darknet search engine
darknet magazine dark web sites links darknet search engine
tor markets 2024 tor market dark web market links
deep web drug url tor market links dark web market urls
dark market link onion dark website tor markets 2024
dark web market tor market links best darknet markets
dark market 2024 darkmarkets dark websites
dark web market urls deep web drug store dark website
darknet market links darknet drug links free dark web
dark web sites black internet dark internet
darkmarket dark web market darknet site
tor dark web dark web drug marketplace darknet websites
tor markets darknet market links dark web links
darknet search engine dark market link darkmarket link
blackweb official website dark web sites links darknet markets links
dark internet dark web search engine cryptomarkets darknet
darknet magazine dark markets bitcoin dark web
darknet search engine [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet market lists [/url] darknet markets links
darknet drug store dark web market list darknet links
tor markets links darknet drug store tor dark web
darknet drug links darkmarket link dark web marketplaces
dark web markets cryptomarkets darknet the dark internet
deep web markets dark web websites darknet links
dark internet dark market deep web search
darknet marketplace dark website darkmarkets
dark web market urls dark web link tor drug market
dark web site blackweb official website darknet markets onion
dark market dark web sites dark web search engines
drug markets dark web darkmarkets drug markets onion
dark web site dark market link deep web drug store
onion dark website darknet drugs tor market links
dark websites blackweb official website dark web search engines
darknet drug links how to get on dark web dark web drug marketplace
deep web drug markets darknet markets links darkmarket list
dark web links tor market links dark web drug marketplace
drug markets dark web darknet seiten darknet seiten
darknet magazine tor markets darknet drugs
darknet magazine how to access dark web dark web websites
darknet seiten black internet dark internet
darknet markets links darkmarket 2024 dark market onion
deep web drug links darknet magazine darknet markets
darknet markets onion address darknet market lists the dark internet
dark web access dark web site deep web drug links
dark web access dark market url darknet sites
dark web websites [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet magazine [/url] dark web links
blackweb official website darknet sites deep web drug links
darknet marketplace dark market list darkmarket url
deep web drug links dark market dark web market list
tor markets 2024 darknet markets links darknet market lists
deep web drug url dark web market urls drug markets onion
dark web search engine tor darknet darkmarket link
tor market best darknet markets dark web markets
dark net deep web sites darknet markets 2024
bahis siteleri child porn yaralandinmieycan.HFc0QUtu34PE
deep web drug url darknet markets url tor markets 2024
dark internet black internet tor drug market
dark web markets darknet drugs darknet drug links
darknet seiten darknet drug links darknet market links
deep web drug url dark market link dark markets
dark web websites drug markets dark web deep web drug markets
darknet marketplace tor dark web blackweb
dark website tor market links darkmarket 2024
darknet drug store darknet markets dark web marketplaces
darkmarket link darknet drugs dark web link
dark market onion dark web link the dark internet
free dark web dark market list darknet drug market
dark market onion onion market dark web site
dark web sites links darknet market dark market url
dark market onion [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web link [/url] dark web market links
dark website [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet market list [/url] darknet marketplace
the dark internet dark internet dark web links
darkmarket list darknet links dark web market links
dark web link dark websites dark web market list
darknet drug store dark market onion black internet
dark market link tor drug market darkmarket list
tor market links dark web websites darknet magazine
darknet websites how to get on dark web dark market onion
darknet seiten dark market 2024 dark market 2024
dark web links darknet markets url tor marketplace
deep web markets darknet magazine tor darknet
deep web drug store tor markets links dark web websites
drug markets dark web dark websites dark web link
tor market links dark web market links dark internet
darknet markets links dark net darknet marketplace
dark websites darknet links drug markets onion
best darknet markets drug markets dark web dark web drug marketplace
tor market darknet market lists the dark internet
dark web links darkmarket link tor marketplace
darkmarkets dark market onion tor dark web
dark web sites dark web market links darkmarket 2024
dark market the dark internet darkmarket list
dark web search engines darkmarkets darkmarket list
tor markets links darkmarket link darknet magazine
cryptomarkets darknet dark web links darknet site
darkmarket best darknet markets tor dark web
dark web drug marketplace darknet market lists dark web search engine
darknet magazine [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet websites [/url] tor market
the dark internet darknet marketplace darknet drug store
darkmarket url dark market url darknet seiten
darkmarket darknet marketplace darknet drug market
dark web search engines cryptomarkets darknet drug markets dark web
dark market url dark web drug marketplace tor dark web
dark internet dark web sites links tor markets
darknet sites dark market 2024 drug markets onion
onion market dark net deep web drug links
dark web market dark web market links dark website
dark web access dark web marketplaces dark web links
deep web markets dark web market deep web search
dark web links onion dark website darkmarket 2024
darknet markets onion dark web market darknet market lists
darknet site how to get on dark web dark web sites links
cryptomarkets darknet dark web search engine deep web drug markets
tor drug market dark web sites dark market link
dark web links tor market dark market url
dark market deep web search dark market 2024
dark markets dark markets 2024 darknet markets onion
darknet markets 2024 darknet drug market darknet websites
dark markets 2024 dark market deep web drug links
darkmarket list dark market onion dark web search engines
how to access dark web darkmarkets cryptomarkets darknet
the dark internet darknet websites dark web drug marketplace
dark web sites links dark web access deep web search
darknet links darknet market list deep web drug url
tor darknet dark market dark market url
darknet markets onion address [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]onion dark website [/url] dark market onion
free dark web [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet markets [/url] dark web markets
tor markets 2024 best darknet markets tor market links
deep dark web tor market dark market
darknet market how to access dark web free dark web
darknet markets onion blackweb official website darknet drug market
dark web marketplaces deep web drug store dark web market links
deep web links the dark internet dark web sites
darknet drug market dark web search engine dark market 2024
dark web site dark web access dark internet
darknet markets darknet seiten darknet markets
blackweb onion dark website dark markets 2024
dark net bitcoin dark web darknet sites
blackweb official website dark internet darknet markets url
darkmarkets how to access dark web tor market links
darkmarket link deep dark web darknet markets 2024
darknet market lists free dark web darkmarket link
how to access dark web how to get on dark web darknet markets links
tor marketplace dark market url darknet magazine
dark market onion dark internet darknet sites
dark web site dark market 2024 darknet drug store
dark market onion dark market tor market links
deep web sites darkmarket link darknet markets url
how to get on dark web bitcoin dark web dark market
darknet markets links darknet websites dark web market links
black internet dark web search engines darkmarket 2024
tor markets links onion market darknet markets 2024
dark web market list deep web drug store dark web drug marketplace
darknet markets free dark web dark web websites
tor market deep web search darknet market list
dark market link best darknet markets darknet links
dark market link darknet markets links darknet markets onion
darknet drug store [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darkmarket link [/url] dark markets 2024
darknet links how to get on dark web darknet websites
deep web sites dark web market urls darknet sites
dark market url dark web sites darknet drug market
best darknet markets best darknet markets darknet drugs
darknet seiten darknet market darknet market lists
dark web link dark market 2024 dark web market
darkmarket list tor darknet dark market list
технические двери металлические купить в спб [url=https://texnicheskiedveri.ru/]https://texnicheskiedveri.ru/[/url].
darkmarket link black internet darkmarket link
darkmarket link dark websites dark web search engines
darkmarket list blackweb official website darkmarket 2024
dark net dark web links tor marketplace
tor drug market deep web markets tor dark web
darknet search engine deep web sites dark web market links
dark web sites links darknet drugs darkmarket
dark market url tor darknet darknet marketplace
drug markets onion dark websites dark web market
blackweb darknet markets onion tor markets 2024
dark web markets darknet drugs dark web access
darknet site deep web markets dark market 2024
tor marketplace dark market darknet markets onion
dark market list darknet markets onion tor markets links
darknet markets dark web websites darkweb marketplace
darknet drug store deep dark web dark web sites
tor market url darknet site darknet markets
darknet market list tor drug market deep web sites
dark markets 2024 darknet links darkmarkets
dark web link tor darknet deep web drug store
dark market onion darknet market deep web links
darknet markets links darknet market list dark web market list
how to access dark web darknet market links darknet markets links
dark website tor market deep web drug markets
dark websites darknet drugs dark web sites
deep dark web darknet markets onion drug markets onion
deep web sites [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark web market [/url] dark market url
darknet links [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web market urls [/url] darknet market lists
darknet search engine darknet market list darknet market lists
tor market url dark web market list darknet drug links
dark web link dark web market tor markets 2024
darknet sites darkmarket link dark market link
darknet drug store darknet markets 2024 drug markets dark web
dark markets 2024 dark websites dark web drug marketplace
dark internet blackweb official website darkmarket 2024
drug markets onion dark web marketplaces dark web market links
darknet market list dark web market dark web site
tor market links deep web sites tor drug market
dark market list darknet market lists dark markets
deep web drug links darkmarket darknet drug links
darknet drug store dark web market links how to access dark web
darkmarket link drug markets onion darkmarket url
blackweb official website dark web websites dark market link
darknet search engine dark web search engine darknet markets
darkmarket url how to get on dark web darknet seiten
dark web links dark web sites links tor drug market
dark website darkmarket deep web sites
darknet drug market deep web drug markets darknet drugs
darknet drug market tor darknet dark web search engines
deep web search darknet seiten dark web markets
dark market url dark web search engines dark market url
blackweb onion market dark market 2024
black internet drug markets dark web tor marketplace
darknet markets url best darknet markets dark web marketplaces
onion dark website dark market 2024 darknet seiten
dark web search engines darknet site deep web links
darknet drugs dark web market darknet market
darknet websites deep web drug links the dark internet
deep web drug store [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet magazine [/url] darknet seiten
darkmarket url how to get on dark web darknet magazine
darkmarket 2024 darknet links dark web sites
darknet websites dark web sites dark web websites
deep web markets dark web link darknet magazine
darknet site dark market 2024 darknet sites
darknet drugs darknet drug store dark web link
darknet drugs onion dark website how to access dark web
dark web sites links darknet drug market darkmarket 2024
darknet drug market deep web drug links darknet markets
black internet dark markets blackweb official website
darknet markets onion dark web site deep web drug url
deep web markets dark web search engines onion dark website
onion market darknet market links dark web links
darknet market deep web markets dark web access
darkmarket list deep web drug store blackweb official website
dark web drug marketplace deep web links drug markets onion
tor dark web tor market url dark websites
tor drug market dark websites dark markets 2024
darkmarkets darkweb marketplace dark web site
dark web market list cryptomarkets darknet tor marketplace
darknet drug store deep web sites deep web drug store
deep web markets dark web link cryptomarkets darknet
dark web access tor market links dark web search engines
black internet darknet market links tor market url
deep web search deep web drug markets onion dark website
cryptomarkets darknet drug markets onion darknet markets 2024
darkmarket darknet markets onion dark internet
darkmarket url darknet markets onion dark internet
dark websites darkmarket 2024 deep web drug links
deep web drug links drug markets onion dark net
blackweb deep web search darkmarket 2024
tor market links dark market 2024 best darknet markets
darknet markets onion address dark web links darknet markets
darkmarket link darknet market tor dark web
darknet markets onion address [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet market links [/url] deep web drug markets
deep web drug store dark web sites links blackweb
dark web links free dark web darkmarket url
darknet drugs darknet market links darknet sites
tor market url darknet seiten tor markets 2024
darkmarket link darkmarket dark web search engine
darkmarket dark website darknet markets
darkmarket url deep web drug url best darknet markets
darknet marketplace tor marketplace tor darknet
dark markets tor markets 2024 darkmarket
dark website darkmarket link darkmarkets
dark web links darkmarket 2024 drug markets onion
dark market 2024 darknet market list drug markets dark web
dark market 2024 darkmarket url darknet market lists
cryptomarkets darknet dark web market darknet websites
deep web links deep web drug store darknet seiten
dark markets darknet market lists darknet marketplace
darknet markets onion address darkweb marketplace darknet markets
darknet markets onion address darkmarkets darknet markets onion address
dark markets 2024 dark market list dark web sites links
darkmarket list darknet market lists dark websites
drug markets onion darknet drugs dark web links
deep dark web tor darknet onion dark website
darknet markets onion address darknet marketplace darkmarket
dark web websites darknet market lists dark internet
tor drug market drug markets onion darknet market links
dark web links dark internet dark market 2024
darknet market lists deep web drug markets dark websites
darknet market list tor markets the dark internet
deep web drug markets tor market dark web markets
deep dark web how to get on dark web darkmarket url
darknet site [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]deep web drug markets [/url] darknet market links
dark market darknet drug market darkmarket 2024
dark web search engines darknet market dark market link
darknet market darkmarket link darkmarkets
dark web links blackweb official website darknet magazine
tor market deep web drug links dark web marketplaces
dark markets deep web sites dark web drug marketplace
dark web drug marketplace tor drug market onion market
dark market url bitcoin dark web deep web links
dark web sites free dark web darknet site
dark web market list dark web link darknet market lists
deep web links dark web drug marketplace darknet markets 2024
dark web sites darkmarket darknet markets 2024
dark web market list bitcoin dark web darknet sites
dark web market links darknet market darknet markets 2024
best darknet markets darknet drugs tor market url
dark web search engines dark web site dark website
darknet market list dark market onion dark web link
darknet search engine deep web sites dark market 2024
dark web markets deep dark web darkmarket list
darknet markets onion dark markets dark net
darkmarket url deep dark web dark market 2024
darknet markets url darkmarkets dark web marketplaces
dark websites darknet markets onion address dark markets 2024
blackweb official website dark market 2024 darkmarket 2024
dark web market darknet drugs dark markets 2024
the dark internet dark internet tor market
darkmarket list dark internet deep web links
cryptomarkets darknet dark web marketplaces cryptomarkets darknet
dark web sites links dark net dark web market
tor markets 2024 darknet drugs darkmarkets
darkmarket link dark web markets darknet markets url
darknet markets onion how to get on dark web darknet market list
darknet markets [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet seiten [/url] darknet market list
darkmarkets tor darknet dark web markets
tor market links darknet drugs dark web search engine
darknet sites deep web search dark websites
drug markets onion tor markets tor marketplace
darkmarkets darknet marketplace darknet markets 2024
перетяжка мебели недорого [url=https://peretyazhka-bel.ru/]https://peretyazhka-bel.ru/[/url].
deep web search dark market 2024 dark web websites
darknet websites darknet market lists blackweb
dark market dark web access drug markets onion
tor marketplace dark web markets tor dark web
deep web drug links tor market deep web drug links
deep web drug markets tor dark web black internet
drug markets onion darknet markets url dark web site
dark web link dark internet darknet sites
dark web market dark website dark market url
dark market onion tor market url deep web links
tor markets links dark web websites darknet market links
dark web drug marketplace tor market url black internet
deep web search darkmarket url best darknet markets
dark web links dark web websites dark websites
dark market onion dark web market urls dark web site
darknet site dark web sites dark web link
dark web search engine darknet drug market drug markets onion
darknet site dark market darknet websites
tor market darkmarket 2024 darknet markets 2024
darknet markets onion address tor markets links dark web site
dark market 2024 tor marketplace darknet drugs
tor markets links darknet market blackweb
darknet markets links dark web search engines darknet market list
tor drug market dark web access darknet search engine
tor market deep dark web blackweb official website
research chemicals tadalafil purchase peptides
darknet market list [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web sites links [/url] dark web market links
dark web access deep web sites dark web search engine
tor marketplace dark market link dark market url
darknet drugs deep web drug url darknet markets onion
the dark internet darkmarket link darknet search engine
onion dark website deep web drug links best darknet markets
dark web links tor marketplace darknet marketplace
how to get on dark web best darknet markets darknet websites
dark web marketplaces deep web drug links darkmarkets
black internet dark web market dark markets 2024
darknet drug links tor darknet dark web market list
tor markets 2024 darkmarket list darknet marketplace
deep web links darkweb marketplace darkmarket url
deep web search dark web market links tor marketplace
darknet drugs darknet site dark internet
tor markets links best darknet markets dark web sites
darkweb marketplace dark web websites tor market
darknet site dark market link dark internet
blackweb tor markets 2024 darknet site
dark web site dark web search engine darknet markets onion address
dark web sites drug markets dark web tor markets 2024
deep web search darknet drug market best darknet markets
tor market bitcoin dark web darkmarket list
bitcoin dark web darknet seiten darkmarket list
dark web access darkmarkets dark web websites
darknet markets links dark web market list dark market 2024
onion dark website darknet websites dark markets 2024
tor darknet darknet markets 2024 tor dark web
darknet markets links [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]tor market url [/url] tor markets 2024
dark web markets dark markets dark market
tor dark web darkmarket list dark web marketplaces
deep web sites tor marketplace dark market list
tor markets darknet market links the dark internet
dark web markets darknet search engine bitcoin dark web
darknet markets onion address dark website dark web links
dark markets darknet sites darknet magazine
darkmarket list free dark web darknet drug store
darknet site darknet drug market dark web search engines
dark web sites links darknet markets 2024 tor markets links
bitcoin dark web dark market dark web drug marketplace
darknet markets darknet markets onion how to access dark web
dark web market deep dark web darknet markets url
dark web access darknet magazine tor dark web
dark internet darknet websites dark market
darkmarkets deep web drug links darknet drug market
darknet market list dark market list dark web search engines
tor marketplace dark web search engine how to get on dark web
darknet drug market darkweb marketplace darknet market
dark web link darknet drug store dark market onion
tor markets darkmarket darknet markets 2024
cryptomarkets darknet deep web markets darknet markets 2024
tor markets links dark web link darknet markets 2024
dark markets 2024 dark internet darkmarket link
darknet magazine black internet blackweb official website
deep web drug markets darknet drug market dark web search engines
deep web drug markets deep web markets deep web drug markets
darkmarket list the dark internet dark web websites
dark web drug marketplace [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]cryptomarkets darknet [/url] deep web drug url
darknet markets onion dark web access tor dark web
how to get on dark web darknet markets onion deep dark web
darknet drug store onion dark website darknet market lists
tor darknet dark market 2024 dark web marketplaces
darknet drug store deep web drug markets darknet drug links
tor markets links dark market list dark web markets
dark market link dark web market darknet sites
darknet market links darknet seiten darknet markets
dark website dark web search engine dark internet
onion dark website dark market list darknet drug links
cryptomarkets darknet darknet markets dark market 2024
dark websites dark web marketplaces dark market onion
deep web drug markets deep web search best darknet markets
onion market deep web drug url bitcoin dark web
deep web links darknet marketplace dark web drug marketplace
dark market 2024 deep web links darkmarket url
darknet site darknet marketplace dark market 2024
deep web drug url darknet drug market dark web market
best darknet markets dark net dark web search engine
tor markets tor markets how to get on dark web
dark web markets dark web links darkmarket 2024
dark web links darknet sites dark web sites links
dark market link deep web search tor markets
darknet markets onion dark market 2024 dark web market urls
deep web search dark web marketplaces darknet market lists
deep dark web dark market list dark markets
dark market tor markets 2024 best darknet markets
darknet sites dark web market darknet site
dark web market urls deep web drug url deep web drug url
dark market 2024 [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web marketplaces [/url] darkmarket link
deep web markets deep web search black internet
onion market dark web drug marketplace darkweb marketplace
best darknet markets darknet market links darknet markets links
best darknet markets darknet markets onion address darknet markets url
dark market url dark web site deep web markets
darknet drug links tor market links dark web drug marketplace
darknet websites darknet markets 2024 dark web drug marketplace
dark web markets how to access dark web tor drug market
darknet site dark web access deep web links
darknet websites tor markets links bitcoin dark web
tor dark web dark web search engine dark websites
dark markets darkmarkets darknet markets 2024
dark market link dark web market list dark web market
dark web market list dark market list dark market link
dark web link darknet marketplace darkmarket url
darknet sites onion dark website darkmarket link
darknet search engine drug markets onion deep web drug links
darknet drug store tor markets 2024 dark web market
darknet drugs dark markets 2024 dark market
dark website onion dark website deep web sites
tor darknet darknet markets url darknet marketplace
dark markets 2024 dark web search engines the dark internet
darkmarket dark net dark web link
darkmarket dark market 2024 darknet drug store
tor market links darknet seiten dark markets 2024
deep web sites dark web websites darknet markets onion
cryptomarkets darknet dark web market urls darknet drug store
dark web drug marketplace tor market url dark market list
darknet drugs tor markets dark web markets
dark internet tor markets 2024 dark web websites
drug markets onion tor market url drug markets dark web
drug markets onion darknet links dark web market list
darknet drug market dark markets darknet drug market
how to get on dark web [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web search engine [/url] how to access dark web
deep web markets tor drug market how to access dark web
darknet drugs drug markets dark web tor marketplace
darknet marketplace deep web drug links tor markets 2024
dark websites tor marketplace darkweb marketplace
dark market link darknet magazine tor drug market
dark web sites links tor darknet darknet markets onion address
darknet drug store blackweb official website dark web market list
darkmarket 2024 dark market link dark market list
darkmarkets black internet darknet drug links
bitcoin dark web darkmarket 2024 dark web websites
dark web search engines dark web search engines dark market url
cryptomarkets darknet best darknet markets darkmarket link
darkmarket 2024 dark web websites deep web search
darknet site darknet drug store darkmarket url
darknet markets onion address how to access dark web deep web markets
tor markets links dark market list drug markets dark web
dark web market links dark markets how to get on dark web
drug markets dark web dark web drug marketplace tor markets links
tor marketplace dark web market dark web site
tor marketplace tor drug market blackweb
darknet sites tor drug market dark net
darkmarket url drug markets dark web dark web market urls
dark market 2024 darknet market links drug markets onion
darknet seiten tor market url blackweb official website
deep web markets darknet search engine darknet market links
how to get on dark web drug markets dark web dark web market urls
tor drug market tor market url dark web markets
tor market darknet markets dark web search engine
tor markets 2024 darknet seiten darknet markets url
darkmarket url blackweb official website tor marketplace
dark market onion [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark websites [/url] deep web drug store
deep web sites dark web drug marketplace tor drug market
dark web search engine darknet search engine darknet markets
darknet markets onion dark internet darknet links
dark web markets drug markets dark web dark web links
darknet drug store deep web markets cryptomarkets darknet
tor markets 2024 darknet websites how to access dark web
dark web market urls deep web sites tor markets
darkmarket darkmarket 2024 darknet markets links
dark web link deep web drug store tor markets links
dark market 2024 dark market 2024 dark web sites
darknet site dark markets 2024 darknet magazine
deep web markets dark web search engine darknet magazine
darkmarket url the dark internet darknet drugs
bitcoin dark web drug markets dark web tor market links
darknet magazine tor drug market tor dark web
dark web market the dark internet dark web search engines
darknet markets onion address darknet links darkmarket url
tor drug market dark web site darkmarket url
onion dark website drug markets onion free dark web
darknet markets onion blackweb darknet market list
deep dark web darknet seiten dark market 2024
darknet site darknet market links darknet websites
dark web market drug markets onion cryptomarkets darknet
drug markets dark web darknet markets 2024 dark web marketplaces
black internet tor darknet darkmarket 2024
deep web drug url drug markets onion dark markets
dark internet how to get on dark web darkmarkets
tor darknet darknet market links black internet
darknet market lists dark website dark web links
dark web search engine cryptomarkets darknet drug markets dark web
deep web sites blackweb official website darkweb marketplace
dark website [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark net [/url] darknet markets url
dark web market list dark market url dark market link
dark web marketplaces onion dark website tor markets
deep dark web darknet drug store darknet markets url
darkweb marketplace dark web marketplaces dark web marketplaces
tor market url deep web drug url dark market list
darknet market links onion market tor drug market
blackweb dark market url dark markets
darkmarkets deep web drug url darknet markets
dark web market list drug markets onion darknet sites
darknet site deep web markets darkmarket link
tor markets 2024 blackweb official website darknet magazine
the dark internet dark web market urls darkmarket
deep web drug url dark market link darkmarkets
darknet market lists darkmarket link darknet markets 2024
best darknet markets deep web drug url dark web link
dark web link dark web market urls dark web sites links
darkmarkets darknet site dark web market list
deep web drug links dark web access dark web market list
how to get on dark web bitcoin dark web dark market url
dark markets 2024 bitcoin dark web dark markets
deep web drug store tor market url darknet magazine
darknet links dark web websites darknet drug market
darknet search engine darknet search engine deep web links
dark web markets deep web drug links tor market url
darknet site dark web market list deep web markets
darknet market list onion market deep web drug links
dark web search engines dark website dark web market list
dark web marketplaces darknet markets onion address dark markets 2024
dark web search engine dark web markets darknet drug market
dark markets darknet drug links dark web market links
dark net tor market links bitcoin dark web
darknet drug store [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]best darknet markets [/url] darknet site
darkmarket 2024 darkmarket url deep web drug links
best darknet markets dark internet dark markets 2024
darknet sites dark web search engine tor market url
deep web markets darkmarkets darknet drugs
dark web market links dark web marketplaces dark market url
blackweb official website darknet websites dark web link
tor markets links best darknet markets tor dark web
darknet search engine deep web drug markets dark market url
tor market onion dark website darknet market lists
drug markets dark web drug markets onion drug markets dark web
darknet markets 2024 darkmarket url darknet market list
cryptomarkets darknet darkmarket 2024 dark web websites
dark markets darknet markets onion darknet websites
deep web markets dark market dark market
dark web markets darknet drug market dark web sites
darknet marketplace dark web markets deep web drug store
dark website dark web sites darknet market links
darknet drug store darknet marketplace dark internet
darknet drug store dark web websites drug markets dark web
darknet site darknet marketplace deep web links
deep web markets dark web sites links darknet markets onion address
drug markets onion best darknet markets darkmarket list
darknet market deep web drug links deep web sites
tor markets 2024 dark web sites deep web drug links
darkmarket 2024 bitcoin dark web dark web marketplaces
darknet search engine dark web websites darkmarket url
bitcoin dark web deep web drug markets darknet markets
dark web links dark net darkmarket 2024
deep web drug url darknet seiten dark web drug marketplace
deep web drug url darknet markets 2024 darknet drug market
darkmarket list tor dark web dark web search engines
dark markets 2024 [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet magazine [/url] deep web search
darknet websites dark market list dark web links
darknet drug store darknet seiten darknet markets onion address
tor market best darknet markets darknet markets
darknet markets onion address dark websites dark web search engine
dark web sites dark web websites darkmarket 2024
darknet market lists darknet websites deep web markets
darknet markets onion dark markets 2024 darknet drug links
deep web links darknet markets darknet markets links
dark web markets darknet market tor markets links
how to access dark web deep web markets deep web search
tor marketplace darknet markets 2024 dark market list
dark websites dark web markets darknet drug market
dark web link darkmarket dark web links
free dark web dark website deep web links
dark web websites darknet seiten dark market link
darkmarket tor markets dark markets
dark web market links dark market darknet markets onion address
how to access dark web tor darknet dark internet
darknet marketplace darknet markets links drug markets dark web
tor market dark web market deep web links
onion dark website dark market list deep web drug store
dark market how to get on dark web darkweb marketplace
darknet links tor dark web dark web access
free dark web darknet search engine darkmarket url
dark web links [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet links [/url] dark web marketplaces
how to access dark web darkmarket dark web search engine
darknet markets dark web search engine darknet market lists
darknet market lists tor marketplace dark web marketplaces
black internet dark markets 2024 dark web sites
Отдых для Москвы зовет ознакомиться с характеристиками изумительных женщин, которые готовы скрасить Ваш час или ночь прям сейчас. На интернет сайте newswomanblog.win Вы сможете найти подругу на всякий вкус, как для молодых людей, так и для девушек, а также влюбленных пар.
По запросу [url=https://newswomanblog.win/tolstye]проститутки толстушки[/url] заходите к нам как можно скорее. Если Вы напряжены от тупых и тусклых будней, а также загруженных рабочих смен, то пришло время наградитьни в чем не ограждать себя и получить настоящее удовлетворение.
Скрасить любой вечер, а также праздник помогут прекрасные и обладающие отличным опытом девочки, которые придут в любое указанное Вами место. Будь то гостиница или квартира, а также событие – день рождения или корпоратив. По любым вопросам мы готовы Вам помочь, чтобы заказчик был удовлетворен в полном объеме.
Выбрать секс услуги возможно тут [url=https://newswomanblog.win/marfino]проститутки марфино[/url] уже сейчас. Мы работаем без выходных и праздничных дней, круглосуточно. На нашем веб сайте возможно даже пользоваться сокращенным поиском девочки, указав: необходимый район, возраст девочки, рост, размер груди, стоимость. Так Вам будет быстрее осуществить выбор под свои собственные критерии. А также у нас есть конкретные категории: девушки без ретуши, VIP индивидуалки, новые девушки, новые девушки и другие.
darknet market lists darknet drugs deep web links
darknet drugs dark web link deep web drug links
dark net darknet seiten tor dark web
Dealing with an [url=https://social-me.co.uk/]Instagram deactivated[/url] account requires a nuanced approach. At social-me.co.uk, we specialize in understanding and resolving such issues. Our expertise in Instagram’s policies and procedures enables us to offer tailored solutions that address the specific reasons for your account’s deactivation. We focus on providing a comprehensive service that includes not only reactivation but also advice on maintaining a secure and active Instagram presence, ensuring your digital identity is preserved.
onion dark website dark web market links how to access dark web
darknet sites darknet markets onion address dark web market links
tor markets links [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]deep web markets [/url] dark web market
dark website black internet dark net
dark web site darkmarket url darknet market
deep web drug url dark web market list deep web drug url
dark web websites darknet links darknet market links
dark market tor markets links darknet sites
darknet market list dark market 2024 dark website
dark web websites darknet markets url darknet sites
blackweb how to get on dark web darknet drug market
darknet market links darkmarket darknet markets onion address
drug markets onion dark markets dark net
dark market url darknet magazine darknet market list
dark web websites darknet seiten dark market list
darknet drug store darknet websites dark web market links
перетяжка дивана [url=https://csalon.ru/]обивка мебели[/url].
dark market link darknet seiten deep dark web
tor markets links tor darknet darknet sites
deep web drug markets darknet drug links deep web drug markets
tor marketplace tor markets 2024 dark web websites
dark web markets tor markets 2024 darknet drug market
darkmarket url dark market list darkmarket list
deep dark web darknet markets onion address tor drug market
tor dark web dark web search engines deep web links
the dark internet dark markets dark internet
darkmarket 2024 tor darknet deep web links
the dark internet [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]bitcoin dark web [/url] darkmarket list
tor marketplace darknet drug store tor drug market
darknet markets onion address darknet drug links onion dark website
darknet market lists dark web market links darkmarket
darknet market onion dark website dark web market urls
darknet websites darknet markets tor drug market
darknet drug store onion dark website darknet marketplace
tor dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark net [/url] how to access dark web
darkweb marketplace tor drug market darknet seiten
dark market url best darknet markets darknet seiten
dark market link darknet markets 2024 dark website
darkmarkets how to access dark web deep web search
deep web links tor darknet darknet markets 2024
darknet seiten dark net darknet market list
dark market 2024 tor market url deep web search
dark web sites links onion dark website dark web markets
dark web market the dark internet dark web market list
drug markets onion how to get on dark web darknet drug links
darknet market lists best darknet markets dark website
tor darknet tor markets 2024 tor drug market
dark market onion darknet search engine dark websites
dark market onion tor dark web dark web market urls
dark market link tor drug market dark web websites
tor markets darknet seiten darkmarket url
dark web sites links darknet drug market darknet drugs
darkmarket link darkmarket url darknet market
[url=http://lexapro.cfd/]otc cipralex[/url]
how to access dark web tor market cryptomarkets darknet
darkmarket darknet drug market dark market 2024
darknet markets onion dark web site cryptomarkets darknet
darkmarket link dark net darkmarket link
dark market darknet drugs tor markets
tor market links dark market url darkmarket list
deep web drug url darkmarket link darkmarkets
deep web search dark web marketplaces cryptomarkets darknet
darknet drug links dark website darknet links
dark website blackweb official website deep dark web
dark web links [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet market lists [/url] dark web websites
darknet markets onion deep web drug url blackweb
dark market url dark web market links deep dark web
darknet markets onion address dark web search engines darknet drug market
darkmarket darknet market list dark website
cryptomarkets darknet darknet marketplace deep web drug url
dark websites dark web links darknet markets onion
dark websites [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]blackweb official website [/url] darknet markets onion address
blackweb darknet market links dark markets 2024
black internet cryptomarkets darknet tor dark web
dark markets how to access dark web tor dark web
darknet magazine dark market url onion market
how to get on dark web dark web marketplaces darknet markets onion
tor market dark web market list dark web link
deep web drug markets darkmarkets dark internet
darknet seiten dark web drug marketplace darknet market
darknet websites dark markets darknet market lists
darkmarket 2024 dark market dark web sites links
dark web market urls darknet magazine darkmarket link
dark web market darknet market list darknet site
blackweb tor markets darknet sites
darknet drug links dark web websites tor market
dark market dark web market list darknet search engine
dark internet dark web markets darkmarket
darknet site darkmarkets darknet search engine
darknet websites darknet markets onion darknet markets 2024
dark web links darknet market list tor darknet
dark web sites dark websites bitcoin dark web
dark web websites tor market dark web sites
darkmarket darknet market dark web sites links
bitcoin dark web deep web drug url tor marketplace
darknet market tor markets darknet markets url
tor markets darkweb marketplace deep web links
deep web drug markets tor market url deep web sites
dark market link dark market link dark market url
darknet links [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets onion address [/url] deep web drug url
deep web links darkweb marketplace darkmarket 2024
dark market url dark web market urls dark markets
deep dark web drug markets dark web darknet markets url
drug markets onion onion market free dark web
darknet websites the dark internet how to access dark web
darknet markets url [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets onion [/url] dark websites
darknet sites deep web sites dark web market links
darknet markets url darknet marketplace dark web links
darkweb marketplace dark web links darknet marketplace
onion market darkmarket dark market 2024
dark markets dark net tor markets links
darknet drug market bitcoin dark web dark web market list
darknet sites onion dark website dark market onion
darknet market lists tor markets links darkmarket url
deep web links darknet site free dark web
dark web search engine dark web search engines tor marketplace
dark web search engine dark markets dark web search engine
dark internet darknet site dark web markets
dark market url dark market 2024 deep web links
deep web links dark net darknet market list
tor market links dark web drug marketplace darknet search engine
darkmarket darkweb marketplace tor markets
black internet deep dark web dark web link
darknet market lists drug markets onion darknet drug market
dark web site darkweb marketplace darknet magazine
darknet markets url deep web drug url darknet drug market
dark web market urls dark web site darkmarkets
darkmarket url dark web search engines bitcoin dark web
dark web marketplaces deep web sites dark internet
drug markets onion dark web links darkmarket list
dark market onion darknet websites tor market
how to access dark web tor market darkweb marketplace
darknet drug market darkmarket list dark market link
best darknet markets darknet links dark web search engine
dark market list darknet market links darknet search engine
free dark web [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets onion address [/url] dark market url
dark websites tor market links how to access dark web
tor markets 2024 darknet marketplace tor darknet
darknet markets 2024 deep web markets tor markets links
onion dark website darknet market links darknet market lists
tor drug market darkweb marketplace blackweb
[url=http://prednisolone.directory/]cheap prednisolone tablets[/url]
darknet market lists [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web websites [/url] onion dark website
tor dark web dark web link darknet market links
darknet seiten darkmarkets deep web markets
blackweb darknet market links dark market 2024
tor drug market best darknet markets dark net
how to access dark web deep web drug links darknet market
dark market link dark web market list darkmarket list
drug markets onion deep web drug markets deep web drug links
dark market link darknet drug market dark market onion
darkmarket url free dark web drug markets dark web
dark web market links tor markets 2024 dark market 2024
dark web market links tor market links darkmarket link
darknet magazine tor market url deep web drug url
deep web markets dark web sites deep web markets
tor markets 2024 dark web sites deep dark web
dark web site tor market url dark web sites links
tor markets links darknet seiten darkmarket list
dark web market links darknet market tor market links
dark web market dark web market darknet site
dark web marketplaces darknet search engine deep web markets
deep web drug links tor drug market dark websites
dark web marketplaces onion dark website dark web search engines
free dark web deep web links darknet drugs
darkmarket drug markets onion dark markets
darknet search engine tor market onion dark website
cryptomarkets darknet dark market url dark website
best darknet markets darknet links darknet drug store
dark web search engines [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]deep web sites [/url] darknet drug market
Братан, хотел обновить геймерский арсенал, но бабла не хватало. Друг подсказал mikro-zaim-online.ru – взял там займ на 30 тысяч, прямиком без проверок. Теперь у меня новейшие игры, и я в полном восторге. Этот сайт – настоящий рай для геймеров, кто ищет быстрые деньги на свои увлечения.
MIKRO-ZAIM – [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/]займ взять онлайн[/url]
Наши контакты: Зеленодольская улица, 36к2, Москва, 109457
bitcoin dark web darknet market links tor market links
best darknet markets darknet market list darkmarket list
darknet market links dark markets darkmarket link
dark markets 2024 dark websites deep web drug store
darknet drug links darkmarket drug markets onion
tor market dark web search engines darknet markets links
darkmarket how to access dark web darknet markets
dark market 2024 best darknet markets tor darknet
darkmarkets [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet magazine [/url] darknet markets onion
dark web market list darknet search engine cryptomarkets darknet
dark market onion dark web websites tor market
dark markets dark websites black internet
darknet sites darknet markets onion darknet links
deep dark web tor marketplace blackweb official website
tor dark web deep web links dark web link
darknet market darknet market lists tor markets links
darkmarket link best darknet markets blackweb official website
how to get on dark web darknet markets onion address dark internet
dark web link tor market darknet markets
deep web drug markets darknet marketplace darknet market links
deep web search tor market url darknet drug market
free dark web deep web drug store deep web links
dark web drug marketplace onion dark website darknet market
darknet marketplace dark web market links dark market url
darkmarket url dark web market list dark market 2024
dark market onion tor drug market dark web market list
darkmarket best darknet markets tor drug market
dark markets 2024 deep web markets onion dark website
darknet magazine how to get on dark web dark markets
darknet drug links the dark internet darknet market list
dark market free dark web how to access dark web
darknet search engine how to access dark web dark market 2024
darkmarket link dark website darknet markets url
blackweb dark markets 2024 blackweb official website
darknet market dark market dark web market
tor markets 2024 tor market links deep web markets
dark web link tor market url dark market onion
darknet marketplace the dark internet tor marketplace
deep web links darknet markets onion address blackweb
dark web market urls [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darkmarket 2024 [/url] dark market 2024
deep web drug links dark web search engines dark web sites links
darkmarket 2024 dark web link darknet site
darknet magazine the dark internet dark market onion
deep web drug store deep web drug store dark website
darkmarket url darkmarket list tor markets 2024
darknet site [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web site [/url] dark markets
dark web market blackweb cryptomarkets darknet
deep web drug markets dark web access tor market url
dark web market links dark websites darkmarket
dark web market urls darknet site the dark internet
dark market 2024 bitcoin dark web dark web search engines
deep web markets darknet market dark web market list
darknet markets darknet markets links tor market url
darknet drug links the dark internet darknet drugs
darknet market deep web drug store how to get on dark web
black internet drug markets dark web tor marketplace
darkmarkets darknet drug market tor market url
tor dark web dark web market list darkmarkets
onion market darknet markets links dark website
tor market tor markets 2024 darkmarket
darknet markets onion address dark web link darknet market
dark markets darknet markets links dark internet
dark web market list darkmarket darknet drugs
darknet sites drug markets dark web dark web drug marketplace
dark web search engine dark market link drug markets onion
dark web market list darknet markets url darknet links
darknet sites dark market 2024 best darknet markets
deep web sites tor drug market darknet markets
dark web search engine dark web site darknet websites
darkmarket 2024 darknet seiten tor market links
deep dark web darknet marketplace blackweb official website
dark web market [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]tor dark web [/url] deep web sites
dark web marketplaces darkmarket url darkmarket 2024
darkmarket darkmarket url dark web markets
drug markets dark web deep web drug links dark web site
deep web markets darkmarket list darkweb marketplace
darknet market lists how to get on dark web darknet market lists
dark web markets dark markets 2024 darknet marketplace
darknet market list [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets links [/url] drug markets dark web
tor marketplace deep web drug markets dark web sites links
dark web access dark web market urls dark web links
how to access dark web blackweb official website dark markets 2024
dark web market list deep web links deep web search
dark market link tor market links darknet search engine
deep dark web drug markets onion dark markets
darkweb marketplace dark web sites dark web market list
darknet markets links blackweb dark websites
darkmarket tor markets darknet markets 2024
dark web access deep web markets blackweb official website
dark web site the dark internet dark market onion
dark web market urls blackweb dark web market
darknet markets links darknet search engine darknet seiten
darknet markets onion dark web marketplaces dark web search engines
tor dark web dark web markets dark web search engines
deep web drug markets tor market dark web access
dark web markets deep web search darknet site
dark internet how to get on dark web dark market link
deep web drug url darknet magazine tor markets 2024
how to get on dark web blackweb official website darknet site
tor marketplace the dark internet darknet marketplace
darknet links darknet drugs darknet sites
dark web markets deep web search tor drug market
dark web markets dark market 2024 dark market 2024
dark internet deep web markets darknet marketplace
darknet drugs dark market list dark web links
tor markets 2024 dark net darkmarket url
black internet [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark internet [/url] darknet marketplace
darknet drugs dark market url dark web market urls
dark web drug marketplace darknet markets onion address dark web sites
how to access dark web darknet links blackweb
darknet markets onion address the dark internet darknet site
darknet market darkmarket list dark web market links
darkmarket 2024 [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web market list [/url] darknet site
tor markets links best darknet markets onion dark website
darknet market dark market link dark website
deep web markets deep web links darkweb marketplace
tor marketplace dark market list deep web markets
tor market url dark web market darknet markets onion address
dark internet tor market url deep dark web
deep web drug markets dark market onion tor market
bitcoin dark web darknet drug store dark web link
darknet markets onion address tor markets dark web marketplaces
how to access dark web tor dark web dark markets 2024
darkmarket list darknet drug links blackweb official website
darknet drug market dark websites darknet markets
free dark web darknet market darknet site
best darknet markets darknet drug links dark market list
dark web access dark web sites dark internet
tor markets darknet markets 2024 dark market url
deep web drug store dark web sites darknet drug store
darknet search engine dark market onion tor markets
darknet websites dark web market links deep web sites
dark web websites deep web markets deep web drug links
darkmarket 2024 dark websites darknet markets url
darkmarket link darkmarket url cryptomarkets darknet
how to access dark web how to access dark web dark internet
deep web links dark web access dark web links
darkmarket 2024 drug markets dark web bitcoin dark web
dark market link deep web drug store darknet magazine
how to access dark web dark web market list darknet search engine
blackweb darknet market links tor markets
dark internet dark web sites links deep web sites
dark web search engine tor market dark market url
darknet search engine [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web sites [/url] bitcoin dark web
tor dark web deep dark web drug markets onion
darkmarket 2024 darknet drug links drug markets onion
dark web market urls darknet links darknet site
dark web sites links dark market onion blackweb
tor markets links onion dark website dark market onion
free dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]deep web links [/url] drug markets onion
darknet links tor markets links blackweb official website
dark web market dark market onion darknet seiten
darknet magazine darknet drug store darknet sites
black internet darknet drug links deep dark web
best darknet markets black internet dark web site
darknet market list darknet markets onion tor darknet
dark web market list how to access dark web dark markets 2024
dark web site dark web market urls deep web drug links
dark web market urls free dark web best darknet markets
dark websites dark website darkmarkets
tor dark web dark internet dark websites
darknet websites dark web access dark web market links
darknet market list drug markets onion darknet markets url
darknet drugs darkweb marketplace darkmarket 2024
dark website darknet sites dark web site
dark web sites links dark web market links blackweb
darknet markets url dark web site dark internet
deep web markets darkmarket list dark market onion
darknet sites tor darknet deep web markets
dark web site drug markets dark web deep web markets
darknet magazine deep web drug markets dark web market
tor markets dark web market urls tor markets
bitcoin dark web dark internet darkmarket link
dark web links [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]deep web drug store [/url] dark market 2024
darkmarket tor market darknet search engine
dark market darknet drugs darknet market lists
dark web marketplaces blackweb official website tor market url
darkweb marketplace dark market url deep web drug links
darknet markets url dark web market list dark websites
dark market url darknet market lists darknet seiten
how to get on dark web onion market dark market 2024
darknet drug links darknet links darknet marketplace
dark web market list darkweb marketplace darknet market list
darknet marketplace free dark web dark market url
tor markets links best darknet markets dark web search engines
darknet sites [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]tor marketplace [/url] tor markets
dark markets dark net dark web links
the dark internet dark web websites deep web drug store
darknet markets url free dark web darknet markets links
dark web search engines dark web market urls darknet markets
darknet marketplace deep web drug store darknet drug market
darknet drug store dark websites blackweb official website
приворот парня черная магия – Обратится к магу – https://dzen.ru/id/653538d7d6100f7a6fee8469
приворот черный по фото
tor market links deep web markets darknet drug market
darkmarkets tor darknet dark web drug marketplace
bitcoin dark web darknet market lists darknet markets url
dark website dark market cryptomarkets darknet
dark website dark web search engines tor marketplace
dark web search engine darkweb marketplace darknet marketplace
tor dark web darknet markets links darknet magazine
darknet markets url darkmarket darknet market list
dark web link darknet seiten cryptomarkets darknet
darknet links tor market links how to get on dark web
dark web site darknet markets links tor market links
darkmarket url dark market link darknet drug market
dark websites darknet markets url bitcoin dark web
darknet markets links darkmarket list tor market links
dark web websites tor dark web how to get on dark web
darknet sites darknet markets 2024 darknet markets onion
dark markets dark websites best darknet markets
tor marketplace darknet markets onion dark web sites
darknet markets url darknet drug store black internet
dark web link best darknet markets darkmarket link
darknet markets onion address dark web search engine darknet sites
dark internet darknet drug store tor market url
deep web links darkmarkets blackweb official website
how to get on dark web cryptomarkets darknet dark web site
darknet market links dark web market urls dark website
deep web drug markets deep web drug store the dark internet
darknet drug store [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets links [/url] darknet market
bitcoin dark web deep dark web darkmarket url
deep web search black internet black internet
tor marketplace darknet drug links darknet drugs
free dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]best darknet markets [/url] dark web links
dark web search engines blackweb dark markets
onion dark website darkmarket 2024 dark web sites links
dark market url how to get on dark web dark web links
dark web websites darkmarket 2024 tor market url
deep web sites dark market url how to access dark web
darknet drug market darkmarket link blackweb
darknet links dark market url dark market
dark web marketplaces deep web drug url how to access dark web
darknet drug links dark web market list darknet markets url
dark web access darknet marketplace darknet websites
dark web sites dark web marketplaces deep web drug store
deep web drug markets darknet market lists darkmarket url
cryptomarkets darknet darknet markets 2024 dark market onion
drug markets onion darknet site dark web search engines
deep web drug links dark web market darknet drug links
drug markets onion cryptomarkets darknet darknet marketplace
darknet websites darknet market darknet drug store
dark web market dark web search engine darknet market
dark internet free dark web darknet market list
dark website tor marketplace darknet marketplace
darkmarket drug markets dark web deep web drug store
darknet websites dark market dark web link
darknet magazine dark web site darkweb marketplace
dark market onion dark market link deep web drug markets
deep web links darknet sites dark market
deep web search black internet cryptomarkets darknet
dark web access dark web market list darkmarket
dark websites how to access dark web tor market url
deep web drug store deep web sites darknet drug store
dark web link [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet site [/url] dark website
tor markets 2024 deep web drug store the dark internet
deep web sites deep dark web darkmarket list
darknet drug links onion market tor marketplace
darknet market list [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark market link [/url] dark market link
dark market onion onion market free dark web
darknet marketplace deep web search darknet markets onion
bitcoin dark web tor market drug markets onion
tor market tor markets 2024 free dark web
deep web markets dark market 2024 darknet markets links
dark web link blackweb official website dark web search engine
how to access dark web dark web site darkmarket
drug markets dark web darknet marketplace tor drug market
darkmarket url tor markets links darknet magazine
tor markets deep web drug store deep web drug url
dark net tor darknet dark websites
tor drug market dark websites free dark web
dark web marketplaces dark web markets darknet links
darkmarket url the dark internet darknet drugs
dark websites darknet websites dark web search engines
dark web marketplaces dark web markets bitcoin dark web
black internet deep web links dark internet
deep web markets dark market 2024 darknet drugs
dark markets dark web market links best darknet markets
dark web websites darknet site darknet markets links
darknet market list blackweb darknet markets links
dark market 2024 darknet drug market black internet
dark market list dark web sites darknet markets onion address
tor market url deep web sites dark web search engines
dark internet dark web search engine how to get on dark web
how to access dark web drug markets onion deep web drug markets
dark web markets dark web marketplaces deep web drug store
tor drug market tor markets links darknet market lists
tor market links how to access dark web darkmarket 2024
cryptomarkets darknet darknet links dark internet
drug markets dark web [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet sites [/url] tor dark web
darkmarket 2024 darknet markets 2024 darknet market links
dark market 2024 dark website tor markets
darkmarket darknet markets onion best darknet markets
deep web drug links deep web markets dark website
drug markets dark web dark web markets dark websites
dark website tor market url tor market links
darkmarket tor markets 2024 tor marketplace
dark website deep web markets dark markets 2024
darknet seiten darknet seiten tor darknet
darknet drug store dark website dark web links
darknet markets url tor drug market tor drug market
dark market 2024 dark web drug marketplace tor markets 2024
tor markets links darknet magazine dark web market urls
best darknet markets darkmarket url how to get on dark web
onion market darknet site dark market list
darknet markets onion address deep web links how to access dark web
darknet market lists darknet drug market deep web drug url
dark web drug marketplace free dark web dark web market links
dark market 2024 dark web websites darknet markets onion
dark web market urls darknet magazine darknet marketplace
blackweb official website drug markets onion deep web links
cryptomarkets darknet dark web sites links darknet drug market
dark web market urls tor markets 2024 darkmarket link
darknet markets url black internet darknet sites
deep web drug store free dark web onion dark website
dark web site darknet markets drug markets onion
dark web market urls dark market link darknet drug store
darkweb marketplace free dark web free dark web
dark web markets deep web markets onion market
dark internet onion market darknet search engine
tor darknet darknet markets onion address darknet drugs
dark web marketplaces dark web search engine darknet markets onion
darknet site darknet magazine darknet markets onion address
dark markets 2024 [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web links [/url] tor dark web
dark web markets dark internet darknet markets onion
Для тех, кто увлекается историей и героическими сюжетами, [url=https://turkbiz.tv/voenie/]турецкие сериалы военные[/url] на turkbiz.tv предложат глубокие и захватывающие истории. Эти сериалы не только показывают военные действия, но и раскрывают человеческие эмоции и драмы, связанные с войной и её последствиями.
tor markets 2024 dark web access darknet websites
dark net tor market darknet seiten
darknet search engine drug markets onion dark market link
dark web sites dark web markets dark market link
dark web link [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darkmarket [/url] deep web drug url
darknet links onion dark website dark market link
darknet markets onion blackweb darknet market
dark web link darknet sites dark web sites
darkmarket list deep web drug url dark market list
darknet sites onion dark website black internet
dark web sites how to access dark web tor marketplace
how to access dark web dark web sites darknet markets
tor dark web the dark internet darknet marketplace
darknet drug links dark web site darknet drug market
darknet market lists bitcoin dark web darknet seiten
dark markets 2024 dark web links the dark internet
darknet markets 2024 dark market url darknet market links
dark market onion dark web links tor markets
tor markets 2024 tor marketplace dark web drug marketplace
onion market darknet markets onion address drug markets dark web
dark web market list dark markets 2024 darknet drugs
dark web access how to get on dark web dark web access
darknet markets onion address cryptomarkets darknet deep web markets
darknet links dark web market list blackweb official website
dark web markets darknet market lists darknet links
deep web search darknet site dark websites
darknet drugs darknet seiten tor drug market
dark market url tor market darknet drug links
blackweb official website dark website dark web drug marketplace
deep web sites dark web link darknet magazine
darkmarket 2024 dark website dark web link
darknet market lists deep web search dark market onion
blackweb dark web websites black internet
dark web site dark websites dark market 2024
deep web search darknet markets onion darknet drug links
darknet market links darknet seiten darknet drug store
dark web site deep web drug markets the dark internet
free dark web [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]tor market url [/url] deep web links
dark web drug marketplace dark market onion darknet sites
dark websites tor market links deep web sites
darknet market links darknet site blackweb official website
dark web market dark internet tor dark web
darknet drug links darknet markets links best darknet markets
tor market links [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]tor markets [/url] tor dark web
drug markets dark web tor markets dark net
darknet markets onion address deep web drug store how to get on dark web
the dark internet deep web drug links dark web search engine
dark market dark market 2024 tor market
dark market link dark website dark markets
deep web markets dark markets dark net
deep web search dark web market list dark web market list
tor markets darknet markets onion the dark internet
dark web access darknet sites tor dark web
deep web search how to access dark web dark web markets
dark market list dark web search engine darknet markets onion
darknet markets 2024 darknet sites darknet drug links
darkmarket link darkmarket list darkmarket 2024
darkweb marketplace dark web market darknet market links
dark web access darkmarket link dark web search engine
deep web drug links darkmarket url darknet seiten
dark market list the dark internet darknet search engine
dark websites deep web search deep web drug url
how to get on dark web darkmarket list darkweb marketplace
bitcoin dark web dark market drug markets onion
dark web access dark website dark market url
dark markets 2024 dark markets 2024 dark web websites
dark web market urls darknet market dark web market list
blackweb darkweb marketplace darkmarket list
tor market best darknet markets deep web drug links
tor market links dark market onion deep web drug markets
dark web links darknet market lists dark web search engine
dark web marketplaces dark web sites deep web drug store
darkmarket list [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet markets url [/url] dark web drug marketplace
deep web drug links tor dark web cryptomarkets darknet
tor markets darknet markets links tor market url
darknet search engine tor dark web dark market onion
dark web marketplaces [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark websites [/url] deep dark web
best darknet markets dark web markets darknet drugs
tor drug market dark web drug marketplace darknet market
dark web drug marketplace drug markets dark web dark web access
darknet markets onion blackweb official website onion dark website
dark web markets darknet websites dark market 2024
tor markets links darkmarkets dark web drug marketplace
Магическая помощь – сильные экстрасенсы
присушка на женщину https://gadalkindom.ru как понять что приворожили парня
как удержать мужчину возле себя на всю жизнь заговор
deep web markets deep dark web drug markets onion
darknet markets onion address tor drug market tor markets 2024
tor markets links darknet market lists dark net
dark web drug marketplace dark web sites dark web sites links
darknet markets onion address tor markets links drug markets onion
darkmarket url deep web search darkmarket link
darknet websites dark markets dark web drug marketplace
darknet market lists tor markets blackweb official website
darkweb marketplace darknet markets url dark website
dark web market darkweb marketplace dark web search engine
dark web sites dark web marketplaces blackweb
dark web marketplaces dark market link darknet site
generic cialis canada
darkweb marketplace dark markets dark web markets
drug markets onion tor drug market darknet market lists
darknet markets onion dark web market best darknet markets
darknet search engine darkmarket list the dark internet
best darknet markets deep web drug links tor market
how to get on dark web darkmarket link dark web link
dark web drug marketplace deep web drug markets dark web links
tor markets links darknet market links darkmarket 2024
tor darknet [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark net [/url] onion market
darknet drugs dark web marketplaces dark web sites links
dark web market links darkmarket 2024 darkmarket
darkmarket 2024 darknet markets onion address onion market
dark web websites darknet search engine darknet marketplace
darkmarket link [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]how to get on dark web [/url] darknet drug store
black internet tor market links tor market
darkmarket link black internet blackweb official website
darknet drugs dark web markets darkmarket list
dark web sites links darkweb marketplace darkmarket list
drug markets dark web deep dark web dark market
darkweb marketplace dark web link darknet drug store
tor markets links onion dark website dark web sites links
dark web marketplaces black internet bitcoin dark web
darkmarket list how to access dark web darkmarkets
deep web drug store tor market links darknet market links
darknet market links dark web access deep web drug url
dark web sites darknet market list darknet site
darknet magazine darknet magazine dark web search engines
darknet markets links tor market links darknet search engine
dark web marketplaces drug markets onion drug markets dark web
deep web drug links dark web market list tor market links
darknet links free dark web darknet drugs
free dark web tor darknet dark market url
deep web sites deep web drug markets darkmarket url
tor market links dark market link dark web drug marketplace
deep web drug markets deep web drug store dark market list
darknet market lists darknet markets 2024 dark market link
dark web access deep web drug links darkmarket
best darknet markets tor darknet darkmarket
drug markets onion darknet markets links deep web drug store
dark web search engine tor market dark markets 2024
deep web sites dark web marketplaces darknet drug links
darknet drugs darkmarket list deep web markets
darkmarket url deep web sites onion dark website
darknet marketplace dark web market urls darkmarket url
deep web drug links [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark internet [/url] dark websites
darknet market darknet magazine darkweb marketplace
darknet websites darkmarkets deep dark web
deep web links deep web sites dark web search engine
darkmarket 2024 darkmarket deep web drug links
blackweb dark web links dark web websites
tor darknet tor market darknet links
darknet links darknet search engine dark market list
deep web drug store darkmarkets how to get on dark web
deep web drug store dark web marketplaces tor darknet
dark markets 2024 [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark market 2024 [/url] dark web sites
deep web search darknet magazine tor market
dark market onion darknet site dark market
deep web links drug markets onion deep web sites
black internet darkmarket url tor marketplace
dark market link tor market darknet drug store
dark web market list blackweb dark web market links
darkmarket 2024 dark web market list darknet market lists
darknet marketplace tor darknet deep web drug links
tor market url dark web access dark web market list
deep web drug url how to get on dark web dark web sites links
deep web markets dark web market darknet market links
darknet markets onion address dark web websites darknet market list
darknet market list dark web search engines drug markets onion
darknet links darknet markets blackweb
deep web search free dark web dark market link
darkmarket list darkmarket url dark markets 2024
deep web search deep web drug store tor drug market
deep web drug store darknet magazine dark web drug marketplace
darknet marketplace dark net dark web links
best darknet markets tor market links tor markets links
dark web sites links dark market list cryptomarkets darknet
darknet market darknet market list deep web markets
tor drug market darknet drug market darkweb marketplace
darknet links dark market url deep dark web
blackweb dark web market tor market
dark web market [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]bitcoin dark web [/url] darknet market
darknet site tor markets links darknet drugs
darknet markets onion address dark websites darkmarket link
tor marketplace [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet drugs [/url] deep web markets
deep web search dark web links deep web drug markets
dark internet darknet drug market deep web drug url
darknet magazine darkmarket link free dark web
tor markets how to access dark web dark web site
dark web link tor dark web dark web marketplaces
darknet market list darkmarket list darknet market lists
dark market deep web search darknet market list
darknet drug store tor drug market darknet sites
darkmarket 2024 dark market list dark web market
tor markets darknet websites darknet links
dark web markets tor marketplace darknet search engine
tor markets 2024 darknet markets links darknet sites
dark market list dark web market urls tor markets
dark web link darkmarket 2024 dark market 2024
darknet drug store darknet markets onion onion market
drug markets onion tor drug market dark markets 2024
магия цены на услуги ->>>>>>>услуги экстрасенса стоимость https://www.magecam.ru <<<<<<<<<<-
dark web links darknet drugs deep web markets
darknet magazine tor darknet darknet market
blackweb official website darknet websites darknet market lists
deep web drug store darknet markets 2024 blackweb
darknet markets url darknet market lists darknet market list
dark web search engines dark internet darknet marketplace
darkmarket link darknet markets onion address deep web sites
tor markets links darknet market links darkmarkets
dark web markets darknet markets onion address dark market
darkmarket link deep web search dark web sites links
drug markets dark web blackweb dark markets
dark websites [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]best darknet markets [/url] dark market onion
deep web sites blackweb official website deep web drug links
dark web market list darknet seiten deep web drug store
deep web links tor darknet black internet
dark market link dark web market list dark web access
darkmarket 2024 darkmarket 2024 darknet market list
darknet market links [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet drug market [/url] dark web site
darknet magazine dark market link dark market
darkmarket list darknet search engine onion dark website
dark web sites links dark web access blackweb
the dark internet dark web search engine deep web drug url
how to get on dark web how to get on dark web drug markets onion
darknet market lists tor markets dark website
dark markets 2024 dark website deep web markets
onion market best darknet markets dark market onion
blackweb darknet sites bitcoin dark web
blackweb dark web market darknet markets 2024
bitcoin dark web tor market url darknet site
darknet market tor dark web darkmarket
dark net dark web markets dark market link
darknet site dark market link dark market link
darkmarket list darkmarket link darkmarket url
dark website the dark internet darknet markets onion address
dark web market links dark market link dark market list
dark website tor darknet cryptomarkets darknet
dark web sites tor market links darknet sites
the dark internet dark web sites darknet site
dark web marketplaces darknet sites how to get on dark web
dark web search engines deep dark web black internet
drug markets onion darkmarket 2024 deep web drug url
dark web marketplaces darknet seiten dark market
darknet sites dark web market links drug markets onion
darkmarket dark net darknet sites
darkmarket link tor market links dark web site
tor market darkmarket link darknet site
darknet drug links dark market url tor dark web
dark market link dark web market dark web links
darknet magazine [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark net [/url] darknet drug market
tor dark web the dark internet bitcoin dark web
deep web sites onion market darknet marketplace
dark web access [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet markets [/url] drug markets onion
dark web access dark market deep web markets
onion dark website dark market link dark websites
dark market link darknet links darkmarket list
bitcoin dark web tor dark web deep web links
the dark internet dark web market deep web drug markets
deep web drug links darknet marketplace darknet markets onion
dark web market links darknet market list dark web search engine
bitcoin dark web dark web market darknet markets onion
tor markets links tor market url dark web market urls
dark web sites tor marketplace darknet drug market
blackweb dark markets darknet market links
darknet links tor markets links drug markets onion
deep web drug store onion market darknet markets onion address
black internet tor market dark web market urls
dark web websites darknet markets onion address darknet drugs
dark web sites links cryptomarkets darknet how to get on dark web
tor market links darknet markets 2024 dark website
dark web search engine dark market drug markets onion
deep web markets tor markets 2024 darknet market lists
dark internet darknet markets url dark web sites links
onion market darknet magazine dark web site
tor market links dark web market dark web market
dark market 2024 dark market onion darkweb marketplace
https://www.magecam.ru
Услуги магов
-привороты
-наведение порчи на смерть
-отнятие удачи
-возврат любимого
сильный приворот на парня который нельзя снять
darknet drug links darknet seiten free dark web
tor darknet tor markets 2024 darknet markets onion
tor drug market dark market url dark markets 2024
black internet deep dark web deep web drug links
dark web sites blackweb official website darkmarket list
darkmarkets tor marketplace onion market
dark web sites links darknet drug links darknet links
darknet links [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark market [/url] black internet
tor markets drug markets onion darkmarket list
dark web websites drug markets onion how to access dark web
tadalafil compounding pharmacy
darkmarket url cryptomarkets darknet dark web marketplaces
darknet drug market tor drug market deep web drug store
deep dark web [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]blackweb [/url] deep web drug markets
darkmarket list dark web sites links darknet drug store
deep web drug markets dark web websites tor market
darkweb marketplace dark web marketplaces dark web market
dark web sites links tor markets links darknet sites
darkmarkets darkmarket darknet links
darknet markets onion address tor drug market blackweb
darknet drug market tor market dark web sites
dark web market links tor market url dark web sites
darkmarket onion market black internet
darknet drug links dark web websites darknet drug store
how to access dark web darknet websites deep web drug links
dark markets deep web sites dark web market list
darknet markets deep web search deep web drug url
dark web access dark markets 2024 tor market links
darknet sites dark markets deep web links
dark market 2024 darknet market links how to access dark web
free dark web dark website darkmarket
dark web site darkmarket list darknet market
darkmarket link tor darknet dark web drug marketplace
black internet dark web websites deep web search
darkmarket 2024 darkmarket link darknet market lists
dark website the dark internet dark market
dark web market links the dark internet dark web sites
cryptomarkets darknet dark website blackweb official website
tor market dark web market list darkmarket
darknet drug market tor market tor dark web
darkmarket url darknet market links deep web search
darknet seiten dark market url darknet markets links
deep web drug store darknet markets links dark markets
dark web market darkmarkets tor markets links
darkmarket link tor market darknet websites
dark web marketplaces dark internet darknet markets 2024
darkweb marketplace blackweb darknet market links
darknet drugs dark web access deep web links
darknet markets onion tor market url dark web site
darknet markets onion address dark web site dark internet
dark web access [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web market urls [/url] drug markets onion
tor markets 2024 dark web market links dark market list
dark market dark web market list drug markets onion
onion market [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet seiten [/url] dark web link
darkmarkets tor market drug markets onion
deep dark web darknet search engine dark web marketplaces
darknet links darknet market list darkmarket link
how to access dark web blackweb dark web link
darknet market list dark web links deep web links
darkmarket url darknet markets links deep web drug url
darkmarket list darknet site dark web links
deep dark web darknet links dark website
dark web search engines deep web sites tor markets
dark internet deep web sites dark markets
bitcoin dark web the dark internet tor market url
blackweb official website darknet drug links onion market
tor market onion market dark websites
dark web websites deep web drug links darknet markets links
darknet markets 2024 deep dark web darknet links
tor markets onion market darknet markets links
dark web sites best darknet markets darknet markets url
dark web search engine dark market url darkmarket list
dark web market urls dark net darknet market lists
blackweb official website blackweb official website darknet market lists
dark web links blackweb darknet markets onion
the dark internet dark web markets dark market onion
deep web sites darknet marketplace free dark web
bitcoin dark web dark web search engine dark web links
tor market dark web search engines darknet drug store
drug markets onion deep web drug url deep web drug store
darknet search engine deep web markets dark websites
darknet magazine dark web access darkmarket link
darknet drug market deep web search tor market links
dark web sites [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet markets links [/url] darkmarket list
darknet markets onion address onion dark website dark web market list
darknet drugs how to access dark web darknet seiten
dark market bitcoin dark web darkweb marketplace
dark web sites links [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark market onion [/url] black internet
darknet market dark web search engine tor marketplace
dark web link dark market url darknet links
darkmarket list darknet market links darkmarket url
darknet drugs dark market tor drug market
darknet sites darknet search engine darkmarket list
dark market list best darknet markets deep web drug url
dark market link dark web websites deep web sites
dark market link darknet markets url best darknet markets
dark web drug marketplace darknet seiten dark market
dark markets darkmarket link dark web market urls
darknet drugs tor markets links drug markets onion
dark market 2024 darknet markets onion address darknet search engine
tor marketplace darkmarket 2024 dark web marketplaces
onion dark website tor markets links dark market onion
dark web search engine best darknet markets cryptomarkets darknet
dark web market list dark web link tor dark web
darkmarkets darkmarkets dark market list
deep web links dark market 2024 darknet markets onion
dark market list deep web markets drug markets dark web
darkweb marketplace dark market link darknet links
dark web sites deep web drug url tor markets 2024
dark web market urls dark web access dark market list
dark market dark web marketplaces darknet drug links
dark web links dark web market urls dark web link
darknet market links the dark internet darknet links
deep web markets deep web drug markets darkmarket
dark web market urls how to access dark web tor market url
darkmarkets darknet site dark web market links
dark web sites links dark market list dark web market links
deep dark web dark web site dark market url
dark web websites [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web link [/url] dark web search engine
darkmarket link dark markets 2024 cryptomarkets darknet
dark web market list tor market url dark web sites links
darkweb marketplace black internet tor market links
dark markets 2024 dark market 2024 how to get on dark web
how to get on dark web tor drug market darknet seiten
dark web markets [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet websites [/url] dark net
darknet drugs dark websites deep web drug links
dark web sites links dark website dark markets
dark web link darkmarket list bitcoin dark web
Черный маг
сильные заговоры на любовь парня https://gadalkindom.ru заговор на слюну на любовь мужчины читать белая магия
заговор на еду для мужа
deep web drug url blackweb drug markets onion
onion dark website how to get on dark web cryptomarkets darknet
tor markets darknet markets onion dark web websites
deep web drug url darknet drug market darknet market list
dark market link dark net dark markets 2024
tor drug market dark website dark market url
black internet deep dark web dark web drug marketplace
dark websites dark web sites darknet site
deep dark web darknet site dark markets
darknet market list darkweb marketplace dark websites
onion dark website tor darknet darkmarket link
cryptomarkets darknet deep web sites deep web sites
dark web search engine onion market darkmarket url
tor markets bitcoin dark web tor market
darknet search engine darknet market darkmarket
tor market darknet market lists tor markets 2024
tor drug market darknet markets url how to access dark web
blackweb dark web sites links dark web links
dark web market list darknet drug market blackweb
free dark web deep web search dark web search engine
dark website deep web links deep web drug store
darknet market lists deep web links onion dark website
dark web markets darknet market list darkmarket list
dark web links best darknet markets deep web drug url
darknet markets links blackweb official website darknet market lists
порча на сгоревших спичках https://www.magecam.ru народная медицина порча
cryptomarkets darknet [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]deep web drug markets [/url] dark web sites links
dark web link darkmarkets black internet
deep web links dark web search engines cryptomarkets darknet
darknet markets onion address darknet market list darknet markets 2024
blackweb official website [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]deep web markets [/url] black internet
free dark web deep web links how to access dark web
dark market onion darkmarket 2024 darknet markets 2024
dark web market urls darkmarket 2024 tor marketplace
darknet markets links darknet market lists dark market url
bitcoin dark web deep dark web dark web site
blackweb dark web drug marketplace deep web drug url
how to get on dark web dark web market urls deep web search
dark web market drug markets dark web bitcoin dark web
deep web markets deep web sites dark web market
dark market list deep web links dark web market list
cryptomarkets darknet deep web drug store deep web drug markets
tor marketplace tor darknet dark markets
dark net tor markets links tor markets 2024
darknet drugs darkmarkets deep web drug links
как сделать приворот на удачу https://www.magecam.ru приворот для любви с заклинаниями
приворот на 40 свечей
dark markets 2024 tor darknet deep web drug store
dark web marketplaces deep web sites how to get on dark web
darknet markets dark web drug marketplace darknet markets links
dark market url darknet markets links dark web market
tor markets links dark web websites deep web search
dark web market urls dark web site darknet drug market
dark markets dark net best darknet markets
dark net dark web sites links darknet magazine
dark web market list dark website dark web site
darknet site dark web market deep web sites
blackweb official website darknet websites dark web access
dark web markets dark net blackweb official website
onion dark website dark markets 2024 dark market url
dark web access bitcoin dark web darkmarket url
how to access dark web darknet market lists darknet drug store
darknet drugs dark internet darknet sites
darknet links darkmarket url dark markets
darknet site deep web markets dark internet
deep web markets dark web access onion dark website
darknet drug links [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark market link [/url] blackweb
dark internet darknet search engine darkmarket
tor markets 2024 how to get on dark web darknet drug store
dark net darkmarket link tor market
darkweb marketplace tor market black internet
darknet market links [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]deep web drug links [/url] deep web search
darknet marketplace deep web markets darknet seiten
darknet sites darkmarket 2024 dark internet
deep web drug markets the dark internet dark web market urls
dark net darknet market lists tor marketplace
darknet market darknet markets links darkmarket url
dark web access dark web marketplaces darknet seiten
dark web link bitcoin dark web dark web markets
dark markets 2024 dark web marketplaces deep web links
deep web markets dark market 2024 darknet search engine
tor dark web tor market darkmarkets
tor markets 2024 drug markets dark web dark web market urls
dark web drug marketplace darknet search engine dark web drug marketplace
bitcoin dark web bitcoin dark web onion dark website
dark market link darknet markets links tor markets
tor markets links drug markets onion drug markets onion
free dark web tor market links dark market list
darkmarket url dark market link onion market
darknet markets onion address dark market list dark web market list
dark web market list drug markets onion how to access dark web
dark web sites links dark web access deep dark web
dark market link darknet markets links deep web links
darknet seiten best darknet markets darknet drugs
darknet markets 2024 dark web market list dark web sites
dark market link darknet marketplace darknet drugs
darkmarket list dark market url darkweb marketplace
onion dark website drug markets dark web darknet links
tor markets darkmarket tor markets links
darknet links dark web market list dark market link
dark websites dark web websites darknet drug store
dark market onion deep web drug store tor dark web
dark web market links [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark market 2024 [/url] darknet websites
dark market 2024 darkmarket link darknet markets onion
tor marketplace how to get on dark web tor marketplace
deep web markets darkweb marketplace the dark internet
darknet drugs darknet drugs darknet market links
tor market dark web market urls darknet markets 2024
drug markets onion deep web markets drug markets dark web
cryptomarkets darknet deep web drug url deep web search
dark web markets darknet markets 2024 darknet market
deep dark web dark market link tor markets
dark web drug marketplace dark web sites darknet market
dark markets darknet drug store darkweb marketplace
dark net dark web search engines darkmarket link
deep dark web darkmarket list dark web links
dark web marketplaces blackweb official website darknet marketplace
deep web drug links dark market list dark web market links
dark web drug marketplace deep web sites darknet markets onion
dark market list darkmarket link deep web links
how to access dark web dark web drug marketplace dark web market urls
darknet drugs dark web market links dark web market links
dark market onion dark web drug marketplace dark markets 2024
darkmarket 2024 tor market darkmarket url
dark web websites best darknet markets blackweb
dark web markets dark web marketplaces dark web sites links
black internet dark web markets dark web site
tor markets links darknet drug market tor market url
dark markets dark markets best darknet markets
dark markets 2024 darknet site deep web sites
dark web drug marketplace blackweb official website dark web market urls
dark market 2024 [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web link [/url] darkmarket 2024
best darknet markets free dark web dark web site
tor markets 2024 tor markets links dark net
darkmarket url darknet markets onion tor market url
dark web websites deep web drug store deep web links
darkmarket url darknet sites deep web search
darknet magazine [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darkmarket 2024 [/url] darknet drug links
deep web drug url darknet markets darknet drugs
tor market url dark web marketplaces drug markets onion
dark web link darknet markets url dark market link
dark market link cryptomarkets darknet best darknet markets
dark internet dark markets tor markets links
darknet market lists dark web drug marketplace darknet markets links
drug markets onion darknet marketplace deep web drug store
dark market list dark web search engine dark web links
darknet markets onion address darkmarkets dark market list
drug markets onion dark web market list drug markets onion
tor drug market deep web drug url dark market 2024
darkmarket darknet market links dark web markets
deep web markets dark market onion dark websites
tor drug market dark markets darknet markets 2024
dark web links darknet market list dark web market list
darknet market list deep dark web darkmarket
dark market url darknet seiten dark web market
darkmarket link deep web markets tor dark web
dark market deep web drug url dark web websites
dark market onion darkmarket 2024 dark web market
dark internet dark web websites dark web markets
deep web drug links tor markets links deep web drug markets
dark market list darknet markets url darkmarket url
darkmarket url dark website dark web sites
tor market url darknet sites blackweb official website
dark websites [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet seiten [/url] darknet drug market
darknet market list darkmarket 2024 darknet markets
dark market list darkmarket 2024 dark web sites
dark net tor market links tor drug market
tor markets links darknet markets links darknet seiten
dark web search engines the dark internet dark web search engines
dark web market list darknet seiten darkmarket
how to get on dark web darknet site darknet market lists
drug markets dark web darknet search engine darknet search engine
darknet links onion dark website dark web site
dark web access dark market list dark web market list
darknet market darknet drug market dark market
darknet markets url dark markets 2024 darkmarket list
dark website tor markets links cryptomarkets darknet
darknet links deep web drug markets dark web marketplaces
the dark internet deep web search darknet links
darknet search engine darknet markets 2024 darknet market
darknet seiten black internet darknet sites
dark web drug marketplace dark market url dark web marketplaces
dark market list dark web websites dark web market
darknet drug market darknet market darknet drug store
deep web sites deep web links dark web marketplaces
tor dark web darknet websites darknet drug market
tor market url darknet search engine tor market
darknet seiten black internet darkmarkets
dark web search engines cryptomarkets darknet dark web search engines
darknet drug store darknet markets links darkmarket 2024
drug markets dark web darkmarket link darknet drugs
darknet drugs tor darknet darknet drugs
dark markets 2024 darknet links dark website
bitcoin dark web onion market deep web search
tor markets darkmarket link dark web websites
dark web access [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darkweb marketplace [/url] darknet market links
darkmarkets dark market link tor market url
deep web drug links free dark web dark web drug marketplace
dark market url [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]deep web markets [/url] tor market
dark market url dark website darknet drugs
darkmarket link free dark web bitcoin dark web
dark internet darknet markets onion address darknet search engine
dark market darknet markets url darknet drugs
dark net deep web sites deep web drug url
darkmarket list darknet drugs tor market links
darknet marketplace dark markets 2024 darknet markets 2024
darknet markets 2024 dark markets 2024 darknet markets onion address
dark website darknet market list dark web site
how to access dark web onion market deep web drug store
darkmarket dark web markets blackweb official website
darkmarket tor markets bitcoin dark web
dark web market darkweb marketplace darkmarket url
dark web market list darkmarket url deep web links
dark web search engines bitcoin dark web dark market onion
darkmarket url darknet links dark website
dark websites best darknet markets dark web market links
darknet markets url dark websites darknet markets
darknet market list darkmarket url deep web drug url
dark markets dark web websites dark market list
dark markets dark web site deep web drug markets
dark web links darkmarket 2024 dark websites
tor market onion dark website dark web access
deep web search [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darkmarket link [/url] tor market
darknet market darknet site onion dark website
darkweb marketplace dark internet darknet seiten
best darknet markets [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet site [/url] dark market onion
cryptomarkets darknet onion dark website dark market url
darkweb marketplace darknet markets 2024 darknet markets 2024
darknet market list darkweb marketplace darkmarket link
black internet darknet markets url darknet markets
заговоры на любовь мужчины читать в домашних условиях на расстоянии – Помощь экстрасенса https://www.magecam.ru – сексуальный приворот отзывы влюбить в себя мужчину на расстоянии заговор
cialis buy paypal
dark web drug marketplace deep web drug store darknet market links
darknet market lists black internet cryptomarkets darknet
dark market url tor dark web dark web link
dark web access blackweb dark web markets
deep web sites dark market deep web sites
darknet markets dark web markets dark website
darknet markets onion darkmarket link darknet markets 2024
darknet markets links dark web site tor market links
darknet sites free dark web the dark internet
how to get on dark web dark web sites links darknet markets 2024
deep web markets tor markets deep web sites
dark web market urls dark market onion blackweb official website
deep web markets dark web market list dark web market urls
darkmarket 2024 dark websites darkmarket url
dark web links how to access dark web darknet market list
deep dark web darknet links onion dark website
darkmarket list darknet markets onion dark web market links
dark web search engines dark web websites dark web site
dark web site darknet drug store darknet markets url
darknet markets onion address darknet magazine darknet market
darknet drug market tor markets links darknet links
tor marketplace darknet search engine darknet market lists
black internet darknet links blackweb
drug markets dark web darkmarkets deep web links
drug markets onion bitcoin dark web dark websites
darknet drug store darknet market lists darkmarket
tor darknet darkmarkets darknet websites
drug markets onion [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark markets 2024 [/url] darknet websites
dark web marketplaces dark website dark websites
dark market link dark web search engine tor market
dark web markets darknet site deep web markets
deep web drug store dark market 2024 dark market onion
darknet market lists dark market 2024 tor markets links
tor drug market darkmarket darknet drug market
darknet drug market darknet market links dark internet
dark web search engine dark web sites darknet markets
darkmarket dark web sites deep web drug store
onion dark website darknet seiten darknet marketplace
onion market how to get on dark web cryptomarkets darknet
darknet marketplace darkmarkets free dark web
darknet drug links deep web drug url darknet market links
drug markets onion dark web markets darknet marketplace
deep web markets tor drug market deep web drug links
darkmarket tor markets 2024 deep web drug url
dark web site dark market onion darknet market
dark markets 2024 dark website darkmarket link
deep web links tor market url darknet seiten
По вопросу [url=https://newswomanblog.win/begovaya]проститутки метро беговая[/url] заходите к нам прямо сейчас. Если Вы напряжены от скучных и одинаковых будней, а ещё ответственных рабочих смен, то пришло время побаловать себя и получить огромное развлечение.!
darkmarket list darknet site dark market onion
dark web search engine tor markets 2024 tor market
blackweb dark web market links dark website
tor markets darknet drug links blackweb
darkmarket list tor markets onion market
darknet magazine tor marketplace deep web drug markets
darknet websites tor drug market drug markets dark web
darknet search engine dark markets dark web site
black internet dark web search engines drug markets onion
drug markets onion dark web markets dark web market
darknet markets url [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]tor markets [/url] darknet markets url
dark net deep web markets dark web search engine
darknet marketplace dark web market urls darkmarket url
dark market url [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet sites [/url] how to get on dark web
dark web link tor dark web darknet drugs
deep web markets how to access dark web tor drug market
dark web market list darknet links darknet site
blackweb official website dark market url dark web site
tor dark web darknet drug market dark market list
dark web markets the dark internet deep web drug store
darknet market list darkmarket 2024 dark web sites
best darknet markets dark market onion dark web market
tor market tor market free dark web
cryptomarkets darknet onion market tor dark web
dark website dark market link darknet market lists
darknet magazine blackweb official website dark web markets
blackweb the dark internet free dark web
deep web markets dark web drug marketplace dark websites
tor drug market dark web market tor dark web
tor markets 2024 black internet tor drug market
darknet site deep web search dark web drug marketplace
drug markets onion darknet drug links dark web websites
dark markets dark web link darknet market
tor market links darknet market links darknet markets links
darknet magazine dark web search engine darknet markets onion address
tor markets darknet markets onion onion market
darkweb marketplace dark web marketplaces darknet markets url
darknet site darknet site onion market
darknet search engine deep dark web dark web market list
dark market onion market deep web drug url
darknet links darknet seiten tor dark web
dark web sites [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darkmarket link [/url] darkweb marketplace
deep web drug markets onion market blackweb official website
deep web sites deep web drug url deep dark web
dark web markets [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet seiten [/url] darknet drug links
best darknet markets dark web sites links darknet site
dark market url dark market 2024 tor drug market
deep web sites deep web drug links drug markets onion
dark web access darknet marketplace deep dark web
dark market list darknet drugs darknet marketplace
onion dark website darknet markets onion address darknet market
darknet seiten darknet search engine drug markets dark web
best darknet markets free dark web darknet drug market
darkmarket url darknet drugs deep web drug url
dark web search engines dark market onion deep web drug store
[url=https://augmentin.best/]amoxicillin 825 125 mg[/url]
dark web market links deep dark web tor markets 2024
dark web drug marketplace cryptomarkets darknet tor market
deep web markets the dark internet black internet
darkmarket dark market url tor dark web
cryptomarkets darknet darknet search engine deep web drug markets
dark web access tor marketplace drug markets onion
cryptomarkets darknet the dark internet dark web marketplaces
tor markets links dark markets 2024 blackweb
tor market dark market url dark web sites links
dark web sites links tor drug market darknet market lists
dark net dark web market links dark web search engines
free dark web darknet sites blackweb
tor dark web dark market list onion market
darkmarket link dark market list darknet magazine
the dark internet tor dark web darkmarket link
dark web access [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet drug market [/url] darknet markets url
dark web websites tor markets darknet links
darknet markets onion darknet websites the dark internet
dark web market list dark markets dark web market links
darkmarket 2024 [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet sites [/url] tor market
darknet drug links dark web market urls darknet markets url
tor dark web cryptomarkets darknet deep web drug url
onion market tor market url darknet seiten
darkmarket 2024 darknet markets links tor markets
tor marketplace darknet marketplace tor market url
dark web market links dark net blackweb
dark web links darknet websites dark market 2024
tor marketplace darknet seiten dark web market urls
dark web search engines darknet market list deep web drug url
darknet markets dark web market dark websites
dark net darknet markets onion deep web markets
tor dark web darknet market black internet
onion market cryptomarkets darknet darknet site
onion dark website darknet markets links tor darknet
dark web site how to access dark web tor marketplace
tor markets 2024 darknet market links dark markets
deep web drug url blackweb dark web sites links
dark market list darknet drug links bitcoin dark web
deep web links darknet drug store darknet drug links
dark markets darknet markets 2024 darknet websites
tor market links bitcoin dark web dark web site
darknet markets blackweb official website dark web market
dark web websites darknet search engine tor dark web
onion dark website darknet market links darknet markets links
darknet websites darknet marketplace darknet markets onion
tor dark web darknet markets how to get on dark web
darknet market deep web search dark web markets
dark market url darknet drug market the dark internet
dark web drug marketplace dark web search engine dark web drug marketplace
darknet drugs darknet links darkweb marketplace
dark web market list [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet market lists [/url] how to access dark web
darkmarket tor drug market dark websites
dark net dark web market list darknet drug links
tor markets darknet markets url dark web market links
darknet markets onion address deep web search dark web market
darknet market lists deep web drug url dark web links
cryptomarkets darknet drug markets dark web deep web drug url
darknet markets [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]deep web links [/url] dark web links
dark web links darknet markets onion address tor market
dark internet darkweb marketplace darknet site
darkmarket cryptomarkets darknet dark web site
tor markets 2024 free dark web deep web drug store
dark markets 2024 darknet markets links drug markets dark web
tor market url darkmarkets dark web markets
deep web drug markets deep web drug markets darkweb marketplace
dark web links deep web drug url dark web sites
deep web markets deep web markets dark market list
darknet site black internet drug markets onion
darkmarket dark internet blackweb official website
blackweb official website tor dark web onion market
blackweb official website darknet links darknet markets onion address
darknet market darknet seiten darknet markets
drug markets dark web deep web sites darknet sites
dark net bitcoin dark web darknet markets
tor dark web dark web search engine dark market onion
darknet market free dark web dark websites
deep web links darknet markets 2024 darkweb marketplace
tor market url deep web links darknet drug links
darknet links the dark internet dark web drug marketplace
black internet darknet market lists darkmarket link
free dark web dark web drug marketplace deep web links
onion market [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]tor market links [/url] darknet drug market
dark market dark markets dark web sites links
darknet seiten deep web drug store darknet market
dark web sites dark web websites deep web sites
dark web link free dark web dark web search engine
dark web market list tor dark web deep web drug url
dark web sites dark market url darknet market
dark web websites darknet markets 2024 darknet site
how to get on dark web dark web drug marketplace dark web site
darknet drug store [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet markets [/url] darkmarket 2024
darknet sites dark web search engines blackweb official website
tor marketplace darknet links dark web link
dark web search engines tor dark web dark websites
darknet websites best darknet markets best darknet markets
darknet markets 2024 onion market deep web drug links
darknet market list dark markets 2024 darknet markets
tor markets links darknet site dark web search engine
dark market url darkmarkets darkmarket 2024
dark markets 2024 dark web link deep web drug markets
darknet drug links darknet market list darknet drug store
bitcoin dark web deep web drug markets darknet marketplace
darknet drug market tor drug market dark market 2024
tor market url tor market links dark website
free dark web drug markets onion dark market
darkmarket url tor dark web dark web market links
dark market list tor market url dark web search engines
deep web search darknet market darknet site
dark web access blackweb official website tor market url
deep web links darkmarket list bitcoin dark web
tor market url dark market onion deep web drug store
dark web market onion dark website darknet drug market
dark web market urls tor darknet darknet drug store
darknet market lists dark web market bitcoin dark web
dark web market urls darknet markets onion deep dark web
darkmarket 2024 tor markets 2024 dark website
deep web drug store [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark market [/url] drug markets dark web
deep web drug markets dark web websites darknet drugs
dark market onion blackweb official website dark web drug marketplace
tor market links tor market links dark web search engine
dark markets 2024 darknet markets links tor drug market
deep web drug markets tor market url cryptomarkets darknet
dark web marketplaces darkmarket url darknet marketplace
darknet markets onion address dark market darknet magazine
darknet markets 2024 blackweb official website dark web markets
deep web drug markets [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]how to get on dark web [/url] dark web market list
darknet markets onion how to get on dark web tor markets links
drug markets onion dark web sites links tor market url
dark web drug marketplace tor market url dark market 2024
dark internet dark web market urls darknet marketplace
deep web search dark web market list dark market list
darknet site darknet websites darknet market
dark web link darknet drug market darknet marketplace
darkweb marketplace how to get on dark web black internet
black internet black internet dark net
darknet markets url dark web market dark markets
darknet market lists darknet market list darknet drug links
tor market darknet markets onion address dark web sites links
dark web site dark market url dark market 2024
tor markets links blackweb official website darknet markets onion address
dark websites onion dark website how to get on dark web
deep web drug url deep web drug links tor markets 2024
darknet market lists drug markets dark web darkmarkets
dark web link dark web links darknet seiten
dark markets dark markets darknet marketplace
dark markets dark web site deep web sites
dark market 2024 how to access dark web tor market links
darkmarket 2024 tor market darknet market links
free dark web dark web access dark market url
dark market list darknet markets onion darknet drug market
deep web drug markets how to get on dark web deep web drug store
dark market [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web search engine [/url] dark web access
deep web markets deep web drug links free dark web
darknet magazine blackweb official website how to get on dark web
darknet seiten dark web link dark web links
dark websites tor dark web blackweb official website
dark web market drug markets dark web dark web websites
darknet drugs tor dark web dark web access
darknet market links darknet markets onion darknet markets onion
dark web market links dark market deep web sites
free dark web dark web websites drug markets dark web
darkweb marketplace [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]tor market links [/url] dark web sites
cryptomarkets darknet dark web links dark web market
deep web markets dark web market list dark market link
deep web sites dark web market urls deep web markets
deep web markets dark websites dark web websites
how to get on dark web black internet darkmarket url
darknet market darknet market lists bitcoin dark web
deep web drug url dark web market links how to get on dark web
darknet websites the dark internet deep web drug store
dark web marketplaces darkmarket url dark market list
darknet sites drug markets dark web deep web links
blackweb dark web markets dark web websites
dark web access dark internet dark markets 2024
darknet drugs dark web marketplaces best darknet markets
black internet darkmarkets best darknet markets
darkmarket link darknet drugs dark web market list
darknet drug store tor markets links darknet market
dark web market urls darknet links darknet drugs
darknet markets links bitcoin dark web darknet search engine
dark web sites links tor market url onion market
dark web search engine darknet market dark web market urls
tor darknet darkmarkets how to access dark web
tor markets links deep web markets deep web sites
black internet tor markets darknet search engine
tor markets links [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web link [/url] darkmarkets
the dark internet tor dark web dark market list
dark web sites darknet search engine dark market list
tor market links darkweb marketplace tor dark web
deep web sites dark markets dark market 2024
drug markets onion darknet magazine darknet websites
darknet markets links darknet markets dark market link
dark web markets darknet markets 2024 dark market list
darkmarket darkmarket darknet sites
dark web sites links darknet market links darknet marketplace
dark web sites links tor dark web dark web links
dark internet darknet sites tor markets 2024
tor darknet [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web link [/url] deep web drug links
tor market url darknet markets tor market url
the dark internet dark web links free dark web
dark web links dark web market urls dark web links
darknet drug market darknet market links tor market url
dark web market links deep web drug links dark web sites links
darknet drug store dark markets darkmarket url
dark web sites links dark market link dark internet
tor markets 2024 how to get on dark web darknet links
darknet markets url tor market free dark web
dark web market list deep web drug links deep web drug links
drug markets onion dark market list darkmarket 2024
darknet websites darkmarket list dark web sites links
dark web sites blackweb official website deep web search
darknet drug market darkmarket deep web sites
dark market link darknet seiten dark market url
tor dark web dark web market darkmarket link
dark web markets onion dark website darknet site
deep web drug markets darkmarket blackweb official website
deep web search dark website tor markets links
tor darknet dark market 2024 dark web drug marketplace
darknet markets the dark internet dark market
darkmarket url dark markets 2024 dark net
darknet markets url darknet market lists darknet magazine
blackweb official website darknet markets onion address deep web drug url
dark market url tor drug market dark web marketplaces
darkmarket list [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]tor darknet [/url] tor market
drug markets dark web free dark web dark web websites
dark market dark web search engines deep web links
dark website onion dark website darknet markets links
dark market 2024 deep web search darknet search engine
darknet market list darkmarket list cryptomarkets darknet
darknet market links dark web access deep web drug links
dark web websites [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark market list [/url] dark web sites
darkmarket 2024 dark markets dark web marketplaces
tor drug market darkmarket 2024 darknet markets url
darknet search engine darknet drug store dark net
deep web markets deep dark web deep web sites
free dark web bitcoin dark web dark web links
dark web websites dark web sites links dark web sites
onion market deep web drug links dark market url
tor market links darknet drug market black internet
deep web drug url darknet markets darkmarket 2024
dark market link deep web search deep web sites
blackweb cryptomarkets darknet dark market 2024
darknet site darknet drug links dark web sites links
darknet markets onion tor market url tor marketplace
darkmarket darkmarket list darkweb marketplace
darknet market list blackweb official website darknet sites
darknet markets onion dark market onion darkmarket
darknet drugs free dark web cryptomarkets darknet
onion market deep web sites deep dark web
dark market tor marketplace dark net
darknet markets onion address tor markets 2024 dark website
blackweb darknet markets onion deep web search
darknet market black internet dark market 2024
the dark internet darknet market links dark websites
dark web market list deep web links darkmarket
dark web market list [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]deep web links [/url] dark web site
darkmarket 2024 dark web drug marketplace deep web search
tor dark web deep web search how to get on dark web
the dark internet dark web sites links dark web links
darknet market list darknet markets 2024 dark web market links
cryptomarkets darknet dark web drug marketplace onion dark website
darknet market lists drug markets dark web darknet markets links
darkmarkets darknet market list deep web drug markets
dark markets darknet drug store dark web websites
darknet drug store darkmarkets tor markets links
deep web drug links darkmarket list deep web drug store
tor markets links [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]darknet drug market [/url] dark web sites
tor dark web darknet markets darknet markets onion
darknet markets dark web market list darknet websites
deep web search how to get on dark web darknet markets onion address
dark internet dark web link dark web markets
darknet drug links dark web sites tor dark web
onion market dark web websites darknet markets url
blackweb tor market url how to get on dark web
bitcoin dark web tor darknet tor market url
onion market tor markets 2024 deep web drug url
darknet markets 2024 drug markets dark web onion dark website
darknet markets 2024 darknet market dark web sites links
dark market 2024 blackweb deep web drug store
black internet blackweb blackweb
dark market dark web websites deep web drug markets
dark web sites dark net darkmarket
dark market dark web sites links dark net
dark market onion cryptomarkets darknet dark markets 2024
darknet markets links darkmarket url tor markets 2024
dark markets cryptomarkets darknet darknet links
darknet drug links how to get on dark web darknet sites
tor dark web [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web sites links [/url] darkmarket
tor markets links tor markets links darknet drug store
the dark internet onion market onion dark website
free dark web darknet market lists deep web drug markets
deep web drug url tor drug market dark website
the dark internet dark web marketplaces dark web drug marketplace
dark market dark web market urls the dark internet
darknet site dark web market links dark markets 2024
tor drug market darknet market lists darknet markets
dark websites [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]deep web drug markets [/url] dark web marketplaces
darkmarket tor markets 2024 dark web market list
dark website onion dark website dark net
darknet site darknet drug links darknet markets
dark markets darknet site dark websites
dark web search engines tor markets links dark web market
dark web drug marketplace black internet dark web market urls
tor market links deep web drug store dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket list onion dark website dark websites
blackweb darknet markets onion the dark internet
tor market darkmarket link darknet markets
deep web search drug markets dark web onion dark website
darkmarkets dark web search engine darknet market
dark web access darknet markets onion address tor marketplace
bitcoin dark web deep web links darknet markets onion
dark web search engines darkweb marketplace tor markets 2024
dark web marketplaces darknet markets url deep web drug links
black internet drug markets dark web dark market list
dark web market list dark web market blackweb
the dark internet darknet markets onion tor drug market
darkmarket list blackweb official website deep web drug markets
tor market links dark web market dark market list
deep web drug markets [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet magazine [/url] darkmarket list
[url=https://azithromycin.digital/]where can you get azithromycin[/url]
darknet market list dark web link deep web markets
dark web site tor markets how to access dark web
free dark web dark market 2024 dark market onion
drug markets dark web dark markets 2024 darknet drugs
dark market onion bitcoin dark web dark market list
how to access dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark web site [/url] cryptomarkets darknet
deep web drug url darknet magazine darknet markets
dark market tor drug market onion market
bitcoin dark web darkmarket deep web drug markets
dark market list dark market list bitcoin dark web
deep web drug url dark market url dark web drug marketplace
dark web market urls tor markets 2024 darknet websites
dark web site deep web drug store cryptomarkets darknet
tor markets links darknet drug market free dark web
dark markets darknet drug store dark web markets
darknet markets onion address dark web search engines free dark web
dark websites dark market list deep dark web
darkmarket link dark market onion tor market
darknet seiten dark web sites links dark web sites links
tor markets darkmarket url dark web drug marketplace
darknet markets darknet markets 2024 darknet markets 2024
darknet site tor darknet darkmarket url
darknet markets darkmarket link deep web markets
drug markets onion how to access dark web cryptomarkets darknet
darknet websites dark markets darknet market lists
blackweb official website darknet drugs dark web links
darknet seiten darknet markets onion darknet markets
onion dark website dark website darkmarkets
tor dark web [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web market list [/url] dark web marketplaces
darknet market list dark market darkmarket
dark internet bitcoin dark web darknet market lists
dark net [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]how to access dark web [/url] darknet site
dark markets 2024 darknet market lists best darknet markets
onion dark website the dark internet dark web market
dark web links darkmarkets darkmarket url
darknet links darknet links dark market 2024
deep dark web tor drug market drug markets dark web
deep dark web dark web search engines dark market 2024
dark markets 2024 darknet markets onion address tor dark web
tor drug market darknet search engine dark websites
darkmarket dark market 2024 tor dark web
darkmarket 2024 darkmarket best darknet markets
darknet drug store tor markets dark web markets
darknet markets onion address darknet search engine dark web links
dark web market free dark web dark web access
darknet links how to access dark web dark web market urls
the dark internet dark market onion dark internet
onion dark website dark web market urls darknet drug store
tor market links dark web access the dark internet
dark market darknet market dark internet
drug markets dark web darknet websites darknet markets onion
dark web market urls darknet market links free dark web
dark net darknet markets dark web websites
deep dark web darkmarkets dark market link
drug markets onion [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web sites links [/url] darknet markets links
darknet websites deep web drug links black internet
deep web drug url darknet market links darknet market lists
darknet websites darknet site dark market
dark markets 2024 dark internet blackweb official website
deep web drug store dark web search engine dark markets 2024
deep web drug url dark web sites dark web sites
dark web market urls darkweb marketplace darknet drug market
dark web market links [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web search engine [/url] tor market links
darknet site dark web markets dark net
darkmarket 2024 darknet market lists dark websites
darknet market list dark web search engine dark markets
deep web drug store bitcoin dark web darkmarket 2024
the dark internet dark market url tor markets
deep web drug links darknet sites dark market list
blackweb official website dark web market list blackweb official website
dark net darknet marketplace black internet
dark web marketplaces dark web sites links darknet markets onion
dark web marketplaces bitcoin dark web the dark internet
dark web drug marketplace dark web market links the dark internet
darkmarket link dark markets dark markets
deep web links darknet market links darkmarket link
dark website blackweb cryptomarkets darknet
dark market list tor markets links onion dark website
darknet markets 2024 dark web links dark web markets
how to get on dark web darkmarket list darknet seiten
dark markets darknet market list dark market
darknet drug links darkmarket link darknet search engine
the dark internet [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darkmarket list [/url] dark web market links
tor market deep web drug markets blackweb
tor drug market drug markets onion darkweb marketplace
dark web websites bitcoin dark web drug markets dark web
dark web market list deep web drug store darknet markets links
dark web market [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]black internet [/url] dark web search engines
drug markets onion dark market darknet search engine
dark web markets dark website dark web search engines
drug markets onion dark market onion darknet sites
deep web sites dark web search engine tor darknet
deep web sites dark market link tor drug market
dark web market urls dark internet drug markets dark web
the dark internet tor market url darknet magazine
darknet markets links darkmarket list dark web search engines
deep web sites tor dark web drug markets onion
dark website darknet drugs dark web sites
deep web search dark web site darknet drugs
dark web websites dark web drug marketplace darknet markets onion address
black internet tor markets links dark market list
dark markets darknet seiten darknet drug links
dark web link darkmarket dark market 2024
darknet site dark market onion deep web links
deep web links dark internet deep web drug links
darknet links darknet drug store dark web market
darknet markets dark web link tor drug market
dark net [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets [/url] darknet marketplace
darkmarket tor darknet bitcoin dark web
tor markets tor market url dark internet
deep web drug markets drug markets dark web tor market url
dark markets 2024 [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web links [/url] darkmarket 2024
dark market deep web drug store darknet markets
darknet marketplace darknet seiten darknet markets url
the dark internet dark web drug marketplace dark market 2024
dark web drug marketplace darkmarket link onion dark website
darknet markets links how to get on dark web dark web access
dark web websites darkmarket url darkmarkets
cryptomarkets darknet dark market link darknet markets onion
drug markets dark web darknet market dark net
dark web link dark web market how to access dark web
darknet markets 2024 tor markets 2024 darknet market lists
black internet blackweb official website dark web sites links
darkmarket 2024 tor marketplace tor markets links
tor market dark website darknet marketplace
deep web drug links dark market link darkmarket
tor darknet [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]deep web sites [/url] dark website
darknet site the dark internet darknet markets links
deep web drug markets tor markets links tor markets 2024
darkmarkets dark web links dark web search engines
darkmarket link darknet markets url dark web market urls
darknet markets onion address [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]deep web sites [/url] deep dark web
deep web drug url darknet marketplace darknet marketplace
the dark internet dark web market urls tor markets 2024
darkmarket 2024 dark web markets deep dark web
dark web market links dark web link free dark web
darknet markets links how to access dark web darkmarket url
dark market onion dark website darknet market lists
deep web drug store tor darknet deep web markets
dark websites dark market url dark web sites links
dark web marketplaces dark web links dark market url
dark market list dark market 2024 tor dark web
black internet darknet drugs darknet search engine
dark web links darkmarket darkmarket 2024
dark markets onion dark website dark web site
dark web drug marketplace darknet drug store dark web market
darkmarket 2024 dark market link darkmarkets
dark net tor market links dark web drug marketplace
tor marketplace darknet markets links darknet drug store
dark web access dark market dark web market
darknet markets links [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark markets [/url] darknet markets onion
blackweb official website darknet markets darknet market lists
darknet market darknet market list onion market
dark web market links darknet marketplace darknet market lists
tor drug market dark web site the dark internet
cryptomarkets darknet blackweb official website deep web sites
darkmarket [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]tor darknet [/url] dark market onion
deep web search dark web link darknet market links
deep web drug url darknet markets url darknet markets links
onion dark website darkweb marketplace best darknet markets
deep web drug links darkmarket url onion market
dark net darkmarket darknet markets links
blackweb dark market 2024 darknet market lists
onion dark website onion dark website the dark internet
dark web market links bitcoin dark web dark market url
how to access dark web tor markets links deep web drug links
darkmarket dark web market deep web drug store
tor dark web dark web market darknet markets links
dark market onion cryptomarkets darknet dark market url
darkweb marketplace deep web links how to get on dark web
darknet market links [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets onion [/url] tor dark web
deep web drug url black internet dark web market list
darknet links tor market url darkmarket link
black internet dark web market links darknet links
darknet drug store dark web site darkmarket list
best darknet markets best darknet markets darknet market lists
deep web markets [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet markets onion address [/url] dark web access
dark market url dark markets tor markets
dark market list deep web drug links black internet
best darknet markets darkmarket 2024 darknet markets onion address
bitcoin dark web darknet links darknet markets onion address
deep dark web darknet market list the dark internet
darknet marketplace deep dark web onion market
onion dark website onion dark website free dark web
dark market darknet markets 2024 darkmarket list
darknet marketplace dark net dark market link
darknet drug market darkmarkets dark web websites
dark markets darknet markets 2024 tor darknet
darknet market links darknet markets onion address dark web link
dark web markets dark web sites dark web search engines
deep web links darknet marketplace darknet markets 2024
deep web drug markets [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark web link [/url] dark internet
dark web drug marketplace darknet seiten darkmarket list
darknet market links darknet markets url darknet marketplace
dark internet darknet websites tor markets
dark web market links dark market link deep web drug markets
drug markets dark web darknet markets onion address darknet markets onion address
darknet sites darknet markets 2024 dark market url
darknet market list darkmarket link drug markets onion
tor darknet dark web markets free dark web
dark website best darknet markets darknet site
->>>>>>>>>>>>>как приворожить мужчину без последствия в домашних условиях на любовь на месячную кровь<<<<<<<<<-
______________приворот на мужчину читать в домашних условиях на расстоянии без фото на любовь _____________
заговор чтобы девушка отстала
приворот на замужнюю женщину https://privorot4.wordpress.com заговор на возвращение любимого читать белая
бесплатный черный приворот
как снять приворот с сына, а также:
->>>>>>приворот на возвращение мужа
dark web search engine drug markets dark web darknet drug store
dark markets deep dark web tor drug market
tor market url [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]deep web drug store [/url] tor dark web
dark markets 2024 blackweb official website darknet markets 2024
darkmarkets dark net darknet markets 2024
dark net blackweb darknet markets url
tor market deep web drug url darkmarket link
dark market list darknet drugs tor markets links
deep web sites darknet site dark web markets
dark web link deep web search darknet market links
tor market [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]deep web links [/url] deep web drug markets
darknet marketplace dark markets 2024 dark web markets
darknet markets url dark web search engines dark market link
darknet websites tor markets links darknet markets onion address
dark internet darknet links darknet magazine
dark website tor markets links blackweb official website
darknet site dark web link dark web link
dark web site deep dark web dark web sites
deep web markets black internet drug markets onion
dark web websites cryptomarkets darknet free dark web
deep web sites dark market url dark web access
dark web search engines deep web drug links deep web search
black internet darkmarket link bitcoin dark web
how to get on dark web dark web search engines darkmarket url
deep web drug markets darknet market darknet search engine
dark web marketplaces tor market onion market
darkmarkets darknet markets onion drug markets dark web
darknet marketplace dark market list dark web market links
tor drug market dark web sites darknet search engine
dark market url dark market free dark web
->>>>>>>>>>>>>приворот на пепел<<<<<<<<<-
______________приворот на любовника _____________
как влюбить в себя мужчину заговор https://privorot4.wordpress.com
как быстро вернуть мужа домой, а также:
->>>>>>приворот на могиле
->>>>>>сильный заговор вернуть любимого человека
->>>>>>сильный приворот на воду
->>>>>>как приворожить мужчину дома
tor markets links tor markets links darknet marketplace
darknet drug store tor markets 2024 darknet sites
darknet markets darknet marketplace deep dark web
blackweb official website darknet market list darknet markets
dark web sites darknet search engine dark website
dark web sites links darknet markets links deep web drug store
dark web market cryptomarkets darknet tor market url
deep web drug markets darknet markets onion address how to get on dark web
dark market 2024 deep web links tor markets 2024
dark web markets darknet links darkmarket
darknet drug store dark web market deep dark web
darknet magazine tor market url dark web links
tor market links darkmarket dark web access
darknet market darknet drug links tor darknet
tor marketplace deep web markets tor markets links
the dark internet darknet magazine tor market url
darknet market lists darknet drugs darkmarket url
dark net dark market onion how to get on dark web
darknet websites darknet search engine darkmarket url
deep web markets darknet markets 2024 tor markets links
darkweb marketplace darknet markets onion best darknet markets
[url=https://dzen.ru/spravkin]Новые МФО без отказа и проверок[/url] – мы всегда следим за обновлениями на рынке финансовых услуг. У нас вы найдете новые и надежные микрофинансовые организации, которые готовы предоставить вам займы без лишних проверок и отказов.
dark net dark web marketplaces darknet markets onion address
dark web market links darkweb marketplace darkmarket
darknet magazine dark web access tor dark web
tor markets 2024 darknet site how to get on dark web
deep web drug links deep web drug url free dark web
dark web access darknet marketplace darkmarket
dark internet [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darknet markets onion address [/url] drug markets onion
deep web drug markets darknet markets darknet links
dark web market tor market links deep dark web
the dark internet [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]deep web sites [/url] tor markets links
darkmarket url darknet markets onion dark web access
dark web market urls darknet site deep web drug markets
how to get on dark web dark web market links dark web drug marketplace
cryptomarkets darknet darkmarkets dark web sites links
darkmarket dark web search engines tor markets
dark web market list dark web sites darknet markets onion
deep web markets darknet markets links dark web market
darknet search engine drug markets dark web dark market list
dark market url darkmarket 2024 dark web site
dark web market urls dark market link darknet market lists
tor markets 2024 [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]deep web drug markets [/url] dark web search engines
darkmarket 2024 darkweb marketplace dark website
dark web drug marketplace [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web sites [/url] darknet drug market
black internet darknet drug links darknet drug market
darknet drugs dark markets 2024 onion dark website
dark internet darknet markets url dark web sites links
dark web sites links dark web drug marketplace deep web drug store
free dark web dark market onion darknet markets onion address
dark website darknet drug store dark web marketplaces
darknet drug market darknet marketplace dark market onion
dark web sites links [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark markets [/url] darknet markets onion
dark markets bitcoin dark web black internet
drug markets dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]deep dark web [/url] deep web links
darknet links darknet drug links dark markets 2024
darknet market black internet dark websites
dark web search engines deep web links darkmarket
darknet drugs deep web drug links onion market
dark markets 2024 dark web market list deep web search
darknet markets url bitcoin dark web drug markets dark web
dark web search engine [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darkmarket link [/url] darkweb marketplace
blackweb tor markets 2024 how to get on dark web
darknet market lists best darknet markets darknet markets onion address
blackweb official website [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]free dark web [/url] tor market url
dark internet tor market dark website
tor market url dark internet dark web websites
darknet market lists dark web market urls dark market link
dark market 2024 dark web websites free dark web
dark market darknet market lists dark web drug marketplace
onion market dark market list dark web market list
blackweb [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]deep web drug links [/url] darkmarket 2024
deep web drug markets [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark web access [/url] dark web links
tor market links tor market links free dark web
dark web market links darknet websites deep web drug url
darknet websites black internet tor markets links
dark web market dark web link how to access dark web
dark market how to access dark web darknet market links
deep web drug markets darknet markets onion free dark web
deep dark web [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark market url [/url] drug markets dark web
darknet site [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]deep web drug links [/url] darknet market links
deep web drug links darknet market links darknet drug links
darknet markets links blackweb official website darknet sites
dark market list dark web search engines darknet drugs
drug markets dark web [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]deep dark web [/url] darknet drug links
darknet magazine tor markets darknet sites
приворот девушки на любовь читать в домашних условиях по фото приворот мужчину домашних условиях на месячные – https://magic-white.net приворот для золушки читать онлайн
free dark web [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark web drug marketplace [/url] darkmarket url
darknet markets onion dark internet dark web websites
приворот с откатом приворот ритуалы черная магия привороты любовь мужа читать
https://chudotvorstvo.ru
darknet markets links darknet market links dark web sites
dark market url darknet markets onion address darknet drugs
best darknet markets darkmarket url dark web links
чем привязка отличается от приворота приворот на секс по фото
магия приворота на любовь девушки – https://magizmo.ru приворот на жену без последствия сразу действует в домашних
darkmarket url [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]darkmarket link [/url] dark market onion
dark web link [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]deep web drug url [/url] deep web drug store
bitcoin dark web dark web drug marketplace deep web sites
dark web market list dark market url how to access dark web
darknet magazine dark web sites links how to get on dark web
how to get on dark web drug markets onion black internet
darknet search engine dark web access tor markets 2024
black internet [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]tor market url [/url] darknet seiten
tor markets 2024 dark markets dark websites
dark web market urls [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]darknet market list [/url] dark market link
deep dark web darknet markets links darkmarket url
dark market onion best darknet markets dark market link
deep web links darknet drug links darknet magazine
bitcoin dark web darkmarket link black internet
the dark internet [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web site [/url] dark web links
dark web websites [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]black internet [/url] drug markets onion
dark internet how to get on dark web free dark web
dark web markets darkmarket 2024 darknet seiten
deep web drug url deep web search onion market
bitcoin dark web [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darknet markets links [/url] dark web links
how to get on dark web how to get on dark web darknet magazine
darknet markets url tor market url how to get on dark web
how to get on dark web darknet drugs darknet drug links
dark net [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]blackweb [/url] dark web links
darknet markets links darknet site deep web markets
darknet drug store [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web marketplaces [/url] dark web market
dark web sites links darkmarket url darknet magazine
[url=http://rybelsus.us.com/]rybelsus 7 mg tablet[/url]
black internet bitcoin dark web darknet market
the dark internet darkweb marketplace darknet market lists
darkmarket url [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]tor markets 2024 [/url] deep dark web
darknet markets 2024 [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark websites [/url] darknet websites
tor markets deep web markets darknet markets url
deep web markets tor market url dark web marketplaces
darknet search engine darknet links dark internet
darknet seiten [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark market onion [/url] dark market 2024
самостоятельное снятие приворота возможно – https://магиявера.рф
dark market url best darknet markets darknet markets links
darkmarket list [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]deep web sites [/url] darkmarket list
bitcoin dark web dark web search engines dark web site
darkmarket list darknet market dark web market list
darkmarket link darknet markets links best darknet markets
dark web search engines [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]darkmarket [/url] deep web drug markets
darkmarket url [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]cryptomarkets darknet [/url] darknet websites
dark web websites darknet markets 2024 darknet links
darknet drugs dark web sites links darknet markets 2024
onion market blackweb dark web market links
dark web link [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]deep web drug store [/url] darknet markets onion
как в домашних условиях сделать приворот сильный белый приворот
приворот на мужчину без последствия по фото – https://omagi.ru приворот на яйце
dark market link [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark market url [/url] tor drug market
darknet search engine tor dark web darknet markets 2024
drug markets dark web darknet drug links darknet marketplace
dark markets deep web markets dark web marketplaces
dark web market [url=https://darknet-marketspro.com/ ]dark web marketplaces [/url] tor darknet
deep web markets [url=https://alldarkwebmarkets.com/ ]dark market url [/url] dark web marketplaces
darknet magazine darknet market tor market links
tor market links darknet seiten deep web search
приворот на куклу вуду – https://docgid.ru как распознать приворот у мужчины и узнать
darkmarket link darkmarket darknet markets
deep web drug store [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]dark web drug marketplace [/url] dark market 2024
tor markets links [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]dark web search engines [/url] deep web links
Когда мой автомобиль неожиданно вышел из строя, я искал быстрое решение. На mikro-zaim-online.ru я просмотрел все МФО, выбрал подходящее и получил займ под 0.8% в сутки. Процедура была простой и без проверки кредитной истории.
MIKRO-ZAIM – [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/]онлайн займы[/url]
Наши контакты: Зеленодольская улица, 36к2, Москва, 109457
dark web sites links deep web sites blackweb
dark websites tor market links dark market onion
dark web market links deep web drug url onion dark website
bitcoin dark web [url=https://alldarknetmarkets.com/ ]deep web drug markets [/url] tor darknet
tor drug market [url=https://darkweb-storelist.com/ ]blackweb official website [/url] darknet markets url
[url=http://semaglutide.download/]wegovy diabetes medication[/url]
darknet links darknet market dark web search engine
– приворот на высокооплачиваемую работу
– https://приворот-инфо.рф чувствует ли мужчина приворот
– снять приворот это
– чернуха приворот
защита от приворота руны есть ли на мне приворот онлайн гадание бесплатно
молитвы на снятие приворота с мужчины – https://xram58.ru как сделать приворот на парня в домашних условиях без последствия по фото
приворот на фотографиях человек который сделал приворот самые сильные и быстрые вызовы и привороты
https://plachu.net
обряд снятия приворота – https://ольгапратура.рф заговор приворота мужчины
– привороты в домашних условиях отзывы
– https://darknwhite.ru приворот на мужа с 27 читать бесплатно
– привороты, заговоры на любовь в г.кирове и области
– слова приворотные на любовь
– приворот на волос свой в нижнее бельёпривороты nadin krasnoslobodcevaсильный обряд приворот
приворот на девушку как снять приворот на деньги в домашних условиях – астрология синастрия приворот на фотографию
хоррор астрология изучение астрология
астрология расклад
Для тех, кто ищет лучший способ [url=https://denezhnye-perevody-iz-rossii.top/]перевод денег в египет из россии[/url] в 2024 году, denezhnye-perevody-iz-rossii.top является идеальным выбором. Мы предоставляем широкий спектр опций для перевода средств, включая новейшие финтех решения. Наша цель – сделать процесс как можно более простым и доступным для каждого, кто отправляет деньги в Австралию.
приворот по вуду действует с первого дня срочный гарантированный приворот привороты это плохо
https://yourspells.ru
привороты во время беременности
сонливость у заказчика приворота
у всех ли получается приворот
===============================================================================
приворот на фото на расстоянии читать
поведение мужчины после приворота приворот на бумаге читать на парня в домашних
на какую фазу луны делать приворот – https://na-lazarevskom.ru все привороты
======================
что происходит с заказчиком после снятия приворота – https://molotokrus.ru как вернуть жену приворот читать
энтропия в социологии – энтропия юниверс игра.
геометрическая энтропия – https://privorot-vsem.ru энтропия экономики.
шифрование энтропия
биологической энтропии
энтропия пентана
мусульманская порча ритуал и привороты – https://artgrom.com порча-заморочки.
отзывы у кого была порча
чёрная магия порча отзывы людей
собачий череп волосы человеческие на дороге магия колдовство порча
гк порча имущества
снятие приворота с человека = https://magicwishes.ru приворот штоб дети вернулись к отцу
снять приворот самому черные приворот в санкт петербурге
– приворот на месячную кровь в бокале
– https://morfeos.ru приворот настя киев
приворот парня со свечой приворот под новый год
результат приворот форум снять приворот гипнозом
приворот чтоб парень сох приворот на любовь девушки по волосам
flagyl suolisto
приворот на лавровом листе приворот с оплатой по результату – астрология карикатура очень быстрый приворот
ватикан астрология астрология бадзы.
астрология трансформации. астрология бадзы астрология профориентация.
приворотное зелье из крапивы
привороты белой магии на яблоке .
чёрные сильные любовные привороты снять приворот самостоятельно с помощью молитва
сильный приворот на любовь и верность – https://morfeos.ru признаки наведенного приворота .
старые кладбищенские привороты приворот невернои жены.
===============================================================================
как узнать есть ли на человеке приворот в домашних условиях
приворот на 3 церкви.
приворот от измен снять приворот в церкви.
приворот на воск – https://duhmaga.ru как сделать приворот на любовь девушки читать.
порча приворот
сколько раз можно делать приворот на парня
======================
приворот сильный и быстрый – https://shmk.ru языческие привороты.
как действует белый приворот
приворот на мужчину чтобы вернулся
как отчитать человека от приворота
– приворот на парня соль на сковородке – приворот на рождение ребенка.
– https://privorot-zagovori.ru эротика приворотное зелье фильм
-приворот.присуха снятие сильного приворота в церкви.форум бабушка сняла приворот.
-приворот помощью мака приворот на восковое сердце.привороты белой магии.
-скачать книгу приворотное зелье привороты заговоры действующие
как самой снять приворот с мужа что будет если сделать приворот на любовь парня последствия – анастасия астрология приворот на любовь мужа к жене
совместимости астрология руна астрологии.
значение астрологии. значение астрологии
стрижки астрология.
[url=https://музейкупец.рф]1xbet вход[/url]– это популярная букмекерская контора, предоставляющая широкий выбор ставок на спорт и казино. Сайт обладает удобным интерфейсом, мобильной версией и приложением для удобства пользователей. 1xBet также известен разнообразными акциями и бонусами, делая игровой опыт более захватывающим.
можно ли делать приворот на убывающую луну привороты на ивана купала.
легкий приворот без последствия в домашних условиях на мужчину приворот на парня без последствия в домашних условиях днем.
приворот мужчины на растущую луну – https://sueveriya.com привороты на любовь мужчины читать в домашних условиях на расстоянии на фото.
приворот егильет читать как снять заговор на приворот с любимого человека самостоятельно приворот на любовь парня читать в домашних условиях сильный
приворот по фото скачать бесплатно. приворот утечка энергии признаки самоприворота
https://artgrom.com .
////черная пантера привороты приворот самостоятельно сатанизм.
////приворот на моче любимого.
////провереные ритуалы на деньги привороты
[url=https://rybelsus.pics/]ozempic pill form[/url]
привороты на мужчину без последствия белая магия слов овер – https://shmk.ru приворот на крови месячных как снять.
сильный приворот на любовь. как сделать приворот на мужчину в домашних условиях читать бесплатно рецепт на любовь
как сделать приворот на мужчину в домашних условиях читать бесплатно приворот на женщине симптомы
как сделать любовный приворот на девушку читать в домашних условиях.
– чтобы муж думал только обо мне привороты на – чем опасен рунический приворот.
– https://mimiledi.ru самый сильный рунический приворот
-снять приворот с мужчины cfvjcnjzntkmyj приворот чтобы взяли замуж.приворот по цветочной луковицей.
-сильный приворот по фотографии, его действия приворот по фотографии самостоятельно в домашних условиях бесплатно.черная магия отсуха приворот заклинания.
-приворот это беда что такое приворот и как его делают в книге судьбы
приворот на волосы мужчины сколько действует приворот на женщину – https://kak.pedagogik-a.ru сильные привороты на любовь мужчины читать в домашних условиях
программа астрология астрология вакансии.
квантовая астрология. эзотерика астрология
акубенс астрология.
приворот чертогрыз форум. привороты моей бабушки приворот на кодированного мужчину.
https://masterveda.ru .
рпц – о приворотах приворот на удачу и дружбу бесплатно.
как снять любовный приворот с мужчины молитвой дома приворот на женатого мужчину без последствия сразу действует на расстоянии.
какие бывают привороты и их последствия когда начинает действовать приворот и как понять его.
вернуть любимую приворот – https://duhidolmenov.ru как понять что на муже приворот от другой женщины.
рунический став приворот приворот на красную свечу читать любовный приворот на девушку в домашних условиях
приворот на мужчину на расстоянии без фото – https://turk-sinema.ru приворот на парня белая магия.
снять приворот солью. приворот на чувства
как сделать приворот на женатого мужчину в домашних условиях читать без последствия белая магия приворот на парня по фото на телефоне в домашних условиях
через сколько начинает действовать приворот на месячные.
любовница сделала приворот на мужа приворот на красную нить читать в домашних на мужчину на расстоянии – https://slovomaga.ru реальны ли привороты
гадание астрология астрология исследования.
джабхат астрология. астрология трансформации
камни астрология.
Доброго!
Дезинфекция и Дератизация Участков в Москве и Московской Области: Эффективная Защита от Вредителей
Живя в Москве и Московской области, владельцы приусадебных участков сталкиваются с проблемой вредителей, которые могут повлиять на комфорт и безопасность жизни. Профессиональная обработка территории от насекомых и грызунов становится ключевым шагом для обеспечения здоровья и сохранности имущества
Применение современных методов и безопасных средств обеспечивает высокую эффективность процесса, минимизируя риски для здоровья человека и домашних животных.
Профессиональные службы предлагают комплексную обработку, включая дезинсекцию и дератизацию, учитывая все возможные источники вредителей на участке.
Вот сайт профессионалов дезинсекции: https://dezinfekciya-mcd.ru
[url=https://dezinfekciya-mcd.ru/unichtozhenie/unichtozhenie-os-i-shershnej/]уничтожение ос[/url]
[url=https://dezinfekciya-mcd.ru/tarakan/]обработка от тараканов в квартире[/url]
[url=https://dezinfekciya-mcd.ru/unichtozhenie/klopov/]дезинфекция от клопов[/url]
Применение высококачественных средств обеспечивает долгосрочный эффект, что означает продолжительную защиту от насекомых и грызунов.
Использование профессиональных инсектицидов и репеллентов, которые обеспечивают эффективное уничтожение вредителей.
Удачи!
вывести клопов из квартиры
уничтожение насекомых
обработка участка от комаров и клещей
дезинфекция от крыс
дезинсекция от блох
тоска-приворот. приворотные заговоры на вине рабочий приворот мужчины.
https://zserials.ru .
приворот с помощью куклы отзиви уберечься от приворота.
приворот мужа на кладбище молитва о снятии приворота с любимого человека.
приворот на мужчину без атрибутов . приворот на церковные свечи читать 1 день , самый сильный приворот самостоятельно.
как снять приворот на волосы – https://magi-pravda.ru чем опасен приворот и его последствия.
вернуть любимую девушку с помощью приворота по фотографии приворот на лавровом листе обряд на возврат любимого без приворота
сильный приворот на женатого мужчину который нельзя снять в домашних условиях – https://themaykl.ru можно ли делать приворот в месячные.
приворот сильный и быстрый на словах. приворот мужчины к женщине
приворот на женщину в полнолуние приворот самой
приворот на месячную.
Discover the Ultimate Adult Comic Experience at Erotoons.net! Our platform is dedicated to bringing you the finest selection of adult comics from around the globe. Each comic is a unique blend of captivating storylines and exquisite art, designed to enthral and entertain an adult audience. With our constantly updated collection, you’ll always find something that resonates with your tastes. Step into the world of Erotoons.net and transform your ordinary evenings into extraordinary adventures.
If it’s a mix of excitement and artistry you’re after, our [url=https://erotoons.net/category/all-porn-comics/the-loud-house/]loud house porn comics[/url] at Erotoons.net will not disappoint. Dive into a world of wonder and sensuality.
скарлатина уход за ребенком – https://xigra.ru
презентация уход за новорожденным ребенком – https://ladytoday.ru ->>>>>>>>> стаж при уходе за ребенком !
У меня дома живет моя дорогая собака, и ей внезапно потребовалась операция. Чтобы не медлить, я воспользовался услугами [url=https://postabank.ru/]сайта[/url], где нашел подходящее МФО и получил срочный займ.
порча на фото читать в домашних условиях камни от сглаза и порчи если яйцо разбить в воду и оставить на ночь что будет
[url=https://mr-sports.ru/]казино онлайн[/url]– это популярная букмекерская контора, предоставляющая широкий выбор ставок на спорт и казино. Сайт обладает удобным интерфейсом, мобильной версией и приложением для удобства пользователей. 1xBet также известен разнообразными акциями и бонусами, делая игровой опыт более захватывающим.
отзывы о привороте на менструальную кровь – фильм черный приворот отзывы – отзывы о привороте кладбищенском
Привет всем!
Хочу поделится полезной информацией, приходилось обращаться в данную компанию за дератизацией в Москве, все прошло отлично!
Дезинфекция и дератизация в Москве: Эффективная Защита от Вредителей
В условиях городской среды, в том числе в Москве, вопрос обработки от вредителей становится особенно актуальным. Санитарно-эпидемиологическая служба (СЭС) в Москве предоставляет специализированные услуги по дезинфекции и дератизации, обеспечивая эффективную борьбу с насекомыми и грызунами.
Профессиональная дезинфекция:
Процесс дезинфекции представляет собой комплекс мероприятий, направленных на уничтожение насекомых, бактерий и других вредных организмов в помещениях. СЭС в Москве осуществляет профессиональную дезинфекцию, используя эффективные методы и современные средства, обеспечивая безопасность для жильцов и окружающей среды.
Вот сайт профессионалов дезинсекции: https://dezinfekciya-mcd.ru
[url=https://dezinfekciya-mcd.ru/unichtozhenie/blohi/]дезинсекция блох[/url]
[url=https://dezinfekciya-mcd.ru/unichtozhenie/plesen/]избавиться от плесени[/url]
[url=https://dezinfekciya-mcd.ru/tarakan/]обработка от тараканов[/url]
Дератизация и борьба с грызунами:
Специалисты СЭС проводят дератизацию для уничтожения грызунов, таких как мыши и крысы. Это важный этап в обеспечении здоровья и безопасности, особенно в городской среде, где эти вредители могут стать источниками различных заболеваний.
Удачи!
обработка от клеща
дезинсекция в москве
обработка от моли
обработка от клопов
дезинсекция помещений
digiapk.com
상인들이 물고기를 팔아 많은 돈을 벌고 있는 것을 보고, 어찌 서둘러서 장사를 하지 않을 수 있겠습니까?
ремонт мягкой мебели в минске [url=https://peretyazhka-mebeli-minsk.ru/]https://peretyazhka-mebeli-minsk.ru/[/url].
приворот черное венчание кто может сделать через сколько действует приворот – эффект астрология приворот через зеркало
сила астрологии карака астрологии.
бетельгейзе астрология. числа астрологии
склонения астрология.
приворот кладбищенский кто вернуть жену приворотом.
приворот на красную ленту читать . какой самый сильный приворот , приворот на парня у которого есть девушка.
приворот степановой – https://magiya-vedovstvo.ru приворот на мужчину самостоятельно читать.
приворот на фото с красной нитью кто делал приворот на мужчину без последствия в домашних условиях на месячные приворот на безымянный крест
приворот на суженого с березой на троицу. сделать приворот в онлайне бесплатно привороты на сигаретах.
https://magprivorot.ru .
сколько по времени действует рунический приворот приворот с волосами с лобкина.
– сильные привороты на парня в домашних условиях – привороты заговоры от пьянства.
– https://gigabaza.ru приворот парня в домашних условиях отзывы
-признаки приворота сглаза хороший сильный приворот самостоятельно.приворот на любовь для гея.
-черный сильный приворот для мужчин приворотный практикум елена звездная.приворот по сигарете царь дым дымок.
-самый сильный приворот в лесу приворот тернопыль
Предлагаем купить диплом магистра с возможностью проверки на [URL=http://diplom-sale.ru]http://diplom-sale.ru[/URL] , подлинность гарантируем. Получите диплом бакалавра онлайн!
обивка мебели [url=https://peretyazhka-mebeli-minsk.ru/]https://peretyazhka-mebeli-minsk.ru/[/url].
приворот на женщину без последствия сразу действует – https://zagrevo.ru белый приворот без последствия.
приворот на мужчину на любовь без последствия в домашних. приворот на мужчину без последствия сразу действует в домашних на имя на расстоянии
поможет ли сорокоуст от приворота приворот на мужчину без последствия в домашних условиях по фото в телефоне в домашних условиях
через какое время срабатывает приворот.
последствия приворотов – https://www.blackpantera.ru как проверить приворот есть ли.
как действует приворот на женщину последствия. черные привороты на узлы
сильный приворот по фото в домашних приворот на любовь мужчины читать
снять приворот с солью.
приворот и его последствия молитва приворот на мужчину без последствия сразу.
приворот на мужчину на расстоянии читать с солью в домашних условиях приворот на мужчину без последствия на волосы.
приворот на мужчину читать на воду – https://pitfiz.ru навести приворот.
симптомы приворота приворот на свечах в домашних условиях что будет с заказчиком после снятия приворота с жертвы
ремонт и перетяжка мебели [url=https://peretyazhka-mebeli-minsk.ru/]https://peretyazhka-mebeli-minsk.ru/[/url].
Обратившись к нашей компании, вы гарантируете себе получение профессиональных юридических консультаций от квалифицированных юристов. Узнайте больше на нашем сайте по ссылке
[url=https://kioski.by/blog/pomoshh-yurista/metody-rascheta-alimentov-iz-zarabotnoj-platy-v-2024-godu-novye-podhody.html]минимальная сумма алиментов на двух детей[/url].
[url=http://wegovy.directory/]semaglutide medicine[/url]
Can I just say what a relief to find a person that really understands what they are talking about on the internet.
You definitely know how to bring an issue to light and make
it important. More and more people have to read this and understand this side
of the story. I can’t believe you’re not more popular since you certainly possess the gift.
wonderful points altogether, you simply won a emblem new reader.
What could you recommend about your submit that you simply made a
few days in the past? Any certain?
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know a lot about this, like you
wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with some pics to drive the message
home a little bit, but instead of that, this is magnificent blog.
A great read. I will definitely be back.
Hi there, everything is going well here and ofcourse every one is sharing information, that’s really fine, keep up writing.
рецепты приворотов на любовь https://www.magecam.ru приворот через пентакль
Не могу не поделиться своим восторгом от [url=https://h-100.ru/collection/sokovyzhimalki-dlya-granata]гранатовой соковыжималки[/url] от “Все соки”. Это устройство стало настоящим спасением для меня в пути к здоровому питанию. Свежий сок каждое утро – это залог хорошего настроения на весь день!
homefronttoheartland.com
Shen Wen의 말은 칼처럼 Hongzhi 황제의 마음을 찔렀습니다!
Доброго!
Меня зовут Вика)
Учусь в универе на 4 курсе, время дипломных подготовок, курсовых и рефератов, но Я девушка и у меня другие интересы….
Пришло время расплаты, и меня чуть не отчислили, хорошо подруга сказала что оказывается можно купить диплом или курсовую, конечно Вы не получите твердую 5, но 4 или 3 точно, пройдете дальше по учебе что и необходимо)
Вот сайт компании, дипломы на заказ для любых вузов под ключ: http://dodip.ru/
[url=http://dodip.ru/]купить морской диплом[/url]
[url=http://dodip.ru/]купить диплом в мичуринске[/url]
[url=http://dodip.ru/]купить диплом инженера по охране труда[/url]
Кстати у конкурентов сразу просили предоплату, каике-то там условия это пугает, тут ничего такого нет, все после результата, спасибо им большое!
Если Вы хотите купить диплом Гознак онлайн с доставкой оригинала в любую точку России, Вам к этим ребятам.
Удачи и хороших оценок!
купить диплом в белгороде
купить диплом штукатура
купить диплом в рязани
купить аттестат за 9 класс
купить диплом в старом осколе
купить диплом в муроме
купить диплом сварщика
купить диплом в биробиджане
[url=http://rybelsus.company/]rybelsus where to buy[/url]
Обратившись к нашей компании, вы обеспечите себе доступ к профессиональных юридических консультаций от опытных специалистов. Узнайте больше на нашем сайте по ссылке
[url=https://kioski.by/blog/pomoshh-yurista/pravila-i-usloviya-obshhej-dolevoj-sobstvennosti-vazhnaya-informatsiya-dlya-sobstvennikov.html]общей собственностью является[/url].
Здравствуйте!
Меня зовут Вика)
Учусь в универе на 4 курсе, время дипломных подготовок, курсовых и рефератов, но Я девушка и у меня другие интересы….
Пришло время расплаты, и меня чуть не отчислили, хорошо подруга сказала что оказывается можно купить диплом или курсовую, конечно Вы не получите твердую 5, но 4 или 3 точно, пройдете дальше по учебе что и необходимо)
Вот сайт компании, дипломы на заказ для любых вузов под ключ: http://dodip.ru/
[url=http://dodip.ru/]купить диплом в череповце[/url]
[url=http://dodip.ru/]купить диплом в мичуринске[/url]
[url=http://dodip.ru/]купить диплом бухгалтера[/url]
Кстати у конкурентов сразу просили предоплату, каике-то там условия это пугает, тут ничего такого нет, все после результата, спасибо им большое!
Если Вы хотите купить диплом Гознак онлайн с доставкой оригинала в любую точку России, Вам к этим ребятам.
Удачи и хороших оценок!
купить диплом в обнинске
купить диплом во владивостоке
купить диплом инженера механика
купить диплом колледжа
купить диплом в березниках
купить диплом в сургуте
купить диплом фармацевта
купить диплом физика
[url=http://ozempic.monster/]buy wegovy in canada[/url]
Greetings, Earth!
I am a Capybara, a small creature cherished for its endearing appearance and charming qualities!
Curious about my recent endeavors? I’ve decided to swap the jungle for the bustling city life.
Currently residing in the Netherlands, I’ve found a companion in the virtual realm!
Meet Xrumer, a software product, and its invaluable sidekick, Xevil. Together, we collaborate on ambitious projects that extend promotional messages to everyone in our database.
Our impact spans the globe, disseminating information about new projects, materials, and the lives of capybaras, both in the wild and in zoos – a truly significant endeavor!
Leveraging Xrumer for posting allows us to reach a vast audience, creating a robust link profile. We specialize in constructing site networks, establishing link levels, and enhancing domains for cohesion – a testament to the camaraderie of the capybara herd + Xrumer + Xevil!
If you’ve received a message from our team, why not consider availing our posting services? We’re open for business, friends, and eagerly await your tasks!
The Capybara herd tirelessly works around the clock to fulfill advertising tasks for leading SEO companies. We’re grateful for the opportunity, whether it’s to buy food or secure funds for our lives.
Curious about how people find us online? Here’s a glimpse of what we do:
https://capybara333.wordpress.com/
Xrumer mailing
Xrumer run
Xrumer posting
Xrumer website promotion
Xrumer site run
PBN site network boosting
Xrumer profile run, and much more!
And now, the English version!
Привет, мир!
Я Капибара, небольшое существо, которое полюбили за свою внешность и характерные черты!
Хотите узнать, чем я занимаюсь последнее время? Решил переместиться из джунглей в большой город.
В настоящее время я живу в Нидерландах и подружился с хорошим виртуальным спутником!
Его зовут программный продукт Xrumer, а его незаменимый компаньон — Xevil. Мы работаем вместе, создавая грандиозные проекты, позволяя каждому в нашей базе получать рекламные сообщения.
Информация распространяется по всему миру; люди узнают о новых проектах, материалах, жизни капибар в суровой дикой природе и зоопарках – это действительно важно!
Постинг с использованием Xrumer позволяет охватить огромную аудиторию и создать мощный ссылочный профиль. Мы строим сети сайтов, уровни ссылок, улучшаем домены для их склейки – всё это часть дружбы стада Капибар + Xrumer + Xevil!
Вы получили сообщение от нашей команды, и что мешает вам заказать постинг и наши услуги? Мы открыты для сотрудничества, друзья, и ждем ваших задач!
Стадо Капибар работает круглосуточно на благо рекламных задач ведущих SEO-компаний и очень благодарно за возможность купить еду или получить средства на жизнь.
Как нас ищут в сети, или, скорее, что мы делаем:
рассылка Хрумером
прогон Хрумером
постинг Хрумером
раскрутка сайта Хрумером
прогон сайта Хрумером
прокачка PNB сеток сайтов
прогон по профилям Хрумером и многое другое!
Удачи!!!
[url=https://wegovy.click/]semaglutide tablets[/url]
doeaccforum.com
Hongzhi 황제는 자세히 살펴보고 차 한 모금을 뿌릴 것입니다.
The other day, while I was at work, my sister stole my iPad and tested to see if
it can survive a 25 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple
ipad is now destroyed and she has 83 views.
I know this is entirely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
You are so cool! I do not suppose I’ve read through something like this before.
So good to discover someone with some unique thoughts on this subject matter.
Really.. thank you for starting this up. This site is something that is required on the
web, someone with some originality!
[url=https://test3semrush.net/]тест 3[/url].
This piece of writing will help the internet visitors for creating new
blog or even a weblog from start to end.
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all of
us you actually understand what you’re speaking about!
Bookmarked. Kindly additionally discuss with my website =).
We can have a link change contract between us
agonaga.com
홍지황제는 “사실 궁금하다”고 말했다.
Hello!
Have you ever heard of X-GPT Writer: a unique keyword content generator based on the ChatGPT neural network?
I also haven’t, until I was advised to automate routine tasks with this software, I want to say one thing! Then I couldn’t believe
for a long time that ChatGPT is such a powerful product if it is used simultaneously in streaming, under the control of X-GPT Writer.
I thought it was just a utility, it was inexpensive, a friend gave a coupon for a 40% discount%:
94EB516BCF484B27
details of where to enter it are indicated on the website:
https://www.xtranslator.ru/x-gpt-writer/
I started trying, delving into it, bought 50 ChatGPT accounts at low prices and it started!
Now I easily generate and launch 3-4 new sites a week, batch unify entire folders and even create images
using the ChatGPT neural network and X-GPT Writer.
It’s worth a try, Friends, there’s a demo, everything is free, you won’t regret it)
Good luck!
автоматическое создание текстов через ChatGPT
Генератор синонимов с ChatGPT
Где найти промо коды на X-GPTWriter
Секреты создания контента с ChatGPT
Как ChatGPT помогает в создании уникального текста
ChatGPT и создание качественного контента
X-GPTWriter: мощный инструмент для контент-креации
Синонимизация текста с X-GPTWriter и ChatGPT
Автоматизированное создание текстов с помощью ChatGPT
ChatGPT и X-GPTWriter для уникальных текстов
Заключение образовательного документа обÑзательно Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð·Ð°Ð½ÑтоÑти на поÑÑ‚. Иногда ÑлучаютÑÑ Ñитуации, когда диплом, полученный ранее не подходит Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð²Ñ‹Ð±Ñ€Ð°Ð½Ð½Ð¾Ð¹ трудовой Ñферы. Покупка образовательного документа в МоÑкве решит Ñту проблему и предоÑтавит процветание в будущем – [URL=https://kupit-diplom1.com/]https://kupit-diplom1.com/[/URL]. СущеÑтвует множеÑтво факторов, Ñтимулирующих закупку диплома в МоÑкве. ПоÑле неÑкольких лет работы внезапно может понадобитьÑÑ Ð´Ð¸Ð¿Ð»Ð¾Ð¼ универÑитета. Работодатель вправе менÑÑ‚ÑŒ Ñ‚Ñ€ÐµÐ±Ð¾Ð²Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ñ Ðº перÑоналу и принудить Ð²Ð°Ñ Ñделать выбор – диплом или увольнение. Очное обучение занимает много времени и Ñнергии, а обучение на заочной форме — потребует ÑредÑтва Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð¿Ñ€Ð¾Ð²ÐµÐ´ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ñкзаменов. Ð’ подобных обÑтоÑтельÑтвах более разумно купить готовую копию. ЕÑли вы уже знакомы Ñ Ð¾ÑобенноÑÑ‚Ñми будущей профеÑÑии и научилиÑÑŒ необходимым навыкам, нет необходимоÑти тратить годы на обучение в ВУЗе. ПлюÑÑ‹ Ð¿Ñ€Ð¸Ð¾Ð±Ñ€ÐµÑ‚ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ð´Ð¸Ð¿Ð»Ð¾Ð¼Ð° воÑпринимают мгновенное изготовление, полное Ñовпадение Ñ Ð¾Ñ€Ð¸Ð³Ð¸Ð½Ð°Ð»Ð¾Ð¼, доÑтупную цену, гарантированное трудоуÑтройÑтво, ÑамоÑтоÑтельный выбор оценок и удобную доÑтавку. Ðаша Ð¾Ñ€Ð³Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ð·Ð°Ñ†Ð¸Ñ Ð¿Ñ€ÐµÐ´Ð»Ð°Ð³Ð°ÐµÑ‚ возможноÑÑ‚ÑŒ каждому клиенту получить желаемую работу. Цена Ð¸Ð·Ð³Ð¾Ñ‚Ð¾Ð²Ð»ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ ÑвидетельÑтв приемлема, что делает доÑтупным Ñтот вид уÑлуг Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð²Ñех.
Привет Всем!
Хотел сказать что постинг Хрумером реально работает, применяется
и имеет место быть, если рассматривать экономическую составляющую,
это в сотни раз выгоднее покупки ссылок, постов и др,
так же прогон Хрумером идет реальным образом,
Вас не размещают на каких-то самоподнятых сетках что будут забанены или закрыты,
совершенно разные сайты, домены, IP и локации, все как нужно!
Наша компания делала здесь:
https://progonxrumerom.wordpress.com/
Xrumer рассылка это отличный инструмент для SEO, дорвейщиков лого уровня, СМИ,
веб мастеров и тех кто имеет цель донести до других свою информацию.
Удачного развиия)
рассылка Хрумером
прогон Хрумером
постинг Хрумером
раскрутка сайта Хрумером
прогон сайта Хрумером
прокачка PNB сеток сайтов
прогон по профилям Хрумером и многое другое!
Перетяжка мягкой мебели: обновите дом в деньгах
перетяжка минск [url=https://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]https://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/[/url] .
[url=https://wegovy.top/]rybelsus where to buy[/url]
приворот черная магия сайт – Обратится к магу – https://dzen.ru/id/653538d7d6100f7a6fee8469
сильный черный приворот на мужчину
Перетяжка мягкой мебели: советы от профессионалов
реставрация мебели в минске [url=https://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]https://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/[/url] .
Hello!
I’m Dina, I’m 35, beautiful and sweet, I want to tell you about my discovery)
I used to have a negative view of many things, often worried about the environment, people, politics, and it began to have a bad effect on my health and quality of life in general.
The psychologist advised me to laugh more, and not to study what I can’t change, what’s the point!
I began to regularly read jokes and sites with humor, and after 2 months I became a different person, calmer and kinder, things went to the mountains and people want to be in my company more, there is no end of men.
I advise everyone who likes jokes, this site
https://www.anekdotor.ru/anekdoty-pro-skleroz-zabyvchivost-plohuju-pamjat/
Everything is simple and about the case, read, laugh and be healthy!
Good luck friends)
Hello everybody!
I’m Masha, I’m 32, I live in England, I raise 2 children who go to school)
School is quite a lot of stress, both for children and for parents, and constant lessons and preparation for tests in specialized subjects drove Me crazy (
I became nervous, stopped sleeping with my husband and a nervous tic began, it was terrible…
It’s good that my friends advised me to find sites with solutions, and try to do homework according to their methodology.
By the way, a good website
https://www.controlworks.ru/kontrolnaja-rabota-nomer-10-klass/
There are no ads, convenient search and a lot of valuable information about test papers!
To be honest, I began to sleep peacefully, sex and peace in the family were restored, thanks to such sites where you can find solutions and devote more time to your favorite things!
Good luck!
[url=http://semaglutide.click/]wegovy tablets for weight loss cost[/url]
Hello everybody!
I want to share a real experience, with age my sex power began to decrease, and eventually came to a deplorable level (
Even the most beautiful and young girls did not excite the right level of energy in me…
It was terrible and depression began when a friend told me that you need to read jokes and laugh every day, and everything will gradually get better.
Recommended this site to me
https://www.kompotanekdot.ru/anekdot-pro-apelsiny/
I thought what nonsense, but there was nothing to do, and I began to laugh systematically and read everything about humor!
I didn’t believe it, but after 2 weeks, my potency became normal, and I was able to return to the love spaces and walk with models!
Thanks to the laughter and jokes, and be healthy)
I’m already 87 years old, but I’m still strong in bed)
Isso pode ser irritante quando seus relacionamentos são interrompidos e o telefone dela não pode ser rastreado. Agora você pode realizar essa atividade facilmente com a ajuda de um aplicativo espião. Esses aplicativos de monitoramento são muito eficazes e confiáveis e podem determinar se sua esposa está te traindo.
Discover the top money-making games in Kenya
online casino games that pay real money [url=https://realmoneygameskenya.com/]online casino games that pay real money[/url] .
Если вы не знаете где недорого и безопасно купить диплом, то обратитесь к нам на сайт [URL=https://diplomguru.com]https://diplomguru.com[/URL]. Мы гарантируем качество и доставку от производителя.
chasemusik.com
예연은 갑자기 억울하게 울기 시작했고, 한동안 야멘홀 안팎에서 신이 났습니다.
digiapk.com
그러나 Liu Jian은 오히려 비웃고 떠나기를 거부했습니다.
certainly like your website but you need to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to inform the reality nevertheless I will definitely come back again
[url=http://ozempic.guru/]brand ozempic[/url]
Monitore o celular de qualquer lugar e veja o que está acontecendo no telefone de destino. Você será capaz de monitorar e armazenar registros de chamadas, mensagens, atividades sociais, imagens, vídeos, whatsapp e muito mais. Monitoramento em tempo real de telefones, nenhum conhecimento técnico é necessário, nenhuma raiz é necessária.
Hello!
Have you ever heard of X-GPT Writer: a unique keyword content generator based on the ChatGPT neural network?
I also haven’t, until I was advised to automate routine tasks with this software, I want to say one thing! For a long time afterwards, I couldn’t believe
that ChatGPT was such a powerful product if it was used simultaneously in streaming, running X-GPT Writer.
I thought it was just a utility, it was inexpensive, a friend gave me a coupon for a 40% discount%:
94EB516BCF484B27
the details of where to enter it are indicated on the website:
https://www.xtranslator.ru/x-gpt-writer/
I started trying, delving into it, bought 50 ChatGPT accounts at low prices and off I went!
Now I easily generate and launch 3-4 new sites per week, batch unify entire folders and even create images
using the ChatGPT neural network and X-GPT Writer.
It’s worth a try, Friends, there’s a demo, everything is free, you won’t regret it)
Good luck!
автоматическое создание текстов через ChatGPT
синонимайзер текста на базе ChatGPT
Секреты создания контента с ChatGPT
X-GPTWriter: лучший софт для создания текстов
ChatGPT как генератор уникального контента
ChatGPT в качестве синонимайзера текста
Уникальные тексты с ChatGPT и X-GPTWriter
ChatGPT и его роль в создании уникального контента
X-GPTWriter купоны на скидку
Легкий способ создавать контент с X-GPTWriter
Желаете получить диплом без промедления и без заморочек? В Москве имеется обилие вариантов приобрести аттестат о высшем образовании – [URL=https://diplom4.me/]diplom4.me[/URL]. Профессиональные агентства предлагают услуги по приобретению документов от различных учебных заведений. Обращайтесь к непреложным поставщикам и получите свой диплом сегодня!
Hello!
Have you ever heard of X-GPT Writer: a unique keyword content generator based on the ChatGPT neural network?
I also haven’t, until I was advised to automate routine tasks with this software, I want to say one thing! For a long time afterwards, I couldn’t believe
that ChatGPT was such a powerful product if it was used simultaneously in streaming, running X-GPT Writer.
I thought it was just a utility, it was inexpensive, a friend gave me a coupon for a 40% discount%:
94EB516BCF484B27
the details of where to enter it are indicated on the website:
https://www.xtranslator.ru/x-gpt-writer/
I started trying, delving into it, bought 50 ChatGPT accounts at low prices and off I went!
Now I easily generate and launch 3-4 new sites per week, batch unify entire folders and even create images
using the ChatGPT neural network and X-GPT Writer.
It’s worth a try, Friends, there’s a demo, everything is free, you won’t regret it)
Good luck!
X-GPTWriter: лучший софт для создания текстов
X-GPTWriter: купоны и акции на скидки
автоматическое создание текстов через ChatGPT
X-GPTWriter купить со скидкой
ChatGPT в качестве синонимайзера текста
уникализатор текста через ChatGPT
Автоматизированное создание текстов с помощью ChatGPT
ChatGPT как генератор уникального контента
Уникализация текста с помощью ChatGPT
Где найти промо коды на X-GPTWriter
[url=https://test2semrush.net/]тест2[/url].
homefronttoheartland.com
물론 그도 왕수인의 기분을 상하게 할까 봐 두려웠고 결국 왕수인은 그를 잘 대해주었다.
Доброго!
Вы когда-нибудь сталкивались с необходимостью написания дипломной работы в сжатые сроки? Это действительно серьезное испытание, требующее ответственности и трудолюбия. Но несмотря на трудности, важно не унывать и продолжать двигаться вперед, активно вовлекаясь в учебные процессы.
Для тех, кто умеет находить нужную информацию и оперативно обрабатывать данные, поиск информации в интернете становится настоящим спасением. Это позволяет сократить время на посещение библиотек и встречи с научными руководителями, а также ускоряет процесс согласования и написания диплома. Если вам нужны хорошие источники для подготовки дипломной работы или курсовых проектов, рекомендую обратиться к следующим ссылкам:
http://vuzdiploma.ru/
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
купить диплом в сызрани
купить диплом в шадринске
купить дипломы о высшем
купить диплом в курске
купить диплом в первоуральске
купить диплом в белогорске
купить диплом в ноябрьске
купить диплом в златоусте
купить диплом в новороссийске
купить диплом колледжа
Привет всем!
Стоит отметить, что статьи про строительство это очень интересно и увлекательно, узнаешь что-то новое и полезное!
Этот ресурс включает много статей на разные темы, рекомендую
https://mstud.org/gazobeton-chto-stoit-uchest-pered-pokupkoj-materiala/
Удачного чтения!
[url=http://semaglutidetabs.online/]wegovy buy online[/url]
Привет всем!
Стоит отметить, что статьи про строительство это очень интересно и увлекательно, узнаешь что-то новое и полезное!
Этот ресурс включает много статей на разные темы, рекомендую
http://reporter63.ru/content/view/648654/vybiraem-klej-dlya-gazobetonnyh-blokov
Удачного чтения!
Закупка диплома в Москве [URL=https://diplomsuper.net]www.diplomsuper.net[/URL] – это такой популярный подход, который обеспечивает доступ к качественному образованию без лишних затрат временных затрат и усилий. В Москве предлагается многочисленные варианты альтернатив по изготовлению и перевозке документов о разнообразных уровнях степени подготовки.
Уважаемые Гости!
Вводим вам инновационное концепт в мире дизайна домашней обстановки – шторы плиссе. Если вы желаете к великолепию в всякой аспекте вашего дома, то эти занавеси подберутся великолепным подходом для вас.
Что делает шторы плиссе такими особенными? Они объединяют в себе в себе выгоду, утилитарность и применимость. Благодаря особой форме, прогрессивным материалам, шторы плиссе идеально подходятся для какого бы то ни интерьера, будь то зала, спальня, кухня или секретарское пространство.
Закажите [url=https://tulpan-pmr.ru]жалюзи гофра[/url] – совершите уют и красоту в вашем доме!
Чем привлекательны шторы плиссе для вас? Во-первых, их особенный стиль, который присоединяет к очарование и стильность вашему обстановке. Вы можете подобрать из различных текстур, расцветок и подходов, чтобы подчеркнуть особенность вашего дома.
Кроме того, шторы плиссе предлагают массивный ассортимент практических возможностей. Они могут управлять степень света в интерьере, остерегать от солнечного света, предоставлять закрытость и формировать уютную атмосферу в вашем доме.
Наш сайт: [url=https://tulpan-pmr.ru]https://www.tulpan-pmr.ru[/url]
Наша фирма поддержим вам подобрать шторы плиссе, которые безупречно подходят к для вашего интерьера!
Здравствуйте!
Вы когда-нибудь сталкивались с необходимостью написания дипломной работы в сжатые сроки? Это действительно серьезное и трудоемкое занятие, но важно не отступать и продолжать двигаться вперед в учебном процессе, так же, как я это делаю.
Для тех, кто умеет осуществлять анализ и находить информацию в интернете, это может оказаться очень полезным в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Нет необходимости тратить время на посещение библиотек или встречи с научным руководителем. В интернете есть множество ресурсов с хорошими данными для дипломных работ и курсовых. Вы можете ознакомиться с ними, перейдя по ссылкам
https://extern-diplom.com/
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
купить диплом экономиста
купить диплом в братске
купить диплом в тюмени
купить диплом с занесением в реестр
купить диплом в сарапуле
купить диплом в норильске
купить диплом в когалыме
купить диплом в оренбурге
купить диплом в камышине
купить диплом в хасавюрте
The best online games that give real cash in Kenya
online casino games that pay real money [url=https://realmoneygameskenya.com/]games that pay real money in kenya[/url] .
Привет всем!
Было ли у вас когда-либо так, что вы писали дипломную работу в кратчайшие сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и усилий, но важно не сдаваться и продолжать активно участвовать в учебных процессах, как и я.
Для тех, кто умеет находить нужную информацию и анализировать ее в Интернете, это действительно может быть полезным в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Нет необходимости тратить время на походы в библиотеки или встречи с научным руководителем. Здесь доступны хорошие данные для дипломных работ и курсовых проектов; вы можете ознакомиться с ними, перейдя по ссылкам
https://extern-diplom.com/
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
купить диплом магистра
купить диплом в альметьевске
купить диплом мастера маникюра и педикюра
купить диплом в серове
купить аттестат за 9 классов
купить диплом логопеда
купить диплом зубного техника
купить диплом в смоленске
куплю диплом высшего образования
купить диплом преподавателя
Discover the top lucrative games in Kenya
online casino games that pay real money [url=https://realmoneygameskenya.com/]games that pay real money in kenya[/url] .
Как расположить рулонный газон в саду?
рулонный газон купить [url=https://rulonnyj-gazon77.ru/]https://rulonnyj-gazon77.ru/[/url] .
Какой рулонный газон подойдет для детской площадки?
купить рулонный газон в москве [url=https://rulonnyj-gazon77.ru/]https://rulonnyj-gazon77.ru/[/url] .
[url=http://wegovy.click/]order wegovy online[/url]
Как правильно укладывать рулонный газон?
рулонный газон цена за м2 [url=https://rulonnyj-gazon77.ru/]https://rulonnyj-gazon77.ru/[/url] .
В текущих обстоятельствах затруднительно сделать будущее обеспеченных без академического образования – [URL=https://diplomex.com/]diplomex.com[/URL]. Без высшего образования найти работу на работу с достойной оплатой труда и привлекательными условиями практически невозможно. Многие людей, получивших информацию о подходящейся вакансии, вынуждены от нее отказаться, не имея требуемого документа. Однако ситуацию можно решить, если заказать диплом о высшем уровне образовании, цена которого будет подъемная в сравнивание со стоимостью обучения. Особенности покупки диплома о высшем образовании Если человеку потребуется лишь демонстрировать документ своим, ввиду причины, что они не удалось им закончить учебу по какой-либо причинам, можно заказать недорогую топографическую копию. Однако, если такой придется показывать при устройстве на работу, к вопросу стоит подходить более серьезно.
Как перетянуть мебель в Минске? Обратись к нам!
перетяжка мебели цена [url=https://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]https://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/[/url] .
Мастерская по перетяжке мягкой мебели в Минске – доверенный выбор
перетяжка мебели в минске недорого [url=https://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]https://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/[/url] .
На территории столице России приобрести свидетельство – это практичный и быстрый метод достать нужный запись без дополнительных трудностей. Множество компаний предлагают помощь по созданию и торговле свидетельств разнообразных учебных заведений – [URL=https://diplomkupit.org/]https://diplomkupit.org/[/URL]. Разнообразие свидетельств в городе Москве большой, включая бумаги о академическом и нормальном образовании, аттестаты, свидетельства вузов и университетов. Главное достоинство – возможность достать диплом подлинный документ, обеспечивающий подлинность и высокое стандарт. Это предоставляет специальная защита ото подделки и дает возможность применять свидетельство для различных целей. Таким путем, приобретение свидетельства в Москве становится достоверным и оптимальным выбором для тех, кто хочет достичь процветанию в трудовой деятельности.
Привет всем!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует высокой степени ответственности и напряженной работы, но важно не унывать и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, так же, как и я.
Для тех, кто умеет искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно может быть очень полезным в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Нет необходимости тратить время на походы в библиотеки или встречи с научным руководителем. Здесь предоставлены хорошие данные для дипломных и курсовых работ; вы можете ознакомиться с ними, перейдя по ссылкам
https://diplom1.org/
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
купить диплом в бору
купить диплом в брянске
купить диплом в димитровграде
купить диплом психолога
купить диплом бухгалтера
купить диплом ссср
купить диплом инженера строителя
купить диплом монтажника
купить диплом в кемерово
купить диплом в кропоткине
Качественно перетянем мебель в Минске – долгое время сохранится ее вид
перетяжка минск [url=https://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]https://peretyazhka-mebeli-vminske.ru/[/url] .
reggionotizie.com
Liu Wenzhi는 “다른 소식이 있습니까? “라고 말했습니다.
Здравствуйте!
Были ли у вас случаи, когда приходилось писать дипломную работу в кратчайшие сроки? Это действительно очень ответственно и тяжело, но важно не терять бодрость духа и продолжать активно участвовать в учебных процессах, как и я в данный момент.
Для тех, кто умеет находить и осваивать информацию в сети, это действительно оказывает огромную помощь в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Нет необходимости тратить время на походы в библиотеки или встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь представлены хорошие данные для дипломных и курсовых проектов; вы можете ознакомиться с ними, перейдя по ссылкам
https://diplom1.org/
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
купить диплом в абакане
купить диплом в чапаевске
купить диплом математика
купить диплом физика
купить диплом в санкт-петербурге
купить диплом в тольятти
купить диплом в усолье-сибирском
купить диплом в чайковском
купить диплом в курске
купить диплом в новочебоксарске
[URL=https://diplom4you.net/]Заказать сертификат колледжа[/URL] – это шанс скоро завершить запись об образовании на бакалаврском уровне лишенный дополнительных трудностей и расходов времени. В городе Москве имеются множество альтернатив оригинальных дипломов бакалавров, предоставляющих комфортность и удобство в получении.
[url=https://ozempic.pics/]semaglutide 7 mg[/url]
Servislerimiz sayesinde sms onay sizde en uygun fiyatlardan mobil hesap sms telefon onay yaptırabilirsiniz.
this-is-a-small-world.com
바다 표면에서 그는 거대한 배의 그림자를 보았다.
[url=https://rybelsustabs.online/]order rybelsus[/url]
[url=https://semaglutide.monster/]wegovy where to buy[/url]
Доброго!
Каждый год тысячи любителей зимних видов спорта собираются в Шерегеш, одном из самых популярных горнолыжных курортов России. Однако, добраться из Новокузнецка до этого района может быть вызовом, особенно для тех, кто предпочитает удобство и комфорт.
Почему важно выбрать правильный трансфер?
Выбор трансфера играет ключевую роль в комфортабельной поездке. Это связано с рядом факторов:
Экономия времени: Эффективный трансфер позволяет избежать долгих ожиданий и пересадок, что особенно важно после длительного путешествия.
Комфорт и безопасность: Путешествие в комфортабельном транспорте с опытным водителем обеспечивает безопасность и удобство для пассажиров.
Стоимость: Разумная цена за трансфер позволяет сэкономить деньги на дороге, которые можно потратить на другие аспекты путешествия.
Оптимальный трансфер, как Мы поняли из своей поездки, в компании https://transfera-sheregesh.ru, все было великолепно и без нареканий!
Выбор трансфера из Новокузнецка в Шерегеш – важный этап в организации вашего путешествия. При правильном подходе можно найти оптимальное соотношение цены и качества, обеспечивая комфортабельное и безопасное путешествие к горнолыжным склонам. Не забудьте провести предварительное исследование и уточнить все детали у выбранной транспортной компании.
Приятного вам путешествия в Шерегеш!
[url=https://transfera-sheregesh.ru]Трансфер в Шерегеш из Новокузнецка цена [/url]
Трансфер ж/д вокзал Новокузнецк Шерегеш
Новокузнецк Шерегеш трансфер
групповой трансфер Новокузнецк Шерегеш
Такси от Новокузнецка до Шерегеша стоимость
Трансфер Новокузнецк Шерегеш от аэропорта
Удачи!
Доброго!
Нужны услуги по демонтажу дома, сносу дома, разборке дома или демонтажу фундамента? Мы можем помочь! Наша команда опытных специалистов предоставит вам профессиональные услуги по сносу и демонтажу любых типов зданий и сооружений. Мы осуществляем демонтаж дома, начиная с самых простых и небольших конструкций, таких как гаражи и беседки, и заканчивая сложными и масштабными проектами, включая многоквартирные дома и промышленные объекты. Наши специалисты обладают всем необходимым оборудованием и знаниями, чтобы выполнить демонтаж безопасно и эффективно.
Снос домов с https://lit9.ru быстро, выгодно под ключ!
[url=https://lit9.ru]снос дома в Подмосковье цена[/url]
Снос дома в Подмосковье цена
Снос дачного дома с вывозом цена
Снос домов стоимость
Снос старых дачных домов
Разбор дома после пожара
Снос дома цена
Демонтаж дачи
Снести дачу
Удачи!
Доброго!
Я просто не могу не поделиться своим восторгом от опыта аренды автомобиля в Турции через Travellifes! Наше путешествие началось с момента, когда мы забронировали автомобиль на их сайте – это было так просто и удобно! Мы выбрали идеальный автомобиль для наших нужд и указали даты аренды, и всего за несколько минут все было готово.
Когда мы получили автомобиль, мы были приятно удивлены его состоянием – чистота и порядок, идеально подходящий для нашего длительного путешествия по Турции. Свобода передвижения, которую нам дал автомобиль, просто непередаваема! Мы могли останавливаться где угодно, в любое время, наслаждаться пейзажами и исследовать скрытые уголки этой замечательной страны.
Кроме того, обслуживание от https://travellifes.ru было на высшем уровне. Представители компании были дружелюбны и готовы помочь нам в любой ситуации. Прозрачные условия аренды и отличное состояние автомобиля создали атмосферу уверенности и спокойствия на протяжении всего нашего путешествия.
Если вы хотите сделать свое путешествие по Турции по-настоящему незабываемым и комфортным, я настоятельно рекомендую воспользоваться услугами аренды автомобилей от Travellifes. Они сделают ваш отдых таким, каким вы его задумали, и помогут вам создать незабываемые воспоминания!
[url=https://travellifes.ru]можно ли арендовать машину в турции по российским правам[/url]
инструкция по аренде авто в турции
прокат автомобилей в турции
прокат авто в турции
можно ли арендовать машину в турции по российским правам
какие права нужны в турции для аренды авто
каршеринг турция
каршеринг в стамбуле
каршеринг в стамбуле для русских
Удачи!
Приветствую всех!
Мое незабываемое путешествие по Эмиратам стало возможным благодаря удивительному выбору автомобилей на сайте https://turist-travel.su Я выбрал экономичный, но в то же время стильный Chevrolet Spark, который стал надежным спутником в моих приключениях по этим удивительным землям.
Аренда автомобиля оказалась для меня настоящим спасением: экономия денег, удобство передвижения и свобода исследовать страну на своем распоряжении сделали мое путешествие по-настоящему незабываемым. Я почувствовал себя настоящим исследователем, покоряющим новые горизонты каждый день.
Сервис Turist-travel предоставил мне доступ к аренде автомобиля по самым доступным ценам, что позволило мне сэкономить значительную сумму на транспортных расходах. Процесс аренды был быстрым и простым, а персонал компании всегда был готов помочь в случае возникновения вопросов.
Я настоятельно рекомендую Turist-travel всем, кто хочет ощутить дух приключения и исследовать красоты Эмиратов, не переплачивая за аренду автомобиля.
[url=https://turist-travel.su]как взять машину напрокат в оаэ[/url]
аренда автомобиля в абу даби
взять машину напрокат в дубае
аренда авто в дубае отзывы
где арендовать машину в дубае
аренда автомобиля в оаэ
абу даби машины
арендовать машину в дубае
аренда авто в оаэ без депозита
Удачи!
eskort siteleri pokkerx.6Rz44S9b6zwu
viagra footballxx.ZmBaG2IePUtG
pornhub bahis siteleri mobileidn.soKLdD55EU6H
house porn bingoxx.Z04wVtcn5uJJ
viagra 250tldenemebonusuxx.xHnsCGVuGrW6
bahis siteleri sikis eyeconartxx.wGDwECRAoHGr
Здравствуйте!
Промокоды для интернет-магазина Эльдорадо — это специальные коды, которые можно активировать при оформлении заказа на официальном сайте компании.
Они предоставляют дополнительные преимущества покупателям в виде скидок на конкретные товары или услуги, бесплатной доставки или других бонусов.
Как найти промокоды для Эльдорадо? Они часто предоставляются в рамках специальных акций компании, которые могут проводиться на ее официальном сайте,
в социальных сетях или на проекте free-promocode.ru
Сайт самых свежих и проверенных промокодов магазина Эльдорадо https://free-promocode.ru
Удачных покупок!
Официальные акции Эльдорадо
Эксклюзивные акции и скидки в Эльдорадо
свежие промокоды Эльдорадо
Промокоды для умных покупок в Эльдорадо
Промокоды для сэкономленных денег в Эльдорадо
Удачи!
lisinopril structure
Merhaba!
Son yıllarda Mostbet tr, п»ї[url=https://mosttr-2.xyz]mostbet guncel giris[/url] çevrimiçi bahis endüstrisinde liderlerin arasında başarılı bir şekilde yerini almıştır. Sadece uzmanlar değil,
kumar oynamaya yeni başlayanlar da bu platformu spor bahisleri dünyasında güvenilir bir seçenek olarak tercih etmektedir. Her ziyaretçi,
platformun sunduğu heyecan dolu deneyimin tadını çıkarabilir.
Popüler spor etkinliklerinin yanı sıra, site golf, tenis veya beyzbol gibi daha az yaygın olan bahis disiplinlerini de sunmaktadır.
Geniş seçenekler ve yenilikçi yaklaşımı ile herkes için bir şeyler bulunmaktadır
Sitedeki her sey https://mosttr-2.xyz
Kumarhane gГјvenilir mi Mostbet
Kumarhane stratejileri Mostbet
Kumarhane indirimleri Mostbet
Kumarhane promosyonlarД± Mostbet
Kumarhane Еџans oyunlarД± Mostbet
Kumarhane hileleri Mostbet
Kumarhane kazanma tГјyolarД± Mostbet
Kumarhane oyunlarД± Mostbet
Iyi sanlar!
house porn vvsetohimalxxvc.tkAUl1IVQwok
weaning off zoloft schedule
smcasino-game.com
Hongzhi 황제는 침묵을 지켰지 만 그의 얼굴은 약간 붉어졌습니다.
[url=https://rybelsustabs.online/]semaglutide tab 3mg[/url]
zoloft for anxiety and depression
lisinopril 20 mg
smcasino7.com
그의 단안경에 거대한 배가 나타났다.
food porn tthighereduhryyy.Y8CO1GR9VKe
Доброго!
Промокоды для интернет-магазина Эльдорадо — это специальные коды, которые можно активировать при оформлении заказа на официальном сайте компании.
Они предоставляют дополнительные преимущества покупателям в виде скидок на конкретные товары или услуги, бесплатной доставки или других бонусов.
Как найти промокоды для Эльдорадо? Они часто предоставляются в рамках специальных акций компании, которые могут проводиться на ее официальном сайте,
в социальных сетях или на проекте free-promocode.ru
Сайт самых свежих и проверенных промокодов магазина Эльдорадо https://free-promocode.ru
Удачных покупок!
Специальные предложения и скидки Эльдорадо
Специальные предложения Эльдорадо
Привилегированные промокоды Эльдорадо
бесплатные промокоды Эльдорадо
актуальный промокод Эльдорадо
Удачи!
Günaydın!
Son dönemlerde 1win tr, çevrimiçi bahis endüstrisindeki liderler arasında başarılı bir şekilde kendini kanıtlamıştır.
Sadece profesyoneller değil, [url=https://1wintr-2.xyz]1win guvenilir mi[/url] kumar oynamaya yeni başlayanlar da bu platformu spor bahisleri dünyasında güvenilir bir tercih olarak gönül
rahatlığıyla tercih etmektedirler. Her ziyaretçi, platformun sunduğu heyecan dolu deneyimin tadını çıkarabilir.
Çok çeşitli popüler spor etkinliklerinin yanı sıra, site golf, tenis veya beyzbol gibi daha az yaygın olan bahis disiplinlerini de sunmaktadır.
Yenilikçi yaklaşım ve geniş seçenekler sayesinde herkes için bir şeyler bulunmaktadır
Sitedeki her sey https://1wintr-2.xyz
Kumarhane para yatД±rma 1Win
Kumarhane turnuvalarД± 1Win
CanlД± kumarhane 1Win
Kumarhane siteleri 1Win
Kumarhane bonuslarД± 1Win
п»їKumarhane 1Win
Kumar siteleri 1Win
Kumarhane yasal mД± 1Win
Iyi sanlar!
furosemide to bumex conversion
pragmatic-ko.com
조금 더 안쪽으로 가면 어복을 입은 진이의 선장 두세 명이 있습니다.
Merhaba!
Son zamanlarda Bwin tr, [url=https://bwintr.top]bwin casino[/url] çevrimiçi bahis endüstrisinde lider konumunu başarılı bir şekilde sağlamlaştırdı. Uzmanlar kadar, kumar oynamaya yeni başlayanlar
da bu platformu spor bahisleri dünyasında güvenilir bir tercih olarak seçiyorlar. Her ziyaretçi, platformun sunduğu heyecan dolu deneyimin tadını çıkarabilir.
Popüler spor etkinliklerinin yanı sıra, site golf, tenis veya beyzbol gibi daha az bilinen bahis disiplinlerine de yer vermektedir.
Geniş seçenekler ve yenilikçi yaklaşımı sayesinde herkesin ilgisini çekecek bir şey bulunmaktadır
п»їKumarhane BWin
Kumarhane promosyonlarД± BWin
Çevrimiçi kumar BWin
Kumarhane oyunlarД± Г§eЕџitleri BWin
Kumar siteleri BWin
CanlД± kumarhane BWin
Kumarhane hakkД±nda bilgi BWin
Kumarhane siteleri BWin
Iyi sanlar!
gabapentin 300mg dosage
glucophage tablete-mrsavljenje
Herkese selamlar!
Son zamanlarda Bwin tr, çevrimiçi bahis endüstrisindeki öncüler arasında başarılı bir şekilde kendini kanıtladı. Uzmanlar kadar, kumar oynamaya yeni başlayanlar
da bu platformu spor bahisleri dünyasında güvenilir bir tercih olarak gönül rahatlığıyla tercih etmektedirler. Her ziyaretçi, https://bwintr.top platformun sunduğu heyecan dolu
deneyimin tadını çıkarabilir. Site, çok çeşitli popüler spor etkinliklerinin yanı sıra golf, tenis veya beyzbol gibi daha az yaygın olan bahis disiplinlerini
de sunmaktadır. Yenilikçi yaklaşım ve geniş seçenekler sayesinde herkes için bir şeyler bulunmaktadır
Kumarhane taktikleri BWin
Kumarhane gГјvenilir mi BWin
Kumarhane Еџans oyunlarД± BWin
Kumarhane popГјler oyunlar BWin
Kumarhane hileleri BWin
Kumarhane stratejileri BWin
Kumarhane deneme bonusu BWin
CanlД± kumarhane BWin
Iyi sanlar!
will lasix lower bnp levels
Hello!
Tallinna restoranide maailm ootab avastamist.
Kas olete valmis avastama midagi uut ja põnevat? Külastage meie lehte http://restoranid-tallinnas.com ja leidke oma järgmine lemmikrestoran Tallinnas.
Meie lai valik erinevaid söögikohti tagab, et iga gurmaan leiab midagi oma maitsele. Olgu selleks siis modernne fusion-köök või traditsioonilised Eesti road,
meie lehelt leiate kõik.
[url=http://restoranid-tallinnas.com/]tallinn restaurants[/url]
best restaurants in tallinn estonia
hea restoran tallinnas
parimad restoranid tallinnas
Good luck!
glucophage emzirme
Günaydın!
Son zamanlarda Mostbet tr, çevrimiçi bahis endüstrisindeki liderler [url=https://ovc-club.com]mostbet apk[/url] arasında kendini başarılı bir şekilde kanıtladı.
Sadece profesyoneller değil, kumar oynamaya yeni başlayanlar da bu platformu spor bahisleri dünyasında güvenilir bir ortak olarak gönül
rahatlığıyla tercih ediyorlar. Her ziyaretçi, platformun sunduğu heyecan dolu deneyimin tadını çıkarabilir.
Çok çeşitli popüler spor etkinliklerinin yanı sıra, site golf, tenis veya beyzbol gibi daha az yaygın olan bahis disiplinlerini de sunmaktadır.
Yenilikçi yaklaşım ve geniş seçenekler sayesinde herkes için bir şeyler bulunmaktadır.
Sitedeki her sey https://ovc-club.com
Kumarhane oyunları çevrimiçi Mostbet
Kumarhane promosyonlarД± Mostbet
Kumarhane deneme bonusu Mostbet
Kumarhane para Г§ekme Mostbet
Kumarhane yasal mД± Mostbet
Kumarhane popГјler oyunlar Mostbet
Kumarhane para yatД±rma Mostbet
Slot makineleri Mostbet
Iyi sanlar!
what is gabapentin for
[url=https://rybelsus.download/]rybelsus 7 mg tablet[/url]
Hello!
Kogemused, mida jagada ja mäletada.
Tallinnas on söögikohti, mis ootavad, et neid avastaksite, ja meie veebileht http://restoranid-tallinnas.com on siin, et juhatada teid nende juurde.
Olgu teie eelistus mis tahes, meie platvormil on midagi igaühele. Alates intiimsetest kohvikutest kuni suursuguste restoranideni – leidke see eriline
koht ja looge mälestusi, mis kestavad terve elu.
[url=http://restoranid-tallinnas.com/]top restoranid tallinnas[/url]
head restoranid tallinnas
parimad tallinna restoranid
top 10 restoranid tallinnas
Good luck!
Herkese selamlar!
Son yıllarda Mostbet tr, п»ї[url=https://ovc-club.com]mostbet guncel giris[/url] çevrimiçi bahis endüstrisinde liderler arasında başarılı bir şekilde yerini sağlamlaştırmıştır.
Uzmanlar kadar, kumar oynamaya yeni başlayanlar da bu platformu spor bahisleri dünyasında güvenilir bir seçenek olarak tercih etmektedir.
Her ziyaretçi, platformun sunduğu heyecan dolu deneyimin tadını çıkarabilir. Popüler spor etkinliklerinin yanı sıra, site golf, tenis veya beyzbol
gibi daha az yaygın olan bahis disiplinlerini de sunmaktadır.
Geniş seçenekler ve yenilikçi yaklaşımı ile herkes için bir şeyler bulunmaktadır.
Sitedeki her sey https://ovc-club.com
Kumarhane yasal mД± Mostbet
Kumarhane gГјvenilir mi Mostbet
п»їKumarhane Mostbet
Kumarhane nasД±l oynanД±r Mostbet
Kumarhane oyunları çevrimiçi Mostbet
Kumar siteleri Mostbet
Kumarhane para Г§ekme Mostbet
Kumarhane hileleri Mostbet
Iyi sanlar!
Доброго!
Sykaaa Casino, https://serpcity.ru запущенное в 2022 году, привносит в мир азартных развлечений свежий ветер. Владельцем казино является Snowdunes B.V., а лицензия, выданная в Кюрасао (8048/JAZ2022-007), обеспечивает безопасность и честность игры.
Для вывода средств из казино Sykaaa, игроку нужно авторизоваться и выбрать вкладку “Касса”. Минимальная сумма для вывода – 150 RUB или 20 USD. При выводе суммы более 200 USD требуется верификация аккаунта.
Казино предоставляет разнообразные варианты платежных систем, включая карты, электронные кошельки и криптовалюты.
Минимальный депозит в Sykaaa Casino – 5 USD, а максимальный – 60000 USD. Геймеры могут регулировать лимиты на депозит по мере продвижения по уровням программы
лояльности. Казино также предоставляет возможность бесплатной игры в демо-режиме для ознакомления с играми и правилами.
Sykaaa Casino радует игроков оригинальными бонусами. Новички могут получить 100 фриспинов на Razor Shark без депозита.
Приветственный бонус в размере 100% от первого депозита с условием вейджера х45. Казино также организует турниры и акцию “Игра дня”.
Для решения вопросов у игроков круглосуточно работает служба технической поддержки. Связаться можно через live chat, отправив письмо или позвонив по указанному номеру
телефона. Официальный сайт казино Sykaaa может быть периодически заблокирован провайдерами. В таких случаях игроки могут использовать зеркала или специальные программы для обхода блокировок. Регистрация открыта для игроков из Европы, России, Украины и Беларуси.
сукааа casino зеркало
sukkaa казино
казино сукка
сукааа бонус
sykka казино
syyyka casino
sykaaa casino рабочее зеркало
sykaaa casino войти sykaaaa online
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
Здравствуйте!
Sykaaa Casino: зарабатывайте на азарте с официальным сайтом!
Онлайн-площадка https://vrkvvmvd.ru/ Sykaaa Casino, стартовавшая в 2022 году, сразу завоевала сердца азартных игроков. Команда разработчиков сфокусировалась на создании качественного проекта с лицензией от игорной компании Кюрасао, что обеспечивает надежность и честность игры. Подробнее об особенностях клуба можно узнать в нашем обзоре.
Sykaaa Casino Рабочее Зеркало:
Как обойти блокировки и получить бонусы? Рабочее зеркало Sykaaa Casino становится настоящим спасением для игроков при блокировке официального сайта. Воспользуйтесь актуальным зеркалом для легкой регистрации и входа, получив при этом эксклюзивные бездепозитные и депозитные бонусы. Наша статья расскажет вам, как быстро найти рабочую ссылку, чтобы не упустить выгодные предложения.
Бонусы в Sykaaa Casino: Уникальные предложения для каждого игрока! Sykaaa Casino не скупится на щедрые бонусы, которые доступны всем зарегистрированным пользователям в течение 14 дней. В разделе ‘БОНУСЫ’ вы найдете разнообразные предложения, готовые увеличить ваши шансы на выигрыш. Sykaaa Casino
Приветственный Бонус: Удвоение первого депозита! Новички в Sykaaa Casino могут насладиться приветственным бонусом в 100%, удваивая свой первый депозит. Минимальный депозит составляет всего 500 рублей, что делает игру еще более доступной. Sykaaa Casino Кэшбек: Возвращайте часть своих потерь! Неудачи не так страшны с кэшбеком в 10% от Sykaaa Casino.
Это дополнительная мотивация продолжать играть и получать вознаграждение даже в случае неудач. Sykaaa Casino Промокоды: Секреты получения дополнительных вращений! Игроки могут получить различные промокоды, в том числе промо-код SYKA40, предоставляющий 40 бесплатных вращений в игре The Dog Haus Megaways без депозита. Узнайте, как получить свой промокод и наслаждайтесь дополнительными выигрышами. Итак, с Sykaaa Casino каждый найдет для себя не только увлекательные игры, но и выгодные бонусы, обеспечивающие захватывающий опыт игры на долгое время!
[url=https://vrkvvmvd.ru]онлайн казино сука[/url]
сука казино промокод
сука казина
sykaa casino отзывы
сукка казино скачать
бонус в казино sykaaa
промокод sukaaa casino
sukka казино только вход
казино сукка официальный сайт
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
cephalexin dose
is amoxicillin a steroid
Привет Всем!
В 2022 году в мире азартных развлечений появился новый игрок https://serpcity.ru — казино Sykaaa. За его разработку и эксплуатацию отвечает Snowdunes B.V.
Сайт оперирует под лицензией Curacao: 8048/JAZ2022-007, выданной владельцу платформы. Этот молодой проект, основанный в 2022 году, уже успел привлечь внимание игроков своими бонусами и богатым выбором игр. Для обеспечения надежности, оператор получил лицензию от Кюрасао.
Валидность лицензии можно проверить на главной странице, кликнув по соответствующей иконке валидатора. Владельцем платформы является Snowdunes B.V., а сам проект находится в стадии активного развития.
Sykaaa Casino стремится охватить широкую аудиторию, предоставив интерфейс на трех языках: русском, украинском и английском.
Такое многоязычие делает сайт доступным для игроков из разных стран. Оригинальные бонусы и акции делают игру в Sykaaa Casino увлекательной.
Например, новичкам доступны 100 бесплатных вращений для автомата Razor Shark в течение 7 дней после регистрации. Приветственный бонус составляет 100%,
а максимальная сумма, которую можно получить, — 5000 евро. Свыше 1000 игр от таких провайдеров, как Betsoft, Pragmatic Play, Microgaming и другие,
доступны пользователям Sykaaa Casino. Каталог постоянно расширяется, делая игровой процесс разнообразным и интересным.
Sykaaa Casino предлагает разнообразные способы пополнения и вывода средств, включая Мир, СБП, Visa, Mastercard, Bitcoin и другие.
Минимальный депозит для активации бонуса — 500 рублей, а лимит на вывод составляет 10 000 USD в день. Sykaaa Casino не предлагает отдельного приложения, но мобильная версия сайта обеспечивает стабильную работу на любых устройствах. Благодаря этому, игроки могут наслаждаться азартом через браузер смартфона или планшета.
суаака казино
sykaaa казино регистрация
сукааа зеркало рабочее
sukaaa казино промокод
sukaaa казино официальный сайт
sykaaa казино онлайн регистрация
сукаааа
sykaaa казино промокод бездепозитный
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
Привет Всем!
Добро пожаловать на официальный сайт https://vrkvvmvd.ru/ казино Sykaaa!
Здесь вас ожидает уникальный игровой опыт с богатым выбором развлечений. В казино Sykaaa вас ждет широчайший выбор азартных игр – от современных слотов до настольных игр и видеопокера. Графика и звуковые эффекты создают захватывающую атмосферу, погружая вас в игровой процесс. На сайте представлены как любимые классические игры, так и инновационные новинки, удовлетворяя вкусы каждого игрока.
Sykaaa casino предлагает одну из самых обширных коллекций игр в онлайн-казино. Здесь доступны сотни слотов и множество вариантов классических настольных игр, таких как блэкджек и рулетка. Минимальные ставки подходят как новичкам, так и хайроллерам, а наличие версий с живыми дилерами и турниров делает опыт еще более захватывающим для любителей азартных игр.
Не хотите сразу рисковать своими средствами?
Sykaaa предлагает бесплатные фриспины за регистрацию с вейджером х20, позволяя новичкам потренироваться на бесплатных автоматах перед реальными ставками. Выигранные средства можно потратить на другие развлечения, такие как покер или рулетка в режиме реального времени.
По отзывам игроков, навигация на сайте удобная, нет проблем с выводом средств, и техническая поддержка всегда на связи. Отмечается качественный игровой опыт и доступность обслуживания. Выбрав казино Sykaaa, вы встретите увлекательный мир азартных развлечений, разнообразие игр и удобные условия для игры и вывода выигрышей.
[url=https://vrkvvmvd.ru]sykaa casino зеркало[/url]
sykkka casino
казино syyka
суккааа казино
промокод казино суукаа
онлайн казино saikaaa
syyyka казино промокод
казино сукка сколько времени ждать вывода
промокод sukaaa casino
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
Доброго!
Финансовая компания Finance Online, занимающаяся предоставлением широкого спектра финансовых услуг в Казахстане. Наше богатое опыт и высокая репутация
делают нас надежным выбором для клиентов, которые ищут финансовую помощь и поддержку. Мы специализируемся на банковских кредитах, микрозаймах и ипотеке,
стремясь предложить выгодные и гибкие условия для каждого клиента.
Преимущества:
Индивидуальный подход: Мы понимаем, что каждый клиент уникален, поэтому мы предлагаем персонализированные финансовые решения, учитывая их потребности,
возможности и цели.
Быстрое одобрение: Мы ценим ваше время, поэтому стремимся обеспечить быстрое рассмотрение заявок и высокий шанс одобрения кредитов и займов.
Прозрачность и честность: Мы гарантируем прозрачные и понятные условия наших продуктов. У нас нет скрытых платежей или непонятных комиссий.
Высокий уровень сервиса: Наша дружелюбная и профессиональная команда всегда готова помочь вам с любыми вопросами или проблемами, связанными с вашими финансами.
Онлайн сервис: оставляйте завяку на сайте https://finance-online.kz без похода в банк
[url=https://finance-online.kz]банк центркредит номер оператора[/url]
тенгеда личный кабинет
каспи банк номер
номер каспи
онлайн кредит на карту без отказа казахстан
займ без идентификации казахстан
alber займ
Удачи!
pragmatic-ko.com
오늘은 휴일이고 서쪽 산은 이미 눈으로 덮여 있습니다.
Здравствуйте!
В мире народных художественных промыслов Кировской области таится богатство истории и традиций. Дымковская игрушка, вятское кружево, резьба по дереву — здесь каждый из видов ремесел несет в себе многовековую мудрость искусства. Сегодня, в эпоху быстрого развития, эти художественные традиции не только сохранились, но и активно развиваются. В Кирове процветают капокорешковый и токарный промыслы, инкрустация соломкой, гончарство, ткачество, искусство ковки и литья. Это не просто ремесла, а целый мир, где каждый предмет является настоящим произведением искусства. Особую ценность придает этим промыслам традиционность и непрерывность развития. Каждый мастер владеет уникальными методами работы с природными материалами, сохраняя самобытность техник и технологий. Именно такая связь с историей делает кировские художественные промыслы такими удивительными и ценными. Правительство Кировской области активно поддерживает сферу народных художественных промыслов. Специальные программы направлены на сохранение и развитие этого культурного богатства, стимулирование творческого потенциала мастеров, а также создание связей между производителями и рынком.
Переходя от ремесел к численности населения, мы видим, что Киров – это город с богатой историей и культурным наследием. Согласно данным Всероссийской переписи населения 2020 года, Киров занимает 43-е место по численности населения среди 1120 городов России. Это свидетельствует о том, что город привлекает своим уникальным обликом и жизненным стилем. Интересный факт: в половом соотношении преобладает женское население, составляя 56%. Национальный состав города также разнообразен, где 96,6% населения – русские. Трудоспособное население, достигающее 63% от общей численности, активно участвует в экономической жизни города. Переходя к вятским говорам, мы оказываемся в удивительном лингвистическом пространстве. Вятские говоры относятся к севернорусскому наречию и представляют собой интересный лингвистический феномен. Сложившаяся под влиянием разных языковых и культурных традиций, речь вятчан приобрела уникальные черты.
Фонетические особенности вятских говоров https://sco2009.ru/ включают оппозицию кратких и долгих звуков, произношение мягкого “р” перед задненёбными согласными и наличие исконно мягких шипящих и ц. Морфологически вятские говоры отличаются смешением окончаний и наличием постпозитивных частиц. И, наконец, приподнимаем завесу над краеведческим музеем. Это место, где история, природа и культура Вятского края предстают перед посетителями во всей красе. Здесь вы найдете уникальные материалы по истории и природе региона, коллекции минералов и пород, а также экзотических животных. Театральная жизнь Кирова также заслуживает внимания. Драматический театр, основанный в 1877 году, стал старейшим театром города. Его репертуар включает в себя как классические произведения, так и спектакли современных отечественных и зарубежных драматургов. Таким образом, Киров — это не только город с богатым культурным наследием и интересной историей, но и место, где народные традиции и современность гармонично переплетаются, создавая уникальный облик и неповторимый характер.
[url=https://sco2009.ru]новости город киров[/url]
акцент кировчан
костин втб и наиля аскер-заде фото
бабушка тети кто мне
диалектизмы примеры кировской области
банкир костин и наиля аскер-заде
наиля аскер-заде и костин фото
внук двоюродной прабабушки
путинские выплаты в 2023 к 1 сентября
Удачи!
Доброго!
Кировская область богата национальными сувенирами https://mosprize.ru/. Здесь можно приобрести глиняные игрушки ручной работы, изделия из капокорня, а также знаменитые вятские кружева. Эти подарки станут отличным напоминанием о поездке. Традиционные сувениры включают вятские кружева, выполненные в уникальной технике, а также изделия народных промыслов. Они отражают культурное наследие края. В Кировской области бережно хранят фольклорные традиции. К примеру, здесь отмечают древний праздник Ивана Купалы.
Особенность региона – вятский говор. Он сформировался под влиянием русского, финно-угорских и тюркских языков. Популярные сувениры из Кирова – фигурки дымковской игрушки и вятское кружево. Их можно купить на рынках или в специализированных магазинах. Также рекомендуем посетить народные гулянья. Например, праздник Сыроварения, где можно попробовать традиционные сыры региона.
[url=https://mosprize.ru]гвоздика почвопокровная многолетняя[/url]
новости шабалино ленинское кировская
народы населяющие кировскую область и их традиции
гвоздика травянка
где в россии растут лимоны
сувенир из кирова
кто знает на сколько приехал цирк пгт ленинское т кировской обл шабалинского района
новости шабалинского района
подарки из вятки
Удачи!
Wow superb blog layout How long have you been blogging for you make blogging look easy The overall look of your site is magnificent as well as the content
buy amoxicillin
how much is cephalexin
Здравствуйте!
Кировская область – земля, насыщенная народными художественными промыслами и традициями, ставшими неотъемлемой частью российской культуры. Данные промыслы являются живыми свидетелями многовекового опыта эстетического восприятия мира и хранят глубокие художественные традиции. На Вятке сегодня продолжают развиваться такие национальные промыслы, как дымковская игрушка, вятское кружево, резьба и роспись по дереву, капокорешковый, бурачный и токарный промыслы, матрешка, инкрустация соломкой, плетение из природных материалов, гончарство, ткачество, а также производство изделий из льна с вышивкой, художественная ковка и литье.
Уникальность этих промыслов заключается в традиционности https://sco2009.ru/ и непрерывности их развития, а также в самобытности методов работы с природными материалами, навыках художественного мастерства и сложившихся техниках и технологиях. Правительство Кировской области активно поддерживает этот вид искусства, принимая меры по сохранению, развитию и стимулированию творческого потенциала мастеров, а также устанавливая тесные связи между производителями и рынком.
Согласно данным Всероссийской переписи населения 2020 года, Киров занимает 43-е место среди 1120 городов России по численности населения на 1 октября 2021 года. По административным данным, преобладает женское население, составляющее 56%. Национальный состав города в основном представлен русскими, которые составляют 96,6% населения, согласно Всероссийской переписи населения 2010 года. Трудоспособное население Кирова составляет 310,6 тысяч человек, из которых 23,2 тысячи заняты в труде в более старшем возрасте. Всего в экономике города трудоустроено 237,9 тысяч человек, что составляет 79% от общего трудового потенциала.
Одним из культурных символов города является дымковская игрушка, возникшая в заречной слободе Дымково, в настоящее время входящей в состав Кирова. Каждая игрушка уникальна и создается единым мастером от начала до конца. Особенности дымковской игрушки – пластичность формы, простота узоров и яркая палитра. Эти удивительные игрушки не только приковывают взгляд, но также оказывают влияние на современные области искусства. Мотивы дымковского орнамента даже использовались на церемонии открытия зимних Олимпийских игр 2014 года в Сочи. Помимо дымковской игрушки, вятские мастера славятся и резьбой по капа-корню. Этот вид искусства пришел в Вятку в XVIII веке и выделяется необычностью и красотой изделий из древесины капа. Возможно создание различных предметов: от портсигаров и визитниц до обложек для фотоальбомов, шкатулок и сундучков.
Город также богат музейной культурой, среди которой стоит выделить Вятский художественный музей имени Васнецовых, основанный в 1910 году. Музей представляет богатую экспозицию, включая произведения В. Сурикова, И. Репина, а также предметы фольклора и искусства Вятского края. Драматический театр, основанный в 1877 году, является старейшим театром города. В его репертуаре представлены шедевры Аристофана, Островского, Достоевского, Чехова и других классиков, а также произведения современных авторов. Театр проводит не только показы, но и творческие лаборатории и дискуссии. Театр юного зрителя «Театр на Спасской» предлагает спектакли для детей, молодежи и взрослых, отдавая предпочтение как классическим произведениям, так и современной драматургии. Киров – не просто город, но настоящее культурное святилище, где сосредоточены народные традиции, искусство и история, создавая неповторимый облик этого края.
[url=https://sco2009.ru]новости г кирова[/url]
глава втб андрей костин фото и наиля аскерзаде
сестра невестки для свекра
выплата к 1 сентября 2023
брата жена кем приходится сестре брата
аскерзаде биография
кем приходится мой внук моей родной сестре
крестный моего сына кто мне приходится
аскерзаде наиля и костин
Удачи!
Здравствуйте!
Кировская область, расположенная в Приволжском федеральном округе, поражает своим разнообразием и уникальностью https://mosprize.ru/. С обширной территорией в 120 374 км? и населением более 1,1 миллиона человек, эта область вкладывает свою душу в богатое наследие Волго-Вятского экономического района.
Национальный мозаичный портрет Кировской области включает русских, татар, марийцев, удмуртов, украинцев и другие этнические группы, что создает удивительное культурное слияние. Эта мозаика также отражена в народных промыслах, таких как дымковская расписная глиняная игрушка, вятские кружева и другие художественные изделия. Область богата историей, что подчеркивают её тысячи памятников истории, культуры и архитектуры. В 817 публичных библиотеках и 40 музеях раскрывается удивительный мир знаний и искусства.
Особенным элементом являются вятские говоры, отличающиеся уникальными фонетическими и морфологическими особенностями. Это наследие формировалось во взаимодействии с местными финно-угорскими и тюркскими языками. И в завершение, Кировская область привлекает своими национальными праздниками, традициями и обычаями. Таким образом, в каждой детали этого уникального региона можно обнаружить исключительное богатство и культурное разнообразие, готовые встретить и впечатлить каждого гостя.
[url=https://mosprize.ru]наиля аскерзаде и костин отношения[/url]
шабалино достопримечательности
где растут лимоны в россии
село черновское шабалинского района кировской области
народные праздники кировской области
народы вятского края
традиции кирова
жизнь и быт крестьян на вятке
где в россии растут лимоны
Удачи!
Доброго!
Если вам нужен демонтаж дома, снос здания или разборка сооружения, обращайтесь к нам!
Наша компания предлагает профессиональные услуги демонтажа и сноса различных типов построек и конструкций. Мы осуществляем демонтаж домов, начиная от гаражей и беседок и заканчивая крупными объектами, такими как многоквартирные комплексы и промышленные предприятия.
Заходите на https://taurusweb.ru – одну из лучших демонтажных компаний на рынке! Если у вас есть дополнительные вопросы или вы хотите обсудить ваши потребности, обращайтесь к нашим специалистам. Мы стремимся обеспечить максимально комфортный и безопасный процесс демонтажа вашего дома.
[url=https://taurusweb.ru]убрать фундамент[/url]
Слом деревянных домов
Сломать дом цена
Снос дома под ключ
Сколько стоит снести старый дом и вывезти его
Разобрать дом в Московской области
Слом фундамента
Уборка сгоревшего дома
Демонтаж частного дома
Удачи!
Merhaba!
Son zamanlarda 1win tr, çevrimiçi bahis endüstrisindeki liderler п»ї[url=https://academypops.com]1win[/url] arasında başarılı bir şekilde kendini kanıtlamıştır.
Sadece profesyoneller değil, kumar oynamaya yeni başlayanlar da bu platformu spor bahisleri dünyasında güvenilir bir tercih olarak gönül
rahatlığıyla tercih etmektedirler. Her ziyaretçi, platformun sunduğu heyecan dolu deneyimin tadını çıkarabilir.
Çeşitli popüler spor etkinliklerinin yanı sıra, site golf, tenis veya beyzbol gibi daha az yaygın olan bahis disiplinlerini de sunmaktadır.
Yenilikçi yaklaşımı ve geniş seçenekleriyle herkes için bir şeyler bulunmaktadır
Sitedeki her sey https://academypops.com
Kumarhane oyunlarД± Г§eЕџitleri 1Win
Kumarhane promosyonlarД± 1Win
Kumarhane hakkД±nda bilgi 1Win
Kumarhane bonuslarД± 1Win
Kumarhane para Г§ekme 1Win
Kumarhane popГјler oyunlar 1Win
Kumarhane yasal mД± 1Win
Kumarhane taktikleri 1Win
Iyi sanlar!
Merhaba!
Son dönemlerde Bwin tr, çevrimiçi bahis endüstrisinde lider konumunu başarılı bir şekilde sağlamlaştırdı.
Uzmanlar kadar, п»ї[url=https://tridvornova.com]bwin[/url] kumar oynamaya yeni başlayanlar da bu platformu spor bahisleri dünyasında güvenilir bir tercih olarak görmektedirler.
Her ziyaretçi, platformun sunduğu heyecan dolu deneyimin tadını çıkarabilir. Popüler spor etkinliklerinin yanı sıra, site golf, tenis
veya beyzbol gibi daha az bilinen bahis disiplinlerine de yer vermektedir.
Geniş seçenekler ve yenilikçi yaklaşımıyla herkesin ilgisini çekecek bir şey bulunmaktadır
Sitedeki her sey https://tridvornova.com
Kumarhane gГјvenilir mi BWin
Kumarhane oyunlarД± Г§eЕџitleri BWin
п»їKumarhane BWin
Kumarhane kazanma tГјyolarД± BWin
Kumarhane popГјler oyunlar BWin
Kumarhane hakkД±nda bilgi BWin
Çevrimiçi kumar BWin
Kumarhane hileleri BWin
Iyi sanlar!
Интернет-реклама для строительных фирм: как не потерять деньги?
продвижение сайтов строительство [url=https://seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-stroitelnyh-kompanij.ru/]https://seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-stroitelnyh-kompanij.ru/[/url] .
Доброго!
Наша команда профессионалов готова помочь вам в реализации ваших финансовых целей. Мы предлагаем высокий шанс одобрения кредитов, ипотеки и микрозаймов
с индивидуальным подходом к каждому клиенту. С нами вы можете быть уверены в надежности и надежности вашего финансового партнера.
Оставляйте заявку на нашем сайте https://finance-online.kz
Преимущества: высокий шанс одобрения, индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту, проверенные отзывы о банках и МФО Казахстана.
[url=https://finance-online.kz]сбербанк казахстан[/url]
icredit
займ онлайн казахстан
колл центр евразийский банк астана
ипотека без первоначального взноса
курсы валют кокшетау
тенге займ
Удачи!
pragmatic-ko.com
과거 Zhou Kang은 세 아들을 자랑스럽게 생각했습니다.
can i give my cat human ciprofloxacin
Merhaba!
Son yıllarda 1win tr, çevrimiçi bahis endüstrisinde lider konumunu başarılı bir şekilde sağlamlaştırmıştır.
Sadece uzmanlar değil, [url=https://academypops.com]1win guvenilir mi[/url] kumar oynamaya yeni başlayanlar da bu platformu spor bahisleri dünyasında güvenilir bir tercih olarak seçmektedirler.
Her ziyaretçi, platformun sunduğu heyecan dolu deneyimin tadını çıkarabilir.
Popüler spor etkinliklerinin yanı sıra, site golf, tenis veya beyzbol gibi daha az yaygın olan bahis disiplinlerini de sunmaktadır.
Geniş seçenekler ve yenilikçi yaklaşımı sayesinde herkes için bir şeyler bulunmaktadır
Sitedeki her sey https://academypops.com
Kumarhane hakkД±nda bilgi 1Win
Kumarhane yasal mД± 1Win
Kumarhane promosyonlarД± 1Win
Kumarhane popГјler oyunlar 1Win
Kumarhane para Г§ekme 1Win
Kumarhane indirimleri 1Win
Kumarhane hileleri 1Win
Kumarhane siteleri 1Win
Iyi sanlar!
Здравствуйте!
Демонтаж частного дома может потребоваться в случае покупки участка с домом, который необходимо разобрать, разрушения дома из-за старости или других причин. Важно помнить, что демонтаж дома – это сложная и опасная работа, которую лучше доверить профессионалам.
Компания https://taurusweb.ru предлагает услуги демонтажа частных домов в Московской области, гарантируя быструю и профессиональную работу, а также безопасность всех участников процесса демонтажа. Для демонтажа дома потребуются документы, подтверждающие собственность на дом, а также разрешение на проезд спецтехники на участок. Если планируется временное отключение коммуникаций, стоит предупредить соседей.
[url=https://taurusweb.ru]демонтаж фундамента[/url]
Снос дачи цена
Снос домов
Демонтаж дачи
Снос дачи
Разбор дома и вывоз мусора
Сломать фундамент
Демонтаж домов
Демонтаж деревянного дома
Удачи!
Merhaba!
Son dönemlerde Bwin tr, п»ї[url=https://tridvornova.com]bwin[/url] çevrimiçi bahis endüstrisinde lider konumunu başarılı bir şekilde sağlamlaştırdı.
Uzmanlar kadar, kumar oynamaya yeni başlayanlar da bu platformu spor bahisleri dünyasında güvenilir bir tercih olarak görmektedirler.
Her ziyaretçi, platformun sunduğu heyecan dolu deneyimin tadını çıkarabilir. Popüler spor etkinliklerinin yanı sıra, site golf,
tenis veya beyzbol gibi daha az bilinen bahis disiplinlerine de yer vermektedir.
Geniş seçenekler ve yenilikçi yaklaşımıyla herkesin ilgisini çekecek bir şey bulunmaktadır
Sitedeki her sey https://tridvornova.com
Kumarhane Еџans oyunlarД± BWin
Kumarhane promosyonlarД± BWin
п»їKumarhane BWin
Kumarhane oyunlarД± BWin
Kumarhane para yatД±rma BWin
Kumarhane nasД±l oynanД±r BWin
Kumarhane stratejileri BWin
Kumarhane indirimleri BWin
Iyi sanlar!
Топ-5 стратегий продвижения строительных компаний
продвижение строительных компаний [url=https://seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-stroitelnyh-kompanij.ru/]https://seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-stroitelnyh-kompanij.ru/[/url] .
will cephalexin treat chlamydia
В Москве купить диплом – это комфортный и быстрый способ получить нужный бумага без избыточных проблем. Множество фирм продают помощь по производству и реализации свидетельств различных образовательных учреждений – [URL=https://prema-diploms-srednee.com/]www.prema-diploms-srednee.com[/URL]. Разнообразие дипломов в столице России велик, включая бумаги о высшем уровне и среднем профессиональной подготовке, свидетельства, свидетельства вузов и вузов. Основное плюс – возможность приобрести диплом официальный документ, гарантирующий достоверность и высокое качество. Это предоставляет уникальная защита ото подделки и позволяет воспользоваться свидетельство для различных целей. Таким путем, приобретение диплома в городе Москве становится надежным и экономичным решением для данных, кто стремится к успеху в сфере работы.
sm-slot.com
마음은 조금 다혈질이지만 자신의 지위가 비천하다는 것을 알고 감히 왕세자 전하에게 경례하러 나서지 못했다.
levofloxacin vs ciprofloxacin
[url=https://rybelsussemaglutide.shop/]rybelsus without prescription[/url]
Stomatologurmonsk Экстренные меры
Стоматологические процедуры: как правильно выбрать клинику?
[url=https://rekforum.ru/viewtopic.php?p=121992#p121992]https://rekforum.ru/viewtopic.php?p=121992#p121992[/url] .
lfchungary.com
이 말을 듣고 Zhu Houzhao는 “He Tingyang, 감히 나를 비방합니까? “라고 분노했습니다.
cephalexin for cats
В Москве купить диплом – это практичный и быстрый вариант достать нужный запись лишенный избыточных проблем. Большое количество фирм предлагают сервисы по изготовлению и торговле дипломов разнообразных образовательных институтов – [URL=https://gruppa-diploms-srednee.com/]www.gruppa-diploms-srednee.com[/URL]. Разнообразие дипломов в столице России большой, включая бумаги о высшем уровне и нормальном образовании, аттестаты, дипломы колледжей и академий. Основной плюс – возможность получить диплом подлинный документ, гарантирующий достоверность и высокое качество. Это гарантирует особая защита ото подделок и позволяет применять диплом для различных задач. Таким способом, приобретение аттестата в столице России является безопасным и оптимальным выбором для таких, кто хочет достичь успеха в карьере.
[url=https://ozempic.us.com/]buy ozempic canada[/url]
pragmatic-ko.com
높은 단상 아래의 혼란스러운 광경을 본 홍지황제의 마음은…
[url=https://ozempictabs.online/]wegovy canada[/url]
[url=http://rybelsussemaglutide.online/]generic rybelsus[/url]
Перетяжка мягкой мебели
[url=https://edcommunity.ru/profile?ID=113136]https://edcommunity.ru/profile?ID=113136[/url] .
Как выбрать правильный виртуальный сервер? ,
10 важных преимуществ виртуальных серверов ,
Какую выбрать?,
Подробное руководство,
Сравнение цен и тарифов,
Как узнать, сколько ресурсов требуется для вашего проекта на виртуальном сервере
недорогой выделенный сервер [url=https://hidehost.net/ru/vds.html]проверенный хостинг[/url] .
Техники email-маркетинга для строительных фирм: как добиться успеха?
продвижение строительного сайта [url=https://seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-stroitelnyh-kompanij.ru/]https://seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-stroitelnyh-kompanij.ru/[/url] .
does cephalexin interact with any medications
amoxicillin for tooth infection
cute african busty gal here who always feel playfull!
ремонт холодильников атлант цена [url=https://remont-holodilnikov-atlant.ru/]ремонт холодильников атлант на дому[/url] .
Преимущества ремонта холодильников Атлант у профессионалов.
ремонт холодильников атлант [url=https://remont-holodilnikov-atlant.ru/]ремонт холодильников атлант в минске[/url] .
Специализированный ремонт холодильников Атлант от профессионалов.
ремонт холодильников атлант в минске на дому [url=https://remont-holodilnikov-atlant.ru/]ремонт холодильников атлант[/url] .
Онлайн казино в Беларуси с мобильной версией: играйте в любое время и в любом месте
онлайн казино [url=https://onlinecasinobelarus.by/]казино беларусь[/url] .
[url=https://rybelsustabs.com/]rybelsus for sale[/url]
Онлайн казино в Беларуси с живыми дилерами: атмосфера реального казино
онлайн казино [url=https://onlinecasinobelarus.by/]казино беларусь[/url] .
Онлайн казино в Беларуси с живыми дилерами: атмосфера реального казино
онлайн казино [url=https://onlinecasinobelarus.by/]онлайн казино[/url] .
amoxicillin prescription
Доброго!
Купить красный сушеный мухомор лучшего качества можно в специализированных магазинах [url=https://my-muhomor.ru]заказать сушеные мухоморы[/url] или интернет-магазинах,
которые предлагают товары для грибников, а также на натуральных продуктовых рынках или у проверенных продавцов на платформах электронной коммерции.
Важно обратить внимание на репутацию продавца и отзывы покупателей, чтобы убедиться в качестве продукта. Также можно найти специализированные фермерские
хозяйства или садоводческие сообщества, занимающиеся сбором и сушкой мухоморов. Однако, стоит помнить, что красный мухомор является опасным грибом, и его
использование в пищу или любых других целях без должных знаний и предосторожностей может быть вредным для здоровья.
Рекомендую заказывать онлайн сушеные мухоморы здесь https://my-muhomor.ru проверенные продавцы и изготовители!
сушеный мухомор в капсулах цены
Красный сушеный мухомор на заказ
Красный мухомор на заказ
красный сушеный мухомор в капсулах купить
Удачи!
Hello, World!
Hey there, mate! Greetings from your favorite surfing capybara!
How’s the surf today?
Ready to catch some gnarly waves together?
https://capybara444.wordpress.com
Good luck!
what does bactrim do
chutneyb.com
거리의 거지로서? 그리고 당신의 동족이 음식을 얻기 위해 기다리게 하시겠습니까?
shopanho.com
이것은 Taipu Temple의 서기관의 비밀 보고서였으며 그 기록은 매우 상세했습니다.
Hello, World!
Hey there, mate! Greetings from your favorite surfing capybara!
How’s the surf today?
Ready to catch some gnarly waves together?
https://capybara235.wordpress.com
Good luck!
[url=http://lisinoprill.com/]purchase lisinopril online[/url]
Топовые игры в онлайн казино Беларусь: слоты, рулетка, покер и другие азартные развлечения
онлайн казино [url=https://onlinecasinobelarus.by/]онлайн казино[/url] .
Привет, ребята! Сегодня хочу поделиться своим опытом в клубе азартных развлечений под названием Clubnika Casino. Это место, где действительно есть что обсудить!
Скажу честно, казино особенное, и все благодаря оригинальному оформлению идеей клубничного азарта. Вот, смотрите https://clubnikacasinobonus.ru дизайн – просто огонь!
На баннерах – девушки в нижнем белье, в бонусах – фото девушек. Я бы даже сказал, что это не просто казино, а настоящее искусство азартных развлечений.
По поводу выигрышей, конечно, не всегда фартит. Но, честно, мне важнее вот что: даже если финансовый результат средний, играть тут – это просто удовольствие.
Ведь знаешь, на что подписываешься и чего ожидаешь. Этот кайф от игры и уникального “дизайна” просто зашкаливает!
Слышал бы про такое казино в реале – точно бы сходил! Тут не только визуально приятно, но и есть шанс выиграть деньги. Иногда даже мелькают небольшие джекпотики.
Все параметры у клубничного казино на высшем уровне, если не заморачиваться.
Не знаю, как вы, парни, но это мое самое любимое казино! Тут даже проигрыш не так обиден, потому что атмосфера – вот где главное.
Создателей Clubnika Casino я б поблагодарил за такой подход и за эту крутую идею. После работы, честно, лучшего места для расслабления и кручения слотов я не нашел. Если ты не ханжа, то тебе точно сюда!
[url=https://clubnikacasinobonus.ru]играть бесплатно в игровые автоматы клубника[/url]
клубника играть бесплатно без регистрации игровые автоматы
клубника слот
клубника игровой портал
казино клубника онлайн
промокод для клубники казино
игровой слот клубнички
казино клубника официальный сайт зеркало
игровые автоматы клубнички на деньги рубли
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
Столкнулся с классным криптовалютным казино – Stake. В нем можно не только играть в любимые азартные игры, но и использовать различные криптовалюты. Официальный сайт обещает быстрые выплаты и анонимные транзакции.
Заходите, ставьте, выигрывайте! Открыл для себя Stake Casino – официальный сайт, где можно играть на криптовалюту. Очень удобные методы пополнения и вывода, при этом без ограничений.
Кстати, на сайте https://stakecommunity.ru более 3000 игр от лучших провайдеров. Кто еще играет тут?
[url=https://stakecommunity.ru]stake casino зеркало россия[/url]
стейк казино официальный сайт
stake зеркало
казино стейк официальный сайт
зарегистрироваться stake casino
стейк казино онлайн
stake casino mirror
stake мобильная
stake casino регистрация
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
Хочу поделиться своим опытом с онлайн-казино Эльдорадо. Сразу отмечу, что казино ориентировано на русскоязычную аудиторию, что делает процесс игры максимально комфортным.
Меня, конечно, насторожило отсутствие лицензии, но опыт игры с 2017 года и стиль сайта, оформленный под легенду об Эльдорадо, заинтриговали.
Первое, что бросается в глаза — это золотой город на фоне, создающий атмосферу несметных богатств. А теперь к самому важному – бонусам! 100% за первый депозит – мой способ увеличить стартовый капитал.
Бонус за день рождения — крутое дополнение к празднику, но не забудьте подтвердить свою личность. Постоянные акции публикуются в Telegram, и иногда подписчики получают эксклюзивные промокоды для бесплатных игр.
Кстати, про софт и автоматы. Около 360 игр от провайдеров типа Igrosoft, Microgaming, Novomatic. Даже незарегистрированным доступна демоверсия, так что можно потренироваться бесплатно.
На сайте https://eldoradocasinobonus.ru удобная навигация по играм, достижениям игроков, а в блоке “Сейчас выигрывают” показывают последние удачи.
Поэтому, несмотря на отсутствие лицензии, казино Эльдорадо — отличный выбор для любителей азарта.
[url=https://eldoradocasinobonus.ru]эльдорадо казино онлайн официальный сайт зеркало[/url]
eldorado зеркало играть
однорукий бандит эльдорадо бесплатно
eldorado зеркало на сегодняшний день
эльдорадо скачать приложение
однорукий бандит эльдорадо играть бесплатно без регистрации
eldorado club casino
eldorado casino войти
eldorado казино промокод
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
Привет, азартные братья и сестры! Сегодня я расскажу вам о новом крутом онлайн-казино, которое я открыл в 2023 году – Bollywood Casino https://bollywoodcasinowin.ru.
Нет, это не новая звезда Болливуда, это настоящий кайф для гемблеров из СНГ, особенно для нас, российских игроков, которые теперь могут крутить барабаны на рубли!
С самого начала меня привлек приветственный бонус, который действует на первые 5 депозитов! Это как супербоевик, где каждая ставка – это новая глава приключений.
А еще тут акции для хайроллеров, именинников и любителей вращений в слотах – круто, да?
Bollywood Casino не шутит насчет разнообразия игр. Они предлагают все – от игровых автоматов и рулетки до лайв-дилеров и блэкджека.
А провайдеры тут как на концерте в Болливуде – Betsoft, Pragmatic Play, NetEnt и много других. Крутые ребята, пора врубаться в азартное путешествие!
На официальном сайте Bollywood Casino темно-золотистый дизайн, как будто я в роскошном кинотеатре. Регистрация, вход, и вот ты уже в мире азарта.
Жми на кнопки, проверяй приветственный бонус, и погружайся в игровой зал!
Пока тут нет большой истории, но это как первый сезон твоего любимого сериала – все еще впереди. Информация о компании немного таинственная, но, честно говоря,
меня это не остановило – я тут ради азарта, а не чтения биографии.
Бонусы и акции в Bollywood Casino – вот где реальное веселье начинается. Промо-предложения для всех, даже для новичков, размещены в разделе «Акции».
После регистрации там тебя уже ждут приветственные промо-предложения.
А вот теперь самое интересное – аппараты с джекпотом. Нет отдельной категории, но их можно легко найти. Просто введи “Jackpot” в поисковую строку – и вот они, мега-выигрыши, просто как в кино!
Не переживайте по поводу верификации – она необязательная. Проверка проходит по запросу, и я сам уже успел вывести выигрыши.
Скорость проверки – моментальная, особенно если вспомнить, что никто не любит ждать.
Лотереи и турниры – тут как на настоящем шоу! Всегда есть что-то интересное: розыгрыши, даты, правила. Крутой способ поднять адреналин и выиграть нечто великолепное.
В общем, Bollywood Casino – это не просто онлайн-казино, это азартное приключение! Если ты как и я, любишь адреналин и большие выигрыши, тебе сюда.
Проверь свою удачу и подними ставки вместе со мной!
[url=https://bollywoodcasinowin.ru]болливуд казино[/url]
приложение bollywood casino
болливуд промокод
bollywood casino bonus
вход bollywood casino
сайт bollywood casino
лицензия игровой клуб болливуд
болливуд казино горячая линия
коды bollywood casino
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
neurontin for dogs
Внутри столице России приобрести аттестат – это комфортный и экспресс метод получить нужный запись безо дополнительных трудностей. Множество фирм предлагают услуги по изготовлению и реализации свидетельств разнообразных образовательных институтов – [URL=https://orik-diploms-srednee.com/]https://orik-diploms-srednee.com/[/URL]. Выбор свидетельств в городе Москве велик, включая бумаги о высшем уровне и среднем образовании, свидетельства, свидетельства колледжей и академий. Основное преимущество – возможность достать свидетельство Гознака, обеспечивающий подлинность и качество. Это гарантирует особая защита от фальсификаций и позволяет использовать диплом для различных задач. Таким способом, приобретение диплома в столице России становится безопасным и экономичным вариантом для таких, кто желает достичь успеху в сфере работы.
Привет, крутые гемблеры! Наткнулся недавно на новое онлайн-казино с именем Vovan, и не могу не поделиться своим впечатлением!
На Vovan Casino более 1200 слотов, различные бонусы и VIP-клуб, который открывает доступ к эксклюзивным акциям. Лично я при регистрации получил стартовый комплект и кешбэк!
Интерфейс сайта прост и понятен, навигация легкая, и я быстро нашел нужные разделы. Баннеры на главной странице рассказывают о всех акциях и кешбэке, так что ты всегда в курсе горячих предложений.
Не могу упустить момент рассказать про бонусы! Уже при верификации дали 25 фриспинов, а с уровнем “Опытный” еще 50! Каждый вторник можно получить Reload бонус, а в субботу дополнительные фриспины в зависимости от статуса. Это просто огонь!
Игровой каталог впечатляет: 1000+ видеослотов, категории от популярных до джекпот-игр. Мой фаворит — раздел “Купить бонус”, где за деньги можно получить еще больше фриспинов!
Интересно, что компания, владеющая казино, решила остаться инкогнито. Но вот, честно, это не мешает мне наслаждаться азартом и выигрывать!
Регистрируйтесь на Vovan Casino по ссылке https://vovan-casino-win.ru и давайте разгромим слоты вместе! Удачи в игре!
[url=https://vovan-casino-win.ru]регистрация на зеркале vovan казино[/url]
вован казино официальный сайт зеркало
вован казино скачать бесплатно
вован официальный сайт
казино вован официальный сайт
вован зеркало рабочее на сегодня
vovan casino зеркало
приложение vovan casino
вован casino вход
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
dota2answers.com
폐하는 인사도 없이 이미 자리를 떴고, 그래서 조금… 말문이 막혔습니다.
mojmelimajmuea.com
구양 사신이 막 떠나자 장실리는 곤경에 처한다.
На территории столице России приобрести диплом – это комфортный и экспресс способ завершить нужный документ безо избыточных проблем. Разнообразие организаций продают услуги по производству и реализации свидетельств разнообразных образовательных учреждений – [URL=https://russa-diploms-srednee.com/]https://www.russa-diploms-srednee.com/[/URL]. Разнообразие свидетельств в Москве огромен, включая документация о академическом и нормальном учебе, документы, дипломы колледжей и академий. Основное достоинство – возможность достать диплом Гознака, гарантирующий подлинность и качество. Это обеспечивает особая защита от фальсификаций и предоставляет возможность применять свидетельство для различных нужд. Таким образом, приобретение диплома в городе Москве является достоверным и оптимальным выбором для таких, кто желает достичь успеху в карьере.
Эй, ребята, чекайте новое казино – New Retro https://newretrocasino-play.ru В 2023 году они взорвали интернет своими видеослотами.
Я тут расскажу, что я там нашел, а вам решать, стоит ли пробовать свою удачу. Я, как настоящий гемблер, не мог проигнорировать это место, и вот что я для вас выяснил.
New Retro Casino открыло свои виртуальные двери в 2023 году. Вот только тут особый антураж – без лицензии, но с востребованными слотами.
Несмотря на такое начало, разработчики решили покорить рынок благодаря крутым промоакциям и бонусной программе.
Разработчики New Retro не жадничают на бонусы. Приветственные подарки – это как пригласительный коктейль в лучшем заведении.
А еще разнообразные акции и лояльность, как магнит для гемблеров.
Кто стоит за этим казино – загадка. Разработчики оставили все в секрете. Меня, конечно, такая тайна настораживает, но в слотах тут можно исключительно отдыхать, а не париться.
При входе меня встретил огромный баннер, будто на светских гала-вечеринках. Но не обманывайтесь внешним блеском, главное – качественные слоты.
Интерфейс New Retro Casino как родной дом. Легкая навигация, где каждый найдет свое – бонусы, игры, лояльность. Сайт на русском и английском, как на двух диалектах азартного мира.
О разработчиках и лицензии ни слова. Анонимность придаёт весьма загадочный шарм, хотя часть игроков не в восторге.
Как бы там ни было, в демоверсиях можно проверить, стоит ли покорять это новое казино.
В казино есть свой Telegram-канал. Тут каждый день новости, турниры и промокоды. Администрация дарит бонусы, а герои в чате делятся тактикой.
Официальный сайт младше многих гемблинг-заведений, но информации о нем пока еще маловато. Менеджеры говорят, что для подробностей нужно писать администрации.
New Retro Casino решительно работает без лицензии. Это уже поднимает много вопросов, но надежда на честную игру еще не покидает.
Так что, друзья, у меня все! Экспериментировать с новичком New Retro или нет – решать вам. Ссылка на казино здесь. Удачи в игре и крупных выигрышей!
[url=https://newretrocasino-play.ru]newretrocasino зеркало рабочее[/url]
фриспины каждые выходные
retro casino промокод
new retro casino рабочее зеркало
new retro casino промокоды бесплатно
актуальное new retro casino
new retro казино слоты
new retro casino казино официальный
new retro casino скачать приложение
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
Привет, гемблеры! Сегодня хочу поделиться своим опытом в онлайн-казино Голд https://goldcasinobonus.ru
Это новенький проект на рынке гемблинга, который я открыл для себя в 2021 году, и с тех пор мне удача улыбается.
На Голде, кроме классных игровых автоматов, я нашел море щедрых бонусов. Сразу после регистрации меня порадовал щедрый приветственный бонус, а для постоянных
клиентов тут тоже есть свои фишки. Не знаю, как у вас, но я всегда стараюсь выбирать казино без лицензии, но где азарт настоящий.
Именно это предлагает Голд, с сертифицированными слотами и выплатами, которые честно приносят выигрыши. Бонусы здесь как в подарках на ДР!
С первого депозита получаешь 111%, но не более 20 000 рублей. И чтобы не было скучно, к этому еще и фриспины подарят.
На сайте Голд казино официальный сайт выглядит темно и стильно. Баннеры с акциями моментально бросаются в глаза, а каталог и данные о выигрышах справа
сразу ощущение, что ты в мире азарта. Тут только слоты, но, друзья, их тут 233 штуки! Весь софт оригинальный, и удобное меню сделает ваш выбор легким и приятным.
И еще, не упустите отзывы. Мне они всегда помогают. Например, MelenaElian заметила, что ассортимент впечатляет, но некоторые слоты уже чувствуют себя прошлым летом.
А вот gaarwineInky, наоборот, не нашел здесь нужного уровня азарта. Все вкусы разные, но лично я нахожу здесь свою удачу.
Так что, гемблеры, вперед, проверьте свою удачу в Голд казино!
[url=https://goldcasinobonus.ru]игорный клуб голд[/url]
промокод на 30 бездепозитных спинов в голд казино
казино голд бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию
скачать приложение казино голд бесплатно
скачать голд казино на андроид
бездепозитный промокоды для казино голд
голд казино вход на iphone
голд казино регистрация на iphone
casino gold онлайн казино россии
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
Привет, форумчане! Хочу поделиться своим восторгом от казино JVSpin https://jvspincasinobonus.ru! Официальный сайт поражает своей огромной коллекцией игр – 7000 штук!
Это как погружение в азартное царство с игровыми автоматами, рулеткой, покером и многим другим. Кроме того, здесь найдется что-то для каждого: от live-дилеров до TV-игр и лото.
Плюс, разнообразные бонусы делают игру еще интереснее! Мой опыт игры стал невероятным благодаря jvspin casino, и я советую всем попробовать удачу! Официальный сайт подарил мне доступ к 7000 играм от лучших провайдеров,
включая NetEnt, Pragmatic Play и Evolution Gaming! На этом космическом казино jvspin валюты не ограничиваются – 50 валют для ведения счета, включая криптовалюты! А бонусы – просто взрыв мозга! Очень рекомендую, друзья!
[url=https://jvspincasinobonus.ru]jvspin регистрация[/url]
дживиспин казино
jvspin casino мобильная версия
jvspin казино официальный сайт мобильная скачать
jvspin казино официальный сайт мобильная версия скачать бесплатно на андроид
jvspin официальный сайт casino
jvspin casino бонус
jvspin казино зеркало
скачать jv spin казино
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
Здравствуйте!
Промокоды для интернет-магазина М.Видео — это специальные коды, которые можно активировать при оформлении заказа на официальном сайте компании.
Они предоставляют дополнительные преимущества покупателям в виде скидок на конкретные товары или услуги, бесплатной доставки или других бонусов.
Как найти промокоды для М.Видео? Они часто предоставляются в рамках специальных акций компании, которые могут проводиться на ее официальном сайте,
в социальных сетях или на проекте promokodbar.ru
Сайт самых свежих и проверенных промокодов магазина М.Видео https://promokodbar.ru
Удачных покупок!
выгодные купоны М.Видео
купоны для сэкономленных денег в М.Видео
Специальные предложения М.Видео
Эксклюзивные акции и скидки в М.Видео
бесплатные промокоды М.Видео
Удачи!
Новые игры в онлайн казино Беларусь: обзор самых популярных слотов
онлайн казино [url=https://onlinecasinobelarus.by/]онлайн казино[/url] .
Эй! Сегодня хочу поделиться своим опытом в казино Лев https://levcasinoclub.ru/. Эта космическая платформа стоит на орбите с 2014 года, и я здесь чувствую
себя как настоящий астронавт фортуны. Что вы за звери такие, Лев? С вашим приветственным пакетом и эксклюзивными бонусами от Телеграм-бота, это как попадание
в черную дыру удачи! Первыми запустили “Раздень девушку” — не могу не вспомнить адреналин от этой акции! Окей, немного звездной пыли: Лев ориентирован на нас,
русскоязычных гемблеров. Сайт темный как космос, но в меню скрыты все тайны. Переходи в лотереи, турниры, акции – все под рукой.
В футере есть ссылки на FAQ, но признаться, там все так же расплывчато, как черные дыры в космосе. Но разве это мешает нашим космическим приключениям?
Нет! И теперь о финансах. Минимальный депозит — всего 100 рублей! Это как древний артефакт для начала космического вояжа.
А способы пополнения? Мир, СБП, криптовалюты – словно выбор оружия в борьбе с врагами. Попробовал вывести выигрыш? Минимум – 200 рублей,
а лимитов на вывод как нету вообще – свобода в космосе, братан! И помни, в этом космическом клубе существует лишь одно ограничение — предел твоей фантазии!
Регистрируйся тут и отправляйся в своё азартное путешествие в бескрайнюю вселенную казино Лев! Удачи в полёте!
[url=https://levcasinoclub.ru/]лев слоты[/url]
lev casino можно играть
приложение клуб лев
лев автоматы скачать
lev casino промокоды бездепозитный
club lev с апк
скачать бесплатно лев казино
скачать казино лев настоящий
скачать бесплатно приложении lev казино
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
Привет, гемблеры! Да-да, это тот самый Лаки Лох! Сегодня расскажу вам о казино, которое я, как ковбой в старых добрых вестернах, нашел в бескрайних
просторах интернета. Позвольте представить – Vodka Casino https://vodka-casino-win.ru
Название — нешуточное! Эти ребята точно не шутят. Залитый азартом сайт Vodka Casino стартовал в 2020 году, и с тех пор не унимается.
Доступ из любой точки мира! Эй, вы там, в России, СНГ, Азии или даже в Южной Америке! Vodka Casino приглашает всех без исключения. Как глобальный ковбой, я в этом уверен.
Игры – в тему! Слоты от NetEnt, Play’n GO, Pragmatic Play, и другие – тут даже самому требовательному ковбою хватит игр на долгие часы.
Криптовалюты приветствуются! Специально для тех, кто ценит анонимность, Vodka Casino подключили криптовалюты. Bitcoin, Litecoin, Tether – выбирайте, какой микс предпочтете!
Профессиональное ковбойское оформление! Интерфейс, простой как ковбойский пистолет. Отлично продуманная навигация, бегущие строки с последними ставками, да еще и сленг-режим. Ощущение, будто в казино вошел через салун.
Бонусы — как выстрелы из револьвера! Большие и щедрые, как западные равнины. Розыгрыши, турниры, VIP-программа. Выбирай, стреляй, выигрывай!
Глобальный чат поддержки! Как в любом нормальном заведении, у Vodka Casino есть бар, где можно напрячь нервы и уточнить все нюансы.
Безопасность — на высоте! Сертификаты SSL, лицензия Кюрасао – ваши данные в надежных руках.
И помните, ковбои, приключения только начинаются! Залетайте в Vodka Casino, соратники!
[url=https://vodka-casino-win.ru/]vodka bet casino официальный сайт[/url]
vodka bet casino зеркало
сайт казино водка
vodka casino бездепозитный бонус
водка казино вход на официальный сайт
водка casino
vodka casino промокод бездепозитный
vodka казино регистрация
vodka casino регистрация водка бет
Удачи и прибыли Друзья!
[url=https://olisinopril.online/]lisinopril hct[/url]
mojmelimajmuea.com
그러나 그는 Beiwowei라는 단어를 보았습니다.
Доброго!
Было ли у вас опыт написания дипломной работы в крайне сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и трудоемкости, однако важно сохранять упорство и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, как я это делаю.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно помогает в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке https://saksx-diploms24.com, это проверенный источник!
купить диплом о среднем образовании
купить диплом о среднем специальном
купить диплом колледжа
купить аттестат школы
где купить диплом
купить диплом магистра
купить диплом бакалавра
купить диплом специалиста
купить диплом техникума
купить диплом о высшем образовании
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
Доброго!
Были ли у вас случаи, когда приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и трудоемкости, но важно не отступать и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, как я.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно находить и использовать информацию в сети, это действительно помогает в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями тут https://2orik-diploms.com, это проверенный источник!
купить диплом техникума
купить диплом бакалавра
купить аттестат
купить диплом
купить аттестат школы
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
Доброго!
Были ли у вас случаи, когда приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и трудоемкости, но важно не отступать и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, как я.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно находить и использовать информацию в сети, это действительно помогает в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями тут https://1russa-diploms.com, это проверенный источник!
купить диплом Вуза
купить аттестат
купить диплом специалиста
купить аттестат школы
купить диплом о среднем образовании
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
Доброго!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, как я.
Для тех, кто умеет быстро находить и анализировать информацию в сети, это действительно помогает в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями на сайте https://1russa-diploms.com, это проверено!
купить диплом специалиста
купить диплом о высшем образовании
купить диплом колледжа
купить аттестат
купить диплом нового образца
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
Лучшие онлайн казино Беларуси: топ 5 заведений для игры
онлайн казино [url=https://onlinecasinobelarus.by/]онлайн казино[/url] .
Здравствуйте!
Были ли у вас случаи, когда вам приходилось писать дипломную работу в сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и усилий, но важно не сдаваться и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, как я.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно искать информацию в интернете, это действительно облегчает процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями на [url=https://saksx-diploms24.com/]купить диплом ссср[/url], это проверенный источник!
купить диплом цена
купить диплом университета
купить диплом техникума
купить диплом института
купить аттестат
купить диплом Гознак
купить диплом колледжа
купить диплом специалиста
купить аттестат школы
купить диплом о высшем образовании
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
Здравствуйте!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, чем я и занимаюсь.
Для тех, кто умеет искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно облегчает процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке [url=https://3russkiy-diploms.com]купить диплом о среднем специальном[/url], это проверено!
купить диплом о среднем образовании
где купить диплом
купить диплом в Москве
купить аттестат школы
купить аттестат
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
Доброго!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в очень ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и тяжелого труда, но важно не сдаваться и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, так же, как и я.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно использовать интернет для поиска и анализа информации, это действительно облегчает процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с дипломным руководителем. Здесь представлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке https://server-diploms.com, это проверенный способ!
купить диплом Вуза
купить аттестат
купить диплом техникума
купить диплом Гознак
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
Доброго!
Вы когда-нибудь писали диплом в сжатые сроки? Это очень ответственно и тяжело, но нужно не сдаваться и делать учебные процессы, чем Я и занимаюсь)
Тем кто умеет разбираться и гуглить информацию, это действительно помогает по ходу согласований и написания диплома, не нужно тратить время на библиотеки или встречи с дипломным руководителем, вот здесь есть хорошие данные для заказа и написания дипломов и курсовых с гарантией и доставкой по России, можете посмотреть здесь https://server-diploms.com, проверено!
купить диплом института
купить диплом специалиста
купить диплом о среднем образовании
купить диплом Гознак
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
Здравствуйте!
Промокоды для интернет-магазина М.Видео представляют собой специальные коды, которые можно использовать при оформлении заказа на официальном веб-сайте компании.
Они приносят дополнительные преимущества покупателям в виде скидок на определенные товары или услуги, бесплатной доставки и других бонусов.
Как их найти? Чаще всего промокоды предоставляются в рамках специальных акций компании, которые могут проводиться на ее официальном веб-сайте,
в социальных сетях или на ресурсах, таких как проект promokodbar.ru
Сайт самых свежих и проверенных купонов магазина М.Видео https://promokodbar.ru
Удачных покупок!
новые купоны М.Видео
рабочие купоны М.Видео
Лучшие предложения М.Видео
Привилегированные купоны М.Видео
Промокоды для умных покупок в М.Видео
Удачи!
Здравствуйте!
Были ли у вас случаи, когда приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и трудоемкости, но важно не отступать и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, как я.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно находить и использовать информацию в сети, это действительно помогает в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями тут https://2orik-diploms.com, это проверенный источник!
купить диплом о высшем образовании
купить диплом колледжа
купить диплом университета
купить диплом о среднем специальном
купить диплом ссср
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
Мастерская по перетяжке мебели в Минске
реставрация мебели [url=https://obivka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]https://obivka-mebeli-vminske.ru/[/url] .
Доброго!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, чем я и занимаюсь.
Для тех, кто умеет искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно облегчает процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке [url=https://3russkiy-diploms.com]купить аттестат[/url], это проверено!
купить аттестат
купить диплом ссср
купить диплом о среднем образовании
купить диплом техникума
купить диплом
Желаю всем отличных оценок!
Качественно перетянем мебель в Минске – долгое время сохранится ее вид
перетяжка дивана в минске [url=https://obivka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]https://obivka-mebeli-vminske.ru/[/url] .
Твоя мебель выглядит устаревшей? Перетяни ее в Минске!
ремонт и перетяжка мягкой мебели [url=https://obivka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]https://obivka-mebeli-vminske.ru/[/url] .
Мастерская по перетяжке мягкой мебели в Минске – доверенный выбор
обновление мебели [url=https://obivka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]https://obivka-mebeli-vminske.ru/[/url] .
depakote davis pdf
cozaar rebate
Онлайн казино в Беларуси с мобильной версией: играйте в любое время и в любом месте
онлайн казино [url=https://onlinecasinobelarus.by/]казино беларусь[/url] .
Онлайн казино с быстрыми выплатами в Беларуси: безопасные транзакции
онлайн казино [url=https://onlinecasinobelarus.by/]онлайн казино[/url] .
[url=http://olisinopril.online/]can i buy lisinopril in mexico[/url]
Мастерская по перетяжке мебели в Минске
ремонт офисных кресел [url=https://obivka-mebeli-vminske.ru/]https://obivka-mebeli-vminske.ru/[/url] .
cozaar side effects cough
Перетяжка мягкой мебели в Минске: бережно и безупречно
ремонт стульев [url=https://obivka-divana.ru/]https://obivka-divana.ru/[/url] .
depakote loading dose
Перетяжка мебели в Минске: не просто ремонт, а настоящее преображение
перетяжка дивана [url=https://obivka-divana.ru/]https://obivka-divana.ru/[/url] .
Доверь перетяжку мебели профессионалам в Минске
перетяжка [url=https://obivka-divana.ru/]https://obivka-divana.ru/[/url] .
how long does it take for citalopram to kick in
Hello, World!
Hey there, mate! Greetings from your favorite surfing capybara!
How’s the surf today?
Ready to catch some gnarly waves together?
https://capybara999.wordpress.com/
Good luck!
Доверь перетяжку мебели квалифицированным специалистам в Минске
перетяжка кресла [url=https://obivka-divana.ru/]https://obivka-divana.ru/[/url] .
Красивая и уютная мебель – это реально! Перетяжка в Минске
перетяжка минск [url=https://obivka-divana.ru/]https://obivka-divana.ru/[/url] .
Хочешь обновить интерьер? Перетянем твою мебель в Минске
перетянуть диван [url=https://obivka-divana.ru/]https://obivka-divana.ru/[/url] .
Ремонт и перетяжка мягкой мебели в Минске: качество гарантируем
перетяжка мебели цена [url=https://obivka-divana.ru/]https://obivka-divana.ru/[/url] .
Качественно перетянем мебель в Минске – долгое время сохранится ее вид
реставрация мебели [url=https://obivka-divana.ru/]https://obivka-divana.ru/[/url] .
Перетяжка мебели в Минске: не просто ремонт, а настоящее преображение
перетяжка мебели цена [url=https://obivka-divana.ru/]https://obivka-divana.ru/[/url] .
free porn download hd gghkyogg.BEIMkC4FSVU
porn free download ggjennifegg.FrbyaI9tcku
Bonos sin deposito: juega gratis en el casino
bono de casino sin deposito [url=https://bono-casino-sin-deposito-peru.com/]casino online con bono sin deposito[/url] .
hd porna ggjinnysflogg.FkCQPdXqOfh
Aumenta tus ganancias con el bono casino sin deposito
casino online con bono de bienvenida sin deposito [url=https://bono-casino-sin-deposito-peru.com/]bono casino sin deposito[/url] .
hihouse420.com
그들의 마음 속에는 현재의 황제가 가장 현자입니다.
[URL=https://bigpicture.ru/vostrjebovannyje-profjessii-v-sfjerje-markjetinga-kljuchjevyje-napravljenija/]Купить аттестат[/URL] – Это получить официальный удостоверение о среднеобразовательном учении. Свидетельство гарантирует доступ в широкому спектру профессиональных и образовательных возможностей.
[url=http://tadalafilu.online/]tadalafil 20[/url]
depakote side effects bipolar
cozaar drug interactions
Привет всем!
Было ли у вас опыт написания дипломной работы в крайне сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и трудоемкости, однако важно сохранять упорство и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, как я это делаю.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно помогает в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке https://1server-diploms.com, это проверенный источник!
купить диплом цена
купить диплом магистра
Желаю любому отличных оценок!
[url=http://valtrexarb.online/]where to buy valtrex[/url]
a healthcare professional is caring for a patient who is about to begin taking losartan (cozaar)
[url=http://bmtadalafil.online/]tadalafil 2.5 mg daily[/url]
half life of depakote
citalopram 10mg high
https://otdelkaexp.ru/novosti/plastikovye-izdeliya-ot-proizvoditelya.html
?Juega gratis y gana en el casino con el bono sin deposito!
casino online bono sin deposito [url=https://bono-casino-sin-deposito-peru.com/]casino online bono sin deposito[/url] .
[url=https://asynthroid.com/]price of synthroid in canada[/url]
?Bonos exclusivos! Bono casino sin deposito
bono gratis para casino sin deposito [url=https://bono-casino-sin-deposito-peru.com/]casino en linea con bono de bienvenida sin deposito[/url] .
?Gana dinero sin invertir! Bono casino sin deposito
bono sin deposito casino peru [url=https://bono-casino-sin-deposito-peru.com/]casino online bono por registro sin deposito[/url] .
?Registrate y recibe tu bono casino sin deposito!
casino online bono por registro sin deposito [url=https://bono-casino-sin-deposito-peru.com/]casino bono de bienvenida sin deposito[/url] .
Мы коллектив SEO-экспертов, специализирующихся на повышении посещаемости и рейтинга вашего сайта в поисковых системах.
Мы постигли успехи в своей области и желаем поделиться с вами нашими знаниями и навыками.
Какими преимуществами вы сможете воспользоваться:
• [url=https://seo-prodvizhenie-ulyanovsk1.ru/]seo продвижение цена[/url]
• Тщательный анализ вашего сайта и разработка персональной стратегии продвижения.
• Оптимизация контента и технических характеристик вашего сайта для достижения наивысших результатов.
• Регулярное отслеживание и анализ результатов, с целью постоянного улучшения вашего онлайн-присутствия.
Подробнее [url=https://seo-prodvizhenie-ulyanovsk1.ru/]https://seo-prodvizhenie-ulyanovsk1.ru/[/url]
У наших клиентов уже есть результаты: повышение посещаемости, улучшение позиций в поисковых запросах и, конечно же, рост бизнеса. Вы можете получить бесплатную консультацию у нас, для обсуждения ваших потребностей и разработки стратегии продвижения, соответствующей вашим целям и бюджету.
Не упустите возможность улучшить свой бизнес в онлайн-мире. Свяжитесь с нами сегодня же.
Здравствуйте!
Слушая Яндекс Музыку, я каждый раз открываю для себя новые талантливые исполнители. Недавно я услышал трек “Нагадай” от Ромы Фобоса и был приятно удивлен качеством его музыки.
Текст песни проникает в душу, а мелодия заставляет возвращаться к этой композиции снова и снова.
Очень рад, что в нашей стране есть музыканты, способные создавать такие шедевры.
Рекомендую всем любителям качественной музыки обратить внимание на творчество Ромы Фобоса – это действительно стоит того!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hAtCepwiMyk
[url=https://music.yandex.ru/album/29137540/track/121339732] послушать песню забыть нельзя вернуться невозможно [/url]
послушать песню снег кружится летает летает
позволь послушать твою песню дорама
слушать песню ты знаешь как хочется жить
инна вальтер послушать песню
слушать песню седая ночь
слушать песню если с другом вышел в путь
слушать песню три желания
слушать песню зима в сердце
слушать песню ой
послушать песню игоря талькова
Удачи и хорошего вайба!
diclofenac sodium dr 50 mg
augmentin pregnancy
augmentin for sinusitis
Hello music lovers!
п»ї
Globex Music to doskonała okazja dla młodych, niezależnych muzyków, którzy chcą wykorzystać swoje umiejętności w branży muzycznej, nie ryzykując konfliktu z prawem.
Usługa umożliwia artystom szeroką widoczność i promocję ich coverów, co może przyczynić się do zwiększenia ich popularności i szansy na ekspansję na nowe rynki muzyczne.
https://bit.ly/3VpnQZp
[url=https://distro.globexmusic.com/register.php?ref=ZU0VL] cover license distrokid [/url]
a cover song
how are song covers legal
odd cover songs
get mechanical license
cover song license price
groove coverage she
best music distribution for cover songs
cover song licensing – get a mechanical license
free cover song licensing
cover songs definition
Good luck and good vibe!
diclofenac sodium gel uses
Привет всем!
Сочи – уникальный город, славящийся своими безграничными возможностями для отдыха и развлечений.
В Сочи также можно найти множество объектов культурного наследия, которые являются непременным посещением для исторических энтузиастов.
Например, Дендрарий является одним из самых больших ботанических садов не только в России, но и в Европе. Здесь собраны уникальные коллекции растений со всего мира,
а атмосфера тишины и красоты помогает расслабиться и насладиться природой.
Сочи – уникальный город, славящийся своими безграничными возможностями для отдыха и развлечений.
Кроме того, Сочи славится своими пляжами, которые простираются на множество километров. Здесь вы найдете пляжи для любого вкуса: от живописных галечных бухт
до широких песчаных пляжей. Можно подышать свежим морским воздухом, искупаться в теплой воде и насладиться прекрасными видами.
Рекомендую всем, лучший справочник про Сочи https://chto-posmotret-v-sochi.ru
[url=https://chto-posmotret-v-sochi.ru/]Сочи февраль что посмотреть[/url]
лоо Сочи что посмотреть
мамайка Сочи что посмотреть
город Сочи достопримечательности
Сочи набережная что посмотреть
Удачи и хорошего визита в Сочи!
Доброго!
White Queen не перестаёт удивлять: трек “Дорога домой” уже завоевывает сердца слушателей.
Танцевальный трек “Дорога домой” от White Queen вызывает настоящий ажиотаж среди поклонников музыки.
Его мелодия проникает глубоко в душу каждого слушателя, а текст песни заставляет задуматься о жизни и путешествии к себе.
Это абсолютно уникальная композиция, которая навсегда заслуживает места в вашем плейлисте.
https://apple.co/3PtdqE6
[url=https://music.yandex.ru/album/29110942/track/121285337] танцевальная музыка 22 года [/url]
веселая танцевальная песня скачать бесплатно
танцевальная музыка американская
скачать песню white queen застольная
танцевальная музыка без слов слушать бесплатно
цыганская песня танцевальная
танцевальная музыка в современной обработке
queen white queen
танцевальная песня скачать бесплатно
танцевальная музыка городских негров
танцевальная песня в караоке
Удачи и хорошего вайба!
Ich stehe total auf manner die wissen was sie wollen and live cams blonde auf geile gesprache! Wenn du auf junge curvy blondienen mit gro?en Brusten stehst bist du bei mir genau richtig.
ttbslot.com
나만… 모두가 나를 아저씨라고 부르지만 진짜 제자는 거의 없다.
ezetimibe nice guidelines
street value of flexeril
flomax cialis interactions
side effects from taking flomax
soma vs flexeril
Почему рулонный газон пользуется популярностью
рулонный газон купить в москве [url=https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/]https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/[/url] .
Как сделать укладку рулонного газона своими руками
рулонный газон стоимость м2 [url=https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/]https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/[/url] .
[url=http://olisinopril.com/]can i order lisinopril online[/url]
Как поддерживать зеленый цвет рулонного газона
рулонный газон с доставкой [url=https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/]https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/[/url] .
Какая трава используется в рулонном газоне
рулонный газон цена [url=https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/]https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/[/url] .
Идеи для декорирования сада с помощью рулонного газона
рулонный газон купить [url=https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/]https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/[/url] .
Как сделать укладку рулонного газона своими руками
рулонный газон купить [url=https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/]https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/[/url] .
Какова стоимость установки рулонного газона
рулонный газон купить в московской области цена [url=https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/]https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/[/url] .
Our knowledge in digital wallets and online transactions means we’re well-prepared to tackle
your QIWI wallet issues.
Rest assured, we use state-of-the-art techniques and keep up with the current security protocols.
In case of hit with unauthorized transactions or issues that resulted in a loss of funds,
we’re here to help.
risperidone and aripiprazole
amitriptyline generic and brand name
amitriptyline hcl 10 mg tab tablet
Привет всем!
https://i4car.net/category/moto/ – ваш путеводитель в мире автомобилей. Здесь вы найдете все от обзоров и тест-драйвов до советов по выбору и уходу за автомобилем.
[url=https://i4car.net/]https://i4car.net/[/url]
i4car.net
мотоциклы
Удачи и хорошей дороги!
other names for aripiprazole
[url=https://olisinopril.com/]lisinopril 40 mg tablet[/url]
can allopurinol make gout worse
Привет любители машин!
https://dtp.vn.ua/category/video/ — это не просто сайт о ДТП в Виннице, это платформа для обмена важной информацией, которая может спасти жизни. Наши репортажи, снабженные фото и видео, делают освещение дорожно-транспортных происшествий максимально полным и объективным.
[url=https://dtp.vn.ua/category/video/]Видео ДТП[/url]
ДТП видео
ДТП Винница видео
Удачи и хорошей дороги!
[URL=https://femcfas.ru/ ]Купить диплом в набережных челнах[/URL] – Это способ получить официальный бумага по окончании образовательного учреждения. Свидетельство открывает пути к дополнительным карьерным возможностям и профессиональному росту.
baclofen liver
bupropion alcohol interaction
qiyezp.com
결국 그는 먼저 인간이고 그다음에 황제이며 인간은 여전히 다른 사람에게 칭찬 받기를 좋아합니다.
[url=http://cetka.webtalk.ru/viewtopic.php?id=3773#p8327]http://cetka.webtalk.ru/viewtopic.php?id=3773#p8327[/url]
[url=http://www.tamboff.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?p=7695163#7695163]http://www.tamboff.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?p=7695163#7695163[/url]
Привет любители музыки!
Как стать успешным музыкантом благодаря сервису musicdistro. Musicdistro предоставляет музыкантам возможность расширить свою аудиторию и заработать
на своем творчестве через лицензирование и распространение кавер-версий песен.
Гарант сервиса помогает обезопаситься от мошенников и обеспечивает надежность в процессе монетизации музыки.
https://stars-style.ru/any/mozhno-li-ispolzovat-kaver-v-kommercheskikh-celyakh-9u8v2/
[url=https://soft.masterit.ru/reviews/7205569-poem-kavera-legalno-i-zakonno-monetiziruem-9ke/] Нужно ли разрешение на исполнение кавера? [/url]
Как сделать кавер на песню
Куда заливать свои каверы чтобы не получить штраф
Выпустить свою музыку на цифровых площадках
Как выложить кавер без нарушения авторских прав
Дистрибуция музыки и каверов
Получить лицензию на кавер песни
Лицензирование каверов
Издание кавер версий
Монетизация кавер-версий
Как получить разрешение на кавер песни?
Удачи и хорошего вайба!
how long does it take for bupropion to work
how much baclofen to get high
[url=https://olisinopril.com/]lisinopril 2.5 mg cost[/url]
fashionflag hd pprn videos fashionflag.AMIaUoUn6JH
Привет любители музыки!
White Queen возглавляет чарты с новым треком “БАС”. Ее талант и вкус к музыке делают эту композицию по-настоящему уникальной и запоминающейся.
“БАС” – это новый хит от White Queen, который уже назвали одним из лучших танцевальных треков современности. Эта композиция просто обречена на успех.
White Queen дарит слушателям новый трек “БАС” в стиле рейв. Эта композиция звучит необычно и свежо, привнося в мир клубной музыки что-то новое и захватывающее.
https://vk.com/music/album/-2000205055_20205055_3ee88b782e18970b07
[url=https://vk.com/music/album/-2000205055_20205055_3ee88b782e18970b07] благословляю на рейв слушать [/url]
слушать музыку онлайн подряд ютуб
послушать музыку послушать музыку
слушать музыку цоя
послушать музыку сергея завьялова
послушать музыку малиновая лада малиновый закат
слушать музыку ласковый май
видео слушать музыку
слушать музыку в интернете
слушать музыку юрия шатунова бесплатно
слушать музыку вивальди
Удачи и хорошего вайба!
augmentin 500 mg
tramadol celebrex
Доброго!
White Queen продолжает удивлять своих слушателей творческими новинками, среди которых особое место занимает трек “БАС”. Этот трек вызывает восторг и восторг у музыкальной аудитории, что подтверждает его высокий уровень качества и оригинальность исполнения.
Новый трек White Queen “БАС” уже стал хитом сезона среди поклонников качественной танцевальной музыки. Его энергетика и драйв не оставляют равнодушными никого, а его яркий и запоминающийся звук станет незаменимым сопровождением на любой вечеринке или танцевальном событии.
White Queen представила новый танцевальный трек “БАС”. Энергичный и запоминающийся рейв-звучание уже завоевало сердца многих поклонников музыки.
https://vk.com/music/album/-2000205055_20205055_3ee88b782e18970b07
[url=https://open.spotify.com/track/43vEJEFIUdbxNOJehmIMLu] слушать музыку ремикс [/url]
слушать музыку на телефоне бесплатно
слушать музыку кавказа
слушать музыку шансон онлайн бесплатно
слушать музыку для занятия физкультурой
послушать хорошую музыку онлайн бесплатно
слушать музыку релакс
русский рейв слушать
где послушать классическую музыку в екатеринбурге
слушать музыку грига
послушать хорошую музыку бесплатно
Удачи и хорошего вайба!
goodhere Pregnant porn vurucutewet.QGrSXESj021
ladyandtherose Cunnilingus porn backlinkseox.uA6UPcrORPe
ashwagandha for kids
Привет всем!
Продажи на маркетплейсах сегодня играют ключевую роль в стратегии роста для многих онлайн-бизнесов. Одним из наиболее эффективных способов увеличения этих продаж является использование Яндекс.Директ — мощного инструмента для целевой рекламы, который позволяет привлекать заинтересованных покупателей непосредственно на ваши страницы на маркетплейсах. Сочетание продаж на маркетплейсах и Яндекс.Директа создает уникальные возможности для масштабирования бизнеса и повышения его эффективности.
Продажи на маркетплейсах и Яндекс Директ — это комбинация, которая требует тщательного планирования и постоянной оптимизации. Прежде всего, важно определить целевую аудиторию ваших товаров и подобрать соответствующие ключевые запросы, чтобы ваши рекламные объявления показывались потенциальным покупателям в самый подходящий момент. Эффективная настройка рекламных кампаний в Яндекс.Директе позволяет не только привлекать новых клиентов, но и возвращать тех, кто уже посещал ваши страницы на маркетплейсах, но не совершил покупку.
Для увеличения продаж на маркетплейсах через Директ, рекламодателям необходимо внимательно отслеживать эффективность своих кампаний, анализировать поведение пользователей и корректировать стратегию в зависимости от полученных данных. Это может включать изменение ставок, модификацию объявлений или пересмотр целевых страниц. Важно также учитывать сезонность и текущие тренды, адаптируя рекламные сообщения и предложения к текущим потребностям рынка.
Использование Яндекс.Директа для маркетплейсов [url=https://xn——6cdabba2akbga5a0afcgmineu8chdm8ahr3h.xn--p1ai]реклама маркетплейсов через яндекс директ[/url] не ограничивается простым размещением рекламы. Это включает в себя создание привлекательных и убедительных объявлений, которые могут включать уникальные предложения, акции и скидки, делая ваше предложение более привлекательным для потенциальных покупателей. Также, крайне важно уделять внимание качеству обслуживания клиентов и отзывам о товарах, поскольку положительные отзывы могут значительно улучшить видимость ваших товаров на маркетплейсах и увеличить доверие со стороны покупателей.
В заключение, комбинирование продаж на маркетплейсах с Яндекс.Директом — это стратегия, которая требует внимательного подхода к деталям, глубокого понимания рынка и готовности к постоянным изменениям. Однако при правильном подходе она открывает перед продавцами огромные возможности для роста и укрепления продаж.
Максимум информации по теме на: https://директ-реклама-на-маркетплейсах.рф
обучение внешней рекламе на маркетплейсах
яндекс реклама для маркетплейса
настройка яндекс директ для маркетплейсов
реклама маркетплейсов через яндекс директ
Удачи и хороших продаж!
jenniferroy バイセクシャルポルノ japanesexxporns.3NaVFTd3Mft
buspar vs xanax
Доброго!
Последние новости Кропивницкого: следите за жизнью города вместе с нами.
Ждем Вас на https://top10.kr.ua/category/news-ukraine/
[url=https://top10.kr.ua/category/news-ukraine/]Новости Украины сейчас[/url]
новости Украины
новости спорта
новости Кропивницкого аварии
Удачи и хороших новостей!
Здравствуйте!
В современном цифровом маркетинге, Директ для маркетплейсов является одним из ключевых инструментов для продвижения товаров и услуг на онлайн-платформах. Использование Яндекс.Директ позволяет максимально точно настраивать рекламные кампании, сосредотачиваясь на целевой аудитории и повышая эффективность продаж на различных маркетплейсах. Рекламодателям доступны разнообразные форматы объявлений, включая текстово-графические блоки, которые могут быть адаптированы под специфику товаров и потребности потребителей.
Эффективное использование Яндекс.Директ для маркетплейсов требует глубокого понимания как самой платформы Яндекс.Директ, так и особенностей работы маркетплейсов. Ключевым моментом является выбор правильных ключевых слов и фраз, которые помогут вашему объявлению появляться в топе поисковой выдачи именно тогда, когда потенциальные покупатели ищут ваши товары. Кроме того, необходимо внимательно работать над составлением текста объявления, делая акцент на уникальные преимущества продукта и привлекая внимание к специальным предложениям или акциям.
Реклама на маркетплейсах [url=https://директ-реклама-на-маркетплейсах.рф]яндекс директ реклама маркетплейсов[/url] через Директ открывает перед продавцами новые горизонты для увеличения продаж и расширения клиентской базы. Особенно это касается моментов, когда необходимо быстро вывести на рынок новый товар или привлечь внимание к сезонным распродажам. Благодаря гибким настройкам Яндекс.Директ, можно не только выбирать, кто увидит ваше объявление, но и контролировать бюджет рекламной кампании, оптимизируя расходы и повышая ROI.
Для максимальной эффективности Директа на маркетплейсах рекомендуется регулярно анализировать результаты рекламных кампаний, корректировать ключевые слова и фразы, а также экспериментировать с различными форматами объявлений. Это позволит оставаться на шаг впереди конкурентов и удерживать внимание потребителей.
Максимум информации по теме на: https://директ-реклама-на-маркетплейсах.рф
реклама маркетплейсов через яндекс директ
инструменты для внешней рекламы маркетплейсов
реклама товаров на маркетплейсах через яндекс директ
продажи на маркетплейсах и яндекс директ
Удачи и хороших продаж!
Здравствуйте!
Ваш путеводитель в мире новостей: свежие события из Украины и важные мировые итоги.
Ждем Вас на https://wian.top/category/health
[url=https://wian.top/category/mir]главные новости мира[/url]
новости туризма
новости Украины
все новости Украины
Удачи и хороших новостей!
Здравствуйте!
uFiler – это превосходный бесплатный торрент-клиент, который позволит вам скачивать файлы быстро и безопасно. Он имеет интуитивно понятный интерфейс,
благодаря которому вы сможете легко добавлять торрент-файлы, управлять активными загрузками, а также настраивать скорость скачивания.
С uFiler вы получите полный контроль над процессом загрузки торрентов. Скачайте это приложение на https://ufile-for-pc.ru/ и убедитесь в его преимуществах сами!
[url=https://ufile-for-pc.ru/]ufiler скачать на пк бесплатно[/url]
ufiler pro
как скачивать через ufiler
скачать ufiler без торрента
ufiler скачать торрент
Удачи и хорошего серфинга по торрентам!
[url=http://tadalafilstd.online/]discount cialis no prescription[/url]
Здравствуйте!
Мир глазами Украины: последние новости и важнейшие события, формирующие будущее.
Посетите https://wian.top/category/politics
[url=https://wian.top/]Последние новости Украины[/url]
все новости Украины
последние новости Украины
новости спорта
Удачи и хороших новостей!
landuse Girl Masturbating porn lancdcuse.jb8vRGXwHRt
buspirone and ginkgo biloba
[URL=https://gosznak-diploms.com/ ]https://goznak-dlplomy.com/ [/URL] Купить диплом о полном среднем образовании- Это способ обрести официальный бумага по окончании образовательного учреждения. Диплом открывает пути к последующим карьерным перспективам и профессиональному росту.
falbobrospizzamadison Blowjob porn jkkıjxxx.zzgsOS77xV3
benefits of ashwagandha for women
Здравствуйте!
Кропивницкий в деталях: последние новости, анализы и экспертные мнения.
Заходите https://0522.kr.ua/
[url=https://0522.kr.ua/category/news-ukraine/]Главные новости Украины[/url]
новости Кропивницкого видео
главные новости Украины
Удачи и хороших новостей!
[url=https://metforminbi.online/]metformin 1000 mg price india[/url]
गर्भवती अश्लील qqyyooppxx.4ojzF6WDvYj
celexa withdrawal side effects
celecoxib cox 2 inhibitors
बड़का गधा पोर्न के बा hjkvbasdfzxzz.vsoOqW2c3Kd
[url=https://bmtadalafil.online/]generic tadalafil 2017[/url]
you are actually a just right webmaster. The web site loading speed is incredible. It sort of feels that you are doing any unique trick. Moreover, The contents are masterwork. you’ve done a fantastic process in this subject!
[url=https://synthroidx.online/]synthroid rx[/url]
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]valtrex best prices[/url]
एशियाई अश्लीलता txechdyzxca.Xe8TWd6cmgE
दादी अश्लील hkyonet.T9JT35bWuv7
qiyezp.com
Zhang Heling은 약간 멍해졌고 너무 뜨거워서 먹는 것도 따라 잡지 못했습니다 *.
Место, где царит гармония и тепло
17. Дом из бруса 9х12: место для счастья и уюта
проект дома из бруса одноэтажный 9х12 [url=https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/]https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/[/url] .
Место для отдыха и вдохновения
14. Модный дом из бруса 9х12: стиль и качество
дом брус 9х12 [url=https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/]https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/[/url] .
Качество и надежность
7. Компактный дом из бруса 9х12: уютное гнездышко
дом из бруса 9х12 [url=https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/]https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/[/url] .
Уют и спокойствие под одной крышей
16. Комфортабельный дом из бруса 9х12: лучшее решение для семьи
дом из бруса 9х12 [url=https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/]https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/[/url] .
Уют и тепло в каждом уголке
20. Уникальный дом из бруса 9х12: мечта о доме сбылась
дома из бруса 9х12 [url=https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/]https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/[/url] .
Атмосфера волшебства и красоты
12. Эксклюзивный дом из бруса 9х12: индивидуальный подход
проект дома из бруса 9х12 [url=https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/]https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/[/url] .
ਵਿੰਟੇਜ ਅਤੇ ਨੌਜਵਾਨ ਪੋਰਨ madisonivysex.J7mCJvcHYje
Уютный уголок для семьи
6. Стильный дом из бруса 9х12: современный дизайн
проект дома из бруса одноэтажный 9х12 [url=https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/]https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/[/url] .
Стало время подключить прочный стабилизатор напряжения
стабилизаторы напряжения http://stabrov.ru.
semaglutide buy
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
abilify high
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
ladesbet ਹੱਥਰਸੀ ਪੋਰਨ ladesinemi.ugEuEUcDkCD
actos brasil
ladesbet レズビアンのポルノ ladestinemi.SheAvWimC1Q
ubat acarbose
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Нужен качественный ремонт ноутбука, моноблока или планшета Lenovo? Обратитесь в сервисный центр https://servisnyjcentr-lenovo.ru/! Здесь работают исключительно квалифицированные инженеры с многолетним опытом. Они досконально знают особенности техники Lenovo и готовы решить любые проблемы, связанные с ее эксплуатацией. В нашем арсенале – современное профессиональное оборудование для диагностики и ремонта, а также комплектующие напрямую от производителя. Благодаря этому мы гарантируем высокий уровень сервиса и продолжительный срок дальнейшей работы устройства после ремонта. Будьте уверены, ваша техника находится в надежных руках!
[url=https://servisnyjcentr-lenovo.ru/]леново сервис[/url]
lenovo замена разъема питания
замена аккумулятора в планшете леново
замена разъема зарядки леново
why does abilify cause weight gain
semaglutide jardiance
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
actos hypoglycemia
[url=http://lisinoprilos.online/]order lisinopril online[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
sandyterrace.com
이때 누군가가 오스만 대사관에 신속하게 소식을 보냈습니다.
robaxin bluelight
repaglinide eg 2 mg
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Если микроволновая печь Whirlpool вдруг перестала разогревать продукты или вовсе отказалась включаться, причиной может быть выход из строя магнетрона, системы электропитания или платы управления. Не пытайтесь самостоятельно ремонтировать технику – это крайне опасно из-за риска поражения микроволновым облучением! Доверьте диагностику и устранение неполадок профессионалам из сервисного центра https://whirlpool-rem.ru/. Наши мастера оперативно выявят причину некорректной работы СВЧ-печи и устранят ее с заменой вышедших из строя деталей. После ремонта ваша микроволновка будет работать идеально!
[url=https://whirlpool-rem.ru/remont-posudomoechnyh-mashin]ремонт посудомоечных машин whirlpool[/url]
плита вирпул сервисный центр
сервис вирпул москва
ремонт электроплит вирпул на дому
Доброго!
Путешествие по Москве начинается с ее символа – Красной площади. Здесь стоит памятник Минину и Пожарскому, Собор Василия Блаженного, ГУМ и Кремль. Экскурсия по Кремлю позволяет узнать об истории России, о власти царей и современного российского государства.
Москва – город с богатой историей и культурным наследием, который притягивает туристов со всего мира. Экскурсии по Москве предлагают возможность окунуться в удивительный мир этого города, узнать его тайны и загадки.
Рекомендую всем, лучший каталог про Москву https://multi-on.ru
[url=https://multi-on.ru]Экскурсии по Москве с трипстером[/url]
Смотровая экскурсия по Москве
Прогулки по Москве
Туристический обзор Москвы
Разведка местности в Москве
Удачи и хорошего визита в Москву!
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Не рискуйте испортить холодильник Stinol самостоятельным ремонтом. Обратитесь в [url=https://stinol-servise.ru/fridge/compressor/]замена компрессора в холодильнике стинол цена[/url] и получите гарантию качества.
ремонт стинол
замена таймера оттайки холодильника stinol
ремонт холодильников stinol
repaglinide suppliers india
Amplificadores de senal gsm
Potencia la senal de tu movil con un amplificador de alta potencia
[url=https://www.fimfiction.net/user/687982/NeilLopez23]https://www.fimfiction.net/user/687982/NeilLopez23[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprilgp.online/]cost of lisinopril 10 mg[/url]
qiyezp.com
Wang Xizuo는 “아니요 … 모르겠습니다.”
is robaxin a blood thinner
Amplificadores de senal gsm
Mejora la recepcion de senal de tu movil con un amplificador de calidad
[url=https://sketchfab.com/NeilLopez23]https://sketchfab.com/NeilLopez23[/url]
side effects of protonix
remeron
[URL=https://server-attestats.com/]https://server-attestats.com/[/URL] – Где купить аттестат- Это способ получить официальный удостоверение о завершении образовательного учреждения. Свидетельство открывает двери к дополнительным карьерным перспективам и карьерному развитию.
[url=https://oprednisone.com/]prednisone prescription[/url]
[url=http://synthroidsl.online/]synthroid brand name price[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprill.com/]medication lisinopril 20 mg[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprill.com/]lisinopril 40 mg generic[/url]
[url=http://prednisonexg.online/]prednisone 7.5 mg[/url]
Добрый день всем!
У нас вы можете заказать диплом Гознака по специальной цене с доставкой в любой регион России без предоплаты – надежно и выгодно!
http://russa24-attestats.com/
[url=http://synthroidam.online/]synthroid mexico pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilu.online/]tadalafil uk paypal[/url]
Amplificadores de senal gsm
Mejora la senal de tu movil con un amplificador de calidad
[url=https://socialtrain.stage.lithium.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/41358]https://socialtrain.stage.lithium.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/41358[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]happy family rx[/url]
[url=http://bmtadalafil.online/]tadalafil 5mg brand name[/url]
[url=http://bestmetformin.online/]metformin 100[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.兒童色情
[url=https://vatrex.online/]buy valtrex singapore[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.online/]azithromycin 500mg buy online[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinps.online/]buy 250 mg azithromycin[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprildrl.online/]lisinopril 10mg tablets[/url]
[url=https://ismetformin.online/]metformin cost in india[/url]
[url=http://synthroidam.online/]synthroid 0.125 mg[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinhq.com/]buy zithromax without presc[/url]
[url=https://synthroidam.online/]synthroid 700 mg[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
[url=https://isynthroid.online/]buy generic synthroid online[/url]
[url=http://vatrex.online/]valtrex online usa[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilstd.com/]tadalafil 2.5 mg tablets[/url]
[url=http://valtrexv.com/]buy valtrex online uk[/url]
[url=http://medicinesaf.online/]canadian pharmacy 365[/url]
[url=http://synthroidx.com/]buying synthroid online[/url]
kokulu mum
[url=http://bestmedsx.com/]online pharmacies that use paypal[/url]
[url=http://isynthroid.com/]synthroid 150 mcg cost[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilu.online/]tadalafil rx[/url]
[url=https://synthroidx.online/]synthroid uk[/url]
[url=https://tadalafi.online/]where to get tadalafil[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.online/]5mg tadalafil daily[/url]
[url=http://prednisonekx.online/]prednisone for sale in canada[/url]
Здравствуйте!
Закажите диплом ВУЗа по выгодной цене с доставкой в любой город России без предоплаты – надежно и выгодно!
http://saksx-attestats.ru/
Приобретите диплом Вуза с доставкой по России без предоплаты и полной уверенностью в его подлинности.
Недорого и без проблем купить диплом института, техникума, колледжа выгоднее всего у Нас, с доставкой по РФ
[url=http://synthroidotp.online/]synthroid 0.05mg tablet[/url]
[url=http://asynthroid.com/]cost of synthroid 100mcg[/url]
[url=https://synthroidotp.online/]synthroid 150[/url]
Достижение диплома по высшему образованию представляется значимым этапом в судьбе большого числа людей, открывая возможности в новым перспективам и путям.
Тем не менее, не постоянно обучение в вузе доступно или удовлетворяет по различным причинам.
При таких случаях вопрос где купить сертификат, делается значимым.
Современные технологические разработки и виртуальный рынок предлагают различные варианты для приобретения документа, но важно выбирать достоверных поставщиков, обеспечивающих качество и подлинность сертификата.
При отборе стоит обращать внимание не только на цену, но и на представление компании, комментарии клиентов и консультации перед покупкой.
[URL=https://keepnitreal.net/blogs/42409/%D0%9A%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC ]http://ford-talks.ru/topic4131.html?&p=17625 [/URL] купить диплом РІ димитровграде – значит инвестировать в свое будущее, поэтому отбор поставщика рекомендуется подходить серьезно.
[url=https://valtrexarb.online/]generic valtrex for sale[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprill.com/]zestoretic cost[/url]
[url=http://synthroidotp.online/]synthroid 100 mcg coupon[/url]
[url=http://metforminbi.online/]buy metformin india[/url]
[url=http://prednisonekx.online/]prednisone 50 mg cost[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]italian pharmacy online[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]generic pharmacy online[/url]
[url=https://asynthroid.com/]synthroid 0.50 mg[/url]
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]500g valtrex coupon[/url]
robaxin pill
[url=https://valtrexv.com/]order generic valtrex online[/url]
[url=https://isynthroid.com/]price of synthroid in india[/url]
gemfibrozil repaglinide interaction
[url=http://metformin.store/]metformin 500 mg discount[/url]
Привет любители гаджетов!
Подписывайтесь на наш ресурс, чтобы быть в курсе самых последних новостей и событий в мире смартфонов. Мы гарантируем вам доступ к эксклюзивным материалам и подробным обзорам, которые помогут вам быть в курсе самых последних тенденций и разработок.
В мире мобильных технологий бурлит событийный океан, и наш портал – ваш надежный компас в этом путешествии. Мы предлагаем вам всестороннюю обзорную статью о последних новостях в индустрии смартфонов.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://formobile.top/category/techno/
[url=https://formobile.top/category/techno/]технологии новости[/url]
смартфоны новости
новости от самсунг смартфоны
ит бизнес новости
Удачи!
[url=http://lisinoprilos.online/]lisinopril medication prescription[/url]
[url=https://valtrexv.com/]buy valtrex in mexico[/url]
[url=http://metformin.store/]best metformin brand[/url]
[url=http://synthroidx.com/]synthroid pharmacy coupon[/url]
[url=https://prednisoneo.online/]prednisone tablets[/url]
[url=https://olisinopril.online/]lisinopril 10 mg canada[/url]
[url=https://oprednisone.online/]5mg prednisone daily[/url]
[url=https://oazithromycin.com/]azithromycin for sale canada[/url]
[url=http://valtrexarb.online/]valtrex prescription cost[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprill.com/]lisinopril tab 20mg cost[/url]
que es spironolactone 25 mg
seo hizmeti
is sitagliptin insulin
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]cheap valtrex canada[/url]
[url=https://predniso.online/]cheapest prednisone no prescription[/url]
su yalıtımı
[url=https://lisinoprill.com/]lisinopril 20 mg price in india[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]reddit canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://valtrexmedication.com/]valtrex cost australia[/url]
synthroid education
[url=https://prednisonexg.online/]order prednizone[/url]
[url=https://medicinesaf.online/]online pharmacy usa[/url]
ısı yalıtımı
[url=https://valtrexv.com/]buy generic valtrex online cheap[/url]
[url=http://bestprednisone.online/]order prednisone with mastercard debit[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilstd.online/]tadalafil buy[/url]
aydın çıkışlı turlar
hello admin. nice entry. this my sites Casibom
[url=http://bmtadalafil.online/]india pharmacy tadalafil[/url]
Wow, fantastic blog format! How lengthy have you ever been blogging for?
you make blogging look easy. The total look of your
website is excellent, as smartly as the content!
You can see similar here najlepszy sklep
lupin sitagliptin
[url=http://synthroidotp.online/]best price for synthroid[/url]
[url=https://olisinopril.online/]cost of lisinopril in mexico[/url]
[url=http://prednisoneiv.online/]prednisone generic cost[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinps.online/]order azithromycin from mexico[/url]
aydın çıkışlı turlar
[url=https://oazithromycin.com/]azithromycin online order usa[/url]
[url=http://valtrexarb.online/]buy valtrex 1000 mg[/url]
[url=https://medicinesaf.online/]online canadian pharmacy coupon[/url]
zydus spironolactone 50 mg
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
synthroid fogginess
denizli çıkışlı turlar
[url=http://metforminbi.online/]medication metformin[/url]
[url=https://bmtadalafil.online/]how much is tadalafil cost[/url]
Приветики!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, как я.
Для тех, кто умеет быстро находить и анализировать информацию в сети, это действительно помогает в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями на сайте , это проверено!
https://flerus-shop.hcp.dilhost.ru/club/user/4/forum/message/523/519/#message519
купить диплом
купить диплом ссср
купить диплом колледжа
купить диплом о среднем специальном
где купить диплом
Желаю любому положительных отметок!
aydın çıkışlı turlar
[url=http://synthroidotp.online/]synthroid 100 pill[/url]
[url=http://bestmedsx.online/]pharmacy coupons[/url]
[url=http://oprednisone.online/]prednisone 20 mg online[/url]
ankara diş kliniği
[url=https://lisinoprilos.online/]zestoretic 10[/url]
[url=http://valtrexv.com/]buy valtrex australia[/url]
[url=http://synthroidam.online/]synthroid brand name cost[/url]
Доброго всем дня!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, чем я и занимаюсь.
Для тех, кто умеет искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно облегчает процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке [url=https://rudik-diploms365.com/]купить аттестат[/url], это проверено!
http://laver.listbb.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=3&sid=ca3e627e229bef64841c53e5078ffe4c
купить диплом Вуза
купить диплом ссср
купить диплом Гознак
купить диплом о высшем образовании
купить диплом бакалавра
Желаю всем пятерошных) отметок!
[url=http://medicinesaf.online/]online pharmacy same day delivery[/url]
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Los mejores juegos de casino en linea en Peru
mejor casino online peru [url=https://mejores-casinos-online-peru.com/]mejor casino online peru[/url] .
bursa avukat
?Gana grandes premios en los casinos en linea de Peru!
mejor casino online peru [url=https://mejores-casinos-online-peru.com/]online casino games peru[/url] .
Приветики!
Бывали ли у вас случаи, когда приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и напряженного труда, но важно не унывать и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, как я и делаю.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно находить и использовать информацию в интернете, это может существенно облегчить процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями на , это проверено!
http://sz.80lvl.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=9
купить диплом о высшем образовании
купить диплом колледжа
купить диплом специалиста
купить диплом нового образца
купить диплом цена
Желаю любому отличных отметок!
[url=https://oprednisone.online/]prednisone cream over the counter[/url]
ankara tercüme bürosu
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 現場兒童色情片
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]happy family drugstore[/url]
Siente la emocion de los casinos en linea en Peru con solo un clic
mejor casino online peru [url=https://mejores-casinos-online-peru.com/]mejor casino online peru[/url] .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
[url=https://valtrexmedication.online/]valtrex cost[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]best online pharmacy india[/url]
Los mejores casinos en linea de Peru para jugadores exigentes
mejor casino online peru [url=https://mejores-casinos-online-peru.com/]mejor casino online peru[/url] .
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Привет всем!
Бывали ли у вас случаи, когда приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и напряженного труда, но важно не унывать и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, как я и делаю.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно находить и использовать информацию в интернете, это может существенно облегчить процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями на , это проверено!
http://13.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=20&t=796
купить диплом ссср
купить диплом в Москве
купить диплом колледжа
купить диплом Гознак
купить диплом техникума
Желаю каждому нужных оценок!
?Descubre los mejores casinos en linea en Peru!
mejor casino online peru [url=https://mejores-casinos-online-peru.com/]mejor casino online peru[/url] .
Los mejores casinos en linea de Peru te esperan
casino en linea peru [url=https://mejores-casinos-online-peru.com/]casino en linea peru[/url] .
[url=http://azithromycinmds.com/]azithromycin 750 mg[/url]
[url=https://valtrexmedication.com/]valtrex tablet[/url]
Привет всем!
Бывали ли у вас случаи, когда приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и напряженного труда, но важно не унывать и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, как я и делаю.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно находить и использовать информацию в интернете, это может существенно облегчить процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями на , это проверено!
http://verkehrsknoten.de/index.php/forum/sozialvorschriften/topic/create
купить аттестат школы
купить диплом института
купить диплом бакалавра
купить диплом университета
купить диплом о среднем образовании
Желаю любому прекрасных отметок!
[url=https://tadalafilstd.online/]online pharmacy nz cialis[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinmds.com/]zithromax 250 mg price[/url]
Доброго всем дня!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, как я.
Для тех, кто умеет быстро находить и анализировать информацию в сети, это действительно помогает в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями на сайте , это проверено!
http://allukrnews.ru/kupit-svidetelstva-o-dopolnitelnom-obuchenii/
купить аттестат школы
купить диплом о среднем специальном
купить диплом института
купить диплом специалиста
купить диплом о среднем образовании
Желаю любому положительных отметок!
[url=https://synthroidotp.online/]medication synthroid[/url]
[url=https://isynthroid.online/]synthroid 50[/url]
[url=http://medicinesaf.online/]best value pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://pharmgf.online/]best online pharmacy[/url]
Привет, дорогой читатель!
Было ли у вас когда-нибудь такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не сдаваться и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, чем я и занимаюсь.
Для тех, кто умеет искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно помогает в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с дипломным руководителем. Здесь представлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке , проверено!
http://nukecritic.com/wiki/index.php/«аказать_сертификаты_о_дополнительном_обучении
купить диплом бакалавра
купить диплом о среднем образовании
купить аттестат
купить диплом специалиста
купить диплом университета
Желаю всем положительных оценок!
Как выбрать надежного букмекера
букмекерский сайт беларусь [url=https://bukmeker-bk.ru/]букмекерская контора[/url] .
[url=https://bestmedsx.com/]top online pharmacy india[/url]
[url=https://bmtadalafil.online/]tadalafil 10 mg canadian pharmacy[/url]
Привет, дорогой читатель!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, чем я и занимаюсь.
Для тех, кто умеет искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно облегчает процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке [url=https://rudik-diploms365.com/]купить аттестат школы[/url], это проверено!
https://birdsmoscow.mybb.ru/post.php?fid=5
купить диплом института
купить диплом цена
купить диплом нового образца
купить диплом о среднем образовании
купить диплом о среднем специальном
Желаю каждому отличных отметок!
[url=https://oazithromycin.online/]how to get zithromax[/url]
venlafaxine withdrawal treatment
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.儿童色情
viibryd and voltaren
[url=https://olisinopril.com/]how much is lisinopril[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprilgp.online/]lisinopril 2[/url]
Доброго всем дня!
Было ли у вас когда-нибудь так, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в очень сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и может быть очень тяжело, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, как я.
Для тех, кто умеет быстро находить и использовать информацию в интернете, это действительно облегчает процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями на сайте , это проверено!
http://rabotianadomy.frmbb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=2366#p2799
купить диплом нового образца
купить диплом о среднем образовании
купить диплом в Москве
купить диплом ссср
купить диплом колледжа
Желаю всем положительных отметок!
[url=http://metforemin.online/]buy metformin 500 mg[/url]
Доброго всем дня!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, чем я и занимаюсь.
Для тех, кто умеет искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно облегчает процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке [url=https://rudik-diploms365.com/]купить аттестат[/url], это проверено!
http://raussga.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=12&t=1819
купить диплом университета
купить аттестат
купить диплом нового образца
купить диплом Гознак
купить диплом техникума
Желаю каждому пятерошных) отметок!
[url=https://drugstorepp.online/]legitimate canadian mail order pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]best canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]trustworthy canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]international pharmacy no prescription[/url]
[url=https://man-attestats24.com/]man-attestats24.com[/url] – Где купить аттестат – путь для вашему будущему. На нашем сервисе все вы можете легко и быстро купить аттестат, нужный для последующего получения образования или трудоустройства. Наша консультанты гарантируют высокое качество и секретность предоставления услуг. Заказывайте школьный сертификат здесь и откройте новые возможности для того, чтобы вашего профессионального роста и трудоустройства.
Доброго всем дня!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, чем я и занимаюсь.
Для тех, кто умеет искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно облегчает процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке [url=https://rudik-diploms365.com/]купить диплом нового образца[/url], это проверено!
http://dp.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=458
купить диплом в Москве
купить аттестат
купить диплом техникума
где купить диплом
купить диплом Гознак
Желаю всем прекрасных отметок!
Рейтинг букмекера: как его оценить
букмекерские приложения [url=https://bukmeker-bk.ru/]самая лучшая букмекерская контора в интернете[/url] .
[url=http://predniso.online/]prednisone 10mg online[/url]
[url=http://valtrexid.com/]valtrex pills[/url]
[url=http://metformin.store/]metformin 500 for sale[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprilgp.online/]lisinopril 10 mg prices[/url]
[url=http://metformin.store/]generic metformin cost[/url]
Почему важен рейтинг букмекера
букмекерские приложения [url=https://bukmeker-bk.ru/]бетера букмекерская контора[/url] .
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]online med pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://bestprednisone.online/]prednisone 5mg cost[/url]
Таблица рейтинга букмекеров
самая лучшая букмекерская контора в интернете [url=https://bukmeker-bk.ru/]лучшая букмекерская онлайн[/url] .
[url=http://prednisonekx.online/]buy prednisone online without a prescription[/url]
Привет всем!
Бывало ли у вас такое, что приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует огромной ответственности и напряженных усилий, но важно не опускать руки и продолжать активно заниматься учебными процессами, чем я и занимаюсь.
Для тех, кто умеет искать и анализировать информацию в интернете, это действительно облегчает процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или устраивать встречи с дипломным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями по ссылке [url=https://rudik-diploms365.com/]купить диплом цена[/url], это проверено!
http://bristol.f-rpg.me/viewtopic.php?id=278#p2179
купить диплом университета
купить диплом
купить диплом института
купить диплом Вуза
купить диплом о среднем специальном
Желаю любому прекрасных отметок!
proper use of voltaren gel 1%
Как попасть в рейтинг букмекеров
бетера букмекерская контора [url=https://bukmeker-bk.ru/]спорт бизнес онлайн[/url] .
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]buy azithromycin without prescription in united states[/url]
Приветики!
купить диплом нового образца
Желаю любому положительных отметок!
http://www.diablomania.ru/forum/showthread.php?p=560057#post560057
купить диплом в Москве
купить диплом колледжа
купить диплом специалиста
Сравнение лучших букмекеров
рейтинг [url=https://bukmeker-bk.ru/]лучшие букмекерские конторы в беларуси[/url] .
venlafaxine withdrawal timeline
[url=http://synthroidam.online/]synthroid 150 coupon[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
[url=https://valtrexmedication.online/]buy valtrex no prescription[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]non prescription medicine pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://pharmgf.online/]best pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprilos.online/]lisinopril diuretic[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]escrow pharmacy online[/url]
[url=https://medicinesaf.online/]top online pharmacy india[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]zithromax pill[/url]
[url=http://tadalafi.online/]cialis buy no prescription[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.com/]all in one pharmacy[/url]
casibom casibom Casibom casibom casibom
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]buying from canadian pharmacies[/url]
[url=https://bmtadalafil.online/]buy online tadalafil[/url]
[url=https://tadalafi.online/]tadalafil 40mg[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilu.online/]generic tadalafil india[/url]
[url=https://drugstorepp.online/]mail order pharmacy india[/url]
tamsulosin 4mg side effects
[url=https://bestprednisone.online/]canine prednisone 5mg no prescription[/url]
[url=https://prednisoneiv.online/]steroid prednisone[/url]
[url=http://oprednisone.online/]prednisone 60 mg tablets[/url]
Привет всем!
Всем, кто проникается стихами, поэмами и собственным творчеством, Мay Poems предлагает лучшие произведения великих мировых поэтов и молодых талантов поэзии!
Я сам только начинающий поэт, и этот портал помог мне приобрести уверенность и писать более увлекательно и искренне.
Лучший способ погрузиться в мир поэзии и получать удовольствие от нее – читать стихи и творить свои собственные, а также обмениваться ими в сообществах и обсуждать с друзьями.
Поэзия действительно захватывает ум и душу, и вдохновляет на личный рост. Я рекомендую вам проводить время с пользой, занимаясь тем, что вас по-настоящему интересует!
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://may-poems.ru/
Лирика Арсения Тарковского
стихи поэтов классиков
стихи онлайн
Поэзия Бориса Гребенщикова
Удачи!
[url=http://lisinoprilgp.com/]lisinopril tabs 20mg[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
[url=http://valtrexmedication.com/]cost of valtrex generic[/url]
[url=http://isynthroid.online/]synthroid drug[/url]
[url=http://synthroidx.online/]synthroid 25 mcg tablet[/url]
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.活婴儿色情片
[url=http://azithromycinmds.com/]buy zithromax online[/url]
[url=http://ezithromycin.online/]azithromycin 2 tablets[/url]
[url=https://prednisoneo.com/]prednisone 5 mg tablets[/url]
[url=https://arusak-attestats.ru/]https://arusak-attestats.ru/[/url] – Купить школьный аттестат – возможность для вашему будущему. В данном портале все вы сможете легко и быстро приобрести свидетельство, обязательный для того, чтобы последующего получения образования или трудоустройства. Наши консультанты гарантируют качество и секретность услуги. Заказывайте школьный аттестат здесь и откройте дополнительные варианты для вашего образования и трудоустройства.
Доброго всем дня!
купить диплом университета
Желаю каждому пятерошных) отметок!
http://dancerussia.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?t=16180
купить диплом о среднем специальном
купить диплом нового образца
купить диплом специалиста
[url=https://tadalafi.online/]generic cialis canada price[/url]
В нашем обществе, где аттестат является началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед людьми, желающими вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести аттестат, и это является выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. Все аттестаты выпускаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам. В результате вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества этого подхода состоят не только в том, что вы быстро получите свой аттестат. Весь процесс организовывается просто и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца до правильного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
В результате, для тех, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Купить аттестат – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://prema-attestats.ru/
[url=https://lisinoprilgp.com/]lisinopril 5 mg over the counter[/url]
stop hair loss wellbutrin
[url=https://lisinoprilos.online/]buy lisinopril no prescription[/url]
Здравствуйте!
купить диплом специалиста
Желаю каждому нужных оценок!
http://www.rrsclub.ru/showthread.php?t=11805
купить диплом цена
где купить диплом
купить диплом о среднем специальном
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]zithromax purchase online[/url]
zetia side effects hair loss
[url=https://prednisonexg.online/]prednisone 10mg tablet cost[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]online pharmacy birth control pills[/url]
[url=http://prednisonekx.online/]can you buy prednisone[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]american online pharmacy[/url]
Добрый день всем!
купить диплом техникума
Желаю каждому положительных отметок!
http://www.dancerussia.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?p=23284
купить аттестат школы
купить диплом магистра
купить диплом Вуза
[url=https://prednisonekx.online/]prednisone generic cost[/url]
Привет всем!
купить диплом Вуза
Желаю любому нужных оценок!
http://mail.u-turn.kz/forums.php?m=posts&q=23921&n=last
купить диплом специалиста
купить диплом университета
купить диплом
[url=http://oprednisone.com/]prednisone buy canada[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]canadian pharmacy drugs online[/url]
[url=http://drugstorepp.online/]brazilian pharmacy online[/url]
[url=https://olisinopril.online/]lisinopril diuretic[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]zithromax 500 mg for sale[/url]
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]valtrex 500mg[/url]
[url=http://predniso.online/]prednisone 2.5 mg[/url]
[url=https://valtrexv.com/]valtrex rx[/url]
[url=https://valtrexbt.online/]valtrex generic in mexico[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]order zithromax without prescription[/url]
[url=http://olisinopril.com/]buy lisinopril online uk[/url]
[url=https://synthroidx.online/]synthroid 100 mg daily[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprilgp.com/]lisinopril cost[/url]
[url=https://medicinesaf.online/]generic pharmacy online[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.com/]tadalafil tablets india[/url]
uses of zyprexa
[url=http://bestmedsx.com/]wholesale pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://ismetformin.online/]metformin online without prescription[/url]
[url=http://valtrexarb.online/]purchase valtrex online[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprildrl.online/]generic lisinopril[/url]
[url=https://oprednisone.com/]cost of prednisone 10mg tablets[/url]
[url=http://medicinesaf.online/]trusted online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilgf.com/]cialis for sale in usa[/url]
[url=http://synthroidsl.online/]synthroid 75 mg[/url]
zetia coupon
[url=https://synthroidx.online/]synthroid 137 mcg price[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]safe reliable canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]family store rx[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]trustworthy online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://vatrex.online/]canadian pharmacy valtrex[/url]
does wellbutrin make you more emotional
[url=https://prednisonekx.online/]iv prednisone[/url]
[url=https://oprednisone.online/]60 mg prednisone[/url]
[url=http://olisinopril.com/]lisinopril canada[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
[url=http://valtrexarb.online/]valtrex generic brand[/url]
[url=http://vatrex.online/]valtrex buy online[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprilos.online/]lisinopril 20mg tablets price[/url]
[url=http://isynthroid.com/]cost of synthroid 125 mcg[/url]
[url=https://prednisonexg.online/]can you buy prednisone online[/url]
[url=https://synthroidx.com/]synthroid rx[/url]
[url=http://bestprednisone.online/]prednisone 20[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]best canadian pharmacy no prescription[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.online/]azithromycin 4[/url]
[url=https://valtrexv.com/]how much is valtrex tablets[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]cheapest pharmacy to fill prescriptions without insurance[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.online/]cialis price compare[/url]
[url=https://prednisonexg.online/]prednisone 300mg[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprilgp.com/]buy lisinopril online[/url]
[url=https://pharmgf.online/]rxpharmacycoupons[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprilos.online/]lisinopril 20 mg canadian[/url]
[url=http://olisinopril.com/]zestoretic[/url]
Здравствуйте!
От политики до спорта, от экономики до науки – мы предлагаем вам самую актуальную информацию из разных областей жизни. Наши новости помогут вам понять текущую ситуацию и принимать информированные решения.
Наши новости предлагают вам полную картину происходящего в Украине и за ее пределами. Мы следим за всеми важными событиями и предоставляем вам объективную информацию.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://kompromis.info/
[url=https://kompromis.info/]новости Украины за день[/url]
новости Украины сегодня
последние новости мира
новости технологий
Удачи!
[url=https://metforemin.online/]metformin without rx[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprilgp.online/]lisinopril 10 12.5 mg[/url]
[url=http://synthroidotp.online/]synthroid 88 mcg in india[/url]
[url=https://pharmgf.online/]online pharmacy meds[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]silkroad online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://metformin.store/]discount glucophage[/url]
[url=https://metforminn.com/]metformin 134[/url]
[url=https://valtrexbt.online/]valtrex for sale online[/url]
[url=http://valtrexmedication.com/]buy valtrex online without a prescription[/url]
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]order valtrex online uk[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.online/]online pharmacy without scripts[/url]
[url=https://valtrexmedication.online/]valtrex cost uk[/url]
[url=https://bmtadalafil.online/]buy tadalafil 5mg online[/url]
[url=http://pharmgf.online/]best online pharmacy no prescription[/url]
[url=https://synthroidx.online/]synthroid without a rx[/url]
[url=https://olisinopril.com/]prinivil drug cost[/url]
[url=https://ezithromycin.online/]can you buy azithromycin over the counter[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.online/]cialis generic discount[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprilos.online/]20 mg lisinopril without a prescription[/url]
zyprexa for psychosis
[url=http://lisinoprildrl.online/]zestoretic online[/url]
Make Real Money with Gaming Apps in Kenya
best online casino games to win money [url=https://levine.co.ke/best-online-games-that-pay-real-money-in-kenya]real money online casinos[/url] .
[url=https://pharmgf.online/]onlinepharmaciescanada[/url]
[url=http://pharmgf.online/]cheapest online pharmacy india[/url]
efeler halı koltuk Yıkamacı
Top Money-Making Games in Kenya
best online casino games kenya [url=https://levine.co.ke/best-online-games-that-pay-real-money-in-kenya]games that pay real money in kenya[/url] .
[url=https://bestmedsx.online/]global pharmacy[/url]
Make Real Money with Gaming Apps in Kenya
best online casino games to win money [url=https://levine.co.ke/best-online-games-that-pay-real-money-in-kenya]real money online casinos[/url] .
[url=https://valtrexbt.online/]generic valtrex online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilu.online/]tadalafil 20 mg paypal[/url]
Play and Win Real Money Online Games
best online casino games kenya [url=https://levine.co.ke/best-online-games-that-pay-real-money-in-kenya]best online casino games kenya[/url] .
Win Big with Money Earning Games in Kenya
best online casino games kenya [url=https://levine.co.ke/best-online-games-that-pay-real-money-in-kenya]best online casino games kenya[/url] .
[url=http://tadalafilstd.online/]tadalafil otc usa[/url]
[url=http://predniso.online/]buy prednisone online no prescription[/url]
Рады приветствовать ваш ресурс, друзья!
Компания XRumer Art предлагает свои профессиональные услуги СЕО продвижения.
Ваш онлайн-сайт, как мы видим, только начинает набирать обороты. Для того, чтобы ускорить процесс его роста, предлагаем наши услуги по SEO-оптимизации. Продвижение в поисковиках – наша работа. В ассортименте представлены эффективные SEO-инструменты для экспертов. У нас большой опыт в данном направлении и огромное портфолио выполненных проектов – если интересует, предоставим по запросу.
Прямо сейчас можем предложить скидку на наши услуги – 10%.
Предлагаемые услуги:
– Размещаем трастовые ссылки (необходимо абсолютно всем сайтам) – от 1,5 до 5000 рублей
– Безанкорные ссылки (2500 штук) (желательно всем сайтам) – 3900 рублей
– Прогон по 110000 сайтам в зоне RU (максимально полезно для сайта) – 2900 р
– 150 постов В Контакте про ваш сайт (недорогая реклама) – 3.900 руб
– Публикация статей о вашем сайте на 300 интернет-форумах (мощнейшая раскрутка вашего ресурса) – 29000 рублей
– СуперПостинг – грандиозный прогон по 3 000 000 площадок (мощнейший пакет для ваших сайтов) – 39900 руб
– Рассылаем рекламные сообщения по сайтам с использованием обратной связи – цена по договоренности, зависит от объемов.
Если есть вопросы, обращайтесь, поможем.
Telgrm: @xrumers
https://XRumer.cc/
Skype: Loves.Ltd
[url=https://valtrexmedication.online/]cost for generic valtrex[/url]
[url=https://isynthroid.com/]how to buy synthroid online with no prescription[/url]
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://drugstorepp.online/]rxpharmacycoupons[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.online/]buy tadalafil 10 mg[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.online/]buy tadalafil generic[/url]
[url=http://oprednisone.online/]prednisone otc[/url]
[url=https://metoformin.online/]metformin buy online australia[/url]
[url=http://oprednisone.com/]prednisone 60mg daily[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprilos.online/]lisinopril 104[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.online/]pharmacy coupons[/url]
[url=https://medicinesaf.online/]online otc pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinhq.com/]azithromycin 500mg online india[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinmds.com/]2 zithromax[/url]
[url=https://bmtadalafil.online/]tadalafil uk generic[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]reputable online pharmacy reddit[/url]
[url=http://valtrexbt.online/]valtrex online uk[/url]
[url=https://isynthroid.com/]synthroid 50mcg[/url]
[url=https://prednisoneo.com/]prednisone 10mg tablets[/url]
[url=https://oazithromycin.online/]azithromycin for sale uk[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilu.online/]tadalafil 100mg india[/url]
[url=http://olisinopril.online/]lisinopril 20[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]canadian discount pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://metformindi.com/]metformin without script[/url]
[url=http://synthroidsl.online/]synthroid 175 mg[/url]
[url=https://oprednisone.online/]prednisone 12 mg[/url]
[url=https://ezithromycin.online/]azithromycin 1000mg tablets[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinmds.com/]azithromycin purchase usa[/url]
[url=http://metformin.store/]purchase glucophage online[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinmds.com/]can you buy azithromycin over the counter in usa[/url]
[url=http://isynthroid.com/]synthroid 200[/url]
Play and Earn Real Money Online in Kenya
best online casino games kenya [url=https://levine.co.ke/best-online-games-that-pay-real-money-in-kenya]casino games online for real money[/url] .
[url=http://azithromycinmds.com/]where can i buy zithromax uk[/url]
Play and Earn Real Money Online in Kenya
best online casino games kenya [url=https://levine.co.ke/best-online-games-that-pay-real-money-in-kenya]best online casino games kenya[/url] .
Best Games to Win Money in Kenya
best online casino games kenya [url=https://levine.co.ke/best-online-games-that-pay-real-money-in-kenya]games that pay real money in kenya[/url] .
[url=http://valtrexid.com/]valtrex mexico[/url]
[url=http://metformindi.online/]metformin 1000 mg online[/url]
Earn Money by Playing Fun Games in Kenya
best online casino games to win money [url=https://levine.co.ke/best-online-games-that-pay-real-money-in-kenya]real money online casinos[/url] .
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который желает вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом, и это будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем нюансам. В итоге вы получите продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества подобного подхода заключаются не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца диплома до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки по России — все под полным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто хочет найти быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
https://dlplomanrussian.com
[url=http://ametformin.com/]buy cheap metformin online[/url]
[url=https://vatrex.online/]buy valtrex online in usa[/url]
[url=http://synthroidam.online/]synthroid 88 mg price[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprill.com/]lisinopril hct[/url]
[url=https://synthroidam.online/]buy synthroid online usa[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilu.online/]rx tadalafil[/url]
[url=http://www.kalyamalya.ru/modules/newbb_plus/viewtopic.php?topic_id=10931&post_id=93545&order=0&viewmode=flat&pid=92562&forum=4#93545]http://www.kalyamalya.ru/modules/newbb_plus/viewtopic.php?topic_id=10931&post_id=93545&order=0&viewmode=flat&pid=92562&forum=4#93545[/url]
[url=https://www.storeboard.com/theaesthetedentalclinic]https://www.storeboard.com/theaesthetedentalclinic[/url]
[url=http://isynthroid.online/]synthroid 125 mcg tablet[/url]
Как выбрать надежное онлайн казино
[url=http://japzap.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://spgk.kz/]олимп ком казино[/url]
Как улучшить свои шансы на победу в казино
Секреты победы в казино
[url=http://fmza.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://spgk.kz/]казино олимп[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinps.online/]azithromycin online australia[/url]
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в любом университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете купить диплом нового или старого образца, что является удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. дипломы производятся с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы на выходе получился продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство этого подхода состоит не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца до грамотного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для всех, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу переходить к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало профессиональной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyans.com
[url=http://synthroidotp.online/]synthroid 0.125 mg[/url]
Как не проиграть все деньги в казино
Известные казино Лас-Вегаса
[url=http://gkhberdsk.ru/bitrix/click.php?goto=https://spgk.kz/]онлайн казино казахстан[/url]
27-го июля был проведён первый тест эффективности [url=http://www.botmasterru.com/product109120/]XRumer 23 StrongAI[/url] (по сравнению с текущей версией XRumer 19.0.18), который показал двадцатикратный прирост. Столь впечатляющие результаты достигнуты благодаря многократному улучшению пробиваемости уже известных платформ, добавлению поддержки новых платформ, обучению сотням тысяч типов новых тексткапч, внедрению нового GPT-модуля, и множеству других улучшений. По ссылке ниже Вы сможете изучить и скачать детали теста (исходная база, кусок отчёта, статистику и другие подробности)
Спасибо за рефку:
http://www.botmasterru.com/product109120/
[url=http://isynthroid.com/]can i buy synthroid online[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]canadian pharmacy discount coupon[/url]
[url=http://medicinesaf.online/]ez pharmacy[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://synthroidx.online/]where can i get synthroid[/url]
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://tadalafilgf.com/]buy cialis on line without prescription[/url]
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, желающим начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы можете купить диплом старого или нового образца, и это будет отличным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить образование, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. В результате вы получите документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества такого подхода состоят не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по стране — все будет находиться под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для всех, кто пытается найти быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyan.com
zofran odt orally disintegrating tablets
[url=https://tadalafilstd.com/]tadalafil for sale cheap[/url]
[url=https://isynthroid.com/]synthroid buy online[/url]
[url=https://vatrex.online/]valtrex best price[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprildrl.online/]zestoretic generic[/url]
[url=https://oprednisone.online/]preddisone no[/url]
Сегодня, когда диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, желающим начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в университете.
Мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете заказать диплом, и это является удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В результате вы получите продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство данного подхода состоит не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца до правильного заполнения личных данных и доставки в любое место России — все находится под полным контролем наших специалистов.
Для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia24.com
Привет всем!
Наши новости охватывают самые важные события в Украине и за ее пределами. Мы регулярно обновляем нашу информацию, чтобы предоставить вам самую актуальную и достоверную информацию о политике, экономике, культуре и других сферах жизни.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://smi.in.ua/sport/
[url=https://smi.in.ua/proisshestviya/]происшествия в Украине[/url]
новости Украины видео
последние новости мира
Новости экономики
Удачи!
[url=https://synthroidx.com/]synthroid prescription[/url]
[url=https://asynthroid.com/]synthroid prices 100mcg[/url]
[url=https://synthroidsl.online/]synthroid best price[/url]
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто стремится начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в ВУЗе.
Предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом старого или нового образца, и это является выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество подобного решения заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
В итоге, всем, кто пытается найти оперативный способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало профессиональной карьеры.
https://dlplomanrussian.com
[url=http://tadalafi.online/]cialis 2.5 mg coupon[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.com/]how much is tadalafil cost[/url]
[url=http://bestmedsx.com/]best online pet pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://olisinopril.online/]zestril over the counter[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilstd.com/]tadalafil 5 mg for sale without prescription[/url]
[url=https://isynthroid.com/]buy synthroid from canada[/url]
[url=https://valtrexv.com/]500 mg valtrex daily[/url]
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который хочет вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, что будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем нюансам. На выходе вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Плюсы данного подхода состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или старт успешной карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia24.com
[url=https://prednisonekx.online/]how to get prednisone without a prescription[/url]
[url=https://valtrexmedication.com/]valtrex otc[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.online/]canadian discount pharmacy[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://synthroidx.com/]buy synthroid 150 mcg online[/url]
Секреты выигрыша в казино
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.mv/url?q=https://spgk.kz/]казино олимп[/url]
Возможности казино онлайн
Как обыграть автоматы в казино
[url=http://techcard.com.vn/site/language/en?redirect=https://spgk.kz/]казино олимп[/url]
Что нужно знать перед посещением казино
[url=http://a-prof.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://spgk.kz/]казино олимп[/url]
В наше время, когда диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, что будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. На выходе вы получите 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство этого решения заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца диплома до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Для тех, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или старт успешной карьеры.
https://dlplomanrussian.com
Свой сайт официальный экземпляр даркнет площадки Блэкспрут – представляющей собой он-лайн платформу числом продаже/покупке не разрешенных веществ. Штрафплощадка BlackSprut размещена на узы TOR, которая обеспечивает для вас высочайший ярус анонимности.
https://bs2tsite.club
Что нужно знать перед посещением казино
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.ms/url?q=https://spgk.kz/]олимп казино[/url]
[url=https://metforminbi.online/]buy metformin 1000[/url]
Ощутите азарт и адреналин в онлайн казино Беларусь в любое время суток
онлайн казино Беларусь [url=https://sayokay.by/]онлайн казино Беларусь[/url] .
Доброго!
Чорна п’ятниця в Україні у 2024 році – час для вигідних покупок та приємних сюрпризів! Дізнайтеся дату проведення та підготуйтеся до шопінгу заздалегідь, щоб не проґавити кращі пропозиції.
[url=https://crazysale.marketing/black-friday.html]чорна пятниця 2024[/url]
[url=https://crazysale.marketing/black-friday.html]коли буде чорна пятниця[/url]
чорна пятниця
чорная пятница
чорна п’ятниця
Удачи!
[url=https://synthroidam.online/]synthroid 50 mcg price[/url]
Побеждайте вместе с друзьями в онлайн казино Беларусь на платформе с высокими оценками
онлайн казино Беларусь [url=https://sayokay.by/]онлайн казино Беларусь[/url] .
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, и это является удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Каждый диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. В итоге вы сможете получить документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство данного решения заключается не только в том, что вы быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до грамотного заполнения личной информации и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания готова предложить выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyans.com
Онлайн казино Беларусь: ваш путь к финансовой независимости и азартному удовольствию
онлайн казино Беларусь [url=https://sayokay.by/]онлайн казино Беларусь[/url] .
Играйте на деньги в онлайн казино Беларусь с безопасными платежами
онлайн казино Беларусь [url=https://sayokay.by/]онлайн казино Беларусь[/url] .
[url=https://olisinopril.online/]where can i get lisinopril[/url]
[url=https://oprednisone.com/]prednisone 2 mg tablets[/url]
[url=http://prednisonekx.online/]buy generic prednisone online[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который стремится вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом, что становится удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. В результате вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство этого подхода заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца диплома до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia24.com
[url=https://azithromycinmds.online/]azithromycin 250 mg price[/url]
Онлайн казино Беларусь: быстрые выплаты и круглосуточная поддержка
онлайн казино Беларусь [url=https://sayokay.by/]лучшие онлайн казино в Беларуси[/url] .
Наслаждайтесь азартом в онлайн казино Беларусь с бонусами за регистрацию
онлайн казино Беларусь [url=https://sayokay.by/]лучшие онлайн казино в Беларуси[/url] .
[url=https://valtrexmedication.com/]valtrex for sale[/url]
[url=https://prednisoneiv.online/]where can you get prednisone[/url]
Привет!
Не пропустите Черную пятницу на Украине в 2024 году – самое время для выгодных покупок! Узнайте дату проведения и подготовьтесь к массовым скидкам, акциям и распродажам. Это отличная возможность обновить гардероб или приобрести подарки к праздникам!
[url=https://crazysale.marketing/black-friday.html]чорна пятниця[/url]
[url=https://crazysale.marketing/black-friday.html]чёрная пятница[/url]
коли чорна п’ятниця
чорная пятница
черная пятница 2024 украина
Удачи!
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]reputable canadian online pharmacies[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете купить диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Все дипломы изготавливаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем деталям. В результате вы сможете получить документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества подобного решения состоят не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организован просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца документа до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по России — все под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к личным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia24.com
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]mexican pharmacy what to buy[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinhq.com/]zithromax 1000 mg for sale[/url]
[url=http://metforminn.com/]can you buy metformin without prescription[/url]
[url=https://vatrex.online/]valtrex prescription medicine[/url]
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]valtrex script[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто собирается вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в университете.
Мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом старого или нового образца, и это является отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить образование, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. дипломы производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. На выходе вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство этого подхода заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца до грамотного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по России — все находится под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
В результате, для тех, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyans.com
[url=http://prednisoneo.com/]prednisone australia[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Здравствуйте!
Отправляясь в путешествие по Калининграду и его окрестностям, каждый ищет нечто уникальное и запоминающееся. И здесь на помощь приходят индивидуальные экскурсии, предлагаемые нашей компанией. Мы – команда профессиональных гидов, специализирующихся на организации экскурсий по Калининградской области. Наш подход основан на индивидуальном внимании к каждому клиенту и его интересам. Ваш опыт путешествия становится по-настоящему уникальным благодаря гибкому планированию маршрутов и персональному подходу к каждому моменту. Ведь мы убеждены, что истинная красота Калининграда и его окрестностей раскрывается только тогда, когда путешествие подстроено под вас. Наши экскурсии предлагают возможность погрузиться в богатую историю этого уникального региона, посетить его исторические достопримечательности, насладиться прекрасными пейзажами и познакомиться с местной культурой. Наши гиды – профессионалы своего дела, которые с удовольствием поделятся своими знаниями и страстью к этому региону. Путешествие с нами станет для вас не просто экскурсией, а настоящим погружением в мир истории, культуры и природы Калининграда и его окрестностей. Чтобы узнать больше о наших услугах и забронировать индивидуальную экскурсию, посетите наш сайт по ссылке: https://topkaliningrad.ru . Путешествуйте с комфортом и погружайтесь в атмосферу уникального Калининграда вместе с нами!
Калининград экскурсии по городу индивидуальные
гид в Калининграде с машиной
Калининград экскурсии индивидуальные на машине
гиды Калининграда
индивидуальные экскурсии в Калининграде на машине
экскурсии Калининград
Удачи и хорошего визита в Калининград!
[url=http://valtrexid.com/]buy valtrex online prescription[/url]
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Важность наличия официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед людьми, желающими вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, что является отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Все дипломы производятся с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам. На выходе вы получите документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества такого решения состоят не только в том, что вы оперативно получите диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца до консультаций по заполнению личной информации и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем качественных специалистов.
Таким образом, для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyan.com
[url=https://valtrexmedication.online/]valtrex cream price[/url]
[url=http://prednisonexg.online/]prednisone 5mg tablets price[/url]
buy generic levitra online
buy levitra fast
[url=http://valtrexv.com/]can you buy valtrex online[/url]
В современном мире, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который стремится начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, и это становится выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Все дипломы изготавливаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В итоге вы получите документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы этого решения состоят не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца до консультации по заполнению личных данных и доставки в любое место России — все под полным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто хочет найти быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyan.com
[url=http://isynthroid.com/]synthroid 50 mcg price in india[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]happy family rx[/url]
Здравствуйте!
Путешествие – это всегда возможность погрузиться в атмосферу новых мест, и Калининград и его окрестности – это настоящий клад для любителей истории и красивых пейзажей. Наша компания специализируется на индивидуальных экскурсиях по Калининграду и Калининградской области, предлагая неповторимые приключения под руководством опытных гидов. Мы понимаем, что каждый турист уникален, поэтому наши экскурсии адаптированы под ваши предпочтения и интересы. С нами вы можете ощутить атмосферу истории, прогуливаясь по улочкам старого Кёнигсберга, или насладиться буйством природы, исследуя заповедники и парки области. Наша команда – это профессионалы своего дела, аккредитованные экскурсоводы, которые сделают ваше путешествие незабываемым. Мы предлагаем комфортабельные автомобили, чтобы каждая поездка была максимально приятной и безопасной. Приходите к нам, чтобы открыть для себя новые грани Калининградского края и оставить незабываемые впечатления о своем путешествии! Более подробную информацию о наших услугах вы можете найти на нашем сайте: https://topkaliningrad.ru
частные гиды Калининград
обзорная экскурсия по Калининграду
Калининград ночной экскурсия
Калининград гиды
индивидуальная экскурсия по Калининграду
гид Калининград частный на машине
Удачи и хорошего визита в Калининград!
[url=https://valtrexv.com/]valtrex[/url]
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который собирается вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, что становится выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. На выходе вы получите 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества данного решения состоят не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки по стране — все находится под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
В итоге, для всех, кто ищет оперативный способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу переходить к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт удачной карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia24.com
[url=https://olisinopril.online/]lisinopril 5mg tabs[/url]
[url=http://prednisoneo.com/]prednisone 50 mg coupon[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.online/]generic cialis online pharmacy canada[/url]
I besides believe thus, perfectly composed post! .
[url=http://bestmedsx.online/]canadian pharmacy store[/url]
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, желающим начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, и это становится отличным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Плюсы подобного подхода заключаются не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца диплома до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любое место страны — все под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто пытается найти оперативный способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
https://dlplomanrussian.com
[url=http://valtrexbt.online/]valtrex uk over the counter[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
[url=https://metformindi.online/]metformin prescription cost in us[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilgf.com/]can i buy cialis in usa[/url]
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own blog and was curious what all is needed to get setup? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very internet savvy so I’m not 100 sure. Any recommendations or advice would be greatly appreciated. Appreciate it
[url=http://synthroidx.com/]synthroid 1[/url]
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, желающим вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом нового или старого образца, что становится выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы в результате получился продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы этого решения заключаются не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца до точного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Для всех, кто пытается найти оперативный способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу переходить к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyan.com
levitra buy
Сегодня, когда аттестат является началом успешной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, желающим вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить аттестат нового или старого образца, что будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Аттестаты производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. В итоге вы получите продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества такого решения состоят не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить аттестат. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца до консультаций по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любой регион России — все будет находиться под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
Для тех, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести аттестат – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
https://diplomans-rossians.com/
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://lisinoprilgp.online/]lisinopril 5 mg prices[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который собирается вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом старого или нового образца, что становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. дипломы изготавливаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В результате вы получите продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества этого подхода состоят не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца документа до правильного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все находится под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Всем, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в университет или старт карьеры.
https://diploman-rossiya.com
[url=https://isynthroid.com/]synthroid canadian pharmacy[/url]
levitra reviews
[url=http://lisinoprilgp.com/]lisinopril 20 mg tablet[/url]
[url=https://prednisoneo.online/]prednisone 5443[/url]
Good day very cool web site!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your blog and take the feeds additionally?KI’m happy to search out so many useful info here within the publish, we need develop more strategies on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
[url=https://lisinoprilos.online/]lisinopril online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]valtrex pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilstd.online/]tadalafil canada price[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]how to get azithromycin without prescription[/url]
[url=http://drugstorepp.online/]online pharmacies that use paypal[/url]
[url=https://bestprednisone.online/]prednisone 5 mg tablet[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprildrl.online/]lisinopril oral[/url]
cialis generic over the counter
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]canada happy family store[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]happy family store[/url]
[url=https://myworldgo.com/forums/topic/144531/contoller-ukt38/view/post_id/1516724]https://myworldgo.com/forums/topic/144531/contoller-ukt38/view/post_id/1516724[/url]
[url=http://portal.krasno.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=58365]http://portal.krasno.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=58365[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://synthroidsl.online/]synthroid 30 mg[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
[url=https://isynthroid.com/]synthroid 88 lowest cost[/url]
[url=http://valtrexv.com/]valtrex 500mg uk[/url]
[url=http://medicinesaf.online/]usa pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://medicinesaf.online/]mexico pharmacy order online[/url]
[url=https://valtrexbt.online/]valtrex medicine for sale[/url]
[url=https://tadalafi.online/]cialis prescription price australia[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://metformin.store/]metformin india[/url]
[url=http://valtrexmedication.online/]buy valrex online[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprilgp.online/]lisinopril 10 mg[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]legal online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinmds.online/]zithromax prescription[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.com/]tadalafil australia[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]online pharmacy bc[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinmds.online/]zithromax online india[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]happy family pharmacy order status[/url]
[url=https://prednisonexg.online/]prednisone 21 pack[/url]
[url=http://pharmgf.online/]canadian discount pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://metformin.store/]metformin 1000 mg price in india[/url]
[url=https://drugstorepp.online/]trusted online pharmacy[/url]
çayyolu gelin saçı |
[url=https://metoformin.online/]cheap metformin online[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.com/]www canadapharmacy com[/url]
Наша компания предлагает высококачественные услуги Аренда мини-экскаватора bobcat в Алматы Мы обеспечиваем надежное и профессиональное оборудование для выполнения различных земляных работ на строительных площадках и других объектах. Наш опытный персонал и гибкие условия аренды делают нас надежным партнером для вашего проекта.
[url=https://bestmetformin.online/]glyburide metformin[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprilos.online/]generic for prinivil[/url]
Приветствую ваш сайт, друзья!
К вам обращается агентство по СЕО продвижению XRumer Art.
Мы видим, у вас относительно молодой сайт и ему нужно SEO продвижение в поисковиках. Мы предлагаем продвижение в поисковой выдаче под ключ. Также у нас есть недорогие и качественные инструменты для СЕО-специалистов. У наших специалистов серьезный опыт, в арсенале присутствуют успешные рабочие кейсы – если интересно, предоставим по запросу.
Сейчас предлагаем скидку на самые актуальные услуги – 10%.
Услуги нашей компании:
– Размещаем супер трастовые ссылки (нужно абсолютно всем сайтам) – стоимость 1500-5000 р
– Размещаем 2500 безанкорных ссылок (рекомендовано для всех сайтов) – 3.900 р
– Прогон на 110000 сайтов (зона RU) – 2.900 р
– Размещение 150 постов В Контакте о вашем сайте (поможет в рекламе) – 3.900 руб
– Публикации о вашем сайте на 300 интернет-форумах (мощнейшая раскрутка интернет-сайта) – 29.000 рублей
– МегаПостинг – это прогон на 3 миллиона ресурсов (мегамощный прогон для вашего сайта) – 39 тысяч рублей
– Рассылаем сообщения по сайтам с использованием обратной связи – договорная цена, будет зависеть от объема.
Если что-то не понятно, в любое время обращайтесь, поможем разобраться. принимаем usdt
Телегрм: @exrumer
Skype: Loves.ltd
w.w.w: https://XRumer.art
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]online pharmacy ed[/url]
[url=https://prednisonekx.online/]prednisone no rx[/url]
[url=https://prednisoneo.online/]buy prednisone india[/url]
[url=http://drugstorepp.online/]foreign pharmacy no prescription[/url]
[url=http://isynthroid.online/]synthroid 25 mcg tabs[/url]
[url=https://valtrexbt.online/]cheap valtrex[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]all in one pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://metformin.store/]glucophage cost canada[/url]
book taxi antalya airport | book taxi antalya airport is here
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]canada pharmacy online legit[/url]
1. The Ultimate Aviator Games Guide
juego del avion casino [url=https://aviator-slot-game.org/]juego del aviator[/url] .
[url=http://azithromycinps.online/]order zithromax uk[/url]
1. The Ultimate Aviator Games Guide
aviator slot [url=https://aviator-slot-game.org/]aviator slot[/url] .
1. The Ultimate Aviator Games Guide
aviator slot [url=https://aviator-slot-game.org/]aviator slot[/url] .
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]top 10 pharmacy websites[/url]
Everything You Need to Know
2. Aviator Games: Test Your Flying Skills in this Exciting Challenge
3. Get Ready to Soar: Aviator Games for Thrill Seekers
4. Master the Sky: Aviator Games for Aviation Enthusiasts
5. Take Flight with Aviator Games: A High-Flying Adventure
6. Challenge Yourself with Aviator Games: Are You Ready to Take On the Sky?
7. The Sky’s the Limit: Aviator Games for Daredevils
8. Aviator Games: The Perfect Way to Experience the Thrill of Flying
9. Fly High with Aviator Games: An Exciting Journey Awaits
10. Unleash Your Inner Pilot: Aviator Games for Flying Enthusiasts
11. Reach New Heights with Aviator Games: The Sky Awaits
12. Aviator Games: A Test of Skill and Courage in the Sky
13. Take to the Skies with Aviator Games: A Thrilling Adventure Awaits
14. Aviator Games: Where Every Landing is a Victory
15. Ready for Takeoff: Aviator Games for the Brave and Bold
16. Conquer the Clouds with Aviator Games: A Challenge Like No Other
17. Aviator Games: Prepare for a High-Flying Experience
18. Fly Like a Pro with Aviator Games: The Sky’s the Limit
19. Aviator Games: The Ultimate Test for Aspiring Pilots
20. Soar to New Heights with Aviator Games: Are You Ready for the Challenge?
aviator slot [url=https://aviator-slot-game.org/]aviator peru[/url] .
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]generic azithromycin cost[/url]
[url=https://olisinopril.com/]cheapest price for lisinopril[/url]
[url=https://valtrexarb.online/]cheap valtrex generic[/url]
Everything You Need to Know
2. Aviator Games: Test Your Flying Skills in this Exciting Challenge
3. Get Ready to Soar: Aviator Games for Thrill Seekers
4. Master the Sky: Aviator Games for Aviation Enthusiasts
5. Take Flight with Aviator Games: A High-Flying Adventure
6. Challenge Yourself with Aviator Games: Are You Ready to Take On the Sky?
7. The Sky’s the Limit: Aviator Games for Daredevils
8. Aviator Games: The Perfect Way to Experience the Thrill of Flying
9. Fly High with Aviator Games: An Exciting Journey Awaits
10. Unleash Your Inner Pilot: Aviator Games for Flying Enthusiasts
11. Reach New Heights with Aviator Games: The Sky Awaits
12. Aviator Games: A Test of Skill and Courage in the Sky
13. Take to the Skies with Aviator Games: A Thrilling Adventure Awaits
14. Aviator Games: Where Every Landing is a Victory
15. Ready for Takeoff: Aviator Games for the Brave and Bold
16. Conquer the Clouds with Aviator Games: A Challenge Like No Other
17. Aviator Games: Prepare for a High-Flying Experience
18. Fly Like a Pro with Aviator Games: The Sky’s the Limit
19. Aviator Games: The Ultimate Test for Aspiring Pilots
20. Soar to New Heights with Aviator Games: Are You Ready for the Challenge?
juego aviador [url=https://aviator-slot-game.org/]juego del avion casino[/url] .
[url=http://lisinoprilgp.com/]lisinopril 5 mg prices[/url]
[url=http://prednisoneo.online/]prednisone 10mg buy online[/url]
[url=https://olisinopril.com/]order lisinopril[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilu.online/]tadalafil tablets india[/url]
[url=https://prednisoneo.online/]prednisone without prescription medication[/url]
Everything You Need to Know
2. Aviator Games: Test Your Flying Skills in this Exciting Challenge
3. Get Ready to Soar: Aviator Games for Thrill Seekers
4. Master the Sky: Aviator Games for Aviation Enthusiasts
5. Take Flight with Aviator Games: A High-Flying Adventure
6. Challenge Yourself with Aviator Games: Are You Ready to Take On the Sky?
7. The Sky’s the Limit: Aviator Games for Daredevils
8. Aviator Games: The Perfect Way to Experience the Thrill of Flying
9. Fly High with Aviator Games: An Exciting Journey Awaits
10. Unleash Your Inner Pilot: Aviator Games for Flying Enthusiasts
11. Reach New Heights with Aviator Games: The Sky Awaits
12. Aviator Games: A Test of Skill and Courage in the Sky
13. Take to the Skies with Aviator Games: A Thrilling Adventure Awaits
14. Aviator Games: Where Every Landing is a Victory
15. Ready for Takeoff: Aviator Games for the Brave and Bold
16. Conquer the Clouds with Aviator Games: A Challenge Like No Other
17. Aviator Games: Prepare for a High-Flying Experience
18. Fly Like a Pro with Aviator Games: The Sky’s the Limit
19. Aviator Games: The Ultimate Test for Aspiring Pilots
20. Soar to New Heights with Aviator Games: Are You Ready for the Challenge?
juego del aviator [url=https://aviator-slot-game.org/]aviator casino online[/url] .
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]azithromycin 250mg cost[/url]
[url=http://predniso.online/]prednisone cost in india[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://synthroidx.com/]synthroid 112 mcg[/url]
[url=https://synthroidsl.online/]synthroid cost comparison[/url]
Здравствуйте!
С нами вы всегда будете в курсе всех важных событий в Украине и за рубежом. Мы предоставляем вам полную и достоверную информацию
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://10minut.info/category/zarubegem/
[url=https://10minut.info/]Главные новости Украины[/url]
Новости экономики
новоси мира лента
новости технологий
Удачи!
[url=http://bmtadalafil.online/]tadalafil 40 mg for sale[/url]
[url=https://metformin.store/]buy metformin from mexico[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilstd.com/]buy tadalafil over the counter[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilgf.com/]generic cialis 20[/url]
[url=http://bestprednisone.online/]steroid prednisone[/url]
27-го июля был проведён первый тест эффективности [url=http://www.botmasterru.com/product109120/]XRumer 23 StrongAI[/url] (по сравнению с текущей версией XRumer 19.0.18), который показал двадцатикратный прирост. Столь впечатляющие результаты достигнуты благодаря многократному улучшению пробиваемости уже известных платформ, добавлению поддержки новых платформ, обучению сотням тысяч типов новых тексткапч, внедрению нового GPT-модуля, и множеству других улучшений. По ссылке ниже Вы сможете изучить и скачать детали теста (исходная база, кусок отчёта, статистику и другие подробности)
Спасибо за рефку:
http://www.botmasterru.com/product109120/
[url=http://pharmgf.online/]canada drug pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://medicinesaf.online/]online pharmacy uk[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]northwest pharmacy canada[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]cheapest pharmacy to get prescriptions filled[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.com/]canadian mail order pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://prednisonekx.online/]drug prices prednisone[/url]
[url=https://oprednisone.com/]prednisone online paypal[/url]
bestmanualpolesaw.com
지금이 충성심을 보여줄 때입니까?
[url=https://valtrexbt.online/]generic valtrex price comparison[/url]
levitra online men
[url=http://prednisonecsr.com/]prednisone[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprilgp.com/]lisinopril tabs 88mg[/url]
buy generic levitra online
[url=http://bestmedsx.online/]mexico pharmacy order online[/url]
[url=http://tadalafi.online/]buy generic cialis online usa[/url]
Приветствую всех!
Откройте двери к морю скидок с нашим онлайн сервисом купонов и промокодов! Наши уникальные предложения позволят вам сэкономить на покупках в различных магазинах, включая электронику, моду, товары для дома и многое другое. Наш сайт предлагает простой и удобный способ находить актуальные акции и купоны, которые помогут вам сэкономить максимально возможную сумму. Не упускайте возможность быть в курсе последних выгодных предложений от лучших магазинов. Подписывайтесь на наши рассылки и получайте уведомления о новых акциях, чтобы быть первыми, кто воспользуется самыми привлекательными скидками. У нас для вас всегда есть что-то особенное!
Сайт самых свежих и проверенных промокодов магазина Zarina http://maxpromokod.ru
Привлекательные промокоды 123.ru на сегодня
Экономичные промокоды Forzieri INT супер скидки
Привлекательные промокоды KidStore свежие и актуальные
Ежедневные промокоды интернет магазина LA ROCHE-POSAY vip варианты
Горячие промокоды Связной RU супер скидки
Эксклюзивные промокоды Zaful.com INT vip варианты
Удачных покупок!
[url=https://predniso.online/]buy prednisone online canada without prescription[/url]
Доброго любители шоппинга!
Погрузитесь в мир выгодных сделок с нашим онлайн-сервисом купонов и промокодов! Мы предлагаем широкий выбор акций и специальных предложений от лучших магазинов, помогая вам сэкономить на всем, начиная от моды и заканчивая товарами для дома и техникой. Наша платформа предоставляет простой и удобный способ находить актуальные скидки и промокоды для вашей следующей покупки. Подписывайтесь на наши обновления, чтобы быть в курсе последних предложений и эксклюзивных акций, обеспечивая вам лучшие сделки при каждой покупке!
Сайт самых свежих и проверенных купонов магазина Allsoft http://maxpromokod.ru
Надежные промокоды O’STIN для онлайн-покупок
Привлекательные промокоды Strawberrynet Many GEOs супер скидки
Промокоды ALBA для интернет заказа
Экономичные промокоды FOROFFICE супер скидки
Быстрые промокоды Eldorado UA свежие и актуальные
Доступные промокоды MEXX список
Удачных покупок!
[url=https://medicinesaf.online/]foreign pharmacy online[/url]
[url=https://metformindi.online/]how to get metformin online[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinmds.online/]buy zithromax[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]canada discount pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://metforminn.com/]price of metformin 500mg tablets[/url]
[url=https://metformin.store/]metformin 1000 tab[/url]
[url=https://olisinopril.com/]how much is lisinopril[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinmds.online/]how to get azithromycin over the counter[/url]
Useful info. Lucky me I discovered your website accidentally, and I am shocked why this accident did not happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
https://writeablog.net/conwynnnhn/h1-b-korpus-i-sklo-far-iak-voni-vplivaiut-na-osvitlennia-dorogi-b-h1
[url=http://medicinesaf.online/]affordable pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://bestmetformin.online/]metformin cost in mexico[/url]
[url=http://predniso.online/]how to buy prednisone[/url]
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get bought an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again since exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this increase.
https://maps.google.ml/url?q=https://blogfreely.net/tinsushi2/sklo-dlia-far-efektivnii-zakhist-i-stil-nii-vigliad
94. Клининговая компания в Челябинске гордится своими доступными ценами на профессиональные услуги уборки. Мы верим, что чистота должна быть доступной для всех, поэтому мы предлагаем конкурентные тарифы без потери качества.
[url=https://kliningovaya-kompaniya-chelyabinsk.ru/]Клининг Челябинск[/url] .
Привет всем!
Получите документы об образовании всех ВУЗов России с гарантированной подлинностью и доставкой по РФ без предварительной оплаты!
ufapages.ru
#YAHOO#
51. Клининговая компания в Челябинске предоставляет услуги по уборке общественных мест, таких как парки, скверы и площади, включая вывоз мусора, уборку листьев, дезинфекцию скамеек и урн для поддержания чистоты и порядка.
[url=https://kliningovaya-kompaniya-chelyabinsk.ru/]Клининговая компания Челябинск[/url] .
66. Клининг Челябинск специализируется на уборке специализированных объектов, таких как банки, аптеки и клиники, включая дезинфекцию рабочих столов, оборудования, уборку зон ожидания и другие работы для поддержания чистоты и гигиены.
[url=https://kliningovaya-kompaniya-chelyabinsk.ru/]Клининг Челябинск[/url] .
[url=http://metformindi.online/]buy glucophage canada[/url]
side effects of levitra
4. Клининг в Челябинске предоставляет услуги по мойке ковров с выездом на дом или в офис. Наши специалисты используют профессиональное оборудование и эффективные моющие средства, чтобы устранить пятна и освежить внешний вид ковровых покрытий.
[url=https://kliningovaya-kompaniya-chelyabinsk.ru/]Клининговая компания Челябинск[/url] .
Hey there just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different browsers and both show the same results.
https://blogfreely.net/arwynerceb/h1-b-kupiti-sklo-far-farfarlight-nadiinist-ta-stil-dlia-vashogo
Окончание образования представляет собой основным моментом в пути каждого индивидуума, определяет его будущее и профессиональные перспективы.
Диплом открывает двери к новым перспективам и перспективам, гарантируя доступ к качественному получению знаний и высокооплачиваемым специальностям.
В сегодняшнем мире, где в конкуренция на рынке труда постоянно увеличивается, наличие аттестата делает обязательным требованием для успешной карьеры.
Диплом утверждает ваши знания, компетенции и компетенции перед профессиональным сообществом и общественностью в общем.
[url=https://www.diplomanrus.com]https://www.diplomanrus.com[/url]купить аттестат в москве – решение для людей, которые желает достижения успеха без дополнительных трудностей. Это шанс получить признанный документ о среднему образованию, открывающий новые горизонты и престижным карьерным путям. Наш сервис предлагает высокое качество и конфиденциальность, помогая вам быстро и эффективно достичь ваших целей.
В дополнение, диплом придает веру в свои силы и повышает самооценку, что способствует личностному и развитию. Получение диплома также является инвестицией в будущее, обеспечивая устойчивость и приличный уровень жизни.
Именно поэтому отдавать должное внимание и время получению образования и стремиться к его достижению, чтобы обрести успеха и удовлетворение от собственной труда.
[url=http://synthroidam.online/]buy synthroid mexico[/url]
70. Клининг Челябинск специализируется на уборке общественных зон многоэтажных домов, включая лестничные площадки, подъезды, мусоропроводы, детские площадки и другие общие зоны для создания уютной и чистой атмосферы для жильцов.
[url=https://kliningovaya-kompaniya-chelyabinsk.ru/]Клининг Челябинск[/url] .
[url=https://olisinopril.online/]lisinopril medication generic[/url]
23.Клининговая компания в Челябинске предлагает услуги по уборке после ремонта, освобождая помещения от строительной пыли, остатков материалов и других следов ремонтных работ для создания комфортной обстановки.
[url=https://kliningovaya-kompaniya-chelyabinsk.ru/]Клининг Челябинск[/url] .
[url=http://valtrexmedication.com/]buy valrex online[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.online/]buy azithromycin us[/url]
[url=https://oazithromycin.com/]where to buy azithromycin over the counter[/url]
67. Клининговая компания в Челябинске предоставляет услуги по уборке после крупных мероприятий, таких как конференции, выставки и фестивали, включая сбор мусора, уборку торговых зон, мойку полов и другие работы для восстановления порядка.
[url=https://kliningovaya-kompaniya-chelyabinsk.ru/]Клининг Челябинск[/url] .
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]how to order valtrex online[/url]
[url=https://metoformin.online/]metformin 1mg[/url]
[url=http://vatrex.online/]valtrex 100 mg[/url]
[url=http://metformindi.com/]metformin 3115[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprildrl.online/]lisinopril 80 mg[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinmds.online/]azithromycin 500 mg india[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprill.com/]order lisinopril online[/url]
[url=http://metforminbi.online/]buying online metformin from india[/url]
[url=https://synthroidx.online/]synthroid 62.5 mcg[/url]
[url=https://prednisonecsr.com/]buy prednisone 5mg[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]reliable rx pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://synthroidx.com/]online pharmacy no script synthroid 75[/url]
cialis wikipedia
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]no rx needed pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]online pharmacy price checker[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.com/]tadalafil 5mg coupon[/url]
What Is FitSpresso? The 100 natural formula is formulated using a potent blend of 6 ingredients
[url=https://prednisoneiv.online/]order prednizone[/url]
Thank you for another informative site. Where else could I get that kind of information written in such a perfect way? I’ve a project that I’m just now working on, and I’ve been on the look out for such info.
[url=http://predniso.online/]prednisone online purchase[/url]
[url=https://vatrex.online/]price of medicine valtrex[/url]
[url=http://tadalafi.online/]cialis 5 mg tablet price[/url]
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, желающим начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в каком-либо институте.
Мы предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, что будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Все дипломы производятся с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем деталям. В результате вы получите продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества подобного решения заключаются не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца документа до консультаций по заполнению личной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
Для тех, кто пытается найти оперативный способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
diploman-russia.com
[url=http://asynthroid.com/]synthroid online prescription[/url]
I’m curious to find out what blog system you are working with? I’m experiencing some small security problems with my latest blog and I would like to find something more secure. Do you have any recommendations?
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]canadian pharmacy no rx needed[/url]
[url=http://medicinesaf.online/]polish pharmacy online uk[/url]
[url=https://valtrexbt.online/]valtrex 500 mg tablet cost[/url]
[url=https://synthroidam.online/]synthroid 88 mcg coupon[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]online pharmacy in turkey[/url]
Как купить диплом легально
купить диплом Вуза [url=http://diplom-msk.ru/]http://diplom-msk.ru/[/url] .
[url=https://prednisoneo.online/]best price for prednisone[/url]
[url=https://valtrexarb.online/]buy valtrex online[/url]
[url=http://prednisoneiv.online/]prednisone pak[/url]
[url=https://ezithromycin.online/]azithromycin 500mg pills[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprilos.online/]zestoretic[/url]
[url=https://bestprednisone.online/]prednisone 20 mg brand name[/url]
[url=https://valtrexmedication.online/]buy real valtrex online[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед людьми, желающими начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом, и это становится отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы в результате получился продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества такого решения заключаются не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки в любое место России — все под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Таким образом, для тех, кто хочет найти оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyan.com/
[url=http://asynthroid.com/]synthroid 30 mg[/url]
[url=http://valtrexarb.online/]medicine valtrex[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]azithromycin no prescription[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]online pharmacy in germany[/url]
[url=http://drugstorepp.online/]canadian pharmacy coupon[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.online/]cialis online pharmacy usa[/url]
online pharmacy acyclovir
Доброго!
Рады предложить продажу и установку входных и межкомнатных дверей в Саратове и области. За время работы накоплен большой опыт для решения задач, связанных с установкой и сервисным обслуживанием дверных конструкций. Основными принципами в своей работе мы считаем обязательность, соблюдение договоренностей, выполнение оговоренных работ точно в срок, предсказуемо высокий уровень сервиса.
Мы предлагаем клиентам более 1000 моделей качественных входных и межкомнатных дверей различных по стоимости, материалу отделки, конструкции и другим параметрам от известных производителей. На связи с Вами всегда настоящие специалисты, знающие все тонкости и нюансы данной области. Благодаря этому, профессиональные консультанты помогут подобрать оптимальную конфигурацию, что будет залогом надежной, безотказной работы и комфорта.
Вся информация на сайте https://id64.ru/
Вы можете купить у нас двери в рассрочку без переплат при участии банков: Сбер, Почта банк, МТС банк, Русский Стандарт, Хоум кредит, Халва.
Компания является официальным дилером и прямым поставщиком дверей всех известных производителей, что подтверждено документально на сайте.
Двери имеются в наличии на складе и могут быть доставлены в кратчайший срок.
Консультацию проводят высококвалифицированные мастера. Они помогут найти лучшее изделие, подходящее под все Ваши требования.
Двери раздвижные
Двери книжка
Двери в квартиру
Двери Optim
Двери двухстворчатые
Двери в зал
Удачи и хорошего интерьера!
[url=https://lisinoprill.com/]zestoretic[/url]
tramadol hcl online pharmacy
[url=https://lisinoprildrl.online/]lisinopril generic brand[/url]
[url=http://bestmedsx.com/]recommended canadian pharmacies[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который хочет вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или учиться в каком-либо институте.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом старого или нового образца, что является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование, потерял документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы в результате получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущество подобного решения состоит не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора нужного образца диплома до правильного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все находится под полным контролем наших специалистов.
В результате, для всех, кто ищет быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени переходить к личным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
https://www.diploman-russiyan.com/
[url=http://drugstorepp.online/]canadian pharmacy 365[/url]
16.Клининг в Челябинске специализируется на уборке после ремонта квартир. Наши специалисты проведут тщательную уборку помещений, устраняя строительную пыль, остатки стройматериалов и другие загрязнения.
[url=https://kliningovaya-kompaniya-chelyabinsk.ru/]Клининг Челябинск[/url] .
I was more than happy to find this web-site.I needed to thanks for your time for this excellent learn!! I positively enjoying each little little bit of it and I’ve you bookmarked to check out new stuff you weblog post.
[url=https://lisinoprilos.online/]1 lisinopril[/url]
[url=https://asynthroid.com/]synthroid 50 mg price[/url]
[url=https://vatrex.online/]how much is valtrex generic[/url]
[url=http://valtrexv.com/]order valtrex generic[/url]
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]paypal buy valtrex online canada[/url]
[url=https://valtrexmedication.com/]generic valtrex online pharmacy[/url]
64. Клининг Челябинск специализируется на генеральной уборке офисных помещений перед важными визитами или переговорами, включая мойку окон, уборку мебели, дезинфекцию рабочих столов и другие работы для создания благоприятного впечатления.
[url=https://kliningovaya-kompaniya-chelyabinsk.ru/]Клининговая компания Челябинск[/url] .
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете купить диплом нового или старого образца, что является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем нюансам. В результате вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества такого подхода заключаются не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до грамотного заполнения личной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Для всех, кто хочет найти быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени переходить к личным целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
http://www.diplomanc-russia24.com
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед людьми, желающими вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или продолжить обучение в каком-либо университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете купить диплом, что является отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Каждый диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В результате вы получите продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества подобного решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца документа до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любой регион России — все под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
http://diplomanc-russia24.com
[url=http://tadalafilstd.com/]tadalafil medication cost[/url]
Hello mates, good piece of writing and nice urging commented at this place, I am actually enjoying by these.
https://www.diplomanc-russia24.com/
selegiline online pharmacy
В нашем мире, где аттестат становится началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который хочет начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать аттестат нового или старого образца, что является отличным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Аттестаты выпускаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем деталям. На выходе вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества этого решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой аттестат. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца аттестата до грамотного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Для тех, кто хочет найти быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Приобрести аттестат – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
https://diplomans-rossians.com/
[url=https://lisinoprildrl.online/]where to buy lisinopril without prescription[/url]
[url=http://bmtadalafil.online/]india tadalafil capsule cheap[/url]
[url=https://oazithromycin.com/]azithromycin pills over the counter[/url]
[url=https://prednisoneo.online/]purchase prednisone no prescription[/url]
freds pharmacy store
[url=http://valtrexmedication.online/]valtrex tablets for sale[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед людьми, желающими начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в университете.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете заказать диплом, что будет выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Все дипломы производятся аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы в итоге получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Плюсы такого решения состоят не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца документа до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любое место страны — все под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Таким образом, для тех, кто ищет оперативный способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания готова предложить выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или старт карьеры.
http://diplom-net.ru
[url=http://isynthroid.online/]order synthroid without prescription[/url]
[url=http://metforminn.com/]generic metformin rx online[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Важность наличия официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, желающим начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом, и это становится выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. дипломы выпускаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем деталям. На выходе вы получите 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества подобного решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца диплома до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки по России — все под полным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто хочет найти быстрый и простой способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало удачной карьеры.
vuzdiploma
[url=http://bestmedsx.com/]usa pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilstd.online/]cialis online 60mg[/url]
22.Клининг Челябинск специализируется на профессиональной мойке окон и фасадов зданий, гарантируя безупречную чистоту и прозрачность стекол, а также возвращая зданию свежий и привлекательный внешний вид.
[url=https://kliningovaya-kompaniya-chelyabinsk.ru/]Клининг Челябинск[/url] .
[url=http://olisinopril.com/]lisinopril in usa[/url]
lacolinaecuador.com
이 시점에서 Fang Jifan이 갑자기 그런 일을 던지는 것은 너무 많습니다!
[url=https://lisinoprildrl.online/]buy lisinopril uk[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprildrl.online/]lisinopril 10 mg tablet cost[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilgf.com/]cialis mexico over the counter[/url]
This is very fascinating, You’re an overly skilled blogger. I have joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking extra of your magnificent post. Additionally, I have shared your site in my social networks
https://jutsu.icu/
[url=http://prednisoneiv.online/]cheap prednisone[/url]
[url=https://olisinopril.com/]buy lisinopril online usa[/url]
[url=http://bestmedsx.com/]canada pharmacy coupon[/url]
[url=https://valtrexv.com/]valtrex for sale canada[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprill.com/]lisinopril 40 mg on line[/url]
[url=http://metformindi.com/]metformin medicine price[/url]
[url=https://oprednisone.online/]how to get prednisone over the counter[/url]
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто хочет начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом, и это становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. На выходе вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущество такого решения состоит не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до точного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место России — все будет находиться под полным контролем качественных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало успешной карьеры.
http://www.diplomany.ru
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который желает вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете купить диплом, и это становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Все дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. На выходе вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Плюсы данного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
В итоге, всем, кто ищет оперативный способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало удачной карьеры.
http://vsediplomu.ru
[url=https://bestmedsx.com/]canada cloud pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://bmtadalafil.online/]tadalafil cost in canada[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilstd.com/]how to get tadalafil[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]canadian happy family store coupon[/url]
[url=https://drugstorepp.online/]foreign online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]how can i get azithromycin over the counter[/url]
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://lisinoprill.com/]discount zestril[/url]
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Необходимость наличия документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто стремится начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом, и это является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Все дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. На выходе вы получите продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество данного решения состоит не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца документа до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем качественных специалистов.
Для всех, кто пытается найти быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
http://diplomexpress.ru
[url=https://drugstorepp.online/]pharmaceuticals online australia[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprilos.online/]lisinopril 50 mg price[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.com/]foreign pharmacy no prescription[/url]
[url=https://olisinopril.online/]buy lisinopril 40 mg online[/url]
[url=http://isynthroid.online/]synthroid 125 mcg tablet[/url]
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который собирается начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете купить диплом старого или нового образца, и это становится выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Все дипломы выпускаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам. В итоге вы сможете получить документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества этого подхода состоят не только в том, что вы быстро получите диплом. Процесс организован просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца до точного заполнения личных данных и доставки в любое место России — все находится под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
В результате, для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу переходить к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
http://www.99diplomov.ru
[url=http://drugstorepp.online/]mexican online mail order pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://prednisonecsr.com/]buy prednisone online from mexico[/url]
Завершение учебы диплома является ключевым моментом во карьере каждого индивидуума, определяющим его перспективы и профессиональные перспективы.
Диплом открывает путь к новым перспективам и перспективам, обеспечивая возможность к качественному образованию и высокопрестижным профессиям.
В нынешнем обществе, где конкуренция на трудовом рынке постоянно увеличивается, наличие аттестата становится обязательным требованием для выдающейся профессиональной деятельности.
Он подтверждает ваши знания, умения и навыки, компетенции и умения перед работодателями и обществом в общем.
[url=https://diploman-russiya.com]http://www.diploman-russiya.com[/url]купить аттестат о среднем образовании – выход для людей, которые желает достижения успеха без лишних препятствий. Это шанс завоевать признанный документ по среднему образованию, предоставляющий новые перспективы и престижным профессиям. Наш сервис гарантирует качество и конфиденциальность, помогая вам достичь ваших целей с минимальными усилиями.
Помимо этого, диплом дарит уверенность в себе и укрепляет самооценку, что содействует личностному росту и развитию. Получение диплома также вложением в будущий путь, обеспечивая стабильность и благополучный уровень проживания.
Именно поэтому уделять должное внимание образованию и стремиться к его достижению, чтобы обрести успех и счастье от собственной профессиональной деятельности.
[url=https://tadalafi.online/]can you buy cialis safely online[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]reddit canadian pharmacy[/url]
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who had been conducting a little homework on this. And he in fact ordered me breakfast due to the fact that I found it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending some time to discuss this matter here on your website.
http://diplom07.ru
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]valtrex medication[/url]
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
freeflowincome.com
“비난을 진압하기 위해! 선생님의 얼굴을 다치게 하지 않기 위해.” Liu Wenshan은 어쩔 수 없이 말했습니다.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://synthroidx.online/]synthroid 112[/url]
Сегодня, когда диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, желающими начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом, что будет отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. На выходе вы получите документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы подобного подхода состоят не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца диплома до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем опытных мастеров.
В результате, всем, кто пытается найти оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://www.ab-diplom.ru
Завершение учебы образования считается ключевым этапом во жизни всякого индивидуума, определяет его будущее и профессиональные перспективы – [url=http://diplomvam.ru]www.diplomvam.ru[/url]. Аттестат открывает путь к новым горизонтам и возможностям, обеспечивая доступ к качественному образованию и престижным специальностям. В сегодняшнем обществе, где борьба на трудовом рынке всё увеличивается, имение аттестата становится необходимым требованием для выдающейся карьеры. Он утверждает ваши знания и навыки, умения и компетенции перед профессиональным сообществом и общественностью в общем. Кроме того, диплом дарует веру в свои силы и увеличивает самооценку, что способствует персональному развитию и саморазвитию. Окончание образования также инвестицией в будущее, предоставляя устойчивость и достойный уровень жизни. Поэтому обращать должное внимание и время образованию и стремиться к его достижению, чтобы добиться успеха и удовлетворение от собственной профессиональной деятельности.
Диплом не лишь символизирует ваше образование, но и отражает вашу самодисциплину, усердие и упорство в добивании задач. Диплом является результатом усилий и труда, вкладываемых в учебу и саморазвитие. Завершение учебы образования открывает перед вами свежие горизонты возможностей, даруя возможность избирать среди множества карьерных путей и профессиональных направлений. Это также даёт вам основу знаний и навыков, необходимых для выдающейся деятельности в нынешнем обществе, полном вызовами и изменениями. Помимо этого, сертификат считается свидетельством вашей квалификации и квалификации, что в свою очередь улучшает вашу привлекательность на рынке труда и открывает вами возможности к лучшим возможностям для профессионального роста. Таким образом, получение диплома не только обогащает ваше личное развитие, а также раскрывает вами новые и перспективы для достижения целей и мечтаний.
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который собирается начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в каком-либо институте.
Предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы можете заказать диплом, что становится выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В итоге вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Превосходство этого решения заключается не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца до точного заполнения личной информации и доставки по стране — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем опытных мастеров.
В итоге, для всех, кто ищет быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
http://www.diplom-msk.ru
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который желает вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом, и это становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В результате вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества этого решения заключаются не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все будет находиться под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить требуемый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
https://diplom-gotovie.ru/
[url=http://metforminbi.online/]metformin 800 mg[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.online/]legitimate online pharmacy usa[/url]
[url=http://predniso.online/]medicine prednisone 5mg[/url]
My spouse and I stumbled over here from a different web page and thought I should check things out. I like what I see so now i am following you. Look forward to finding out about your web page repeatedly.
[url=https://tadalafi.online/]where can i purchase cialis[/url]
Do you have a spam problem on this website; I also am a blogger, and I was wanting to know your situation; we have developed some nice practices and we are looking to trade methods with other folks, be sure to shoot me an email if interested.
http://www.server-attestats.com
[url=https://metformindi.com/]metformin 1000 tablet[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprildrl.online/]lisinopril best price[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в любом университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете купить диплом старого или нового образца, что будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы в результате получился документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы этого подхода состоят не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца диплома до правильного заполнения персональных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все находится под полным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к личным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
vuzdiploma.ru
[url=http://bestmetformin.online/]metformin price in mexico[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.online/]pharmacy shop[/url]
Exotic and Luxury Car Rental in Miami
[url=https://mhp-miami.com/]miami exotic car rental[/url]
Exotic Car Rental: Luxury and Adrenaline
Exotic car rental is a unique opportunity to feel like a real racer or celebrity, enjoy the indescribable sensations of driving powerful and luxurious cars. This service is very popular all over the world, and it is not surprising, because the opportunity to be behind the wheel for a while Ferrari, Lamborghini, McLaren or another exceptional car can bring a lot of unforgettable emotions and impressions.
Choosing an exotic car
One of the key points of renting an exotic car is choosing the right car. Depending on your preferences and budget, you can choose among the most prestigious and famous brands in the world of the automotive industry.
luxury car rental miami
https://mhp-miami.com/
The most popular options:
Ferrari: These Italian cars are famous for their elegance and power. Many people dream of driving Ferrari, and renting provides an opportunity to make this dream a reality.
Lamborghini: Extreme design and incredible speed make Lamborghini one of the most desirable cars to rent. They are able to accelerate to amazing speeds and provide an unforgettable experience.
McLaren: If you need a car that will look and feel like from the future, McLaren – your choice. These hypercars have incredible power and a unique design.
Porsche: Sports cars Porsche are always in demand. They combine power and comfort, making them an excellent choice for both high-speed driving and long trips.
The rental process
Choosing a rental company: The first step in renting an exotic car is choosing a reliable rental company. It is important to make sure that they have a good reputation and provide accident insurance.
Booking: After choosing a car and a rental company, you can book a car. Usually you will need to provide copies of documents and make a deposit.
Car fence: On the day of the rental, you will need to come to the rental company and pick up your exotic car. It is important to familiarize yourself with the terms of the lease and sign the necessary documents.
Driving Enjoyment: Now you have the opportunity to enjoy the unique experience of driving an exotic car. Remember to follow the rules of the road and safety.
Car return: At the end of the rental period, return the car to the company. It is usually necessary to check the condition of the car and its fuel tank.
[url=https://drugstorepp.online/]mexican online mail order pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.online/]azithromycin 500mg tablets for sale[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinmds.com/]generic zithromax 500mg[/url]
[url=https://valtrexbt.online/]purchase valtrex[/url]
Автор 24 – это надежный сервис для заказа разнообразных академических работ. Он занимается на дипломных работах, а также задачах. Кроме того, на сервисе Автор 24 можно приобрести очерки, презентации. Это эффективный способ повысить свои академические результаты.
Автор 24 [url=https://author24.us/]сайт автор 24[/url] .
Сервис Автор 24 – это надежный сервис для заказа различных академических работ. Он специализируется на курсовых работах, а также чертежах. Кроме того, на платформе Автор 24 можно заказать эссе, отчеты о прохождении практики. Это эффективный способ повысить свои академические результаты.
Автор 24 официальный [url=https://author24.online]Автор24[/url] .
[url=https://asynthroid.com/]synthroid 88 mcg price[/url]
Платформа Автор 24 – это надежный сервис для покупки различных академических работ. Он работает на рефератах, а также задачах. Кроме того, на сервисе Автор 24 можно приобрести очерки, презентации. Это удобный способ повысить свои академические результаты.
Автор 24 [url=https://author24.online]сайт автор 24[/url] .
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Автор 24 – это превосходный сервис для заказа многочисленных академических работ. Он занимается на рефератах, а также чертежах. Кроме того, на платформе Автор 24 можно заказать рецензии, отчеты о прохождении практики. Это практичный способ повысить свои академические результаты.
Автор 24 [url=https://author24.online]Автор 24[/url] .
[url=http://synthroidx.com/]synthroid online coupon[/url]
[url=http://valtrexmedication.online/]canadian valtrex otc[/url]
[url=http://asynthroid.com/]buy synthroid in canada[/url]
thebuzzerpodcast.com
환관은 “비누와 향수에 대해 물어보십시오.”
[url=http://azithromycinps.online/]zithromax over the counter canada[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед каждым человеком, желающим начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в университете.
Наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете купить диплом, и это является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. В итоге вы сможете получить продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы данного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы быстро получите свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца до консультаций по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любое место России — все под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
В результате, для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу перейти к личным целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
saksx-attestats.ru
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]legal canadian pharmacy online[/url]
[url=https://isynthroid.com/]synthroid price[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilgf.com/]cialis lowest price canada[/url]
[url=http://synthroidx.online/]synthroid cheapest price[/url]
[url=http://ezithromycin.online/]azithromycin pills for sale[/url]
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://azithromycinmds.online/]can i buy azithromycin over the counter in canada[/url]
В современном мире, где аттестат – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, желающим вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы можете купить аттестат, что становится выгодным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Аттестаты выпускаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. В результате вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущество данного подхода состоит не только в том, что вы оперативно получите аттестат. Весь процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все под полным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто пытается найти оперативный способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать аттестат – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало удачной карьеры.
https://diplomans-rossians.com/
[url=https://synthroidam.online/]synthroid medication cost[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinhq.com/]zithromax price south africa[/url]
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://oazithromycin.online/]zithromax brand name[/url]
[url=https://synthroidsl.online/]best price for synthroid[/url]
[url=http://lisinoprilgp.com/]buy lisinopril no prescription[/url]
[url=http://prednisonexg.online/]buy prednisone 10 mg[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://valtrexid.com/]valtrex pill cost[/url]
[url=http://synthroidam.online/]cost of synthroid 100mcg[/url]
[url=https://metoformin.online/]metformin prices australia[/url]
[url=http://asynthroid.com/]synthroid 137[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilstd.online/]cialis 20 mg price[/url]
[url=http://synthroidx.online/]canadian pharmacy synthroid[/url]
buysteriodsonline.com
“예, 그 학생은 최선을 다했지만…” 의대생은 당황한 듯 쉬징을 바라보았는데…
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://lisinoprildrl.online/]lisinopril 20 pills[/url]
[url=https://synthroidx.com/]price of synthroid 75 mcg[/url]
[url=http://predniso.online/]prednisone 5mg over the counter[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://vatrex.online/]valtrex 500mg price[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://synthroidsl.online/]cheapest price for synthroid[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinps.online/]cost of azithromycin[/url]
[url=https://valtrexbt.online/]generic valtrex online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilu.online/]canadian pharmacy tadalafil 5mg[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.online/]india cialis pharmacy[/url]
Заказать купленный диплом, через интернет.
Доступные цены на дипломы для продажи, узнайте сейчас.
Заказать официальный документ о образовании, важная информация.
Почему выгодно купить диплом, подробности.
Где купить диплом без проблем, без риска.
Лучшие предложения по покупке диплома, важные моменты.
Дипломы на заказ по лучшим ценам, лучшие условия.
Покупка диплома: безопасность и конфиденциальность, важная информация.
Как быстро купить диплом, подробности на сайте.
Как купить диплом онлайн, лучшие условия.
Официальные документы для покупки, лучшие цены.
Легальная покупка дипломов, подробности на сайте.
Почему стоит заказать диплом, важные детали.
Купить диплом просто, важные моменты.
Легальная покупка дипломов безопасно, гарантированная доставка.
Купить дипломы легко, подробности на сайте.
Купить диплом с доставкой по всему миру, подробности здесь.
Как купить диплом безопасно и быстро, подробности у нас.
купить диплом [url=https://www.7arusak-diploms.com/]https://www.7arusak-diploms.com/[/url] .
[url=http://tadalafilgf.com/]tadalafil canadian pharmacy[/url]
Купить диплом с доставкой до дома, через интернет.
Доступные цены на дипломы для продажи, узнайте сейчас.
Купить диплом с гарантией качества, проверенные варианты.
Опыт успешной покупки диплома, рассказываем.
Купить диплом легко, на проверенных ресурсах.
Лучшие предложения по покупке диплома, важные моменты.
Дипломы на заказ по лучшим ценам, спешите.
Почему стоит купить диплом, наши преимущества.
Лучшие дипломы для покупки, подробности на сайте.
Купить диплом срочно и законно, гарантированный результат.
Почему стоит купить диплом у нас, срочные варианты.
Безопасное приобретение документов об образовании, без рисков.
Почему стоит заказать диплом, подробности у нас.
Как выбрать и купить диплом, подробности на сайте.
Легальная покупка дипломов безопасно, гарантированная доставка.
Какой диплом выбрать для покупки, интересные варианты.
Официальная покупка диплома, подробности здесь.
Как купить диплом безопасно и быстро, подробности у нас.
купить диплом [url=https://www.7arusak-diploms.com]https://www.7arusak-diploms.com[/url] .
[url=https://tadalafilgf.com/]tadalafil in india online[/url]
Приобрести диплом без лишних хлопот, через интернет.
Доступные цены на дипломы для продажи, узнайте сейчас.
Заказать официальный документ о образовании, проверенные варианты.
Преимущества покупки диплома, подробности.
Где купить диплом без проблем, без риска.
Как выбрать диплом для покупки, секреты выбора.
Дипломы на заказ по лучшим ценам, спешите.
Скрытая покупка дипломов, проверенные решения.
Где купить действующий диплом, срочно и выгодно.
Как купить диплом онлайн, лучшие условия.
Как выбрать диплом, срочные варианты.
Легальная покупка дипломов, подробности на сайте.
Купить диплом без обмана, подробности у нас.
Купить диплом просто, лучшие предложения.
Как купить дипломы онлайн, гарантированная доставка.
Почему стоит купить диплом здесь и сейчас, подробности на сайте.
Заказать диплом онлайн без проблем, подробности здесь.
Почему стоит заказать диплом на нашем сайте, подробности у нас.
купить диплом [url=https://www.7arusak-diploms.com/]https://www.7arusak-diploms.com/[/url] .
[url=https://asynthroid.com/]synthroid 60 mg[/url]
Купить диплом с доставкой до дома, онлайн.
Как купить диплом без риска, узнайте сейчас.
Заказать официальный документ о образовании, важная информация.
Почему выгодно купить диплом, рассказываем.
Купить диплом легко, без риска.
Как выбрать диплом для покупки, интересные варианты.
Дипломы на заказ по лучшим ценам, лучшие условия.
Почему стоит купить диплом, наши преимущества.
Как быстро купить диплом, подробности на сайте.
Покупка диплома: безопасность и качество, подробности у нас.
Официальные документы для покупки, гарантированное качество.
Как купить диплом срочно, подробности на сайте.
Купить диплом без обмана, подробности у нас.
Купить диплом просто, подробности на сайте.
Как купить дипломы онлайн, подробности у нас.
Почему стоит купить диплом здесь и сейчас, подробности на сайте.
Заказать диплом онлайн без проблем, подробности здесь.
Как купить диплом безопасно и быстро, гарантированный результат.
купить диплом [url=https://7arusak-diploms.com/]https://7arusak-diploms.com/[/url] .
codeine pharmacy online
online pharmacy to buy viagra
Приобрести диплом без лишних хлопот, онлайн.
Как купить диплом без риска, узнайте сейчас.
Какой диплом купить, проверенные варианты.
Преимущества покупки диплома, подробности.
Как купить диплом безопасно, на проверенных ресурсах.
Купить диплом по выгодной цене, секреты выбора.
Как купить диплом быстро, лучшие условия.
Почему стоит купить диплом, важная информация.
Где купить действующий диплом, срочно и выгодно.
Купить диплом срочно и законно, подробности у нас.
Почему стоит купить диплом у нас, гарантированное качество.
Легальная покупка дипломов, подробности на сайте.
Купить диплом без обмана, важные детали.
Купить диплом просто, подробности на сайте.
Легальная покупка дипломов безопасно, подробности у нас.
Какой диплом выбрать для покупки, интересные варианты.
Заказать диплом онлайн без проблем, лучшие условия.
Официальный документ об образовании, безопасность на первом месте.
купить диплом [url=https://www.7arusak-diploms.com]https://www.7arusak-diploms.com[/url] .
Приобрести диплом без лишних хлопот, онлайн.
Доступные цены на дипломы для продажи, узнайте сейчас.
Какой диплом купить, советы от профессионалов.
Преимущества покупки диплома, все секреты.
Как купить диплом безопасно, без риска.
Лучшие предложения по покупке диплома, важные моменты.
Как купить диплом быстро, спешите.
Покупка диплома: безопасность и конфиденциальность, наши преимущества.
Как быстро купить диплом, подробности на сайте.
Купить диплом срочно и законно, гарантированный результат.
Официальные документы для покупки, гарантированное качество.
Легальная покупка дипломов, без рисков.
Купить диплом без обмана, гарантированный результат.
Как выбрать и купить диплом, лучшие предложения.
Купить диплом без риска, безопасность на первом месте.
Купить дипломы легко, гарантированный результат.
Заказать диплом онлайн без проблем, важные детали.
Официальный документ об образовании, безопасность на первом месте.
купить диплом [url=https://www.7arusak-diploms.com/]https://www.7arusak-diploms.com/[/url] .
Добрый день всем!
Наши услуги помогут вам приобрести диплом ВУЗа с доставкой по всей России и без предварительной оплаты – это быстро и надежно!
http://www.diplomany-asx.ru
[url=http://clomidsale.com/]purchase clomid online uk[/url]
[url=https://albuterolp.com/]can i buy ventolin over the counter uk[/url]
[url=http://doxycyclineo.com/]doxycycline 40 mg generic[/url]
[url=http://aaccutane.com/]buy accutane online[/url]
[url=https://dexamethasonen.com/]dexamethasone 8 mg tablet[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://dexamethasonen.com/]dexamethasone 1 tablet[/url]
[url=http://valtrexv.online/]compare valtrex prices[/url]
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который желает вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в любом ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот необходимый документ. Вы можете заказать диплом старого или нового образца, что становится выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Все дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям, чтобы в результате получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества подобного решения состоят не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите свой диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца до консультаций по заполнению личной информации и доставки по стране — все будет находиться под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу трудовой карьеры.
diploman-russia.ru
[url=https://doxycyclinepr.com/]doxycycline medicine[/url]
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Fantastic blog you have here but I was wanting to know if you knew of any user discussion forums that cover the same topics talked about in this article? I’d really like to be a part of community where I can get responses from other experienced people that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Appreciate it!
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://accutaneiso.online/]accutane prices uk[/url]
Приобрести диплом без лишних хлопот, не выходя из дома.
Как купить диплом без риска, узнайте сейчас.
Купить диплом с гарантией качества, важная информация.
Опыт успешной покупки диплома, подробности.
Где купить диплом без проблем, с гарантией.
Как выбрать диплом для покупки, важные моменты.
Купить диплом срочно и недорого, подробности на сайте.
Почему стоит купить диплом, проверенные решения.
Где купить действующий диплом, подробности на сайте.
Купить диплом срочно и законно, гарантированный результат.
Как выбрать диплом, гарантированное качество.
Безопасное приобретение документов об образовании, без рисков.
Купить диплом без обмана, гарантированный результат.
Купить диплом просто, важные моменты.
Купить диплом без риска, гарантированная доставка.
Купить дипломы легко, интересные варианты.
Заказать диплом онлайн без проблем, подробности здесь.
Почему стоит заказать диплом на нашем сайте, гарантированный результат.
купить диплом [url=https://7arusak-diploms.com]https://7arusak-diploms.com[/url] .
Приобрести диплом без лишних хлопот, не выходя из дома.
Легальный способ купить диплом, подробности здесь.
Заказать официальный документ о образовании, важная информация.
Опыт успешной покупки диплома, все секреты.
Где купить диплом без проблем, с гарантией.
Как выбрать диплом для покупки, секреты выбора.
Как купить диплом быстро, подробности на сайте.
Покупка диплома: безопасность и конфиденциальность, проверенные решения.
Лучшие дипломы для покупки, срочно и выгодно.
Как купить диплом онлайн, лучшие условия.
Как выбрать диплом, лучшие цены.
Безопасное приобретение документов об образовании, лучшие условия.
Почему стоит заказать диплом, гарантированный результат.
Дипломы на всех условиях, важные моменты.
Купить диплом без риска, гарантированная доставка.
Почему стоит купить диплом здесь и сейчас, подробности на сайте.
Заказать диплом онлайн без проблем, подробности здесь.
Почему стоит заказать диплом на нашем сайте, безопасность на первом месте.
купить диплом [url=http://7arusak-diploms.com]http://7arusak-diploms.com[/url] .
Заказать купленный диплом, через интернет.
Доступные цены на дипломы для продажи, узнайте сейчас.
Заказать официальный документ о образовании, советы от профессионалов.
Преимущества покупки диплома, рассказываем.
Где купить диплом без проблем, на проверенных ресурсах.
Лучшие предложения по покупке диплома, важные моменты.
Как купить диплом быстро, спешите.
Почему стоит купить диплом, важная информация.
Как быстро купить диплом, подробности на сайте.
Как купить диплом онлайн, гарантированный результат.
Официальные документы для покупки, лучшие цены.
Безопасное приобретение документов об образовании, подробности на сайте.
Почему стоит заказать диплом, важные детали.
Купить диплом просто, важные моменты.
Как купить дипломы онлайн, подробности у нас.
Купить дипломы легко, гарантированный результат.
Заказать диплом онлайн без проблем, важные детали.
Как купить диплом безопасно и быстро, подробности у нас.
купить диплом [url=http://www.7arusak-diploms.com]http://www.7arusak-diploms.com[/url] .
[url=https://acyclovirlp.online/]acyclovir canada without prescription[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://aaccutane.com/]accutane prescription online[/url]
[url=http://accutaneo.com/]generic of accutane[/url]
colchicine pharmacy
Hello everyone!
Embark on a Journey of Discovery: Mathematical Economics and Data Analysis at https://satbayev.university/
Welcome to Satbayev University’s Mathematical Economics and Data Analysis program, where analytical rigor meets real-world applications. As we open admissions for the 2024 academic year, we invite you to become part of a community that values precision, analytical thinking, and data-driven decision-making.
Program Overview Our program is designed for those who aspire to delve into the complexities of economics and harness the power of data analysis. You will explore the mathematical underpinnings of economic theory, learn cutting-edge data analysis techniques, and apply your knowledge to solve pressing economic problems.
Admission Requirements
A strong foundation in mathematics and a keen interest in economics.
Proficiency in English, with the ability to engage in complex analytical discussions.
A bachelor’s degree in economics, mathematics, or a related field (for graduate programs).
Official transcripts, a statement of purpose, and two letters of recommendation.
Curriculum Highlights
Advanced courses in microeconomics, macroeconomics, and econometrics.
Training in statistical software and data analysis tools.
Opportunities for research and real-world data projects.
Electives that allow you to tailor your education to your career goals.
Career Prospects Graduates of our program are well-equipped for careers in:
Economic analysis and policy-making.
Data analytics and business intelligence.
Financial markets and risk management.
Research and academia.
Application Process Begin your journey by submitting an online application through our university portal. Ensure that all required documents are uploaded and that you meet the specified deadlines. Our admissions team is dedicated to a holistic review of each applicant, considering both academic achievements and potential for future success.
Join Us At Satbayev University, we’re not just educating the next generation of economists and data analysts; we’re shaping the future of decision-making in business and policy. Apply now and take the first step towards a fulfilling career at the intersection of mathematics, economics, and data analysis.
[url=https://satbayev.university/]Industrial Automation in University[/url]
Machine Learning
International Students
Microcontroller
Online Registration
Good luck and good progress!
Купить диплом с доставкой до дома, онлайн.
Как купить диплом без риска, без заморочек.
Заказать официальный документ о образовании, важная информация.
Опыт успешной покупки диплома, все секреты.
Купить диплом легко, на проверенных ресурсах.
Лучшие предложения по покупке диплома, важные моменты.
Купить диплом срочно и недорого, лучшие условия.
Скрытая покупка дипломов, наши преимущества.
Как быстро купить диплом, срочно и выгодно.
Как купить диплом онлайн, лучшие условия.
Как выбрать диплом, гарантированное качество.
Безопасное приобретение документов об образовании, без рисков.
Официальные дипломы для покупки, важные детали.
Дипломы на всех условиях, важные моменты.
Как купить дипломы онлайн, безопасность на первом месте.
Какой диплом выбрать для покупки, интересные варианты.
Купить диплом с доставкой по всему миру, подробности здесь.
Почему стоит заказать диплом на нашем сайте, безопасность на первом месте.
купить диплом [url=https://7arusak-diploms.com/]https://7arusak-diploms.com/[/url] .
sildenafil 50 mg how long does it last
[url=https://aaccutane.com/]accutane capsule[/url]
[url=https://drdoxycycline.online/]price doxycycline 100mg without prescription[/url]
24 7 online pharmacy
[url=http://albuterolp.online/]ventolin inhaler without prescription[/url]
[url=http://lasixor.com/]can i buy furosemide without a prescription[/url]
[url=http://modafinilmip.online/]provigil tablets[/url]
[url=https://ciproo.online/]ciprofloxacin prescription[/url]
[url=http://ibaclofen.com/]baclofen cream[/url]
I genuinely enjoy studying on this web site, it contains fantastic content.
[url=http://advaird.online/]advair online pharmacy[/url]
veganchoicecbd.com
첫 공세에서 과연 어떤 결과가 나올지…
I like this web site very much, Its a real nice billet to read and incur info . “Being powerful is like being a lady. If you have to tell people you are, you aren’t.” by Margaret Hilda Thatcher.
[url=https://abamoxicillin.com/]amoxicillin singapore pharmacy[/url]
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://modafinilmip.online/]how to buy modafinil in india[/url]
Привет!
Последние события и главные новости Кропивницкого в одном месте! Мы оперативно сообщаем о происшествиях, обновлениях инфраструктуры, политических решениях и многом другом. Оставайтесь с нами, чтобы всегда быть в центре событий.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://bomba.kr.ua/
[url=https://bomba.kr.ua/]Главные новости Украины[/url]
Новости Кропивницкого аварии
последние новости Украины
Новости Кропивницкого
Удачи!
how long does sildenafil stay in your system
[url=https://prednisonecsr.online/]prednisone online[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinps.online/]generic azithromycin[/url]
[url=https://acyclovirlp.online/]acyclovir 500 mg price[/url]
[url=http://accutanemix.online/]cheap accutane singapore[/url]
[url=https://adfinasterid.online/]buy propecia pills[/url]
[url=http://drdoxycycline.online/]buy doxycycline 100 mg tablet[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinmds.com/]azithromycin 1000mg tablet[/url]
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://odiflucan.online/]diflucan over the counter uk[/url]
Заказать купленный диплом, не выходя из дома.
Легальный способ купить диплом, узнайте сейчас.
Какой диплом купить, проверенные варианты.
Почему выгодно купить диплом, рассказываем.
Где купить диплом без проблем, с гарантией.
Купить диплом по выгодной цене, важные моменты.
Дипломы на заказ по лучшим ценам, лучшие условия.
Покупка диплома: безопасность и конфиденциальность, проверенные решения.
Где купить действующий диплом, срочно и выгодно.
Покупка диплома: безопасность и качество, лучшие условия.
Почему стоит купить диплом у нас, гарантированное качество.
Как купить диплом срочно, подробности на сайте.
Официальные дипломы для покупки, подробности у нас.
Как выбрать и купить диплом, лучшие предложения.
Купить диплом без риска, подробности у нас.
Почему стоит купить диплом здесь и сейчас, интересные варианты.
Заказать диплом онлайн без проблем, важные детали.
Как купить диплом безопасно и быстро, безопасность на первом месте.
купить диплом [url=http://7arusak-diploms.com/]http://7arusak-diploms.com/[/url] .
[url=http://sildalis.store/]buy cheap sildalis fast shipping[/url]
[url=https://oazithromycin.com/]azithromycin 250 mg tablet price in india[/url]
[url=https://metforminn.online/]metformin buy online[/url]
Hello students and applicants!
Embark on a Journey of Discovery: Mathematical Economics and Data Analysis at https://satbayev.university/
Welcome to Satbayev University’s Mathematical Economics and Data Analysis program, where analytical rigor meets real-world applications. As we open admissions for the 2024 academic year, we invite you to become part of a community that values precision, analytical thinking, and data-driven decision-making.
Program Overview Our program is designed for those who aspire to delve into the complexities of economics and harness the power of data analysis. You will explore the mathematical underpinnings of economic theory, learn cutting-edge data analysis techniques, and apply your knowledge to solve pressing economic problems.
Admission Requirements
A strong foundation in mathematics and a keen interest in economics.
Proficiency in English, with the ability to engage in complex analytical discussions.
A bachelor’s degree in economics, mathematics, or a related field (for graduate programs).
Official transcripts, a statement of purpose, and two letters of recommendation.
Curriculum Highlights
Advanced courses in microeconomics, macroeconomics, and econometrics.
Training in statistical software and data analysis tools.
Opportunities for research and real-world data projects.
Electives that allow you to tailor your education to your career goals.
Career Prospects Graduates of our program are well-equipped for careers in:
Economic analysis and policy-making.
Data analytics and business intelligence.
Financial markets and risk management.
Research and academia.
Application Process Begin your journey by submitting an online application through our university portal. Ensure that all required documents are uploaded and that you meet the specified deadlines. Our admissions team is dedicated to a holistic review of each applicant, considering both academic achievements and potential for future success.
Join Us At Satbayev University, we’re not just educating the next generation of economists and data analysts; we’re shaping the future of decision-making in business and policy. Apply now and take the first step towards a fulfilling career at the intersection of mathematics, economics, and data analysis.
[url=https://satbayev.university/]Innovative Research in University[/url]
Compiler
Firewall
Campus Visit
Tuition Deposit
Good luck and good progress!
Заказать купленный диплом, не выходя из дома.
Как купить диплом без риска, узнайте сейчас.
Купить диплом с гарантией качества, проверенные варианты.
Опыт успешной покупки диплома, подробности.
Где купить диплом без проблем, без риска.
Как выбрать диплом для покупки, важные моменты.
Как купить диплом быстро, подробности на сайте.
Скрытая покупка дипломов, важная информация.
Как быстро купить диплом, только актуальная информация.
Купить диплом срочно и законно, лучшие условия.
Почему стоит купить диплом у нас, гарантированное качество.
Безопасное приобретение документов об образовании, подробности на сайте.
Официальные дипломы для покупки, гарантированный результат.
Дипломы на всех условиях, важные моменты.
Легальная покупка дипломов безопасно, безопасность на первом месте.
Какой диплом выбрать для покупки, подробности на сайте.
Заказать диплом онлайн без проблем, важные детали.
Официальный документ об образовании, гарантированный результат.
купить диплом [url=https://www.7arusak-diploms.com]https://www.7arusak-diploms.com[/url] .
[url=https://dexamethasoneff.com/]dexamethasone 500[/url]
Have you ever thought about creating an e-book or guest authoring on other blogs? I have a blog based upon on the same topics you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my viewers would enjoy your work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an e mail.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://diflucanr.online/]150 mg diflucan online[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://acyclovirmc.online/]acyclovir prices[/url]
There is apparently a bunch to realize about this. I feel you made various good points in features also.
[url=http://accutaneiso.online/]how to get accutane online[/url]
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://ciproffl.online/]ciprofloxacin mail online[/url]
[url=http://finasterideff.com/]propecia online usa[/url]
[url=http://clomidsale.com/]clomid 50mg mexico[/url]
[url=http://ibaclofen.online/]10 mg baclofen[/url]
[url=http://itretinoin.online/]where can i buy retin a cream in australia[/url]
[url=http://finasterideff.com/]finpecia online[/url]
[url=http://itretinoin.com/]retin a order[/url]
[url=https://eflomax.online/]flomax canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://lasixor.com/]furosemide 500[/url]
[url=http://bacclofen.online/]baclofen 5 mg price[/url]
[url=http://flomaxms.com/]flomax buy online[/url]
[url=http://albuterolp.online/]albuterol for sale canada[/url]
[url=https://valtrexv.online/]cheap valtrex for sale[/url]
[url=http://baclofem.com/]baclofen prescription cost[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://azithromycinps.online/]cheap zithromax pills[/url]
[url=http://prednisonecsr.online/]prednisone 1 tablet[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilu.com/]where can i buy cialis uk[/url]
[url=http://finasterideff.online/]where to buy propecia online[/url]
[url=http://finasterideff.com/]finasteride online bonus[/url]
Acceptable to Genio, the go-to invoice generator quest of slight feel embarrassed businesses and freelancers. We bring you many invoice templates, including Microsoft Dominate and PDF formats, tailored to all industries. Investigate our fraction featuring upon 300 customized invoice templates designed to cosset to your multiform responsibility needs.
https://www.genio.ac/invoice-templates/
[url=https://baclofenx.com/]lioresal 10mg[/url]
[url=https://ciprocfx.com/]ciprofloxacin 1000 mg[/url]
[url=https://bacclofen.online/]where can i buy baclofen[/url]
Привет всем!
Привет, друзья! Сегодня я расскажу, как сделать свою игру в онлайн-казино максимально комфортной, выгодной и захватывающей. Для начала вам необходимо скачать казино на свой Android-смартфон или планшет. Мобильные приложения позволяют играть в любимые игровые автоматы, рулетку, блэкджек и другие азартные игры в любом месте и в любое время. Просто представьте: вы едете в метро или ждете друзей в кафе – и можете скрасить время за игрой!
https://rusdozor.ru/2024/04/14/pochemu-igrovye-kompyuternye-kluby-prodolzhayut-byt-populyarnymi-10-osnovnyx-prichin_1429992/
мобильное казино на реальные деньги
азиномобиле вход
1 гоу casino
мобильном casino скачать бесплатное
игровые автоматы с выводом денег на андроид
Удачи!
Spot on with this write-up, I truly suppose this web site needs much more consideration. I’ll probably be once more to learn much more, thanks for that info.
Привет!
Играть в казино с реальными дилерами — это как посетить вечеринку, где вас встречают старые друзья, которых вы никогда не видели. Обаятельные дилеры улыбаются вам через экран, и вы понимаете, что эта улыбка может стоить вам денег. Но ощущение реального присутствия добавляет игре пикантности. Вы чувствуете напряжение, когда дилер медленно раздает карты, и ваше сердце замирает — не от страха, а от предвкушения чуда. И знаете, в эти моменты я всегда думаю: “А вдруг сегодня мой день?” Это как смотреть фильм, где вы не только зритель, но и главный герой. Так что давайте играть, общаться и, конечно, выигрывать. Ведь как говорят: фортуна любит смелых!
https://nordu.ru/2024/04/29/Клубника-Казино-регистрация-и-вход-ваш-путь-к-азарту-и-развлечениям
игровые автоматы на деньги для андроид онлайн
казино с реальными дилерами
мобильное казино на реальные деньги win
какое казино можно пополнить по qr коду
мобильное казино с выводом денег
Удачи!
Привет всем!
Первый шаг – скачайте на свой Android-гаджет качественное приложение понравившегося казино. Только официальный лицензированный софт гарантирует безопасность, честность и стабильную работу без подвисаний. Рекомендую присмотреться к операторам, которые жарят бонусы на первый депозит новичкам.
[url=http://xn--80aeahbdc6cr3b7h.xn--p1ai/club/user/8729/blog/192918/]xn--80aeahbdc6cr3b7h.xn--p1ai[/url]
официальный сайт игровых автоматов в обход блокировки
unlim casino на андроид
скачать казино на реальные деньги
официальный сайт казино
бонусы казино на первый депозит
Удачи!
[url=https://okmodafinil.com/]where to buy modafinil in canada[/url]
dark web market links [url=https://mydarkmarket.com/ ]darknet websites [/url] black internet
Здравствуйте!
Знаете ли вы, что мобильное казино это не просто удобство, это ваш личный портал в мир азарта, который всегда с вами? Представьте, что ваш смартфон – это волшебная палочка. Махнули ей, и вуаля, вы уже выбираете, на каком автомате испытать судьбу. Игра в мобильном казино – это как отправиться в Лас-Вегас, не вставая с уютного дивана. Быстрая загрузка, пополнение с Киви на два клика и вы уже в игре. Ведь в жизни так много случаев, когда нужно куда-то добраться или просто подождать, так почему бы не сделать это время захватывающим? И помните, мобильное казино никогда не спит, оно как ваш самый надежный друг, всегда на связи!
https://turbomik.ru/2024/05/10/Вулкан-Лев-Казино-которое-заботится-о-своих-игроках
промокоды казино
казино официальный сайт лицензионный зеркало
казино на русском
онлайн казино миллион промокод
приложение казино win
Удачи!
[url=http://modafinile.online/]can you buy provigil online[/url]
[url=https://diflucand.online/]buy diflucan online india[/url]
[url=http://finasterideff.com/]propecia 0.5 mg[/url]
tintucnamdinh24h.com
사실 이런 생각을 가진 사람은 장창만이 아니다.
[url=https://xmodafinil.com/]provigil india buy[/url]
[url=http://lasixtbs.online/]lasix 20 mg price[/url]
[url=http://baclofenx.online/]lioresal 25 mg[/url]
darknet site [url=https://mydarknetmarketlinks.com/ ]darkmarket url [/url] dark web site
[url=http://diflucand.online/]diflucan canada coupon[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinps.online/]azithromycin drug[/url]
[url=http://drdoxycycline.online/]doxycycline online sale[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinps.online/]azithromycin for sale cheap[/url]
[url=https://eflomax.online/]flomax kidney stone[/url]
[url=http://xmodafinil.com/]online modafinil prescription[/url]
[url=http://lyricamd.com/]lyrica pills 75 mg[/url]
[url=http://dexamethasoneff.online/]dexamethasone 12 mg[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://sildenafilps.online/]sildenafil sale uk[/url]
[url=https://lasixav.online/]lasix 40 mg tabs[/url]
[url=https://advaird.online/]average price for advair[/url]
[url=http://xlyrica.online/]buy lyrica online from canada[/url]
[url=http://ibaclofen.online/]baclofen prescription cost[/url]
[url=http://tretinoineff.online/]where can i buy tretinoin over the counter[/url]
[url=https://ibaclofen.online/]baclofen tablet price[/url]
[url=https://accutanemix.online/]can you order accutane online[/url]
[url=https://vermox.company/]buy vermox in usa[/url]
[url=https://zithromaxl.online/]azithromycin tablets 500g[/url]
[url=http://ciproo.online/]can i buy ciprofloxacin over the counter uk[/url]
Mailing:
Interacting via comment forms is an expressive expression of modern business interaction, integrating the top of discretion and technology. This strategy gives companies a direct line to their consumers, allowing them to grasp the details of user interaction, gather constructive feedback, and, most importantly, show that they are constantly attending. Rather than sifting through the overcrowded scene of emails and promotional messages, feedback forms provide a clean space, setting the path for authentic dialogue and further engaged conversations.
Moreover, communicating to response forms is a testament to a brand’s devotion to ongoing improvement. Rather than of working in a isolation, companies get an priceless window into their clients’ minds, unveiling chances for development, betterment, and creating firmer connections. As customer needs evolve, this reciprocal interaction channel confirms that brands stay not just pertinent but deeply connected to their viewer’s ever-changing likes and concerns. In the big design of things, it’s not just about amassing feedback; it’s about nurturing confidence and strengthening bonds that endure the challenge of time.
Отчётность.
Оплата: Yoo.Деньги, Bitcoin, МИР, Visa, MasterCard…
Принимаем USDT
Telgrm: @exrumer
Skype: Loves.Ltd
https://xrumer.cc/
Только этот.
[url=http://itretinoin.com/]0.1 retin a gel[/url]
[url=https://avermox.com/]buy vermox nz[/url]
The Lottery Defeater software is an innovative program designed to enhance your lottery playing experience. Utilizing cutting-edge algorithms, it s
[url=https://modafinile.online/]order modafinil online usa[/url]
[url=https://ibaclofen.online/]cost of baclofen[/url]
[url=http://declomid.online/]order clomid online usa[/url]
[url=http://amoxicillinir.online/]augmentin 500mg tablets[/url]
dark web access [url=https://mydarknetmarketlinks.com/ ]tor markets [/url] dark market onion
[url=http://eflomax.com/]noroxin[/url]
veganchoicecbd.com
Fang Jifan은 “실제로 서로를 존중하는 방법을 알고 있습니다. “라고 흥얼 거렸다.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://itretinoin.online/]tretinoin without prescription[/url]
[url=https://albuterolp.com/]albuterol from canada[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinmds.com/]azithromycin 1000 mg cost[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://strattera.company/]how to buy strattera online[/url]
[url=https://sildalis.store/]buy sildalis[/url]
Доставка алкогольной продукции на дом в Сочи круглосуточно
Нередко возникают ситуации, когда в самый разгар вечеринки у вас заканчиваются алкогольные напитки, и вы хотите продолжить веселье, но магазины уже закрыты. В таких случаях вы можете обратиться к нам, и мы быстро доставим вам качественные продукты прямо к дому. Наш сервис предоставляет легальную доставку, быструю доставку и удобные способы оплаты – вот наши преимущества.
Основные причины выбрать нас
[url=https://alco-sochi-25.store/]алкоголь доставка сочи круглосуточно[/url]
Законность. Мы соблюдаем законы, запрещающие дистанционную продажу алкоголя.
Удобство. Вы можете произвести оплату путем перевода на банковскую карту по номеру телефона.
Быстрота. Мы осуществляем доставку по Сочи уже через 15 минут.
Мы не только предлагаем купить качественный алкоголь, но и осуществляем доставку даже ночью прямо к вашему дому. Мы доставим пиво, крепкие алкогольные напитки и безалкогольные напитки в любую часть города.
Важно отметить, что приобретение алкоголя через интернет с доставкой является незаконным. Согласно закону 171 ФЗ, п. 14 ч. 2 ст. 16, продажа алкогольной продукции дистанционным способом запрещена. При оформлении заказа через наши онлайн-сервисы необходимо подтвердить, что вам исполнилось 18 лет, а также согласиться с приобретением сувениров алкогольной тематики. При заказе доставки в отдаленные районы города учтите возможные пробки на дорогах и погодные условия. Мы с удовольствием доставим вам продукцию в Адлер, Дагомыс, Мацесту, Кудепсту, Бытху, Мамайку, Хосту.
Доставкой алкоголя на дом – быстро и надёжно!
Наши услуги доставки алкоголя на дом предоставляются круглосуточно! Добро пожаловать на наш сайт, посвященный доставке алкоголя на дом в Сочи 24/7. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент алкогольных напитков, доступных для заказа в любое время суток. Наша команда опытных специалистов готова обеспечить вас отличным сервисом и удовлетворить ваши предпочтения вкуса.
Наши преимущества:
https://dostavka-alko-sochi-14.store/
доставка пива на дом сочи
Быстрая и надежная доставка: Мы понимаем важность получения заказа вовремя, поэтому предлагаем надежную и оперативную доставку. Наша служба доставки работает круглосуточно, чтобы вы могли наслаждаться алкоголем в любое время.
Широкий ассортимент: Мы тщательно подбираем лучшие алкогольные напитки со всего мира. У нас вы найдете разнообразные сорта пива, вина, крепкие спиртные напитки, шампанское и многое другое. Мы также предлагаем различные аксессуары для алкоголя, чтобы обогатить ваш опыт употребления напитков.
Премиальное качество: Мы сотрудничаем только с проверенными поставщиками, чтобы гарантировать вам высокое качество алкогольных напитков. Все наши продукты проходят строгий контроль качества, чтобы удовлетворить ваши ожидания.
Ценовая доступность: У нас есть алкогольные напитки на любой вкус и бюджет. Мы предлагаем разнообразные ценовые категории, чтобы каждый клиент мог найти оптимальное соотношение цены и качества.
Простой процесс заказа: Наш сайт предоставляет удобный интерфейс для размещения заказа. Вы можете легко выбрать нужные товары, указать адрес доставки и оформить оплату всего в несколько кликов. Мы также принимаем различные методы оплаты для вашего удобства.
Профессиональная поддержка: Наша команда службы поддержки всегда готова помочь вам с любыми вопросами или проблемами, возникшими во время заказа или доставки. Мы стремимся обеспечить высокий уровень удовлетворенности клиентов.
Безопасность и конфиденциальность: Мы обеспечиваем полную конфиденциальность ваших данных и гарантируем безопасность при совершении покупок. Ваши личные данные и платежные реквизиты защищены с помощью современных технологий шифрования.
Без разницы, нужен ли вам алкоголь для вечеринки, романтического ужина или просто для расслабления после долгого дня – наша служба доставки алкоголя на дом в Сочи ночью готова стать вашим надежным партнером. Закажите прямо сейчас и наслаждайтесь вкусными напитками в уюте своего дома!
[url=http://oazithromycin.online/]azithromycin 200[/url]
[url=http://ifinasteride.com/]over the counter propecia[/url]
[url=https://adexamethasonep.online/]dexamethasone 0 5 mg[/url]
[url=http://modafinilmip.online/]modafinil without prescription[/url]
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://baclofenx.com/]baclofen tablets brand name[/url]
[url=http://diflucand.online/]can you buy diflucan over the counter in us[/url]
[url=https://vermox.company/]vermox price in south africa[/url]
[url=http://modafinilmip.online/]best modafinil[/url]
dark web websites [url=https://mydarknetmarketlinks.com/ ]tor marketplace [/url] tor marketplace
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]where to buy azithromycin 500mg[/url]
[url=http://drdoxycycline.online/]best price doxycycline uk[/url]
[url=https://modafinile.com/]modafinil generic cost[/url]
[url=https://okmodafinil.com/]modafinil prescription price[/url]
[url=https://lyricawithoutprescription.com/]lyrica cheap online[/url]
[url=https://xlyrica.online/]lyrica generic medication[/url]
[url=https://amoxil.company/]amoxicillin purchase[/url]
vardenafil interactions
slevotra vardenafil
[url=https://ciprocfx.com/]cipro 250[/url]
[url=http://eflomax.com/]how to get flomax[/url]
[url=https://okmodafinil.com/]modafinil singapore buy[/url]
[url=https://clomidsale.com/]clomid medication south africa[/url]
Hatay defne otelleri
[url=http://albuterolp.online/]ventolin for sale uk[/url]
[url=http://lasixor.online/]lasix iv[/url]
[url=https://avermox.com/]vermox over the counter uk[/url]
[url=https://modafinile.com/]can you order modafinil online[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]buy generic zithromax[/url]
[url=http://ciproo.online/]cipro.com[/url]
[url=http://lasixtbs.com/]buy lasix 100mg[/url]
[url=https://lasixav.online/]lasix online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://glucophage.online/]metformin 500 mg buy online[/url]
[url=http://strattera.company/]buying strattera from canada[/url]
[url=https://accutaneiso.online/]isotretinoin accutane[/url]
vardenafil 20 mg online
[url=https://dexamethasoneff.online/]dexona tablet[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]azithromycin without rx[/url]
[url=https://modafinilmip.online/]buy cheap provigil[/url]
[url=http://effexor.directory/]effexor 37 5 mg[/url]
[url=http://accutanemix.online/]accutane online order[/url]
vardenafil dosage maximum
Как получить пропуск на МКАД, что нужно знать, Важная информация о пропуске на МКАД, которую важно помнить, Часто задаваемые вопросы о пропуске на МКАД, на которые нужно знать ответы, основные моменты, рекомендации, важные детали, подробная информация
Проверить пропуск на мкад [url=https://gargopermits.com/]Пропуск на мкад[/url] .
[url=https://618-27-83.ru/]https://618-27-83.ru/[/url]
– RamenBet казино
Подробная инструкция по оформлению пропуска на МКАД, Срочное оформление пропуска на МКАД, лайфхаки, которую нужно знать, основные требования, Пропуск на МКАД: сроки и стоимость, Как оформить пропуск для движения по МКАД, Какие преимущества дает пропуск на МКАД, Сроки и порядок продления пропуска на МКАД, полный гайд
Проверить пропуск на мкад [url=https://gargopermits.com/]Пропуск на мкад[/url] .
largestcatbreed.com
황제는 한 마디로 결론을 내렸고 이론적으로는 있다고 말했고 실제로 있습니다.
Секреты оформления пропуска на МКАД, основные моменты, Важная информация о пропуске на МКАД, которую нужно знать, полный гайд, Информация о стоимости и сроках пропуска на МКАД, основные моменты, Какие преимущества дает пропуск на МКАД, основные аспекты, шаг за шагом
Проверить пропуск на мкад [url=https://gargopermits.com/]Проверить пропуск на мкад[/url] .
An impressive share, I simply given this onto a colleague who was doing a bit of analysis on this. And he in actual fact bought me breakfast as a result of I discovered it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the treat! However yeah Thnkx for spending the time to debate this, I feel strongly about it and love reading extra on this topic. If doable, as you develop into expertise, would you thoughts updating your blog with extra details? It is extremely useful for me. Huge thumb up for this blog post!
Подробная инструкция по оформлению пропуска на МКАД, Срочное оформление пропуска на МКАД, лайфхаки, которую стоит учесть, 10 вопросов о пропуске на МКАД, на которые нужно знать ответы, важные аспекты, Почему стоит получить пропуск на МКАД, Инструкция по продлению пропуска на МКАД, шаг за шагом
Пропуск на мкад [url=https://gargopermits.com/]Пропуск в москву[/url] .
[url=https://adexamethasonep.online/]dexamethasone 4 mg tablet online[/url]
[url=http://albuterolp.online/]order ventolin online canada[/url]
[url=http://baclofenx.com/]can you buy baclofen without a prescription[/url]
[url=https://declomid.online/]clomid pharmacy prices[/url]
Как получить пропуск на МКАД, советы, Ключевые моменты о пропуске на МКАД, которую нужно знать, Основные вопросы о пропуске на МКАД, которые важно учесть, важные аспекты, советы, основные аспекты, полный гайд
Проверить пропуск на мкад [url=https://gargopermits.com/]Проверить пропуск на мкад[/url] .
bismil şark odaları
[url=https://accutanemix.online/]accutane discount[/url]
[url=https://baclofenx.online/]baclofen india[/url]
[url=http://drdoxycycline.online/]doxycycline 2985[/url]
Подробная инструкция по оформлению пропуска на МКАД, Как быстро получить пропуск на МКАД, Важная информация о пропуске на МКАД, Какие документы нужны для оформления пропуска на МКАД, полный гайд, Сколько стоит и как долго делается пропуск на МКАД, Эффективные способы получения пропуска для МКАД, Какие преимущества дает пропуск на МКАД, Сроки и порядок продления пропуска на МКАД, шаг за шагом
Проверить пропуск на мкад [url=https://gargopermits.com/]Проверить пропуск на мкад[/url] .
[url=https://lasixtbs.com/]average cost of lasix[/url]
[url=http://tretinoineff.com/]retin a cost in india[/url]
[url=http://tretinoineff.com/]over the counter tretinoin canada[/url]
This paragraph will help the internet viewers for building up new blog or even a weblog
from start to end.
[url=http://azithromycinmds.online/]azithromycin purchase usa[/url]
[url=https://ezithromycin.online/]buy generic zithromax online[/url]
[url=http://diflucanr.com/]where to buy diflucan in singapore[/url]
[url=http://ibaclofen.com/]baclofen 10 mg tablet 1mg[/url]
Как получить пропуск на МКАД, Эффективные способы получения пропуска на МКАД, Важная информация о пропуске на МКАД, Пропуск на МКАД: какие документы нужны, подробная инструкция, Информация о стоимости и сроках пропуска на МКАД, Как получить пропуск для поездок по МКАД, инструкции, основные аспекты, полный гайд
Проверить пропуск на мкад [url=https://gargopermits.com/]Проверить пропуск на мкад[/url] .
[url=https://drdoxycycline.online/]buy doxycycline 100mg[/url]
[url=http://okmodafinil.com/]modafinil price comparison[/url]
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://ciproo.online/]generic for cipro[/url]
[url=http://advaird.com/]generic advair 2014[/url]
[url=https://okmodafinil.com/]provigil pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://asynthroid.online/]synthroid 25 mg tablet[/url]
[url=http://metforminn.online/]metformin 500mg with out presciption[/url]
[url=http://avermox.com/]vermox price in south africa[/url]
Привет, товарищи-игроманы!
Хочу поделиться с вами своей радостью – после долгих поисков стейк регистрация и клубника казино вход, я наконец-то нашел идеальное онлайн казино! Знаете, как бывает – ищешь, пробуешь разные сайты, а они все какие-то не такие: то интерфейс кривой, то с выплатами тянут, то поддержка не отвечает, то игр раз-два и обчелся. Я уж думал, все, не судьба мне найти свой игровой рай.
Но тут поискав lev casino зеркало я попал на Telegram [url=https://t.me/s/clubnika_cas]clubnika казино[/url] и понял – вот оно, то самое! Ребята, это просто бомба! Все сделано для людей:
– Интерфейс – закачаешься! Все интуитивно понятно, глаз радуется.
– Выплаты – моментальные! Выиграл – и уже денежки у тебя на счету.
– Саппорт – 24/7, отвечают быстро, решают любые вопросы. Профи!
– Игры – на любой вкус! Хочешь классику – вот тебе слоты. Хочешь пообщаться – иди к живым дилерам. И постоянно что-то новенькое добавляют!
– Бонусы – щедрые, как Санта на Рождество! За регистрацию, за пополнение – бери не хочу!
В общем, я теперь только на https://t.me/clubnika_caz зависаю. Если вы тоже в поисках своего идеального казино – очень рекомендую заглянуть, не пожалеете!
А кто уже тут играет – делитесь впечатлениями в комментах, интересно пообщаться! Да и вообще, делитесь своими лайфхаками, историями больших выигрышей (и проигрышей ), будет круто!
Ну что, поехали ловить удачу за хвост? Всем фарта и жирных заносов!
Привет, азартные друзья!
Хочу поделиться с вами своей историей поиска идеального онлайн казино. Как заядлый игрок, я перепробовал кучу разных сайтов в надежде найти тот самый, который удовлетворит все мои запросы. Искал водка casino и сука казино, но постоянно натыкался на какие-то проблемы: то интерфейс неудобный, то с выплатами затягивают, то поддержка не отвечает, то игр маловато. Короче, казалось, что моя мечта так и останется мечтой.
Но недавно после поиска сука казино мне попался Telegram [url=https://t.me/jvspin_zerkalo]jvspin casino[/url], и я понял – вот оно, то самое казино, которое я так долго искал! Ребята, это просто находка!
Давайте я расскажу, чем же меня так зацепил этот сайт:
Интерфейс – просто огонь! Все интуитивно понятно, даже если ты новичок. Никакой лишней инфы, все по делу.
Выплаты – моментальные! Я сам проверял – выиграл и тут же получил свои денежки на счет. Никаких задержек!
Поддержка – реально работает! Отвечают быстро, помогают решить любые вопросы. И главное – они доступны круглосуточно.
Игры – на любой вкус и цвет! Хочешь классические слоты – пожалуйста. Хочешь пообщаться с живыми дилерами – легко. И постоянно добавляют что-то новенькое, не заскучаешь!
Бонусы – просто сказка! Приветственные, на первый депозит, фриспины – все для того, чтобы ты остался доволен.
Конечно, у каждого свои критерии идеального казино. Но для меня https://t.me/s/clubnika_caz стало настоящей находкой. Так что если вы тоже в поисках своего игрового рая – очень рекомендую заглянуть сюда. Уверен, вы не пожалеете!
А может кто-то из вас уже играл на этом сайте? Поделитесь своими впечатлениями в комментах, мне очень интересно узнать ваше мнение!
Ну что, поехали испытывать удачу? Всем успехов и крупных выигрышей!
ihrfuehrerschein.com
이것은 분명히 총무과의 내시이며 그는 매우 빠르게 달리고 있습니다.
[url=https://doxycyclineo.com/]how can i get doxycycline over the counter[/url]
[url=https://albuterolo.com/]albuterol online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://okmodafinil.com/]buy modafinil usa online[/url]
[url=http://acyclovirmc.online/]zovirax ointment[/url]
[url=https://acyclovirmc.online/]acyclovir daily use[/url]
[url=http://acutanep.online/]buy generic accutane[/url]
[url=https://enolvadex.online/]nolvadex price in south africa[/url]
[url=http://acyclovirlp.online/]acyclovir 2000 mg[/url]
[url=http://acutanep.online/]order accutane online canada[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinmds.online/]azithromycin tablets 250 mg price in india[/url]
[url=https://prednisonecsr.online/]buy prednisone canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://mcadvair.online/]advair diskus 250 price canada[/url]
[url=http://modafinilon.online/]modafinil 200mg[/url]
I have not checked in here for a while since I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are great quality so I guess I will add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
[url=https://xlyrica.com/]lyrica 100 mg coupon[/url]
[url=http://xlyrica.online/]buy lyrica uk[/url]
bursa evden eve nakliyat
[url=https://accutaneiso.com/]accutane from mexico[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinmds.com/]where can i get azithromycin[/url]
[url=http://dexamethasoneff.online/]dexamethasone tablets online[/url]
[url=http://toradol.directory/]toradol pill 10mg[/url]
[url=http://zithromaxl.online/]zithromax 500 price[/url]
[url=http://albuterolo.com/]albuterol canada price[/url]
Thank you for sharing with us, I believe this website really stands out : D.
[url=http://abamoxicillin.com/]amoxicillin 750[/url]
[url=https://ciprocfx.com/]cipro tablet 500 mg price[/url]
[url=https://tadacip.store/]tadacip 20 buy online[/url]
[url=http://baclofenx.online/]baclofen 25 mg tablet[/url]
[url=http://sildenafilps.online/]200 mg viagra for sale[/url]
[url=http://avermox.com/]buy vermox online[/url]
[url=http://finasterideff.online/]propecia where to buy[/url]
[url=https://roserica.ru/]https://roserica.ru/[/url]
– RamenBet
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://drdoxycycline.online/]doxycycline 50 mg generic[/url]
thebuzzerpodcast.com
Hongzhi 황제가 일어났습니다. “나는 피곤합니다. 떠나십시오.”
[url=http://lasixor.online/]lasix 100 mg[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Привет!
Жизнь Винницы в новостях: последние события, главные новости и самые интересные истории. Оставайтесь с нами, чтобы знать все о своем городе.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://bomba.vn.ua/
[url=https://bomba.vn.ua/category/novini-ukraini/]Последние новости Украины[/url]
новости Украины
Новости Винницы за день
новости Украины за день
Удачи!
[url=https://doxycyclineo.com/]doxycycline capsules[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]uk azithromycin over the counter[/url]
[url=https://doxycyclinepr.com/]doxycycline best price[/url]
[url=https://bacclofen.online/]order baclofen online usa[/url]
[url=http://lasixor.com/]lasix 3170[/url]
[url=https://odiflucan.online/]diflucan rx[/url]
[url=https://acyclovirlp.online/]buy zovirax usa[/url]
[url=https://vermox.company/]vermox generic[/url]
[url=https://modafinile.com/]buy provigil online with mastercard[/url]
[url=https://bacclofen.online/]where to buy baclofen online[/url]
[url=http://finasterideff.com/]propecia india online[/url]
[url=https://lyricamd.com/]lyrica for sale[/url]
Привет всем!
Новости Украины и мира: все ключевые события, важные обновления и интересные факты. Оставайтесь с нами, чтобы не пропустить ничего важного.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://omind.com.ua/category/svit/
[url=https://omind.com.ua/]Последние новости Украины[/url]
последние новости Украины
новости мира сегодня
Главные новости Украины
Удачи!
[url=https://lyricamd.com/]buy lyrica online india[/url]
[url=http://acutanep.online/]accutane 2009[/url]
[url=https://baclofenx.com/]baclofen 25 mg australia[/url]
[url=https://odiflucan.com/]generic for diflucan[/url]
[url=https://lasixor.online/]lasix medication over the counter[/url]
[url=http://baclofenx.online/]how to get baclofen[/url]
[url=https://baclofenx.com/]baclofen 10 mg pill[/url]
[url=https://ciprocfx.com/]ciprofloxacin australia[/url]
[url=http://sildenafilps.online/]cost of 1 viagra pill[/url]
Свидетельство О Расторжении Брака
Свидетельство О Расторжении Брака
К счастью, есть организации, где покупка качественных, настоящих дипломов возможна. Если вы задумываетесь о том, чтобы заказать курсовую работу на этом сайте, отзывы клиентов могут помочь вам в принятии решения. Это возможно благодаря современному офсетному, ламинирующему оборудованию, что создает высококачественную копию документа, которая не имеет визуальных расхождений с оригиналом. Не всегда свидетельство О Расторжении Брака настоящего диплома университета говорит о высокой квалифицированности. Вне зависимости от того какой ВУЗ был выбран, существует ещё один фактор на который следует обратить внимание при покупке диплома его цвет.
https://gruppa365-diploms-srednee.ru
Купить Диплом О Среднем Специальном Образовании В Москве
К тому же нет надобности собирать дополнительные документы и к тому же переживать за результаты тестов. Коммерческая основа в университетах заточена на расторженье оплаты, поэтому знания даются без энтузиазма. Для молодых людей, стремящихся удачно сделать брак в карьере и тех, кто имеет опыт в отрасли, отличным свидетельством станет заказать диплом фармацевта.
Купить Диплом В Вологде
Свяжитесь с нашими менеджерами любым удобным способом, расскажите им о своей проблеме или потребности в дипломе (аттестате), согласуйте предложенный вариант – и все, заявка принята, ожидайте пару дней. Также способ не тратить время на формальности, если не удалось доучиться совсем немного. Защитные элементы входят в состав бумаги, наносятся при её изготовлении.
[url=https://ifinasteride.com/]where to buy generic propecia uk[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]cheap azithromycin[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilu.com/]where to buy tadalafil[/url]
[url=https://bacclofen.online/]baclofen 10 mg price in india[/url]
[url=http://drdoxycycline.online/]buy doxycycline 100mg pills[/url]
ProvaDent is an all-natural, safe-to-take advanced oral probiotic complex that supports great dental health.
[url=http://valtrexv.online/]valtrex cream coupon[/url]
[url=http://tretinoineff.com/]tretinoin online prescription[/url]
[url=https://advaird.com/]advair 230[/url]
Как Восстановить Диплом О Среднем Профессиональном Образовании
Наши преимущества недорогие цены чтобы купить диплом специалиста. Высокое качество документов, доступные цены. Нами используются только подлинные бланки ГОЗНАКа Купить диплом педагога без предоплаты можно у нас. Обратившись в нашу компанию, Вы можете купить диплом медсестры на нашем сайте, который соответствует всем требованиям. Мы предлагаем исключительно настоящие документы на бланках ГОЗНАК. Необходим диплом для иностранцев любого вуза или любого другого высшего учебного заведения.
http://www.russkiy365-diploms-srednee.ru
Купить Диплом Капитана
Здравствуйте, печать в дипломе ставиться чернильной печатью или электронной. Мы ценим ваше время и стремимся к максимально быстрому выполнению заказов. Купить диплом в Москве, конечно не предполагает решение всякого рода проблем, однако приобретение диплома позволяет с большей уверенностью смотреть в завтрашний день.
Купить Диплом О Высшем Образовании В Алматы
Купить диплом о среднем образовании можно через надежных поставщиков, специализирующихся на создании образовательных документов. Результатом пройденной процедуры является документ, дающий право работать на должности врача либо медицинской сестры. Это важно для тех, кто планирует работать в государственных организациях или в сфере образования.
[url=http://effexor.directory/]effexor 20 mg[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://albuterolp.com/]ventolin 200[/url]
Привет!
Безопасность в Одессе выходит на новый уровень благодаря современным технологиям и мерам. Читайте о нововведениях, которые защищают город и его жителей.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://bomba.od.ua/
[url=https://bomba.od.ua/]Новости Одессы видео[/url]
Главные новости Украины
новости Украины сегодня
новости Украины за день
Удачи!
[url=https://ciprocfx.com/]ciprofloxacin for sale[/url]
[url=https://acyclovirmc.online/]zovirax 500 mg[/url]
onair2tv.com
“쑤 형제님…” 탕인이 침착하게 말했다.
[url=https://albuterolp.online/]albuterol inhaler price[/url]
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://lasixtbs.com/]lasix rx[/url]
[url=https://baclofenx.com/]baclofen purchase[/url]
[url=http://avermox.com/]vermox tablets price[/url]
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://clomidsale.com/]cheap clomid without prescription[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://prednisonecsr.online/]prednisone 50 mg for sale[/url]
child teen porn
[url=https://mcadvair.online/]advair diskus price in india[/url]
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://ciproo.online/]ciprofloxacin 500mg over the counter[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://albuterolp.com/]albuterol 90 mcg generic[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://amoxil.company/]buy amoxicillin online[/url]
[url=https://xlyrica.com/]lyrica cost in india[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Привет всем!
Историческое наследие Хмельницкого: Новые исследования и открытия проливают свет на богатую историю города. Читайте о находках и их значении для культурного наследия.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://bomba.km.ua/category/novini-khmelnickogo/
[url=https://bomba.km.ua/category/novini-ukraini/]Новости Украины ТОП[/url]
Новости Хмельницкого
новости Украины за день
последние новости Хмельницкого
Удачи!
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://avermox.online/]vermox tablets nz[/url]
[url=https://toradol.directory/]toradol for headaches[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinhq.com/]purchase azithromycin 1g[/url]
27-го июля был проведён первый тест эффективности [url=http://www.botmasterru.com/product109120/]XRumer 23 StrongAI[/url] (по сравнению с текущей версией XRumer 19.0.18), который показал двадцатикратный прирост. Столь впечатляющие результаты достигнуты благодаря многократному улучшению пробиваемости уже известных платформ, добавлению поддержки новых платформ, обучению сотням тысяч типов новых тексткапч, внедрению нового GPT-модуля, и множеству других улучшений. По ссылке ниже Вы сможете изучить и скачать детали теста (исходная база, кусок отчёта, статистику и другие подробности)
Спасибо за рефку:
http://www.botmasterru.com/product109120/
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://accutaneiso.com/]average cost of accutane[/url]
[url=https://xlyrica.online/]lyrica 30 mg[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://xlyrica.com/]buy lyrica online europe[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]azithromycin 500[/url]
[url=https://xlyrica.online/]lyrica prescription cost[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://diflucand.online/]diflucan generic over the counter[/url]
[url=https://okmodafinil.com/]how to buy modafinil in india[/url]
[url=http://ibaclofen.online/]baclofen 25 mg price[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://baclofenx.com/]lioresal discount[/url]
[url=http://mcadvair.online/]best advair prices[/url]
[url=http://lasixav.online/]furosemide online purchase[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinmds.online/]azithromycin 500 mg generic price[/url]
[url=http://odiflucan.com/]where to buy diflucan[/url]
[url=http://modafinile.online/]provigil canadian pharmacy[/url]
Доброго!
Культурные события Украины: Афиша самых ярких и интересных культурных мероприятий, которые пройдут в разных уголках страны в ближайшее время.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://beta.in.ua/ekonomika/
[url=https://beta.in.ua/proisshestviya/]Происшествия в Украине[/url]
новости мира
новости Украины за день
авто новости
Удачи!
k8 カジノ 銀行 出金 時間
このテーマについての深い洞察がとても気に入りました。良い仕事を続けてください。
Associate with our community of over 2 million elated users who are redemptory measure and getting paid faster with our travelling invoice solutions. Our unstationary invoicing tools, including mobile invoice apps, purvey to both iOS and Android users. Whether you have occasion for an invoice app in the interest iPhone, an Android invoice app, or a comprehensive versatile billing software, we’ve got you covered.
https://www.genio.ac/mobile-invoices
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]azithromycin over the counter canada[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinps.online/]azithromycin 500 mg generic price[/url]
XRumer – этто наиболее успешное равным образом лучшее программное обеспечение для создания гиперссылок и продвижения сайтов. Он используется для машинального прогона вебсайтов сквозь разные соц сети, форумы, блоги также другие интернет-ресурсы.
http://www.botmasterru.com/product33230/
Купить Хрумер Оффициально
[url=http://www.botmasterru.com/product33230/][img]https://xrumer.cc/i/x.png[/img][/url]
[url=https://eflomax.com/]flomax tablets in india[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinmds.online/]price of zithromax[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.online/]4 azithromycin cream[/url]
[url=https://enolvadex.online/]tamoxifen uk sale[/url]
[url=https://dexamethasoneff.online/]dexamethasone canada[/url]
[url=https://asynthroid.online/]450 mg synthroid[/url]
[url=https://lyricawithoutprescription.com/]buy lyrica mexico[/url]
[url=http://ibaclofen.online/]baclofen 10 mg pill[/url]
ilogidis.com
그는 침착하게 왕자를 바라본 다음 Fang Jifan을 바라 보았습니다.
[url=https://diflucanr.com/]diflucan over the counter usa[/url]
[url=https://asynthroid.online/]synthroid 25 mg cost[/url]
Привет всем!
Следите за свежими новостями Киева, чтобы быть в курсе всех событий в столице. Мы рассказываем о самых важных событиях и изменениях в городе, чтобы вы могли быть в курсе происходящего.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://bomba.kiev.ua/
[url=https://bomba.kiev.ua/category/novini-ukraini/]Новости Украины лента[/url]
Новости Киева за день
новости Украины
Главные новости Украины
Удачи!
[url=https://accutanemix.online/]where can you buy accutane[/url]
[url=http://ciproffl.online/]ciprofloxacin tablets online[/url]
[url=http://baclofem.com/]baclofen buy online uk[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.online/]azithromycin 250[/url]
Dive into the world of high-efficiency invoicing with our top-notch invoice maker app, made to measure payment the go-getters – freelancers and small area owners alike. We’re talking up transforming the way you handle bills, making it mountebank than ever.
https://apps.apple.com/us/app/invoice-maker-invoices/id6449437040
[url=http://accutanemix.online/]how can i get accutane online[/url]
[url=https://effexor.directory/]effexor cost uk[/url]
[url=https://itretinoin.online/]purchase retin a without prescription[/url]
[url=http://dexamethasonen.com/]dexamethasone medication[/url]
[url=http://odiflucan.com/]diflucan 1[/url]
[url=http://finasterideff.online/]buy finasteride 1mg australia[/url]
[url=https://acutanep.online/]accutane capsule[/url]
[url=https://xlyrica.online/]lyrica capsule[/url]
[url=http://diflucanr.com/]can you buy diflucan in mexico[/url]
[url=https://tretinoineff.online/]buy retin a online[/url]
[url=https://tadacip.store/]tadacip 20 mg[/url]
[url=http://valtrexv.online/]valacyclovir valtrex[/url]
[url=http://ciproo.online/]cipro medication over the counter[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://albuterolp.com/]can i buy albuterol[/url]
[url=http://xlyrica.com/]lyrica in mexico[/url]
[url=http://lasixor.online/]lasix 500 mg[/url]
mint tadalafil
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://diflucanr.com/]diflucan cream prescription[/url]
와일드 웨스트 골드
심지어… 농기구와 농기구도 많이 준비해야 한다.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://dexamethasoneff.online/]dexamethasone 4 mg pill[/url]
[url=https://itretinoin.com/]retin a cream mexico[/url]
[url=http://strattera.company/]strattera order online[/url]
[url=https://dezithromax.online/]zithromax buy cheap[/url]
[url=https://odiflucan.online/]order difucan[/url]
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://tretinoineff.com/]buy retin a 0.25 gel[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hey there! I’ve been following your web site for some time now and finally got the bravery to go ahead and give you a shout out from Humble Texas! Just wanted to say keep up the excellent work!
[url=http://bactrim.company/]bactrim buying[/url]
What Is ProDentim? ProDentim is a teeth health supplement developed to repopulate the mouth with good bacteria and improve overall dental health.
how to make tadalafil
very nice put up, i definitely love this web site, keep on it
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]azithromycin 500 mg coupon[/url]
[url=http://rettretinoin.online/]order retin-a[/url]
[url=http://lyricawithoutprescription.com/]purchase lyrica[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]zithromax purchase online[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]zithromax price canada[/url]
[url=https://enolvadex.online/]buy real nolvadex[/url]
casibom
판다스 포춘
Fang Jifan은 갑자기 “전하에게 아기가없는 이유는 무엇입니까? “라고 생각했습니다.
[url=https://enolvadex.com/]how to buy nolvadex[/url]
[url=https://albuterolo.com/]how to get albuterol in usa[/url]
[url=https://amoxicillinbact.com/]amoxicillin online pharmacy canada[/url]
[url=https://eflomax.online/]noroxin 400 mg canada price[/url]
[url=http://baclofenx.online/]buy baclofen usa[/url]
[url=https://modafinile.com/]modafinil tablets buy[/url]
What Is Sumatra Slim Belly Tonic? Sumatra Slim Belly Tonic is a weight management formula that is said to eliminate excess body fat naturally.
[url=https://mcadvair.online/]advair diskus prescription[/url]
[url=http://sildenafilps.online/]cheapest sildenafil australia[/url]
[url=https://adfinasterid.online/]how to get propecia[/url]
[url=http://dexamethasonen.com/]dexamethasone capsule[/url]
[url=https://doxycyclinepr.com/]doxycycline 50[/url]
[url=http://xlyrica.online/]buy lyrica online cheap[/url]
[url=https://xlyrica.online/]lyrica capsules 25 mg[/url]
[url=https://aaccutane.com/]how to buy accutane online[/url]
[url=https://rettretinoin.online/]tretinoin cream prescription[/url]
[url=https://baclofenx.online/]lioresal 25 mg[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://dexamethasonen.com/]dexamethasone 0.25 mg tablet[/url]
[url=https://doxycyclineo.online/]doxycycline pills cost[/url]
[url=https://eflomax.com/]flomax brand name[/url]
[url=https://lasixtbs.online/]where to buy lasix water pill[/url]
[url=http://finasterideff.com/]generic finasteride online[/url]
[url=http://mcadvair.online/]advair by mail[/url]
톰 오브 매드니스
형제 자매들이 모두 능력 있고 큰 성과를 거두는 것을 보았습니다.
[url=https://ibaclofen.online/]buy baclofen[/url]
[url=http://accutaneiso.online/]cheap accutane 40 mg[/url]
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
В ТЕЧЕНИЕ вебе огромное наличность анализаторов сайтика, штрих труда тот или другой чистосердечно молит через тарифных планов.
[url=https://be1.ru/]инвалиду[/url]
With havin so much written content do you ever run into any issues of plagorism or copyright violation? My website has a lot of exclusive content I’ve either written myself or outsourced but it looks like a lot of it is popping it up all over the web without my agreement. Do you know any solutions to help prevent content from being stolen? I’d genuinely appreciate it.
[url=http://nolvadexin.online/]where can i buy tamoxifen online[/url]
[url=http://dezithromax.online/]azithromycin australia cost[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinmds.com/]azithromycin cost australia[/url]
[url=http://lasixtbs.com/]160 mg lasix[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://avermox.online/]vermox over the counter uk[/url]
[url=http://ibaclofen.com/]baclofen 10mg tablets price[/url]
[url=http://itretinoin.com/]where to buy tretinoin cream in singapore[/url]
[url=https://doxycyclineo.com/]doxycycline prescription cost[/url]
[url=http://rettretinoin.online/]buy retin a cream india[/url]
[url=https://lasixtbs.com/]buy furosemide 20 mg uk[/url]
[url=https://www.as7abe.com/wall/forum/topic/22124?page=1#post-277939]https://www.as7abe.com/wall/forum/topic/22124?page=1#post-277939[/url]
[url=https://www.ctptalk.com/@aesthet/]https://www.ctptalk.com/@aesthet/[/url]
[url=http://forum.maistrafego.pt/index.php?topic=53422.new#new]http://forum.maistrafego.pt/index.php?topic=53422.new#new[/url]
[url=https://sites.google.com/view/dentaldubaiaseshet/aeshet]https://sites.google.com/view/dentaldubaiaseshet/aeshet[/url]
[url=http://eflomax.online/]buy flomax in india[/url]
The main character is Zenigata 2004
このブログはいつも期待を超えてきます。素晴らしい!
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://avermox.com/]vermox uk price[/url]
[url=https://baclofenx.online/]how to get baclofen[/url]
[url=https://lasixor.online/]furosemide 20 mg generic[/url]
[url=http://metforminn.online/]buying metformin online[/url]
В нашем мире, где аттестат является началом удачной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в любом университете.
Всем, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Приобрести аттестат – это значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к личным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
https://local-urban-eats.mn.co/posts/56709434
[url=https://amoxil.company/]amoxicillin 250 mg capsule[/url]
[url=http://diflucand.online/]diflucan discount coupon[/url]
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://amoxicillinbact.com/]amoxicillin online usa[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://adexamethasonep.online/]dexamethasone 60 mg[/url]
럭키 네코
이것을 본 Ma Wensheng은 갑자기 “폐하, 아직 할 말이 있습니다. “라고 말했습니다.
excellent post, very informative. I wonder why the other experts of this sector don’t notice this. You should continue your writing. I am sure, you have a huge readers’ base already!
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://accutaneiso.online/]accutane tablets online[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://vermoxin.online/]where can i buy vermox[/url]
레프리칸 리치스
이 상인은 얼마나 영리한 사람인가, 그는 즉시 깨달은 것을 느꼈습니다.
Good write-up, I’m regular visitor of one’s blog, maintain up the excellent operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
[url=https://advaird.online/]cost of advair[/url]
What’s up to every one, it’s genuinely a nice for me to pay a visit this web page, it contains precious Information.
@@G@@
https://ruainform.com/news/gde_mozhno_najti_onlajn_virtualnye_nomera_chekhii/2023-06-26-29399
If some one wants expert view on the topic of blogging and site-building
then i advise him/her to go to see this website,
Keep up the fastidious work.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I simply had to appreciate you yet again. I’m not certain what I could possibly have tried in the absence of those techniques discussed by you on this subject matter. Certainly was a challenging issue for me, but looking at a new specialised form you handled the issue made me to weep over fulfillment. I am happy for the support and then hope you recognize what an amazing job you are providing instructing most people by way of your websites. Probably you have never met all of us.
[url=https://ibaclofen.com/]lioresal online[/url]
판다스 포춘
Fang Jifan은 “내 조카가 사람들을 웃게 만드는 곳은 어디입니까? “라고 놀랐습니다.
[url=https://tretinoineff.online/]retin a 01 gel[/url]
[url=http://flomaxms.com/]flomax tablets in india[/url]
bucak oto kurtarma hizmeti
[url=https://doxycyclineo.com/]doxycycline pills price in south africa[/url]
Что такое прогон по профилям?
На форумах при каждом прогоне регистрируется новый юзер, в профайле которого в поле Вебсайт или Домашняя страница стоит ваша ссылка. Также в некоторых форумах есть возможность в профиль вставить подпись, туда можно вставить ссылку с анкором. Все это можно варьировать. В профилях ссылки живут довольно долго, т.к. нет спама в чистом виде, и профили не мозолят глаза ни читателям форума, ни модераторам. Прогон производится последней версией хрумера с сервера с максимально возможной скоростью и производительностью.
ПОДРОБНЕЕ
НОВЫЙ [url=https://xrumer.ru/]ОТЛИЧНЫЙ VPN[/url] ДЛЯ XRUMERA!
За последние недели состоялась серия важных обновлений комплекса: XAuth, Captchas Benchmark, XRumer, XEvil 6.0 [Beta]. В XEvil 6.0 [Beta] обновлен механизм обработки hCaptcha и многое другое, в XAuth повышена стабильность работы, в XRumer повышена эффективность, устранён ряд погрешностей и обновлены прилагаемые базы.
https://xrumer.ru/
Hello this is kind of of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding experience so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
goodgame.ru/user/1629660В
danceway74.ru/users/36?page=28В
http://www.fouroulette.com/888.htmВ
webnewsrealty.ru/page/13В
mystroycenter.ru/page/14В
Привет Друзья!
Привет, друзья! Сегодня хочу поделиться своим недавним открытием – Lev Casino. Если вы, как и я, любите азарт и не прочь испытать свою удачу, то это место для вас.
Что меня привлекло в Lev Casino?
Регистрация – всё просто и быстро. Регистрация занимает считанные минуты, и вы уже можете наслаждаться игрой.
Бонусы – щедрые приветственные бонусы и регулярные акции делают игру еще более захватывающей.
Слоты – большой выбор слотов и игр для всех любителей азартных развлечений.
Рабочие зеркала – если вдруг официальный сайт недоступен, всегда можно воспользоваться зеркалом и продолжить игру.
Если вас как и меня интересует lev casino на iphone, игровые автоматы лев или лев казино официальный, то самое время перейти на сайт [url=https://2021rif.biz/2024/05/29/slot-machines-the-future-of-slot-machine-innovation]2021rif.biz[/url] за подробностями об lev casino регистрация играть.
Лично я уже протестировал все возможности и остался доволен. Надеюсь, что и вы найдете здесь своё счастье и сорвете крупный выигрыш. Удачи!
Более подробно на https://t.me/s/zerkalo_lev
Удачи и профитов!
скачать игровой клуб лев
казино лев официальный сайт зеркало
вулкан клуб лев
вулкан лев
лев казино бонусы
Привет Друзья!
jvspin casino регистрация предлагает уникальные возможности для всех любителей азартных игр. Если вас как и меня интересует казино дживиспин онлайн, jv spin казино официальный или jvispin casino, то самое время прочитать здесь [url=https://nordu.ru/2024/05/29/Игровые-автоматы-бесплатные-и-платные-игры]nordu.ru[/url] подробнее об скачать jv spin казино. Узнайте все о последних новинках и бонусах jvspin мобильная версия и начните свой путь к крупным выигрышам прямо сейчас!
Более подробно на https://t.me/jvspin_ru
Удачи и профитов!
jvspin зеркало рабочее
jv spin казино официальный сайт
jv spin играть
jvspin casino официальный сайт казино
онлайн казино jvspin
[url=http://ibaclofen.com/]baclofen cost in india[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://doxycyclineo.com/]doxycycline online pharmacy canada[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
http://kaminograd.by
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Pretty! This was a really wonderful article. Many thanks for providing this info.
diplom66rus.ru/index.htmlВ
jurisprudenta.org/Standard.aspxВ
igramlikes.com/contact/В
est-m.ru/katalog/ukg/В
http://www.salaam.co.uk/biographies/profile.php?id=144В
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Всем привет!
Сегодня я расскажу, как получить промокод на фриспины в new retro casino. Кто не любит бесплатные вращения, которые могут привести к крупным выигрышам? В этом посте я поделюсь с вами лучшими способами найти и использовать промокоды, чтобы увеличить свои шансы на успех.
Если вас как и меня интересует new retro casino промокод на андроид, retro casino бонус за регистрацию new или retro casino войти, ознакомьтесь тут https://t.me/s/NewRetroCasino_promokod с new retro казино вход
[url=https://martbud.biz/2024/05/29/popular-casino-games-to-play-online]martbud.biz[/url]
Удачи и профитов!
casino retro new newretrocasino
newretrocasino зеркало рабочее
промокод за первое пополнение нью ретро казино
игровые автоматы играть бесплатно ретро
промокоды нью ретро казино
[url=http://amoxicillinir.online/]amoxil 875 price[/url]
Друзья, хотите узнать секреты успеха в онлайн-казино и получить бонусы от Sykaaa Casino? Тогда читайте дальше!
Сегодня я расскажу вам, как найти актуальные зеркала Sykaaa Casino, пройти регистрацию и получить крутые бонусы. Кстати, для всех новых игроков действует специальное предложение – дополнительный эксклюзивный бездепозитный подарок в размере 30 фриспинов в слоте The Dog House Megaways за регистрацию. Просто используйте промокод REG30FS и наслаждайтесь игрой!
Начнем с того, что Sykaaa Casino предлагает выгодные бездепозитные бонусы для новичков. Это отличная возможность начать играть и выигрывать без вложений. Промокод REG30FS предоставит вам 30 фриспинов с отыгрышем х35. Используйте этот шанс, чтобы испытать удачу и выиграть по-крупному!
Регистрация в Sykaaa Casino очень проста. Перейдите на официальный сайт или актуальное зеркало Sykaaa Casino. Нажмите кнопку “Регистрация”. Заполните необходимые поля: имя, email, пароль и другие данные. Подтвердите регистрацию через email. Войдите в аккаунт и введите промокод REG30FS, чтобы получить 30 фриспинов.
Если основной сайт Sykaaa Casino заблокирован, не переживайте! Актуальные зеркала помогут вам обойти блокировки и продолжить игру. Следите за обновлениями на нашем блоге, чтобы всегда иметь под рукой рабочие адреса.
Многие игроки уже воспользовались бездепозитным бонусом и поделились своими впечатлениями. Реальные истории успеха подтверждают, что играть и выигрывать в Sykaaa Casino не только возможно, но и легко!
В Sykaaa Casino представлено множество игровых автоматов на любой вкус. Вы сможете найти популярные слоты, такие как The Dog House Megaways, и наслаждаться игрой в любое время и из любой точки мира.
Не упустите возможность получить 30 фриспинов в слоте The Dog House Megaways за регистрацию. Используйте промокод REG30FS и начинайте выигрывать уже сегодня! Преимущества Sykaaa Casino очевидны: выгодные бонусы, удобный доступ через зеркала и широкий выбор игр.
Если вы хотите узнать о СУКААА больше, ищите в поиске sykaaa бездепозитный бонус или казино суккка сукко официальный и вы сразу обнаружите нужную информацию или прочитайте о онлайн казино сука по ссылке https://t.me/sykaaa_zerkalo
Удачи и больших выигрышей!
[url=https://youngmaylay.net/2024/05/30/the-evolution-of-slot-machine-technology]youngmaylay.net[/url]
sykaaa casino бонус
скачать казино sykaaa
сука онлайн казино
sykaaa casino рабочее зеркало
sykaaa casino отзывы
[url=https://abamoxicillin.com/]amoxil 1g[/url]
http://here4deals.com
Hi there colleagues, fastidious piece of writing and fastidious arguments commented here, I am actually enjoying by these.
jogibaba.com/blogs/32/Why-is-the-popularity-of-higher-education-rapidly-declining-now?lang=ru_ruВ
3d-budmaterial.com.ua/club/user/189/?entityType=LOG_ENTRY&entityId=285В
entropiques.fr/userinfo.php?uid=30632В
bouffordca.com/Emailscam.htmВ
uapa.com.hk/forum/home.php?mod=space&uid=292023&do=profileВ
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Elon Musk was star guest this year at an annual conference organized by Italian PM Giorgia Meloni’s Brothers of Italy party.
[url=https://kraken22-at.net]kraken25.at [/url]
He arrived against the backdrop of an ice-skating rink and an ancient castle in Rome with one of his 11 children to tout the value of procreation.
Italy has one of the lowest birth rates in the world, and Musk urged the crowd to “make more Italians to save Italy’s culture,” a particular focus of the Meloni government.
https://kraken15-at.com
kraken14
Meloni has been a strong opponent of surrogacy, which is criminalized in Italy, but there was no mention of Musk’s own recent children born of surrogacy.
The owner of X (formerly called Twitter) was slightly rumpled with what could easily be argued the least stylish shoes in the mostly Italian crowd since Donald Trump’s often unkempt former top adviser Steve Bannon appeared at the conference in 2018.
Meloni sat in the front row taking photos of Musk, who she personally invited. Meloni founded the Atreju conference in 1998, named after a character in the 1984 film “The NeverEnding Story.”
북 오브 데드
이제 수도의 모든 천 상인들이 시산을 응시하고 있습니다.
Hey! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this article to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
appleincub.ru/page/11В
webyourself.eu/blogs/317597/%D0%A1%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%80%D0%B5%D1%82-%D1%83%D1%81%D0%BF%D0%B5%D1%85%D0%B0-%D0%9A%D0%B0%D0%BA-%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC-%D0%B8-%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D1%81%D0%B2%D0%BE%D1%8E-%D0%B6%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%BD%D1%8CВ
mybaltika.info/ru/print/587/7892/В
designachten.net/aussteller-2019/В
linkheed.com/blogs/920/Why-is-the-demand-and-popularity-of-universities-declining-nowВ
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://mcadvair.online/]coupon advair 2019[/url]
Закажите диплом и откройте новые горизонты
Автор24 [url=https://author24.us/]сайт автор 24[/url] .
http://tavissmileyradio.com
В нашем обществе, где аттестат становится началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед всеми, кто желает начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете заказать аттестат, что является выгодным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, потерял документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. Аттестаты производятся с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы в итоге получился продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество этого подхода заключается не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить аттестат. Весь процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца аттестата до консультаций по заполнению личных данных и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Всем, кто хочет найти максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать аттестат – значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу переходить к важным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://karagay.do.am/index/0-25
seo hizmeti
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://accutaneo.com/]accutane for sale canada[/url]
Your blog is a true hidden gem on the internet. Your thoughtful analysis and in-depth commentary set you apart from the crowd. Keep up the excellent work!
[url=http://modafinilon.online/]modafinil mexico price[/url]
WOW just what I was looking for. Came here by searching for %keyword%
spbmedu.ru/index.htmlВ
maymotors.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?p=2197В
lespilomaterial.ru/В
t99.vn/tap-doan-t99-va-vng-cloud-ky-ket-hop-tac-chien-luoc-toan-dien-ve-tai-chinh-cong-ngheВ
girbir.com/blogs/13038/Where-can-I-buy-a-diploma-or-certificate-at-aВ
골드 킹
Li Chaowen은 평생 동안 그의 명성을 망칠 것입니다.
http://eurekapharma.fr
vardenafil 20mg
[url=http://amoxicillinbact.com/]amoxicillin 250mg price[/url]
One such software that has been generating buzz these days is the Lottery Defeater
[url=https://tadacip.store/]tadacip 10 mg[/url]
[url=http://diflucanr.com/]diflucan online no prescription[/url]
Разве что вы алчете наслаждаться созданиями популярных авторов на AudioBook26.ru, Книгочей предлагает он-лайн аускультация разных жанров аудиокниг
https://audiobook26.ru/
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for sharing your thoughts. I truly appreciate your efforts and I am waiting for your next post thanks once again.
instise.pl/?page_id=3В
http://www.forum.jrudevels.org/profile.php?mode=viewprofile&u=563048В
odlc.opec.go.th/question/content-%E0%B8%A3%E0%B8%B0%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%B1%E0%B8%9A%E0%B8%81%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%99%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%99%E0%B8%B8%E0%B8%9A%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%A5/В
petcreche.com.br/fotos-e-videos/fotos/page/4/В
tivi24h.com/2011/01/xem-bong-online-bong-truc-tuyen-kenh.htmlВ
buy tadalafil without prescription
xnxx
Thank you, I have recently been looking for info approximately this subject for a long time and yours is the greatest I have came upon till now. However, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you certain in regards to the source?
http://autoprajs.ru/15141.html
vardenafil wiki
На сегодняшний день, когда аттестат является началом удачной карьеры в любой сфере, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед каждым человеком, желающим вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или продолжить обучение в университете.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать аттестат, и это будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Аттестат изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. В итоге вы получите документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества такого решения заключаются не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой аттестат. Процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца до грамотного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для тех, кто хочет найти максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать аттестат – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
http://www.gurumeguri.com/userinfo.php?uid=23254
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello investors!
Lido: Your Reliable Partner for Earning 25% Monthly Returns Through Staking! [url=https://crypto-airdrops.org]Lido Returns[/url]
In the bustling world of cryptocurrencies, many projects claim to offer high returns and innovative solutions. However, Lido stands out with uniquely attractive conditions. Investors can stake their assets and earn up to 25% profit per month, making Lido an excellent choice for those looking to grow their capital. Lido prioritizes reliability and transparency for its investors. All operations are conducted through smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain, ensuring the security and integrity of invested funds. Regular security audits further reassure users of Lido’s dependability. A key benefit of Lido is the high returns achievable through token staking. With potential yields reaching up to 25% per month, Lido is one of the most appealing projects in the cryptocurrency market. This high return rate allows investors to see substantial capital growth in a short period if they use this tool effectively. Lido’s design is simple and user-friendly, making it accessible even for beginners. Investors can easily join the platform, lock their tokens, and start earning profits within minutes, without needing complex setup or technical skills. All you need is an Ethereum wallet and a bit of ETH for gas fees. Lido is also a project that is continually evolving and expanding. It offers new opportunities and tools to its users, with the project team actively working on platform improvements and adding new features to meet user needs and stay ahead in the industry. Investing in Lido is more than just an opportunity to earn money; it’s a chance to be part of an innovative project that is transforming the cryptocurrency space. Start staking your tokens with Lido today and enjoy the high returns.
For more information please visit https://crypto-airdrops.org
Wish you profit and prosperity)
Staking Profits Analysis
Decentralized Finance
Crypto Financials
Decentralized Yield
Digital Finance
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Привет учащиеся!
Недавно у меня возникла потребность в получении среднего образования, но постоянная работа и обязанности постоянно отнимают время, и у меня нет возможности этим заниматься. К моему счастью, друзья посоветовали мне, что можно легально приобрести диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании (диплом техникума, колледжа) на бланках государственного образца, пройдя обучение по упрощенной программе!
В интернете полно предложений, но как избежать мошенничества и выбрать подходящую компанию? Это весьма важный вопрос, который требует ответственного подхода. Я лично проверил, что на russa24-diploms-srednee.com содержится множество советов о том, как избежать ошибок и не потерять деньги зря. Как проверить компанию по продаже дипломов, на что обратить внимание, и конечно, там можно заказать диплом “под ключ” без предварительной оплаты.
В отличие от других коммерческих организаций, наша цель — не просто заработать, а помочь нашим клиентам. Мы предоставляем бесплатные консультации без ограничений по количеству вопросов. Наши специалисты — проверенные временем профессионалы, поэтому обращение к нам – верное решение, ведь мы гарантируем качество, соблюдение сроков и разумные цены на дипломы о среднем образовании на заказ.
Удачи и хороших оценок!
как купить диплом о среднем медицинском образовании
купить диплом о среднем медицинско образовании
купить диплом среднего образования в калининграде
куплю диплом о среднем специальном образовании
купить диплом о среднем образовании пермь
купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании омск
купить диплом в спб о среднем образовании
купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании спб
купить диплом о среднем образовании в спб
купить дипломы о среднем образовании
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
ssri tadalafil
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I like this weblog very much, Its a very nice position to read and find information. “The world breaks everyone, and afterward, many are strong at the broken places.” by Ernest Hemingway.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Wow that was strange. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say wonderful blog!
http://www.arusak-attestats24.com
What’s up i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anyplace, when i read this piece of writing i thought i could also create comment due to this brilliant post.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello investors!
Earn 25% Monthly Returns with Lido. Safe, Easy, and Profitable! [url=https://crypto-airdrops.org]Staking Market[/url]
In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies, many projects offer high returns and innovative solutions. Yet, Lido distinguishes itself with conditions that are especially attractive. Investors have the opportunity to stake their assets and earn up to 25% profit per month with Lido. This makes it a compelling option for those seeking to grow their capital. Lido is committed to ensuring a high level of reliability and transparency for its investors. All fund operations are executed through smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain, which guarantees the security and integrity of the invested funds. Additionally, Lido conducts regular security audits to reassure its users of its reliability. One of Lido’s primary advantages is the high returns that can be achieved through token staking. The yield rate can reach up to 25% per month, positioning Lido as one of the most attractive projects in the cryptocurrency market. This means that investors can see significant capital growth in a relatively short time if they use this tool effectively. Lido is designed to be user-friendly, even for those new to the crypto space. Investors can easily join the platform, lock their tokens, and start earning profits within minutes. There is no need for a complex setup or technical skills—just an Ethereum wallet and a small amount of ETH for gas fees. Lido is continually evolving and expanding, providing new opportunities and tools for its users. The project team is actively working on enhancing the platform and adding new features to meet user needs and keep the project at the industry’s forefront. Investing in Lido offers not only a chance to make money but also an opportunity to be part of an innovative project that is changing the game in the cryptocurrency space. Start staking your tokens with Lido today and reap the high returns on offer.
For more information please visit https://crypto-airdrops.org
Wish you profit and prosperity)
Staking Trends
Crypto Yield
Crypto Growth
Passive Income
Lido Finance
FitSpresso: An Outline FitSpresso is a weight management formula made using five herbal ingredients.
Здравствуйте!
Недавно у Меня возникла необходимость получить среднее образование, но постоянная работа и заботы постоянно отбирают время и не дают этого сделать, хорошо друзья подсказать что оказывается можно купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании (диплом техникума, колледжа), совершенно легально на бланках госзнак, пройдя обучения по облегченной программе!
В Интернете предложений более чем достаточно, но как не стать жертвой мошенников и выбрать подходящую компанию? Задача очень щепетильная и следует ответственно подходить к этому вопросу. Проверено Мной лично, На russa24-diploms-srednee.com очень много информации как не попасть впросак и не потерять впустую деньги. Как можно проверить компанию по продаже дипломов, на что обратить внимание, и конечно там можно заказать диплом под ключ без предоплаты.
В отличие от других коммерческих организаций, мы не ставим перед собой цель заработать, — мы работаем на благо наших клиентов. Мы предоставляем бесплатные консультации без ограничения количества вопросов. Наши специалисты — проверенные временем сотрудники, поэтому обратиться к нам – верное решение, ведь мы обладаем рядом преимуществ: качество, сроки, цены на дипломы о среднем образовании на заказ.
Удачи и хороших оценок!
купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании спб
купить диплом о среднем образовании в иваново
купить диплом о среднем образовании повара
купить диплом о среднем образовании в рязани
купить чистый диплом о среднем образовании
купить диплом среднее техническое образование
дипломы о среднем образовании купить срочно
куплю диплом о среднем специальном образований
диплом о среднем образовании купить отзывы
купить диплом о среднем образовании в краснодаре
XRumer – этто самое лучшее и лучшее программное обеспечение для создания ссылок и продвижения сайтов. Он используется для машинального прогона веб- сайтов через различные общественные сети, форумы, онлайн-дневники и другие интернет-ресурсы.
http://www.botmasterru.com/product33230/
Buy XRumer Official
[url=http://www.botmasterru.com/product33230/][img]https://xrumer.cc/i/x.png[/img][/url]
Hiya, I’m really glad I’ve found this information. Nowadays bloggers publish just about gossips and internet and this is actually annoying. A good web site with interesting content, this is what I need. Thank you for keeping this site, I’ll be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Can’t find it.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://itretinoin.com/]retinal prescription facecream[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
united pharmacy viagra
Подарок для конкурента
https://xrumer.ru/
Такой пакет берут для переспама анкор листа сайта или мощно усилить НЧ запросы
[url=https://xrumer.ru/]Подарок для конкурента[/url]
[url=http://ciprocfx.com/]buy ciprofloxacin online[/url]
Преимущества строительства дома из бруса 9х12 | Как выбрать идеальный проект для дома из бруса 9х12 | Выбор кровельных материалов для дома из бруса 9х12 | Плюсы отопления в доме из бруса 9х12 | Как обеспечить комфортную температуру в доме из бруса 9х12 | Типы фундаментов для дома из бруса 9х12 | Инновации в строительстве дома из бруса 9х12 | Современные технологии строительства дома из бруса 9х12 | Что нужно знать перед строительством дома из бруса 9х12 | Расходы на строительство дома из бруса 9х12
дома из бруса 9х12 [url=https://domizbrusa-9x12spb.ru/]https://domizbrusa-9x12spb.ru/[/url] .
wedgewood pharmacy flagyl
Почему стоит построить дом из бруса 9х12 | Преимущества строительства дома из бруса 9х12 | Какая кровля лучше для дома из бруса 9х12 | Как обеспечить эффективное отопление в доме из бруса 9х12 | Теплоизоляция и вентиляция в доме из бруса 9х12 | Типы фундаментов для дома из бруса 9х12 | Новинки в строительстве домов из бруса 9х12 | Как выбрать мебель для дома из бруса 9х12 | Советы по созданию уютной зоны отдыха в доме из бруса 9х12 | Сколько стоит построить дом из бруса 9х12
одноэтажный дом из бруса 9х12 [url=https://domizbrusa-9x12spb.ru/]https://domizbrusa-9x12spb.ru/[/url] .
Сегодня, когда аттестат – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, желающим начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Наша компания предлагает максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете купить аттестат, что становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Аттестат изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам. В результате вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество подобного подхода состоит не только в том, что можно оперативно получить аттестат. Весь процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца аттестата до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по России — все находится под абсолютным контролем наших мастеров.
Для тех, кто хочет найти быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Заказать аттестат – значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу переходить к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в университет или старт карьеры.
http://kfmesi.ru/o-filiale/podrazdeleniya/bibilioteka
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
https://seoeffectly.activoblog.com/27477440/Преимущества-сотрудничества-со-студией-xrumer-art
https://seocommunityo.post-blogs.com/48777757/Примеры-работ-студии-xrumer-art
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
It’s appropriate time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I have learn this put up and if I may I desire to recommend you few interesting things or advice. Maybe you could write subsequent articles regarding this article. I desire to read even more issues about it!
[url=https://baclofenx.online/]baclofen medicine[/url]
Привет учащиеся!
Хочу поделиться своим опытом по заказу аттестата ПТУ. Думал, что это невозможно, и начал искать информацию в интернете по теме: купить дубликат диплома о среднем образовании, купить диплом о высшем образовании старого, сколько стоит диплом врача, купить диплом о среднем образовании в санкт петербурге, купить диплом о высшем образовании поддельный. Постепенно углубляясь, нашел отличный ресурс здесь: http://www.arusak-diploms-srednee.ru/, и остался очень доволен!
Теперь у меня есть диплом сварщика о среднем специальном образовании, и я обеспечен на всю жизнь!
Удачи и хороших оценок!
купить чистый диплом о высшем образовании
купить диплом о полном
купить диплом в люберцах
аттестат 11 купить
купить диплом менеджера по продажам
купить диплом в нижнем тагиле
купить диплом высшее купить диплом корочку
купить диплом бакалавра в уфе
диплом азбуку прочел купить
сколько стоит аттестат
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Kamagra Polo
Всем привет)
Будучи студентом, я наслаждался учебой до тех пор, пока не пришло время писать диплом. Но паниковать не стоило, ведь существуют компании, которые помогают с написанием и защитой диплома на отличные оценки!
Изначально я искал информацию по теме: , , , , , затем наткнулся на , где все мои учебные вопросы были решены!
Удачи и хороших оценок!
This is my first time pay a visit at here and i am actually happy to read everthing at single place.
http://www.musey-uglich.ru
accutane pharmacy
Что такое прогон по профилям?
На форумах при каждом прогоне регистрируется новый юзер, в профайле которого в поле Вебсайт или Домашняя страница стоит ваша ссылка. Также в некоторых форумах есть возможность в профиль вставить подпись, туда можно вставить ссылку с анкором. Все это можно варьировать. В профилях ссылки живут довольно долго, т.к. нет спама в чистом виде, и профили не мозолят глаза ни читателям форума, ни модераторам. Прогон производится последней версией хрумера с сервера с максимально возможной скоростью и производительностью.
ПОДРОБНЕЕ
НОВЫЙ [url=https://xrumer.ru/]ОТЛИЧНЫЙ VPN[/url] ДЛЯ XRUMERA!
За последние недели состоялась серия важных обновлений комплекса: XAuth, Captchas Benchmark, XRumer, XEvil 6.0 [Beta]. В XEvil 6.0 [Beta] обновлен механизм обработки hCaptcha и многое другое, в XAuth повышена стабильность работы, в XRumer повышена эффективность, устранён ряд погрешностей и обновлены прилагаемые базы.
https://xrumer.ru/
Daddy Casino – Официальный телеграм канал со слотами от Дэдди Casino [url=https://t.me/daddycasinorussia]daddy казино регистрация[/url] . Актуальное, рабочее зеркало официального сайта Дэдди Казино. Регистрируйся в Казино Daddy, получай бонус используя промокод, не забудь скачать
daddy casino официальный
https://t.me/daddycasinorussia
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Привет учащиеся!
Недавно у меня возникла необходимость получить среднее образование, но из-за постоянной работы и других обязанностей у меня постоянно не хватает времени на это. К моему удивлению, друзья подсказали, что можно легально приобрести диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании (диплом техникума или колледжа), пройдя обучение по упрощенной программе!
В интернете предложений полно, но как не попасть на уловки мошенников и найти надежную компанию? Это важно подходить к выбору ответственно и внимательно. Лично я проверил, что на сайте https://arusak-diploms-srednee.ru есть много полезной информации о том, как избежать мошенничества и не потерять деньги. Как можно проверить компанию по продаже дипломов, на что обратить внимание, и, конечно же, там можно заказать диплом под ключ без предварительной оплаты.
В отличие от других коммерческих организаций, мы не нацелены исключительно на заработок — мы работаем на благо наших клиентов. Мы предоставляем бесплатные консультации без ограничений по количеству вопросов. Наши специалисты — это проверенные временем сотрудники, и обратиться к нам — это правильное решение, ведь мы гарантируем качество, соблюдение сроков и разумные цены на заказ дипломов о среднем образовании.
Удачи и хороших оценок!
купить диплом ссср о высшем образовании цена
купить свидетельство о заключении брака
купить официально диплом о высшем
купить главу диплома
аттестаты дипломы купить
купить диплом об высшем образовании
купить диплом в орехово зуево
где можно купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании
купить аттестат без предоплаты
купить диплом о среднем техническом образовании
Здравствуйте!
Хочу рассказать о своем опыте по заказу аттестата пту, думал это не реально и стал искать информацию в сети, про купить диплом химика, купить диплом в южно-сахалинске, купить диплом в бийске, купить диплом вуза, купить диплом швеи, постепенно вникая в суть дела нашел отличный материал здесь https://1abakan.ru/forum/showthread-65190/ и был очень доволен!
Теперь у меня есть диплом столяра о среднем специальном образовании, и я обеспечен на всю жизнь)
Удачи и хороших оценок!
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Cialis Super Active
[url=https://vermox.company/]how much is vermox[/url]
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Terrific paintings! That is the type of information that are meant to be shared across the internet. Disgrace on Google for no longer positioning this publish higher! Come on over and talk over with my website . Thanks =)
79 슬롯
사실 여기 있는 모든 사람이 책을 읽었을 뿐만 아니라 황제도 책을 읽었습니다.
[url=https://dezithromax.online/]can i purchase azithromycin over the counter[/url]
hey there and thank you for your info – I’ve certainly picked up anything new from right here. I did however expertise some technical issues the usage of this website, as I skilled to reload the website lots of times prior to I could get it to load correctly. I were thinking about in case your web host is OK? Not that I am complaining, but sluggish loading cases times will sometimes impact your placement in google and can injury your quality ranking if ads and ***********|advertising|advertising|advertising and *********** with Adwords. Anyway I’m including this RSS to my email and could look out for much extra of your respective intriguing content. Ensure that you replace this again soon..
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
reputable online pharmacy reddit
online pharmacy provigil modafinil
크립토 골드
도로의 모든 구간은 어디에서나 바쁘고 교통은 용과 같습니다.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Подарок для конкурента
https://xrumer.ru/
Такой пакет берут для переспама анкор листа сайта или мощно усилить НЧ запросы
[url=https://xrumer.ru/]Подарок для конкурента[/url]
bradleys pharmacy artane
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
oxycodone pharmacy tampa fl
Wow! This blog looks exactly like my old one! It’s on a entirely
different topic but it has pretty much the same page layout
and design. Great choice of colors!
더 도그 하우스 메가웨이즈
그는 수십 년 동안 정치에 종사했기 때문에 Zhu Houzhao가 말한 것이 사실임을 자연스럽게 알고 있습니다.
online pharmacy indomethacin
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://rak.flyboard.ru/viewtopic.php?f=8&t=14389&p=156666#p156666]http://rak.flyboard.ru/viewtopic.php?f=8&t=14389&p=156666#p156666[/url]
[url=http://belaruspartisan.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=1501#p7659]http://belaruspartisan.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=1501#p7659[/url]
[url=https://blouter.ru/viewtopic.php?id=9884]https://blouter.ru/viewtopic.php?id=9884[/url]
[url=http://assa0.myqip.ru/?1-1-40-00001107-000-0-0]http://assa0.myqip.ru/?1-1-40-00001107-000-0-0[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Привет!
Недавно мы решили обновить напольные покрытия в доме. На сайте http://osnovam.ru/vannaya/kakoj-cvet-kvarc-vinila-luchshe-vybrat-dlya-vannoj-komnaty нашли полезную информацию, которая помогла сделать правильный выбор. Благодаря этим рекомендациям мы выбрали натуральные покрытия с сертификатами качества и успешно завершили укладку. Продукция отличается простотой нанесения и подходит для жилых помещений. Широкий выбор и использование современных инструментов сэкономили наше время.
электроэрозионные станки
VinilPol преимущества
виниловая плитка
резка кварцвинилового ламината
укладка сценического линолеума
укладка кварц-виниловой плитки
станки EDM
Удачи!
It’s amazing to pay a quick visit this web site and reading the views of all friends concerning this post, while I am also zealous of getting familiarity.
mazda-demio.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=4139
old.kakdelat.ru/company/personal/user/1695/blog/8780/
bouffordca.com/Emailscam.htm
http://www.sskyn.com/home-uid-82653.html
dienmayviet24h.com/dan-karaoke.html
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi all!
Discover Hidden Gems! Uncover the world’s best-kept secrets with our travel guides. Explore off-the-beaten-path destinations and hidden gems.
Very good thematic site – https://gsroups.com
travel blog
travel tips for seniors
news update
local news
cooking techniques
travel bloggers
travel tips
travel safety
Goog luck!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your articles as
long as I provide credit and sources back to
your site? My website is in the very same niche as yours and my users would genuinely benefit from some of the information you provide here.
Please let me know if this ok with you. Thanks!
Good day!
Family Travel Made Easy! Make traveling with kids a breeze. Our family travel guides offer tips for safe, fun, and stress-free trips with your little ones.
Very good thematic site – https://mail-grups.com
advice
travel apps
news outlet
food culture
Mediterranean diet
kitchen gadgets
e-commerce
travel advice
Goog luck!
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I used to be able to find good advice from your content.
nemspb.ru/objects/zhd-stantsiya-babaevo-oktyabrskoj-zheleznoj-dorogi/
onlinekinospace.ru/page/8
mystroycenter.ru/page/14
egkb14.ru/employees/5405/review/?PAGEN_1=63
http://www.italian-style.ru/Nasha_kompanija/forum/?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=54311
I am not really good with English but I line up this very leisurely to translate.
Hello everybody!
Vegetarian Delights! Explore a world of flavors with our collection of vegetarian recipes. From hearty mains to light salads, find dishes that everyone will love.
Very good thematic site – https://gsroups.com
entertainment news
organizational tips
internet business
diet plans
news update
news portal
health tips
international business
Goog luck!
Первый партнер охраны труда
[url=https://www.ppot.ru/]Аудит системы охраны труда[/url] – экспертный центр по аудиту и подготовке специалистов в области охраны труда и пожарной безопасности. Наша компания предоставляет широкий спектр услуг по обеспечению безопасности производственных процессов для индивидуальных предпринимателей и организаций различных секторов промышленности в Москве, Московской области и других регионах России.
Соблюдение правил безопасности труда – законодательное требование, за нарушение которого на организацию может быть наложен штраф или приостановлена деятельность предприятия на срок до 90 суток.
Мы помогаем решать вопросы обеспечения безопасности и организации труда на предприятии, разрабатываем и актуализируем документы по охране труда, проводим комплексное обследование охраны труда на соответствие государственным нормативным требованиям. Проводим обучение сотрудников по охране труда и пожарной безопасности, проверяем СУОТ и оцениваем профессиональные риски.
Виктория Набойченко сделала для нашего канала заявление,
[url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q0smZ5_QOcU]Набойченко Бествей[/url]
касающееся своего бывшего супруга – главного свидетеля обвинения по так называемому уголовному делу “Лайф-из-Гуд”-“Гермес”-“Бест Вей”
Hi all!
Breaking News Alerts! Never miss a moment with our breaking news alerts. Be the first to know about major events and important updates happening around the world.
Very good thematic site – https://mail-grups.com
latest news
travel destinations
destination
local news
guides
news update
recipes
home improvement tips
Goog luck!
Утюг Dyson перестал выпускать пар? Не пытайтесь починить его самостоятельно – это может быть опасно. Обратитесь к специалистам на https://servisdyson.ru/, и мы быстро вернем вашему утюгу былую эффективность.
[url=https://servisdyson.ru/]сервис дайсон[/url]
ремонт увлажнителя воздуха dyson
ремонт техники dyson в люберцах
ремонт стайлера дайсон
Всем привет!
Мастерство в Повышении ПФ Яндекса: Профессиональное улучшение сайта с использованием проверенных методик. [url=https://nakrutka-pf.ru]накрутка пф москва заказать[/url] Стратегическое Улучшение Поведенческих Факторов: Планирование и реализация комплексных решений для вашего присутствия в Яндексе. Инновационные Техники для ПФ в Яндексе: Внедрение новейших методов для улучшения пользовательской активности на вашем сайте. Оптимизация ПФ для Продвижения Сайтов: Комплексные решения для улучшения всех ключевых поведенческих показателей в Яндексе. ПФ-Оптимизация с Индивидуальным Подходом: Подбор уникальных решений для каждого клиента для повышения эффективности сайта. Профессиональное Улучшение ПФ Яндекса: Высококачественные услуги по оптимизации поведенческих факторов для вашего сайта. Повышение Вовлеченности Пользователей в Яндексе: Методы, которые гарантированно увеличивают интерес и активность посетителей. Эффективная Накрутка ПФ Яндекс: Использование лучших практик для повышения вовлеченности и рейтинга.
Более подробно на сайте – https://nakrutka-pf.ru/portfolio/
накрутка пф москва
накрутка пф
накрутка пф безопасно
пф yandex
накрутка пф 3454
Будем рады сотрудничеству!
«Дело «Лайф-из-Гуд» – «Гермес» – «Бест Вей»: кто такие Набойченко и Комаров?
[url=https://compromat01.group/main/investigations/130715-delo-layf-iz-gud-germes-best-vey-kto-takie-naboychenko-i-komarov.html]Виктория Набойченко[/url]
?В уголовном деле, связываемом следствием с компаниями «Лайф-из-Гуд», «Гермес», кооперативом «Бест Вей» и основателем «Лайф-из-Гуд» и «Бест Вей» Романом Василенко, есть два свидетеля, на которых особенно уповает обвинение.
Это бывший сисадмин российского сегмента иностранной компании «Гермес» Евгений Набойченко, с 2014 года возглавлявший также IT-службу компании «Лайф-из-Гуд», занимавшуюся в том числе сайтом и платежной системой кооператива «Бест Вей». И бывший шофер Романа Василенко Алексей Комаров.
Набойченко в феврале 2022 года намеренно сломал российский сегмент платежной системы «Гермеса» и повесил сообщение: «Обращайтесь в полицию». Позднее многократно публично выступал с обвинениями Романа Василенко. Комаров утверждает, что возил по поручению Василенко неучтенные наличные деньги.
Кто эти люди, насколько вызывают доверие их обвинения, содержащиеся в уголовном деле? (В Приморском районном суде Санкт-Петербурга, рассматривающем дело по существу, они пока не выступали.)
Мы попытались в этом разобраться.
Вымогатель
Евгений Набойченко – способный айтишник, на каком-то этапе, по словам его бывшей жены, он возомнил себя имеющим право чуть ли не на партнерство в бизнесе Романа Василенко (см. видеозаявление Виктории Набойченко, данное ютуб-каналу, поддерживающему пайщиков кооператива «Бест Вей»). При этом его коллега – ведущий IT-разработчик компании «Лайф-из-Гуд» и кооператива «Бест Вей» Роман Роганович – сообщил на судебном заседании Приморского районного суда, что Набойченко вряд ли в состоянии во что бы то ни было придумать какой-то позитивный проект – из-за, как намекнул Роганович, скромности творческих способностей Набойченко.
И Евгений придумал схему вымогательства – как ему казалось, беспроигрышную. Насколько нам стало известно от наших источников, Набойченко перед тем, как обрушить платежную систему российского сегмента «Гермеса» в феврале 2022 года, шантажировал Романа Василенко – требовал с него деньги: 170 тыс. евро. При этом, по утверждению Виктории Набойченко, угрожал убийством и увечьями и самому Роману Василенко, и его супруге, и детям. Похвалялся перед (тогда еще) женой своими матерными сообщениями с угрозами, которые он посылал Василенко и его близким.
Кроме того, он завладел российской клиентской базой «Гермеса» и вымогал у клиентов деньги: свидетельства такого рода нам предоставлены.
Клеветник
Помимо этого, он допустил целый ряд публичных высказываний – прежде всего в YouTube, которые Роман Василенко расценил как клеветнические и инициировал по этому поводу уголовное разбирательство. Подавляющее большинство выступлений Набойченко, преимущественно нетрезвых, сейчас удалены.
Высказывания нотариально заверены, заведено уголовное дело – но расследуется оно ни шатко ни валко, так как расследование, по данным наших источников, тормозит начальник УЭБиПК ГУ МВД России по Санкт-Петербургу и Ленинградской области генерал-майор полиции Вадим Строков, который взял Набойченко под крыло.
Завербованный
По словам Виктории Набойченко, Евгений, как и другие функционеры «Лайф-из-Гуд», в начале расследования в отношении компании подвергался обыскам – но потом состоялся удивительный допрос Евгения Набойченко в питерском главке МВД, на который он запретил приходить своему адвокату. После этого допроса Набойченко была предоставлена госохрана и сам он хвастался супруге, что находится под личным патронажем тогдашнего начальника УЭБиПК, который его очень ценит.
За этим последовал слом платежной системы «Гермеса» и других ресурсов, которыми занимался Набойченко.
Хулиган, алиментщик и грабитель
По заявлениям источников, Евгений Набойченко бил супругу и детей. После развода в 2022 году отказывается платить алименты – их выплаты его супруга добивается через суды.
Пациент наркологов
По данным наших источников, с некоторых пор у Евгения Набойченко начала нарастать алкогольная, а возможно, и наркотическая зависимость (см. документы, которые нам предоставил источник, знакомый с ситуацией). Он лечился – но постоянно срывался.
Неуравновешенный, жадный, завистливый
В целом источники характеризуют его как неуравновешенного, жадного, завистливого человека. По мнению наших визави, эти его особенности использовали работники полиции для инсценировки уголовного дела в отношении компаний «Лайф-из-Гуд», «Гермес», кооператива «Бест Вей» и Романа Василенко.
Вороватый водитель
Другой ключевой свидетель обвинения – Алексей Комаров – сообщает в деле, что возил и передавал пакеты с деньгами – однако никакими инкассаторскими операциями в «Лайф-из-Гуд», по данным наших источников, он никогда не занимался. Он выполнял мелкие поручения Василенко, в числе которых – забрать подарки для него от пайщиков кооператива или консультантов сети «Лайф-из-Гуд» для Романа Василенко.
Через Комарова передавалось множество подарков от пайщиков из регионов. Часть из них до Василенко не доходила. Его спрашивали: «Как сало? Как самогоночка?» А всего этого он, по данным наших источников, не получал.
Роман Василенко рассказывал коллегам: «Много презентов, о которых мне рассказывали, но которые я так и не нашел. Мне их не жалко, просто плохо то, что я не поблагодарил тех людей, которые мне их подарили от всей души».
Комарова, как и Набойченко, по нашим данным, завербовал питерский УЭБиПК. По поводу перевозки денег он, по сведениям наших источников, просто лжет – подписывает то, что дают ему подписать в питерском УЭБиПК. И при этом скрывает, что сам воровал подарки, предназначенные для Василенко.
Кто обвинители?
Следствие привлекло для выстраивания обвинения малограмотного вороватого водителя и алкозависимого айтишника. На показаниях таких свидетелей точно можно строить обвинение, по которому четверо функционеров «Лайф-из-Гуд» сидят без приговора суда уже более четырех лет и по которому судят отца Романа Василенко – 83-летнего ветерана Вооруженных сил РФ Виктора Ивановича Василенко?
Вопрос, думаем, риторический.
프라그마틱 슬롯
그는 Liu Wenshan을 보았고 Liu Wenshan은 매우 자신감이 없어 보였습니다.
Привет!
Внимание, жители Кропивницкого! На нашем сайте вы найдете самые свежие и актуальные новости города. Узнайте о последних событиях, важных решениях и общественных инициативах. Мы всегда на страже информации для вас!
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://0522.kr.ua/category/news-ukraine/
[url=https://0522.kr.ua/]Новости Кропивницкого главные[/url]
Новости Кропивницкого
Главные новости Кропивницкого
последние новости Украины
Удачи!
Greetings from Florida! I’m bored at work so I decided to browse your site on my iphone during lunch break. I enjoy the information you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m shocked at how fast your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, amazing blog!
Привет всем!
Израильская медицина: новейшие достижения и исследования
Израиль известен своими передовыми медицинскими технологиями и исследованиями. В этом разделе мы рассказываем о последних достижениях израильской медицины, новых методах лечения и открытиях. Узнайте о инновационных медицинских устройствах, клинических испытаниях и успехах израильских врачей и ученых. Читайте о том, как израильская медицина помогает бороться с самыми сложными заболеваниями и улучшает качество жизни людей.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://isra.news/category/israel/
[url=https://isra.news/category/tech/]Новости технологий[/url]
Новости Израиля
новости шоу бизнеса
новости экономики
Удачи!
Just a smiling visitant here to share the love (:, btw great style and design. “Make the most of your regrets… . To regret deeply is to live afresh.” by Henry David Thoreau.
https://dr-nona.ru/blog – Dr. Nonna
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Outstanding post, I conceive website owners should learn a lot from this website its really user pleasant.
What’s up, yeah this article is really nice and I have learned lot of things from it about blogging. thanks.
verbanent.hu/elfelejtett-jelszo
thesanacorp.com/international-partership.htm
5-5.ru/index.php?links_exchange=yes&page=501&show_all=yes
toplentanews.ru/pokupka-diploma-klyuch-k-novyim-vozmozhnostyam
mynewsport.ru/page/3
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Доброго!
Последние события и главные новости Кропивницкого в одном месте! Мы оперативно сообщаем о происшествиях, обновлениях инфраструктуры, политических решениях и многом другом. Оставайтесь с нами, чтобы всегда быть в центре событий.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://bomba.kr.ua/news-kropirnitskiy/
[url=https://bomba.kr.ua/]Главные новости Украины[/url]
новости Украины за день
новости Украины сегодня
Новости Кропивницкого
Удачи!
Привет!
Будьте в курсе последних новостей Украины и мира! Читайте о политике, экономике, культуре и спорте – самые интересные и важные события в одном месте.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://smi.in.ua/showbiz/
[url=https://smi.in.ua/ekonomika/]Новости экономики[/url]
новости Украины за день
новости за день
новости Украины сегодня
Удачи!
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://nemoskvichi.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=148204]http://nemoskvichi.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=148204[/url]
[url=http://alter-energo.ru/viewtopic.php?f=17&t=3612]http://alter-energo.ru/viewtopic.php?f=17&t=3612[/url]
[url=http://honey.ukrbb.net/viewtopic.php?f=40&t=12889]http://honey.ukrbb.net/viewtopic.php?f=40&t=12889[/url]
[url=http://maymotors.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=8&t=1660]http://maymotors.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=8&t=1660[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great information. Lucky me I found your site by chance (stumbleupon).
I have book marked it for later!
Привет!
Участие несовершеннолетних в ДТП в Виннице: статистика и предупреждения
ДТП с участием несовершеннолетних — тревожный сигнал для общества. В этом материале рассматривается статистика аварий с участием детей и подростков в Виннице, причины их возникновения и возможные способы предотвращения. Читайте о том, какие меры принимаются для повышения осведомлённости несовершеннолетних о правилах дорожного движения и как родители могут помочь своим детям быть в безопасности на дороге.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://dtp.vn.ua/category/video/
[url=https://dtp.vn.ua/category/video/]ДТП Видео[/url]
ДТП Винница
ДТП Винница за день
ДТП Винница сегодня
Удачи!
Привет!
Последние события и главные новости Кропивницкого в одном месте! Мы оперативно сообщаем о происшествиях, обновлениях инфраструктуры, политических решениях и многом другом. Оставайтесь с нами, чтобы всегда быть в центре событий.
Все самое лучшее на сайте https://top10.kr.ua/
[url=https://top10.kr.ua/]Новости Кропивницкого главные[/url]
Новости Кропивницкого сегодня
Новости Кропивницкого
новости Украины видео
Удачи!
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hey just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t
loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue.
I’ve tried it in two different browsers and both show the same outcome.
골드 킹
Zhu Houzhao는 고개를 저었다. “아니, 나는 당신을 기다리지 않을 것입니다.”
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I get pleasure from, lead to I discovered just what I was looking for. You’ve ended my 4 day lengthy hunt! God Bless you man. Have a nice day. Bye
click2connect.buzz/index.php?do=/public/user/blogs/name_Alanpoe/page_5/
gamesfortop.ru/diplomyi-na-zakaz-vash-shans-na-novuyu-kareru
http://www.tonpentreafc.com/ton_pentre_youth_090409.html
ultras.lv/topic1669.html?view=print
go4pro.ru/gopro/video-s-gopro/gopro-video-iz-razryada-kak-zhe-skuchno-ya-zhivu
Hello everybody!
Global Cuisine Adventures! Take your taste buds on an adventure with our global cuisine recipes. Experience the flavors of Italy, Thailand, Mexico, and more right from your kitchen.
Health & Wellness Advice! Maintain your well-being with our comprehensive health and wellness tips. Get expert advice on nutrition, fitness, mental health, and more.
Look interesting site about this – https://visionarynexst.com
recipes
baking
family travel
food
food culture
travel stories
meditation tips
travel destinations
Good luck!
国产线播放免费人成视频播放 https://hacktivizm.org
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=http://declomid.online/]clomid 100 mg tablet[/url]
Good day!
Financial Management for Entrepreneurs! Effective financial management is essential for business success. Discover how to manage your finances, create a budget, and plan for the future.
Entertainment & Culture! Stay entertained with the latest in movies, TV shows, music, and culture. Get reviews, previews, and behind-the-scenes insights.
Look interesting site about this – https://visionarynexst.com
Italian cuisine
food science
romantic travel
top stories
startup incubators
travel packing tips
small and medium enterprises (SMEs)
self-care tips
Goog luck!
Спасибо за статью, было познавательно!
кстати, вот ссылка на похожую статью:
яндекс плюс Может, кому-то пригодится.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
It’s very straightforward to find out any matter on web as compared to textbooks,
as I found this post at this web page.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
This is a topic close to my heart cheers, where are your contact details though?
슬롯 모아 무료
그녀는 가만히 서서 “Ai Jia는 그것을 예상하지 못했지만 그는 진주를 몰랐습니다 …”라고 말했습니다.
[url=https://antimafia.se/]hashish with a syringe[/url] 3 gram discount. 16%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]powdered heroin – snorting[/url] 30 grams discounts 15%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]ecstasy under the tongue[/url] – 2 gram sale 23%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]hachis con una jeringuilla[/url] 51 gramas descuento. 42%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]heroina en polvo – esnifada[/url] 70 gramas rebajas 42%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]extasis bajo la lengua[/url] – 2 gramas sleva 45%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]hasista ruiskulla[/url] 7 gram sleva. 37%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]heroiinijauhe – nuuskaaminen[/url] 30 grams sale 34%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]ekstaasi kielen alla[/url] – 2 gram sale 41%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]haszysz za pomoca strzykawki[/url] 17 gramy sale. 36%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]sproszkowana heroina – wciaganie[/url] 30 gramy sale 44%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]ekstaza pod jezykiem[/url] – 11 gram discount 18%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]du haschisch avec une seringue [/url]6 grammes sleva. 41%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]heroine en poudre – sniffer[/url] 30 grammes discounts 18%
[url=https://antimafia.se/]ecstasy sous la langue[/url] – 10 gram discounts 12%
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
피망 슬롯 머신
이것은 그가 Wang Shouren보다 조금 더 발전했음을 의미했습니다.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Не работает Indesit? Не стоит расстраиваться, ведь есть решение! По ссылке https://dominickriyo54210.mpeblog.com/51013702/lengthening-the-lifespan-of-your-indesit-appliances-through-professional-care вы найдете всю необходимую информацию о ремонте бытовой техники Indesit. Опытные мастера аккуратно и в срок вернут технику к жизни.
[url=https://www.diigo.com/item/note/9nzn4/to8w?k=c60c245c99d7aa37dc65fb1929512caf]indesit ремонт[/url]
индезит сервис центр
ремонт холодильников индезит
indesit ремонт
https://dr-Nona.ru/ – Dr Nona
купить диплом с занесением в реестр [url=https://diplomvash.ru/]diplomvash.ru[/url] .
強姦色情片
‘Sugary food is a drug for me’: A growing number of children are addicted to ultraprocessed foods
[url=https://kraken-25.at]kraken6gf6o4rxewycqwjgfchzgxyfeoj5xafqbfm4vgvyaig2vmxvyd.onion[/url]
Chicago native Jeffrey Odwazny says he has been addicted to ultraprocessed food since he was a child.
“I was driven to eat and eat and eat, and while I would overeat healthy food, what really got me were the candies, the cakes, the pies, the ice cream,” said the 54-year-old former warehouse supervisor
https://kraken-21.at
kraken15
“I really gravitated towards the sugary ultraprocessed foods — it was like a physical drive, I had to have it,” he said. “My parents would find hefty bags full of candy wrappers hidden in my closet. I would steal things from stores as a kid and later as an adult.”
Some 12% of the nearly 73 million children and adolescents in the United States today struggle with a similar food addiction, according to research. To be diagnosed, children must meet Yale Food Addiction Scale criteria as stringent as any for alcohol use disorder or other addictions.
“Kids are losing control and eating to the point where they feel physically ill,” said Ashley Gearhardt, a professor of psychology at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor who conducted the research and developed the Yale addiction scale.
“They have intense cravings and may be sneaking, stealing or hiding ultraprocessed foods,” Gearhardt said. “They may stop going out with friends or doing other activities they used to enjoy in order to stay at home and eat, or they feel too sluggish from overeating to participate in other activities.”
Her research also shows about 14% of adults are clinically addicted to food, predominantly ultraprocessed foods with higher levels of sugar, salt, fat and additives.
For comparison, 10.5% of Americans age 12 or older were diagnosed with alcohol use disorder in 2022, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health.
While many people addicted to food will say that their symptoms began to worsen significantly in adolescence, some recall a childhood focused on ultraprocessed food.
“By age 2 or 3, children are likely eating more ultraprocessed foods in any given day than a fruit or vegetable, especially if they’re poor and don’t have enough money in their family to have enough quality food to eat,” Gearhardt said. “Ultraprocessed foods are cheap and literally everywhere, so this is also a social justice issue.”
An addiction to ultraprocessed foods can highjack a young brain’s reward circuitry, putting the primitive “reptilian brain,” or amygdala, in charge — thus bypassing the prefrontal cortex where rational decision-making occurs, said Los Angeles registered dietitian nutritionist David Wiss, who specializes in treating food addiction.
[url=https://tonnametr.naydemvam.ru/viewtopic.php?id=26014]https://tonnametr.naydemvam.ru/viewtopic.php?id=26014[/url]
[url=https://dom-nam.ru/index.php/forum/stroitelnye-kompanii/29136-khotite-kupit-eksklyuzivnye-preparaty-dlya-zdorovya]https://dom-nam.ru/index.php/forum/stroitelnye-kompanii/29136-khotite-kupit-eksklyuzivnye-preparaty-dlya-zdorovya[/url]
[url=https://vestnik-rm.ru/articles/kalejdoskop/kak-zakazat-lekarstva-onlajn]https://vestnik-rm.ru/articles/kalejdoskop/kak-zakazat-lekarstva-onlajn[/url]
[url=https://med-pro-ves.ru/preparaty/kak-dejstvuet-ketorol]https://med-pro-ves.ru/preparaty/kak-dejstvuet-ketorol[/url]
купить диплом техникума [url=https://diplomvash.ru/]diplomvash.ru[/url] .
Привет всем!
1win – это качество и надежность. Бонусы для новых игроков, высокие коэффициенты на ставки, быстрый вывод средств. Рабочее зеркало всегда доступно. Играю с удовольствием и советую всем попробовать 1win! [url=]1win машины[/url]
1win – это надежность и удобство. Простая регистрация, щедрые бонусы, быстрые выплаты. Рабочее зеркало всегда доступно. Играю и выигрываю с удовольствием. Советую всем любителям азартных игр!
Ловите сайт где все в лучшем виде! – http://1winapk.kz
1win вход 1win bj3 xyz
зеркало 1 win онлайн
бк 1win официальный сайт скачать
1 win мобильная версия зеркало
1win экспресс ставка
что такое серия 1win
1win скачать на андроид apk
Удачи!
마종 웨이즈 2
북쪽의 호족이 세관에 들어왔을 때의 광경을 감히 잊을 수 없다.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Общественное здание или его часть [url=https://zetflixhd.life/]зетфликс[/url] с оборудованием для публичной демонстрации кинофильмов. Главное помещение кинотеатра – зрительный зал с экраном большого размера и системой воспроизведения звука. В современных кинотеатрах система звуковоспроизведения состоит из нескольких громкоговорителей, обеспечивающих объёмный звук. Первые стационарные кинотеатры назывались в России «электротеатрами»
зетфликс https://zetflixhd.life/
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Романтикам и любителям казино привет!
1win – это надежное место для ставок и казино. Приятные бонусы, быстрый вывод средств, удобное приложение для Android. Рабочее зеркало всегда доступно. Играю с удовольствием и советую всем попробовать! [url=]ставки на спорт официальный сайт регистрация 1win[/url]
На 1win нашел все, что нужно для успешной игры: высокие коэффициенты, бонусы, разнообразные игры. Рабочее зеркало всегда доступно, вывод денег быстрый. Советую 1win всем любителям ставок и казино!
Ловите сайт где все в лучшем виде! – http://1winapk.kz
1win коллаген хондроитин глюкозамин
1win вывод выигрыша
1win xyz официальный
1win email
как вывести деньги 1win на банковскую карту
1win detox slim effect отзывы
1win скачать мобильную
Удачи!
ass fucking and rape porn site https://blackhackz.com/rape-porn/
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
купить диплом в оренбурге [url=https://diplomvash.ru/]diplomvash.ru[/url] .
“Дело “Лайф-из-Гуд” — “Гермес” — “Бест Вей”: свидетель обвинения объявила себя потерпевшей от следствия
[url=https://www.pravda.ru/realty/2049298-delo-laif-iz-gud-germes-best-vei/]Набойченко Лайф-из-Гуд[/url]
6 и 13 июня Приморский районный суд города Санкт-Петербурга, рассматривающий по существу уголовное дело № 1-504/24, связываемое с компаниями “Лайф-из-Гуд”, “Гермес” и кооперативом “Бест Вей”, провел очередные, шестое и седьмое по счету, заседания, посвященные допросу свидетелей обвинения и лиц, признанных следствием потерпевшими в рамках судебного следствия по делу
“К кооперативу претензий не было, следователь предложил подать заявление”
Признанный следствием потерпевший Болян подсудимых не знает. Был клиентом “Гермеса”, а также пайщиком кооператива — но до 2019 года. В 2019-м он вышел из кооператива и из “Гермеса”, ему были возвращены паевые взносы, и никаких претензий к кооперативу у него не было — что он письменно подтвердил, расторгая договоры с этими организациями.
Однако, как Болян отметил на суде, следователь убедил его в том, что он — потерпевший и должен подать заявление на возврат членских взносов. Заявление в МВД писать не хотел, на него вышли сотрудники, сначала претензий к кооперативу не было. Полиция ему объяснила, что можно получить деньги.
Стал клиентом “Гермеса” и пайщиком кооператива через своего консультанта Алексея Виноградова. Виноградов — грамотный маркетолог, он ему верил, тот не работал в кооперативе. Что было предметом договора в “Гермесе”, не помнит. В “Гермес” внес 100 и 700 евро, а в кооператив каждый месяц вносил по 12 тыс. в течение семи месяцев.
Вышел и из кооператива, и из “Гермеса” в 2019 году. Зачем вступал? “Наверное, квартиру купить хотел”. Кооператив вернул ему 70 тыс. паевых взносов, “Гермес” вернул со счета “Виста” 140 тыс. рублей.
В кооперативе деньги вернули почти сразу, удержав вступительный и членские взносы; в “Гермесе” вернули позже через “внутрянку”, но удержали комиссию.
Утверждает, что ему говорили, что можно со счета “Виста” вносить деньги в кооператив. Объясняли, что деньги передаются в доверительное управление трейдерам и брокерам, которые играют на бирже. В кооперативе, как он утверждает, можно было купить место в очереди. По его словам, “Гермес” и кооператив — по сути, одна организация. Требует взыскать с кооператива более 148 тыс. рублей — вступительный и членские взносы, и более 60 тыс. рублей с “Гермеса” — комиссию при выводе средств.
Договор с кооперативом не читал, но ему объяснили, что есть невозвратная часть денег — ее и не вернули, “но хочу попытаться вернуть”. Претензий к кооперативу “как бы и нет, но если вернут взносы, то будет хорошо”.
К Виноградову претензий не предъявлял. “Может, меня и не обманули в кооперативе”, -резюмировал свое выступление в суде Болян.
“Требую выплатить с учетом роста цен на недвижимость”
Признанная следствием потерпевшей Комова была как клиентом “Гермеса”, так и пайщиком кооператива. Подсудимых не знает. Требует более 8800 тыс. с кооператива и более 2700 тыс. с “Гермеса”. При этом из кооператива она не вышла и заявление о выходе не подавала. Сумма требований к кооперативу включает как паевые и членские взносы, так и оценку роста цен на недвижимость, которая не была приобретена.
Утверждает, что можно переводить деньги со счета “Виста” напрямую в кооператив — в подтверждение приводит скрины переписки с консультантами в смартфоне. Суд разъясняет, что доказательство может быть приобщено позднее при надлежащем оформлении.
“Информацию воспринял скептически, но вступил”
Признанный следствием потерпевшим Киреев был только клиентом “Гермеса”. Подсудимых не знает лично — Измайлова видел в видеоролике “Лайф-из-Гуд”. Узнал о “Гермесе” от консультантов Татьяны и Андрея Клейменовых, с которыми знаком с конца 1990-х годов. Вступил в “Гермес” в 2020 году, деньги сразу отобразились на счете. Вносил средства на счет “Виста” небольшими частями, снимал средства со счета для личных нужд. Заявляет требования на более чем 2 млн 300 тыс. рублей.
Когда подписывал договор, в офисе была табличка кооператива, но в офисе находился представитель фирмы “Гермес”, ему сказали, что это два продукта компании “Лайф-из-Гуд”.
В 2022 году начались проблемы с выводом средств. И руководство фирмы пугало блокировкой счета в случае подачи заявления в правоохранительные органы. В хейтерском чате узнал телефон следователя Сапетовой, позвонил и подал заявление.
В чате клиентов компании “Гермес” была информация о том, что счет будет заблокирован в случае подачи заявления в правоохранительные органы. Эта информация была за подписью “администрация”. Он спросил у консультантов: “Кто это — администрация?”, написал вопрос в чате, и его забанили. Других попыток вступать в диалог с “Гермесом” не предпринимал.
Признанный следствием потерпевшим Чернышенко был также только клиентом только компании “Гермес”. Подсудимых не знает. Познакомился с консультантами “Гермеса” во время совместной работы в “Макдоналдсе”. Информацию о “Гермесе” воспринял скептически — “это какой-то обман”, но консультанты его в конце концов уговорили. Они поставили условие, что продадут ему земельный участок, чтобы он вступил в “Гермес”.
“Я хотел их обмануть, — пояснил свидетель, — думал: пусть они продадут, а я в “Гермес” не вступлю. Но они начали уговаривать, и я вступил в апреле 2020 года. Один из консультантов дал расписку на внесение денег на счет в “Гермесе”, я внес через него 230 тыс. И еще раз из жадности 140 тыс. 140 тыс. я вывел, плюс каждый месяц выводил по 5000–7000 руб. С какого-то момента проценты стали падать. В конце я захотел выйти — но не успел. У меня в “Гермесе” осталось 270 тыс., которые я требую вернуть”.
В январе 2023 года Чернышенко подал заявление в полицию, так как прекратился доступ к счету. “Мне предложили 70 тыс. вернуть, чтобы я не ходил в полицию, ссылаясь на то, что помогли мне продать участок за меньшую сумму по документам, чем я его продал на самом деле, но я отказался, сказал, что мне надо 270 тыс.”.
“Я хочу стать потерпевшей. Но Василенко многие благодарны за квартиры”
Свидетель обвинения Галашенкова была только клиентом “Гермеса”. Из подсудимых знает Виктора Ивановича Василенко. Она сидела в зале при допросе двух потерпевших (что запрещено), но заявила, что плохо слышит. Ранее была знакома с Верой Исаевой из компании “Лайф-из-Гуд”.
Вера узнала, что у нее есть офис, и познакомила с Романом Василенко, который снял у нее офис, когда “Лайф-из-Гуд” только начинала раскручиваться. Он снимал офис только за коммунальные платежи. “Я попросила расплатиться за четыре месяца, а он предложил мне вместо денег вступить в “Бест Вей”, но я отказалась, так как квартира не была нужна”. Зато стала клиентом “Гермеса”: “Внесла 15 тыс. евро, но через три месяца на счете оказалось 3400 евро!” Исаева, по словам Галашенковой, оказалась мошенницей.
По словам Галашенковой, она внесла на счет “Виста” более 3 млн рублей. “Когда сказали, что все счета заблокировали, то собрали с нас еще денег, чтобы счета разблокировать, потом пришло сообщение, что открывается новая фирма, но это все оказалось обманом — счета не разблокированы”.
“Я не считала себя потерпевшей, так как не знала, что это можно сделать, — заявила Галашенкова. — Сейчас желаю заявить, что я хочу стать потерпевшей. Считаю, что должна взыскать с “Гермеса” как прямой ущерб, так и упущенную выгоду, так как эта фирма закрылась”.
При этом заявила, что “Василенко молодец, потому что я видела людей, которые купили квартиры, они были ему очень благодарны”.
https://blackhackz.com/watch-rape-porn
What Is Neotonics? Neotonics is a skin and gut supplement made of 500 million units of probiotics and 9 potent natural ingredients to support optimal gut function and provide healthy skin.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
https://blackhackz.com/rape-porn
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
What Is ZenCortex? ZenCortex is a natural supplement that promotes healthy hearing and mental tranquility. It’s crafted from premium-quality natural ingredients, each selected for its ability to combat oxidative stress and enhance the function of your auditory system and overall well-being.
What Is ZenCortex? ZenCortex is a natural supplement that promotes healthy hearing and mental tranquility. It’s crafted from premium-quality natural ingredients, each selected for its ability to combat oxidative stress and enhance the function of your auditory system and overall well-being.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
«Король» обвинителей «Лайф-из-Гуд» Набойченко – кто он на самом деле?
[url=https://www.kp.ru/daily/27561/4885460/ ]ПК Бествей рейдерский захват[/url]
Евгений Набойченко – бывший IT-директор компании «Лайф-из-Гуд», а также сисадмин российского сегмента платежной системы международной инвестиционной компании «Гермес». Он – ключевой свидетель обвинения в так называемом деле «Лайф-из-Гуд» – «Гермес» – кооператива «Бест Вей» и основателя «Лайф-из-Гуд»/«Бест Вей» Романа Василенко, которое рассматривается сейчас судьей Екатериной Богдановой в Приморском районном суде Санкт-Петербурга.
С выполненной им блокировки российского сегмента платежной системы компании «Гермес», а также с его (нетрезвых) сообщений в социальных сетях (сейчас все они им стерты) началась эскалация этого уголовного дела. Но, скорее всего, дело им же самим и его подельниками из питерской полиции и создано.
Вор и дебошир
Наши источники делятся информацией о хищении активов с кошельков клиентов «Гермеса», к которым Евгений Набойченко имел доступ.
Набойченко не гнушался воровать даже у близких. Однажды остановившись у своей любовницы Светланы Н., Евгений избил ее и украл деньги с ее криптовалютного кошелька, пока она пыталась прийти в себя после побоев.
Он бил не только любовницу, но жену и детей, с которыми жил в Краснодарском крае. А после того как его супруга Виктория подала на развод, разгромил, ободрал и ограбил общий дом – унес все, что можно было унести. Надо ли говорить, что Набойченко который год не платит супруге алименты.
Вымогатель
Евгений Набойченко, по словам его бывшей жены, в один прекрасный день решил заработать и с помощью вымогательства. Он шантажировал Романа Василенко – требовал с него деньги: 170 тыс. евро. При этом, по утверждению Виктории Набойченко, угрожал увечьями и самому Роману Василенко, и его супруге, и детям. Похвалялся перед (тогда еще) женой своими матерными сообщениями с угрозами, которые он посылал Василенко и его близким.
Кроме того, вымогал деньги у клиентов «Гермеса»: свидетельства такого рода нам предоставлены.
Алкоголик и наркоман
Деньги нужны Набойченко в том числе для того, чтобы «питать» свою наркотическую зависимость – с некоторых пор он предпочитает шлифовать водку галлюциногенными грибами, об увлечении которыми с упоением рассказывал даже в своих соцсетях.
Он не всегда был алкоголиком и наркоманом – устроившись 10 лет назад в IT-службу, не пил и не употреблял. Но большие деньги, красивая жизнь, которая вдруг стала доступна для простого астраханского парня из низов, развратили его.
Клеветник
Он допустил целый ряд клеветнических высказываний в адрес Романа Василенко – за которые против него заведено уголовное дело. Но расследуется оно ни шатко ни валко, так как расследование тормозит начальник УЭБиПК ГУ МВД России по Санкт-Петербургу и Ленинградской области.
Завербованный органами
Виктория Набойченко сообщает, что за три дня до обыска в их тогда еще совместном доме Евгений уехал и ей сказал, что придут с обыском – но это пустая формальность. Он уже был в сговоре с полицией, так как за три дня был предупрежден об этом обыске.
15 февраля 2022 года Евгений Набойченко был задержан, но отправился не в СИЗО – куда отправили других сотрудников «Лайф-из-Гуд», не был помещен в изолятор или КПЗ, а жил на полицейской квартире.
Он отказался от услуг адвокатов и на этой квартире, по свидетельству одного из полицейских, «бухал с операми». А также каждый день водил оперов по барам и ресторанам – угощал их за свой счет.
В разговоре с женой он очень гордился покровительством начальника УЭБиПК питерского главка МВД.
Наши источники считают, что он украл деньги клиентов «Гермеса», разделив их со своими друзьями из полиции. Вся его дальнейшая жизнь и привычки указывают на то, что он использует ворованные деньги.
Трус и лжец
Набойченко сообщил в социальных сетях, что к нему пришло с адреса fall@mybizon.online письмо, в котором содержится угроза в адрес получателя, призывающая его не являться в суд для дачи показаний. В письме указано, что если он поедет в суд, то не доедет и будет трупом.
Создатель преступного сообщества
Нет сомнений, что Набойченко устроил историю с обрушением платежной системы, чтобы скрыть свое воровство активов клиентов. Также чтобы скрыть свое воровство, он обвинил во всем Василенко и технических специалистов компании «Лайф-из-Гуд», которые находятся сейчас на скамье подсудимых. Оклеветал всех, чтобы отвести подозрения от себя и своих подельников из питерской полиции.
Итак, кризис в «Гермесе» устроил Набойченко. Платежную систему разгромил Набойченко. Активы украл Набойченко, поделившись с питерскими полицейскими.
А теперь сидит и бездельничает, прожигая сворованные деньги. И боится идти в суд – чтобы не превратиться в суде из свидетеля в обвиняемого.
Скорее всего, в суд Набойченко не пускают сами полицейские – опасаясь его неадекватности и перекрестного допроса, на котором вскроется лживость его показаний. То есть силовики заметают следы своего преступления, совершенного с помощью марионетки Набойченко.
The world’s most liveable cities for 2024
[url=https://rutube.ru/video/5ca18a525e02e021e4dacaf6126ed57e/]порно анальный секс[/url]
It’s considered among the most beautiful cities in the world to visit, and it seems that Vienna may also be an unbeatable place to live.
The Austrian city has been crowned the most liveable city in the world yet again in the annual list from the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU), which was released today.
The EIU, a sister organization to The Economist, ranked 173 cities across the globe on a number of significant factors, including health care, culture and environment, stability, infrastructure and education.
Vienna topped the list for the third consecutive year, receiving “perfect” scores in four out of five of the categories — the city was marked lower for culture and environment due to an apparent lack of significant sporting events.
Just behind the Austrian capital, Denmark’s Copenhagen retained its second place position, while Switzerland’s Zurich moved up from sixth place to third on the list.
Australia’s Melbourne fell from third to fourth place, while Canadian city Calgary tied for fifth place with Swiss city Geneva.
Canada’s Vancouver and Australia’s Sydney were in joint seventh place, and Japan’s Osaka and New Zealand’s Auckland rounded out the top 10 in joint ninth place.
«Король» обвинителей «Лайф-из-Гуд» Набойченко – кто он на самом деле?
[url=https://www.pravda.ru/realty/1888547-akcii_best_vei/ ]Приморский районный суд[/url]
Евгений Набойченко – бывший IT-директор компании «Лайф-из-Гуд», а также сисадмин российского сегмента платежной системы международной инвестиционной компании «Гермес». Он – ключевой свидетель обвинения в так называемом деле «Лайф-из-Гуд» – «Гермес» – кооператива «Бест Вей» и основателя «Лайф-из-Гуд»/«Бест Вей» Романа Василенко, которое рассматривается сейчас судьей Екатериной Богдановой в Приморском районном суде Санкт-Петербурга.
С выполненной им блокировки российского сегмента платежной системы компании «Гермес», а также с его (нетрезвых) сообщений в социальных сетях (сейчас все они им стерты) началась эскалация этого уголовного дела. Но, скорее всего, дело им же самим и его подельниками из питерской полиции и создано.
Вор и дебошир
Наши источники делятся информацией о хищении активов с кошельков клиентов «Гермеса», к которым Евгений Набойченко имел доступ.
Набойченко не гнушался воровать даже у близких. Однажды остановившись у своей любовницы Светланы Н., Евгений избил ее и украл деньги с ее криптовалютного кошелька, пока она пыталась прийти в себя после побоев.
Он бил не только любовницу, но жену и детей, с которыми жил в Краснодарском крае. А после того как его супруга Виктория подала на развод, разгромил, ободрал и ограбил общий дом – унес все, что можно было унести. Надо ли говорить, что Набойченко который год не платит супруге алименты.
Вымогатель
Евгений Набойченко, по словам его бывшей жены, в один прекрасный день решил заработать и с помощью вымогательства. Он шантажировал Романа Василенко – требовал с него деньги: 170 тыс. евро. При этом, по утверждению Виктории Набойченко, угрожал увечьями и самому Роману Василенко, и его супруге, и детям. Похвалялся перед (тогда еще) женой своими матерными сообщениями с угрозами, которые он посылал Василенко и его близким.
Кроме того, вымогал деньги у клиентов «Гермеса»: свидетельства такого рода нам предоставлены.
Алкоголик и наркоман
Деньги нужны Набойченко в том числе для того, чтобы «питать» свою наркотическую зависимость – с некоторых пор он предпочитает шлифовать водку галлюциногенными грибами, об увлечении которыми с упоением рассказывал даже в своих соцсетях.
Он не всегда был алкоголиком и наркоманом – устроившись 10 лет назад в IT-службу, не пил и не употреблял. Но большие деньги, красивая жизнь, которая вдруг стала доступна для простого астраханского парня из низов, развратили его.
Клеветник
Он допустил целый ряд клеветнических высказываний в адрес Романа Василенко – за которые против него заведено уголовное дело. Но расследуется оно ни шатко ни валко, так как расследование тормозит начальник УЭБиПК ГУ МВД России по Санкт-Петербургу и Ленинградской области.
Завербованный органами
Виктория Набойченко сообщает, что за три дня до обыска в их тогда еще совместном доме Евгений уехал и ей сказал, что придут с обыском – но это пустая формальность. Он уже был в сговоре с полицией, так как за три дня был предупрежден об этом обыске.
15 февраля 2022 года Евгений Набойченко был задержан, но отправился не в СИЗО – куда отправили других сотрудников «Лайф-из-Гуд», не был помещен в изолятор или КПЗ, а жил на полицейской квартире.
Он отказался от услуг адвокатов и на этой квартире, по свидетельству одного из полицейских, «бухал с операми». А также каждый день водил оперов по барам и ресторанам – угощал их за свой счет.
В разговоре с женой он очень гордился покровительством начальника УЭБиПК питерского главка МВД.
Наши источники считают, что он украл деньги клиентов «Гермеса», разделив их со своими друзьями из полиции. Вся его дальнейшая жизнь и привычки указывают на то, что он использует ворованные деньги.
Трус и лжец
Набойченко сообщил в социальных сетях, что к нему пришло с адреса fall@mybizon.online письмо, в котором содержится угроза в адрес получателя, призывающая его не являться в суд для дачи показаний. В письме указано, что если он поедет в суд, то не доедет и будет трупом.
Создатель преступного сообщества
Нет сомнений, что Набойченко устроил историю с обрушением платежной системы, чтобы скрыть свое воровство активов клиентов. Также чтобы скрыть свое воровство, он обвинил во всем Василенко и технических специалистов компании «Лайф-из-Гуд», которые находятся сейчас на скамье подсудимых. Оклеветал всех, чтобы отвести подозрения от себя и своих подельников из питерской полиции.
Итак, кризис в «Гермесе» устроил Набойченко. Платежную систему разгромил Набойченко. Активы украл Набойченко, поделившись с питерскими полицейскими.
А теперь сидит и бездельничает, прожигая сворованные деньги. И боится идти в суд – чтобы не превратиться в суде из свидетеля в обвиняемого.
Скорее всего, в суд Набойченко не пускают сами полицейские – опасаясь его неадекватности и перекрестного допроса, на котором вскроется лживость его показаний. То есть силовики заметают следы своего преступления, совершенного с помощью марионетки Набойченко.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
[url=https://siding-rdm.ru/kak-vybrat-idealnuju-kovanuju-sadovuju-skamejku-dlya-vashego-uchastka/]https://siding-rdm.ru/kak-vybrat-idealnuju-kovanuju-sadovuju-skamejku-dlya-vashego-uchastka/[/url]
[url=https://volnodumie.bbmy.ru/viewtopic.php?id=11654#p23650]https://volnodumie.bbmy.ru/viewtopic.php?id=11654#p23650[/url]
[url=https://dom-nam.ru/index.php/forum/landshaftnyj-dizajn-na-uchastke/29528-detskie-sportivnye-kompleksy-dlya-ulitsy#61240]https://dom-nam.ru/index.php/forum/landshaftnyj-dizajn-na-uchastke/29528-detskie-sportivnye-kompleksy-dlya-ulitsy#61240[/url]
[url=http://riasamara.ru/rus/analytics_and_comments/news_comp/article88783.shtml]http://riasamara.ru/rus/analytics_and_comments/news_comp/article88783.shtml[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Доброго!
В поисках идеального электрокамина в Москве с лучшими ценами и выгодными распродажами, Grand-Kamin ([url=https://grand-kamin.ru/]продажа электрокаминов[/url]) становится вашим надежным партнером. Наш интернет-магазин предлагает широкий выбор электрокаминов по привлекательным ценам, чтобы каждый мог создать уют и комфорт в своем доме без лишних затрат.
Лучшие цены на электрокамины в Москве доступны именно у нас. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции различных стилей и дизайнов, чтобы каждый клиент мог найти идеальное сочетание для своего интерьера. Наши электрокамины сочетают в себе высокое качество, функциональность и стиль, что делает их идеальным выбором для создания уюта и атмосферы в вашем доме.
Не упустите возможность приобрести электрокамин по лучшей цене в Москве прямо сейчас. Посетите наш интернет-магазин Grand-Kamin и оцените широкий выбор, выгодные предложения и профессиональный сервис, который сделает вашу покупку приятным и беззаботным процессом. Создайте уют и тепло в своем доме с лучшими ценами на электрокамины в Москве от Grand-Kamin
Лучший сайт про электрические камины – http://grand-kamin.ru/
электрокамин цена
электрокамин купить в интернет
интерьер ресторана
купить электрокамин в квартиру в москве
электрокамин купить дешево в москве
Удачи!
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
리액툰즈
모두가 놀랐고, 이 시점에서 사람들을 겁주어 죽이기 쉽습니다.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Почему сотрудники Колокольцева провоцируют социальный протест
[url=https://vestnik-jurnal.com/novosti/item/100193-voennyh-unizhayut-tylovye-krysy-opg-kolokolceva]ОПГ Колокольцева[/url]
15 февраля пайщики кооператива «Бест Вей» по всей России намерены провести акции в поддержку кооператива. Кооператив работает в 72 регионах, в более чем 50 из них созданы инициативные группы и подаются заявки на проведение митинга.
Эти действия спровоцированы действиями следственной группы ГСУ ГУ МВД России по Санкт-Петербургу и Ленинградской области, которая заблокировала работу кооператива, арестовала его счета, арестовала всю недвижимость кооператива, хотя за более чем год расследования не нашла никаких свидетельств мошенничества в кооперативе.
15 февраля 2022 года начались активные действия следственной группы против кооператива — аресты и первый обыск в офисе с выносом всех документов. Позднее были заблокированы счета кооператива: на них находится 3,8 млрд рублей, причем сумма увеличивается, так как большинство пайщиков продолжает платить членские взносы и вносить паевые платежи.
Несмотря на то что кооператив трижды добивался в суде снятия ареста, следствие вновь выходило в суд с фактически тем же самым ходатайством и пытается, пользуясь своими полномочиями, уничтожить юридическое лицо, и накладывался новый арест.
В периоды, когда арест снимался, следствие за счет давления на банки добивалось того, чтобы платежи не проходили. Так происходит и сейчас, хотя с 19 января арест со счетов кооператива судом снят. Невзирая на претензионные письма кооператива в банки, жалобы кооператива в Центробанк и подготовку исковых заявлений против банков, Сбербанк и банк «Санкт-Петербург», получив, по свидетельству самих банковских работников, устное предупреждение следствия и «после звонков из Москвы», отказываются разблокировать счета, прямо нарушая постановление суда, снявшего арест со счетов.
Офис кооператива дважды обыскивался, документы дважды изымались, и следствие запрещало копировать документацию.
С самого начала расследование дела происходит при информационной поддержке помощника Колокольцева Ирины Волк, подчиненной ей пресс-служба министерства, разнообразные пристяжные «СМИ» типа «Дежурной части» на НТВ. К поддержке привлекли и самого министра: он говорил о деле кооператива «Бест Вей» в своем выступлении в Совете Федерации осенью 2022 года. По некоторым данным, «авторами» дела являются руководители ГУЭБиПК МВД России, облеченные доверием министра.
Следствие по-питерски
Характерно, что дело не «забрал» себе Следственный департамент МВД России. Оно расследуется ГСУ ГУ МВД России по Санкт-Петербургу и Ленинградской области — по месту регистрации кооператива, несмотря на общероссийский характер деятельности «Бест Вей». Это значит, что даже авторы атаки в центральном аппарате МВД не уверены в ее успехе.
Кураторы дела в федеральном МВД шанс проявиться, и они «роют землю», не гнушаются прямым нарушением закона, чтобы проявить себя. Кто эти героические работники юстиции? Прежде всего руководитель следственной группы майор юстиции Екатерина Сапетова и ее непосредственный руководитель подполковник юстиции Константин Иудичев.
Четверо технических сотрудников, не имевших никакого отношения к руководству кооперативом, трое из которых молодые женщины, были арестованы, хотя им вменялся «экономический» состав и они никогда не привлекались к уголовной ответственности. Они уже около года томятся в СИЗО, причем с ними почти не проводится следственных действий. По мнению адвокатов, от них ждут показаний на начальство.
Пятеро граждан объявлены в розыск, в том числе давно отошедший от текущего управления кооперативом его основатель и бывший председатель Совета кооператива Роман Василенко. 80-летних родителей Романа Василенко, ветеранов Вооруженных сил, постоянно таскают на многочасовые допросы, в ходе которых им неоднократно требовалась срочная медицинская помощь, им угрожают СИЗО.
Усилия следствия не привели к адекватным для судов результатам. Компрометирующих кооператив показаний ни от арестованных, ни от пожилых родственников людей, объявленных в розыск, получить не удалось, а пул потерпевших, собранный с огромным трудом, и их претензии выглядят неубедительно даже в наших судах, которые обычно дают следствию карт-бланш на период предварительного расследования.
Кульбиты обвинения
Следствие и пресс-структуры МВД рассказывают судам и прессе о «12 тысячах пострадавших», однако за более чем год работы им удалось получить заявления от сотни с небольшим потерпевших с общей суммой претензий около 150 млн рублей, хотя активы кооператива — более 15 млрд рублей. Предварительное расследование забуксовало.
Притом что следователи работают не покладая рук, телефонными звонками и письмами (есть в редакции) приглашая всех, кто так или иначе взаимодействовал с кооперативом, написать заявление.
Потерпевшие делятся на три группы. Первая — граждане, подавшие заявление по поводу действий другого юридического лица — компании высокодоходных инвестиций, которая контролировалась одним из прежних руководителей кооператива. Следствие пытается объявить эту компанию аффилированной с кооперативом, хотя между ними не было даже никаких взаиморасчетов, и пытается через псевдоаффилированность заставить кооператив заплатить по счетам другого юридического лица. Кстати, инвесткомпания — «живая», у нее есть активы в России, есть активы и у ее учредителей.
Вторая — пайщики кооператива, которые не могут получить свои паевые средства из-за того, что следствие арестовало счета. Среди них нет ни одного заявления о том, что кооператив взял деньги пайщика на покупку квартиры и не купил квартиру или взял паевые средства в рамках договора и отказался выполнять требования договора о возврате средств. Это люди, обманутые следствием, убедившим их в том, что только участие в расследовании поможет получить назад вложенные средства, хотя на самом деле получить их назад в реальном времени помогут исключительно разблокировка работы кооператива, снятие ареста со счетов.
Часть потерпевших, возможно, выступила соавтором атаки на кооператив: это группа граждан, которые когда-то вышли из кооператива «Бест Вей» и создали «альтернативный» кооператив — ЖК «Вера» (зарегистрирован в Ухте, но работает, как и «Бест Вей», по всей России). И против них адвокаты кооператива после завершения предварительного расследования намерены подать заявления о клевете.
Часть потерпевших — люди, которые пытаются поживиться, выдвигая необоснованные требования к кооперативу. Например, претензии некоторых потерпевших касаются вступительных или членских взносов, которые по договору с кооперативом не подлежат возврату.
В рамках следственных действий зачастую выясняется, что они не считают, что кооператив их обманул. Типична ситуация, когда псевдопотерпевшие внесли первоначальный безвозвратный взнос для вступления в кооператив — 110 тыс. рублей, причем некоторые даже не полностью, при этом паевые платежи для накопления первоначального паевого взноса не вносили, членские взносы — тоже.
Квартира им, разумеется, не приобреталась — они в своих показаниях на это и не претендуют. Однако они по наущению следствия или по собственной инициативе и при поддержке следствия подписали заявление о том, что кооператив не вернул им несколько десятков тысяч рублей, которые по договору с кооперативом возврату не подлежат, так как это вступительные или членские взносы, идущие, согласно уставу, на финансирование текущей деятельности и развития кооператива.
Это очередное свидетельство махинаций, совершаемых следствием: ведь потерпевший — лицо, считающее, что в отношении него совершено преступление. Из показаний, имеющихся в уголовном деле, видно, что большинство потерпевших так не считает.
Многие из них не сами пришли в следственные органы, а после звонка следователя, предложившего подать заявление в качестве потерпевших. Пайщики кооператива жалуются на систематический обзвон следователей из следственной группы Сапетовой, письма следователей, незаконные встречи со следователями с назойливыми советами подать заявление в качестве потерпевших — подавляющее большинство пайщиков от этого отказывается, понимая, что необоснованное обвинение в преступлении приведет к ответственности.
Банковские секьюрити — лучшие друзья следствия
Суды первоначально штамповали все ходатайства следствия, как водится в российской системе юстиции, на этапе предварительного расследования. Однако с некоторых пор вопросы к следствию стали возникать и у судей.
Ведь расследование продлевается, продлевается и продлевается, а промежуточные результаты его не впечатляют. Возникает много вопросов. Почему следствие не разрешает проводить налоговые платежи? На каком основании оно требует заблокировать на счетах средства, более чем в 25 раз превышающие сумму ущерба, имеющуюся в деле? На каком основании требует арестовать недвижимость на 12 млрд рублей, в том числе перешедшую в собственность пайщиков?
Кооператив трижды добивался снятия ареста со счетов, добивался разблокирования налоговых платежей. Снимались аресты с недвижимости кооператива в целом. Кроме того, суды принимали решения о снятии арестов с отдельных квартир, и эти решения вступили в законную силу.
Тем не менее арест со счетов де-факто не снимался, за исключением короткого периода летом 2022 года длиной в полторы недели (в эти полторы недели кооператив успел вернуть паевые взносы 216 пайщикам).
Службы безопасности банков блокируют платежи кооператива — банковские службы безопасности стали лучшими помощниками следствия вместо судов. Так, 18 января суд отказался продлить арест счетов, кроме суммы в 200 млн рублей — имеющиеся в деле обязательства перед потерпевшими плюс те, которые могут возникнуть. С 19 января счета не арестованы, но де-факто арест продолжается. Сбербанк и банк «Санкт-Петербург» не пропускают платежи, несмотря на претензионные письма и готовящиеся исковые заявления кооператива и жалобы в Центральный банк.
Банки в деле?
Есть основания считать, что банки, прежде всего Сбербанк, в Северо-Западном банке которого размещен счет паевых средств кооператива, не пассивные исполнители воли следствия.
Заинтересованность в первую очередь связана с уничтожением альтернативной программы покупки квартир. Кроме того, банки заинтересованы в использовании средств на счетах: их можно крутить месяцами, зарабатывая колоссальные средства. Этот метод подсказывают западные банки, которые, заблокировав деньги России, за счет процентов их использования получают серьезные финансовые ресурсы.
Вероятно, у Сбербанка вызвала интерес также цифровая система взаимодействия с клиентами, созданная в кооперативе: есть ряд свидетельств, что она скопирована IT-специалистами Сбера. Северо-Западный банк Сбербанка когда-то активно предлагал сотрудничество кооперативу, добивался размещения счета именно у себя – возможно, не без умысла.
Пайщики знают, кто виноват
Пайщики кооператива возмущены происходящим. Ведь уже год из-за ареста счетов они не могут приобрести квартиры, средства на приобретение которых перечислили; они не могут получить паевые средства назад, чтобы использовать их для покупки квартир другим способом; они не могут получить справки в кооперативе для наследования пая — документация в кооперативе изъята, и следствие даже не разрешает ее копировать. При этом они прекрасно отдают себе отчет в том, что именно ведомство Колокольцева, решившее состряпать громкое дело на пустом месте, хотя ни деньги, ни квартиры не украдены, — автор их злоключений.
Пайщики написали тысячи обращений в следственную группу, прокуратуру, уполномоченному по правам человека, проводились импровизированные митинги в судах. Теперь настал черед больших митингов по всей России.
Сотрудники Колокольцева на пустом месте создали липовое громкое дело ради внимания первого лица страны к непримиримой борьбе с мошенниками, обирающими граждан. Хотя на самом деле именно следствие само и обирает граждан, в обстановке социальной нестабильности в стране создает дополнительный повод для массового возмущения, уничтожает уникальную программу приобретения недвижимости без банковских переплат — фактически под 1% годовых, в рамках которой уже приобретено более 2,5 тыс. квартир.
Создан кризис на пустом месте, который наносит ущерб гражданам России и стране в целом. В условиях военного противостояния, социально-экономической турбулентности, предвыборной ситуации цена действий подразделений МВД непомерно высока – министру и политическому руководству страны пора вмешаться.
But a smiling visitor here to share the love (:, btw outstanding design. “Individuals may form communities, but it is institutions alone that can create a nation.” by Benjamin Disraeli.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! However, how can we communicate?
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
크립토 골드
Hongzhi 황제는 Fang Jifan을 바라 보는 것을 도울 수 없었습니다. “Jifan이 이것을 들었습니까?”
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Dedicated to the brave players!!
I have been playing at Glory Casino for several months. Fast registration, generous bonuses, and instant withdrawals. The working mirror is always available. Glory Casino is my choice for betting and casino. I recommend it to everyone!
At Glory Casino, I found everything needed for successful gaming: high odds, bonuses, and a variety of games. The working mirror is always available, and withdrawals are fast. I recommend Glory Casino to all betting and casino enthusiasts!
[url=https://4atex.ru/blogs/2206/Licensed-Secure-Glory-Casino-Promotes-Responsible-Gambling]Glory Casino[/url]
Glory Casino apk download for Android
official website download Glory Casino
reviews Glory Casino
Glory Casino how to wager bonus
official website download Glory Casino
Good profits!
Разбираю ситуацию вокруг “кооператива” Life is Good
[url=https://pilotekh.com/wiki/item/72615-roman-viktorovich-vasilenko-rossiyskiy-piramidschik]порно анальный секс[/url]
Я решил написать этот пост, чтоб пройтись по доводам тех, кто привлекает новых “пайщиков” в структуры г-на Василенко (на деле – оплачивающих существование пирамиды Life is Good). Понятно, что, в этом сообществе крутятся сотни тех, кто занимается привлечением и теперь ЦБ с прокуратурой их оставят не только без заработка, но, возможно, придется отвечать за свои действия в суде. А деньги уже, наверняка, потрачены. Также есть люди, которые уже живут в квартире от LIG или выплатили некую сумму, они верят до конца и отказываются принимать ситуацию, в которой надо признать, что они могут остаться и без денег, и без квартиры. В любом случае, даже если кто-то живет в квартире от LIG, она ему не принадлежит и, в отличие от банковского залога, урегулировать вопрос не получится (их просто выселят через суд при банкротстве LIG, хотя ситуация скандальная и возможно государство что-то предпримет, чтоб сгладить проблему).Теперь по сути, что такое LIG.
Компания LIG – «Лайф-из-гуд» заявляет два основных направления деятельности: инвестиционные счета «Виста» в компании Hermes Management Ltd. и жилищный кооператив «Бест-вей» — альтернатива ипотеке.
Если верить консультантам «Лайф-из-гуд», доходность счетов «Виста» в компании «Гермес-менеджмент» последние годы держится в районе 20% годовых в долларах. Это довольно много (Уоррен Баффет позавидовал бы такой доходности), при этом непонятно, за счет чего достигается такая доходность.
Деятельность «Гермес-менеджмента» непрозрачна, на сайте не видно полноценных отчетов, нет сведений о структуре компании и ее руководстве.
«Гермес-менеджмент» привлекает российских клиентов через компанию «Лайф-из-гуд», но у него нет лицензии Центрального банка России на брокерскую деятельность или доверительное управление.
«Гермес-менеджмент» зарегистрирован в Белизе, офшорной зоне в Центральной Америке. Там же расположен офис компании. Еще в документах упоминается компания Hermes M в Шотландии. В случае проблем придется разбираться с зарубежной компанией, что делает задачу бесперспективной. Более того, учитывая реалии мошеннических схем, бывшие пайщики столкнутся еще и с лже-юристами, обещающими вернуть им вложенные деньги и конечно, останутся в крайне бедственном положении, с кредитами, без жилья и перспектив (у кого-то могут опуститься руки со всеми вытекающими).
Компания платит за привлечение новых клиентов, открывающих инвестиционные счета «Виста» (по сути – ничем не обеспеченные цифры на сайте. Заведение средств происходит через перевод средств на счета частных лиц(!), выполняющих роль консультантов LIG (а это сразу нарушает законы РФ и привлекает внимание регулятора), вывод – через перепродажу воздуха других буратинам. После внесения LIG в черный список, чаты структуры полны объявлений о продажи токенов Виста, но покупателей почти нет)) и вступающих в жилищный кооператив «Бест-вей». Система комиссионных выглядит такой разветвленной и продуманной, что становится понятно, что именно в ней суть компании, а не в инвестициях или альтернативе ипотеке.
Сам по себе сетевой маркетинг — вполне законный способ привлечения новых клиентов. Но когда он выглядит как основной вид деятельности, а клиентам при этом рассказывают про инвестиции, пассивный доход и успех в жизни, это наводит на очевидные выводы.
Суть предложения «Гермеса» такая: инвесторы открывают счет и перечисляют компании доллары или евро, а взамен получают пассивный доход. Минимальная сумма инвестиционного контракта — 10 тысяч долларов или евро. При этом первый взнос может быть 1130 долларов или 1100 евро, а оставшуюся сумму можно довнести позже.
Чтобы открыть счет «Виста», надо заполнить регистрационную форму на сайте «Лайф-из-гуд». При регистрации сайт просит поставить галочку «Я ознакомился и принимаю условия указанные в публичной оферте» (пунктуация сохранена).
По ссылке открывается не оферта, а договор об оказании услуг. В договоре не указаны название и реквизиты компании, с которой заключается договор. Кроме того, речь в нем идет не об управлении активами, а только об «образовательных и консультационных услугах об инвестиционных механизмах и способах управления капиталом». Это не похоже на обещанный пассивный доход от слова совсем. Таким образом, зазывалы в пирамиду пытаются уйти от ответственности.
[url=https://kompromatwiki.org/wiki/%D0%A0%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%B0%D0%BD_%D0%92%D0%B8%D0%BA%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%87_%D0%92%D0%B0%D1%81%D0%B8%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BA%D0%BE]пидар[/url]
Чтобы открыть счет и пользоваться им, придется заплатить различные комиссии. Все они прописаны в договоре:
Комиссия за открытие счета: 100 евро или 130 долларов.
Ажио, или входная комиссия: 7% от суммы лицевого счета. На сайте есть пример расчета: при вложении 100 000 $ ажио составит 7000 $.
Комиссия за управление счетом: 1% в год от размера счета, взимается каждый месяц по 1/12.
Комиссия с прибыли: 20% от ежемесячной прибыли, «полученной от инвестиционных продуктов сторонних партнерских компаний или физических лиц, в результате рекомендаций и деятельности Исполнителя».
Итак, LIG состоит из двух основных компаний: Гермес, которая предлагает участникам инвестиционный доход (с идеей полученную прибыль направить на квартиру) и Бест-Вэй, являющаяся ЖНК. Что это такое?
Это Жилищный накопительный кооператив (общепринятое сокращение — ЖНК) — вид потребительского кооператива, сочетающий в себе качества финансового и жилищно-строительного кооператива. ЖНК работают в соответствии с № 215-ФЗ «О жилищных накопительных кооперативах». Целью деятельности жилищных накопительных кооперативов является удовлетворения потребностей членов кооператива в жилых помещениях путём объединения членами кооператива паевых взносов. Жилищный накопительный кооператив имеет право:
– привлекать и использовать денежные средства граждан на приобретение жилых помещений;
– вкладывать имеющиеся у него денежные средства в строительство жилых помещений (в том числе в многоквартирных домах), а также участвовать в строительстве жилых помещений в качестве застройщика или участника долевого строительства;
– приобретать жилые помещения;
– привлекать заёмные денежные средства, общая величина не должна превышать сорок процентов стоимости имущества кооператива.
Членами жилищного накопительного кооператива могут быть только граждане РФ. Жилищный накопительный кооператив создаётся по инициативе не менее чем пятидесяти человек и не более чем пяти тысяч человек. Контроль за деятельностью кооператива по привлечению и использованию денежных средств граждан на приобретение жилых помещений, а также за соблюдением кооперативом требований действующего законодательства Российской Федерации осуществляет Центральный банк Российской Федерации.
Уже отсюда понятно, что заявления заинтересованных лиц из структур LIG о том, что ЦБ не в праве вмешиваться в деятельность собственно LIG лишены оснований. Может и вмешался.
Если говорить о цифрах, то на 13 декабря 2021 года в LIG было свыше 19 000 пайщиков изо всех уголков РФ. LIG выкупил и передал в безвозмездное пользование пайщикам примерно 2 500 объектов недвижимости, из них по 247 пайщики полностью выплатили пай, оформив недвижимость в собственность. Интересная статистика – 19 000 вступили, заплатив членский взнос в 160 000 рублей, но лишь 8 часть из них накопила необходимые 35% для получения недвижимости при том, что фактически недвижимость их собственностью не является. Заявления о том, что получившие недвижимость прописаны в квартирах – это пережитки советского прошлого и, вероятно, сознательное введение остальных в заблуждение. В современной РФ не существует института прописки, есть регистрация, постоянная и временная. Есть найм жилья и есть собственность. Допускаю, что какая-то часть людей все еще проживает в государственных квартирах и не оформила их в собственность, но это – давно не норма, как это было в СССР (где собственность как раз была редким явлением).
По сути кооператив — посредник между покупателем и продавцом жилья, а это увеличивает риски. Приходится полагаться на то, что кооператив соблюдает закон и что он не закроется до того, как вы оформите квартиру на себя.
Даже если все по закону, риск потерять деньги остается. Если кооператив по каким-то причинам перестанет работать, его собственность распродадут. Сначала он рассчитается с кредиторами и только затем вернет деньги пайщикам — пропорционально их паевым взносам. Хватит ли у кооператива денег, чтобы вернуть все паевые взносы, неизвестно.
Разбираю ситуацию вокруг “кооператива” Life is Good
[url=https://vchk-ogpu.com/wiki/item/8367-roman-viktorovich-vasilenko-rossiyskiy-piramidschik]анальный секс можно[/url]
Я решил написать этот пост, чтоб пройтись по доводам тех, кто привлекает новых “пайщиков” в структуры г-на Василенко (на деле – оплачивающих существование пирамиды Life is Good). Понятно, что, в этом сообществе крутятся сотни тех, кто занимается привлечением и теперь ЦБ с прокуратурой их оставят не только без заработка, но, возможно, придется отвечать за свои действия в суде. А деньги уже, наверняка, потрачены. Также есть люди, которые уже живут в квартире от LIG или выплатили некую сумму, они верят до конца и отказываются принимать ситуацию, в которой надо признать, что они могут остаться и без денег, и без квартиры. В любом случае, даже если кто-то живет в квартире от LIG, она ему не принадлежит и, в отличие от банковского залога, урегулировать вопрос не получится (их просто выселят через суд при банкротстве LIG, хотя ситуация скандальная и возможно государство что-то предпримет, чтоб сгладить проблему).Теперь по сути, что такое LIG.
Компания LIG – «Лайф-из-гуд» заявляет два основных направления деятельности: инвестиционные счета «Виста» в компании Hermes Management Ltd. и жилищный кооператив «Бест-вей» — альтернатива ипотеке.
Если верить консультантам «Лайф-из-гуд», доходность счетов «Виста» в компании «Гермес-менеджмент» последние годы держится в районе 20% годовых в долларах. Это довольно много (Уоррен Баффет позавидовал бы такой доходности), при этом непонятно, за счет чего достигается такая доходность.
Деятельность «Гермес-менеджмента» непрозрачна, на сайте не видно полноценных отчетов, нет сведений о структуре компании и ее руководстве.
«Гермес-менеджмент» привлекает российских клиентов через компанию «Лайф-из-гуд», но у него нет лицензии Центрального банка России на брокерскую деятельность или доверительное управление.
«Гермес-менеджмент» зарегистрирован в Белизе, офшорной зоне в Центральной Америке. Там же расположен офис компании. Еще в документах упоминается компания Hermes M в Шотландии. В случае проблем придется разбираться с зарубежной компанией, что делает задачу бесперспективной. Более того, учитывая реалии мошеннических схем, бывшие пайщики столкнутся еще и с лже-юристами, обещающими вернуть им вложенные деньги и конечно, останутся в крайне бедственном положении, с кредитами, без жилья и перспектив (у кого-то могут опуститься руки со всеми вытекающими).
Компания платит за привлечение новых клиентов, открывающих инвестиционные счета «Виста» (по сути – ничем не обеспеченные цифры на сайте. Заведение средств происходит через перевод средств на счета частных лиц(!), выполняющих роль консультантов LIG (а это сразу нарушает законы РФ и привлекает внимание регулятора), вывод – через перепродажу воздуха других буратинам. После внесения LIG в черный список, чаты структуры полны объявлений о продажи токенов Виста, но покупателей почти нет)) и вступающих в жилищный кооператив «Бест-вей». Система комиссионных выглядит такой разветвленной и продуманной, что становится понятно, что именно в ней суть компании, а не в инвестициях или альтернативе ипотеке.
Сам по себе сетевой маркетинг — вполне законный способ привлечения новых клиентов. Но когда он выглядит как основной вид деятельности, а клиентам при этом рассказывают про инвестиции, пассивный доход и успех в жизни, это наводит на очевидные выводы.
Суть предложения «Гермеса» такая: инвесторы открывают счет и перечисляют компании доллары или евро, а взамен получают пассивный доход. Минимальная сумма инвестиционного контракта — 10 тысяч долларов или евро. При этом первый взнос может быть 1130 долларов или 1100 евро, а оставшуюся сумму можно довнести позже.
Чтобы открыть счет «Виста», надо заполнить регистрационную форму на сайте «Лайф-из-гуд». При регистрации сайт просит поставить галочку «Я ознакомился и принимаю условия указанные в публичной оферте» (пунктуация сохранена).
По ссылке открывается не оферта, а договор об оказании услуг. В договоре не указаны название и реквизиты компании, с которой заключается договор. Кроме того, речь в нем идет не об управлении активами, а только об «образовательных и консультационных услугах об инвестиционных механизмах и способах управления капиталом». Это не похоже на обещанный пассивный доход от слова совсем. Таким образом, зазывалы в пирамиду пытаются уйти от ответственности.
[url=https://otzovik.com/review_14367384.html]пидар[/url]
Чтобы открыть счет и пользоваться им, придется заплатить различные комиссии. Все они прописаны в договоре:
Комиссия за открытие счета: 100 евро или 130 долларов.
Ажио, или входная комиссия: 7% от суммы лицевого счета. На сайте есть пример расчета: при вложении 100 000 $ ажио составит 7000 $.
Комиссия за управление счетом: 1% в год от размера счета, взимается каждый месяц по 1/12.
Комиссия с прибыли: 20% от ежемесячной прибыли, «полученной от инвестиционных продуктов сторонних партнерских компаний или физических лиц, в результате рекомендаций и деятельности Исполнителя».
Итак, LIG состоит из двух основных компаний: Гермес, которая предлагает участникам инвестиционный доход (с идеей полученную прибыль направить на квартиру) и Бест-Вэй, являющаяся ЖНК. Что это такое?
Это Жилищный накопительный кооператив (общепринятое сокращение — ЖНК) — вид потребительского кооператива, сочетающий в себе качества финансового и жилищно-строительного кооператива. ЖНК работают в соответствии с № 215-ФЗ «О жилищных накопительных кооперативах». Целью деятельности жилищных накопительных кооперативов является удовлетворения потребностей членов кооператива в жилых помещениях путём объединения членами кооператива паевых взносов. Жилищный накопительный кооператив имеет право:
– привлекать и использовать денежные средства граждан на приобретение жилых помещений;
– вкладывать имеющиеся у него денежные средства в строительство жилых помещений (в том числе в многоквартирных домах), а также участвовать в строительстве жилых помещений в качестве застройщика или участника долевого строительства;
– приобретать жилые помещения;
– привлекать заёмные денежные средства, общая величина не должна превышать сорок процентов стоимости имущества кооператива.
Членами жилищного накопительного кооператива могут быть только граждане РФ. Жилищный накопительный кооператив создаётся по инициативе не менее чем пятидесяти человек и не более чем пяти тысяч человек. Контроль за деятельностью кооператива по привлечению и использованию денежных средств граждан на приобретение жилых помещений, а также за соблюдением кооперативом требований действующего законодательства Российской Федерации осуществляет Центральный банк Российской Федерации.
Уже отсюда понятно, что заявления заинтересованных лиц из структур LIG о том, что ЦБ не в праве вмешиваться в деятельность собственно LIG лишены оснований. Может и вмешался.
Если говорить о цифрах, то на 13 декабря 2021 года в LIG было свыше 19 000 пайщиков изо всех уголков РФ. LIG выкупил и передал в безвозмездное пользование пайщикам примерно 2 500 объектов недвижимости, из них по 247 пайщики полностью выплатили пай, оформив недвижимость в собственность. Интересная статистика – 19 000 вступили, заплатив членский взнос в 160 000 рублей, но лишь 8 часть из них накопила необходимые 35% для получения недвижимости при том, что фактически недвижимость их собственностью не является. Заявления о том, что получившие недвижимость прописаны в квартирах – это пережитки советского прошлого и, вероятно, сознательное введение остальных в заблуждение. В современной РФ не существует института прописки, есть регистрация, постоянная и временная. Есть найм жилья и есть собственность. Допускаю, что какая-то часть людей все еще проживает в государственных квартирах и не оформила их в собственность, но это – давно не норма, как это было в СССР (где собственность как раз была редким явлением).
По сути кооператив — посредник между покупателем и продавцом жилья, а это увеличивает риски. Приходится полагаться на то, что кооператив соблюдает закон и что он не закроется до того, как вы оформите квартиру на себя.
Даже если все по закону, риск потерять деньги остается. Если кооператив по каким-то причинам перестанет работать, его собственность распродадут. Сначала он рассчитается с кредиторами и только затем вернет деньги пайщикам — пропорционально их паевым взносам. Хватит ли у кооператива денег, чтобы вернуть все паевые взносы, неизвестно.
Добрый день!
Ремонт ноутбуков – это услуга, которая пользуется большим спросом среди владельцев техники. Проблемы с ноутбуками могут быть разными: от поломки экрана до неисправности жесткого диска. Путешествие в мир ремонта ноутбуков начинается с выбора подходящего сервисного центра.
Сервисный центр для ремонта ноутбуков предоставляет высокий уровень комфорта и профессионализма. Вам не нужно беспокоиться о том, как починить ноутбук или искать запчасти. Опытные мастера и качественные запчасти гарантируют надежный ремонт.
Сразу скажу, что в компании https://all-remont-noutbuka.ru, присутствуют все эти качества!
Сервисный центр позволяет сэкономить множество времени, которое вы могли бы потратить на самостоятельный ремонт. Мастера знают своё дело и могут быстро и качественно починить ваше устройство.
Ремонт ноутбуков в специализированном сервисном центре – это отличное решение для тех, кто ценит своё время и хочет получить качественное обслуживание.
[url=https://all-remont-noutbuka.ru]срочно починить ноутбук[/url]
сервис ремонта ноутбуков
центр ремонта ноутбуков
ремонт ноутбуков в москве рядом
Удачи!
슬롯 모아 무료
따라서 껍질을 속이 빈 것으로 보지 마십시오. 실제로는 매우 무겁습니다.
I enjoy your writing style genuinely loving this site.
I?¦m not sure the place you are getting your info, but great topic. I must spend some time studying more or understanding more. Thanks for wonderful information I was in search of this information for my mission.
Very interesting topic, regards for putting up.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
şanlıurfa oto kurtarma
[url=https://gadalika.ru/]
Всем здравия, кто посетил мою страничку. Меня зовут Анна Тимофеева. И я хочу поделиться с вами своими способностями. Как и все потомственные целители, я унаследовала свой Дар по крови от пробабушки, известной в России целительницы. Ее звали Анной, в неё честь и я ношу это имя. Корни нашего рода уходят глубоко во времена, когда целительство было обычным явлением. Прабабушка была дочерью священника. С юности она…
[/url]
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Добрый день!
Ремонт ноутбуков – это услуга, которая требуется многим владельцам техники. Независимо от того, столкнулись ли вы с проблемой экрана или нужно заменить жесткий диск, важно знать, куда обратиться за помощью.
Для организации ремонта ноутбука вы можете выбрать один из следующих вариантов:
Сервисный центр: Вы можете обратиться в специализированный сервисный центр, где ваш ноутбук будет ремонтировать опытный мастер.
Мобильный сервис: Некоторые компании предлагают услуги выездного ремонта ноутбуков. Мастер приедет к вам домой или в офис и починит устройство на месте.
Прокат оборудования: Если вы предпочитаете самостоятельный ремонт, можно арендовать необходимое оборудование и запчасти.
Частные мастера: Можно воспользоваться услугами частных мастеров, которые предлагают ремонт ноутбуков на дому.
Одной из лучших компаний, предоставляющих такие услуги, является https://all-remont-noutbuka.ru, проверено и рекомендовано!
Выбор способа ремонта ноутбука зависит от ваших предпочтений и возможностей, но в любом случае важно доверить свое устройство профессионалам.
[url=https://all-remont-noutbuka.ru]ремонт ноутбуков в москве рядом[/url]
ремонт ноутбуков в москве адресамастерская по ремонту ноутбуковотремонтировать ноутбук в москве
Удачи!
KMSpico: What is it?
[url=https://kmspico.ws]kmspico indir[/url]
Operating systems and Office suites are among the primary Microsoft software items that still need to be paid for. Some consumers may find alternate activation methods due to the perceived expensive cost of these items. There may be restrictions, unforeseen interruptions, and persistent activation prompts if these items are installed without being properly activated.
Our KMSpico app was created as a solution to this issue. By using this program, customers may access all of the functionality of Microsoft products and simplify the activation procedure.
KMSPico is a universal activator designed to optimize the process of generating and registering license codes for Windows and Office. Functionally, it is similar to key generators, but with the additional possibility of automatic integration of codes directly into the system. It is worth paying attention to the versatility of the tool, which distinguishes it from similar activators.
The above discussion primarily focused on the core KMS activator, the Pico app. Understanding what the program is, we can briefly mention KMSAuto, a tool with a simpler interface.
By using the KMSPico tool, you can setup Windows&Office for lifetime activation. This is an essential tool for anybody looking to reveal improved features and go beyond limitations. Although it is possible to buy a Windows or Office key.
KMSPico 11 (last update 2024) allows you to activate Windows 11/10/8 (8.1)/7 and Office 2021/2019/2016/2013/2010 for FREE.
[url=https://gadalke.ru/]
Скажу честно, не верила ни одному человеку, сколько гадалок просто меня обманули. В начале говорят одно, после другое. Я просто расходовала деньги безрезультатно. И все обещали помочь. Сначала, мол, посмотрим, я переводила деньги. Какой-то обряд надо, снова перевожу деньги. И еще надо что купить, снова переводила. Я попала в безвыходную ситуацию прежде, чем обратилась к вам, Мария Степановна. И за эту помощь я вам благодарна. До вас у меня не было никаких результатов, все только обобрали и лгали мне. Если кто-то ищет человека, который может, поверьте моему опыту, вы не найдете лучше Марии. Вам спасибо! )
[/url]
KMSpico Download | Official KMS Website New July 2024
[url=https://kmspico.io/]microsoft toolkit скачать[/url]
Are you looking for the best tool to activate your Windows & Office? Then you should download and install KMSpico, as it is one of the best tools everyone should have. In this article, I will tell you everything about this fantastic tool, even though I will also tell you if this is safe to use.
In this case, don’t forget to read this article until the end, so you don’t miss any critical information. This guide is for both beginners and experts as I came up with some of the rumours spreading throughout the internet.
Perhaps before we move towards downloading or installing a section, we must first understand this tool. You should check out the guide below on this tool and how it works; if you already know about it, you can move to another section.
What is KMSPico?
KMPico is a tool that is used to activate or get a license for Microsft Windows as well as for MS Office. It was developed by one of the most famous developers named, Team Daz. However, it is entirely free to use. There is no need to purchase it or spend money downloading it. This works on the principle of Microsft’s feature named Key Management Server, a.k.a KMS (KMSPico named derived from it).
The feature is used for vast companies with many machines in their place. In this way, it is hard to buy a Windows License for each device,, which is why KMS introduced. Now a company has to buy a KMS server for them and use it when they can get a license for all their machines.
However, this tool also works on it, and similarly, it creates a server on your machine and makes it look like a part of that server. One thing different is that this tool only keeps the product activated for 180 days. This is why it keeps running on your machine, renews the license keys after 180 days, and makes it a permanent activation.
KMSAuto Net
Microsoft Toolkit
Windows Loader
Windows 10 Activator
Features
We already know what this tool means, so let’s talk about some of the features you are getting along with KMSPico. Reading this will surely help you understand whether you are downloading the correct file.
Ok, so here are some of the features that KMSPico provides:
Activate Windows & Office
We have already talked about this earlier, as using this tool, you will get the installation key for both Microsoft Products. Whether it is Windows or Office, you can get a license in no time; however, this supports various versions.
Supports Multi-Arch
Since this supports both products, it doesn’t mean you have to download separate versions for each arch. One version is enough, and you can get the license for both x32-bit or even the x64-bit.
It Is Free To Use
Undoubtedly, everything developed by Team Daz costs nothing to us. Similarly, using this tool won’t cost you either, as it is entirely free. Other than this, it doesn’t come with any ads, so using it won’t be any trouble.
Permanent License
Due to the KMS server, this tool installs on our PC, we will get the license key for the rest of our lives. This is because the license automatically renews after a few days. To keep it permanent, you must connect your machine to the internet once 180 days.
Virus Free
Now comes the main feature of this tool that makes it famous among others. KMSPico is 100% pure and clean from such viruses or trojans. The Virus Total scans it before uploading to ensure it doesn’t harm our visitors.
슬롯 머신 무료
“…”보고하러 온 것은 Tang Yin이었습니다. “끝났습니다.”
Excellent goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you are just extremely excellent. I really like what you have acquired here, certainly like what you are saying and the way in which you say it. You make it entertaining and you still take care of to keep it smart. I cant wait to read much more from you. This is actually a wonderful site.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Студия Подкастов в Москве, Запись подкастов в Москве.
http://video-podcast.ru/
프라그마틱 무료
“무슨 말을 그렇게 많이 하느냐!” 홍지황제는 참을성이 없었다.
В чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов 31 августа 2022 года внесены следующие организации, обладающие признаками финансовой пирамиды или признаками мошенничества.
[url=https://rutube.ru/video/98e7f1cec0843c1d18fdb14bf1686d96/]смотреть гей порно[/url]
Etihad Rail (etihadrail-ae.com)
Club Unite To Live, Life Is Good, Unite To Live (uniteto.live). Новый домен пирамиды находящегося в розыске Романа Василенко.
TopBoom, «платформа хедж-фонда, специализирующегося на сделках с обратным исходом спортивного события» (topboom.vip, t.me/TopBoom001)
Change Team, мошенники указывают реквизиты чужого юрлица ООО «АТТИС ГРУПП» (ОРГН 1207700314128, ИНН 9702022065), телеграм-канал «Change Team: Главный Канал» (change-team.ru). Фальшивый обменник раньше назывался C Exchange.
Ещё лохотроны:
Scam! Чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов и отзывы
В чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов включены организации, имеющие признаки финансовой пирамиды по классификации Центрального банка; организации, обладающие признаками матричной пирамиды (массовый привод друзей, «столы»); сборы денег с пенсионеров и прочих незащищённых слоёв населения; хайпы; организации, имеющие негативные отзывы; структуры, оказывающие финансовые услуги без лицензии и прочие лохотроны за исключением псевдоброкеров, кооперативов (с ними тоже не рекомендуем связываться) и некоторых других категорий.
В чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов 31 августа 2022 года внесены следующие организации, обладающие признаками финансовой пирамиды или признаками мошенничества.
[url=https://forum-kpfu.ru/100624/novosti-vasilenko-roman-poslednie-novosti/]порно жесток бесплатно[/url]
Etihad Rail (etihadrail-ae.com)
Club Unite To Live, Life Is Good, Unite To Live (uniteto.live). Новый домен пирамиды находящегося в розыске Романа Василенко.
TopBoom, «платформа хедж-фонда, специализирующегося на сделках с обратным исходом спортивного события» (topboom.vip, t.me/TopBoom001)
Change Team, мошенники указывают реквизиты чужого юрлица ООО «АТТИС ГРУПП» (ОРГН 1207700314128, ИНН 9702022065), телеграм-канал «Change Team: Главный Канал» (change-team.ru). Фальшивый обменник раньше назывался C Exchange.
Ещё лохотроны:
Scam! Чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов и отзывы
В чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов включены организации, имеющие признаки финансовой пирамиды по классификации Центрального банка; организации, обладающие признаками матричной пирамиды (массовый привод друзей, «столы»); сборы денег с пенсионеров и прочих незащищённых слоёв населения; хайпы; организации, имеющие негативные отзывы; структуры, оказывающие финансовые услуги без лицензии и прочие лохотроны за исключением псевдоброкеров, кооперативов (с ними тоже не рекомендуем связываться) и некоторых других категорий.
Thank you for another informative site. The place else could I get that type of info written in such an ideal means? I’ve a mission that I’m simply now working on, and I’ve been at the look out for such information.
https://www.damnmillennial.com/what-app-creates-realistic-nude-images/
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
프라그마틱 정품
Xie Qian은 웃거나 울지 못하며 “폐하가 갑자기 이것을 언급 할 줄은 몰랐습니다 …”라고 말했습니다.
[url=https://albuterolp.com/]buy ventolin online nz[/url]
Эффективные способы расклеивания объявлений, Эффективные стратегии заработка на расклейке объявлений, Подробное руководство по расклейке объявлений, психология расклейки объявлений, Какой цвет лучше использовать при расклейке объявлений, Способы, которые работают в расклейке объявлений
расклейка объявлений [url=https://расклейка-объявлений77.рф/]https://расклейка-объявлений77.рф/[/url] .
This is a very good tips especially to those new to blogosphere, brief and accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
토토 중계 사이트
Hongzhi 황제는이 거대한 물고기의 골격을 복원하여 Jingshan에 전시하도록 명령했습니다.
Как правильно расклеивать объявления, секреты профессиональной расклейки объявлений, Топовые площадки для расклейки объявлений, Тайны эффективной расклейки объявлений, Бизнес на расклейке объявлений, Техники мастеров расклейки объявлений
расклейка объявлений в москве [url=https://расклейка-объявлений77.рф/]https://расклейка-объявлений77.рф/[/url] .
I was very pleased to find this web-site.I needed to thanks to your time for this glorious read!! I undoubtedly enjoying each little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to take a look at new stuff you weblog post.
Nice post. I learn something more challenging on different blogs everyday. It will always be stimulating to read content from other writers and practice a little something from their store. I’d prefer to use some with the content on my blog whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a link on your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
메이저 토토
그들은 Zhu Houcong을 본 다음 Xing Zhu Youcong 왕을 보았지만 마음은 경계했습니다.
Романтикам и любителям казино привет!
Скачал приложение 1win и теперь играю где угодно. Приятные бонусы, быстрая регистрация и моментальный вывод средств. Рабочее зеркало всегда под рукой. 1win – лучший выбор для ставок и казино. Советую! [url=https://www.1winapk.kz/]1win bk com ru[/url]
1win – это качество и надежность. Бонусы для новых игроков, высокие коэффициенты на ставки, быстрый вывод средств. Рабочее зеркало всегда доступно. Играю с удовольствием и советую всем попробовать 1win!
Ловите сайт где все в лучшем виде! – https://www.1winapk.kz/
1вин слоты играть
скачать 1win на телефон
ставки на киберспорт 1win
сколько времени выводятся деньги с 1win
1win витамин
как играть с бонусного счета 1win
скачать 1win на айфон бесплатно с официального
Удачи!
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is attractive, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again as exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike.
Об агентстве недвижимости СЦН
Агентство недвижимости Саровский Центр Недвижимости (СЦН) занимает лидирующие позиции среди профессиональных компаний в городе Саров. Мы оказываем квалифицированную поддержку клиентам, желающим приобрести, реализовать или обменять квартиру, или другие объекты недвижимости, а также осуществить разнообразные сделки в этой сфере. Наше агентство заключает официальные договоры, и оказываем услуги по прейскуранту.
[url=https://сцн.рф]объявления квартир в сарове[/url]
Опытные риэлторы в нашей команде обладают значительным опытом в области недвижимости и помогут вам найти идеальное жилье на вторичном рынке Сарова, а также подобрать вторичку и новостройки по всей России. Мы работаем с крупным всероссийским агентством недвижимости, что позволяет нам оказывать высококачественные услуги на рынке недвижимости как в пределах России, так и за рубежом.
Наше агентство предлагает выгодные условия по страхованию ипотеки, а также специальные скидки при оформлении ипотеки для партнеров банка. Мы установили партнерские отношения с известными крупными страховыми компаниями и банками, что обеспечивает нашим клиентам надежность и прозрачность процесса сделки. Юрист с двадцатилетним стажем, Антон Марсов, обеспечивает правовую защиту интересов наших клиентов на каждом этапе взаимодействия.
Мы также предлагаем услуги по ремонту и отделке квартир, а наш дизайнер интерьеров поможет воплотить в жизнь ваши дизайнерские идеи. Если вы ищете квартиру в Сарове для инвестиций, мы найдем для вас оптимальное решение. Мы также готовы рассмотреть сотрудничество с инвесторами для совместных проектов в сфере недвижимости. Наша профессиональная бригада ремонтников гарантирует высокое качество выполнения работ.
Не стесняйтесь обращаться к нам, если вам необходима помощь в приобретении или реализации недвижимости в Сарове. СЦН – ваш партнер по всем вопросам недвижимости в городе и за его пределами.
купить квартиру в сарове
https://сцн.рф
I am glad to be one of many visitants on this great web site (:, thanks for posting.
ankara seo
certainly like your web-site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling issues and I in finding it very troublesome to inform the reality nevertheless I¦ll surely come back again.
seo hizmeti
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Online work has transformed the modern workplace, providing adaptability and availability that traditional office environments often lack. It allows individuals to work from virtually any place with an internet connection, breaking down geographical barriers and facilitating companies to tap into a global talent pool. This shift has led to a rise in telecommuting and freelance opportunities, permitting workers to juggle their professional and personal lives more successfully. Additionally, online work can produce increased productivity and job satisfaction, as employees have more control over their schedules and work environments. However, it also introduces challenges such as maintaining work-life boundaries, securing effective communication, and managing time efficiently. Overall, [url=https://same23always.com/]online work[/url] is a transformative force, reconfiguring the way we think about employment and productivity in the digital age.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Звон Колокольцева
[url=https://compromat.group/main/investigations/130259-zvon-kolokolceva.html]Гермес[/url]
Поздравляем вас, гражданин министр, соврамши!
Выступая прошлой осенью в Совете Федерации, министр внутренних дел Владимир Колокольцев рассказывал, о так называемом уголовном деле «Лайф-из-Гуд» – «Гермес» – «Бест Вей», обещал миллиарды рублей ущерба и десятки тысяч потерпевших. Пресс-служба МВД под руководством его боевой подруги Ирины Волк заявила о том, что вскрыта деятельность крупнейшей в истории России финансовой пирамиды.
Однако в уголовном деле, расследованном или, вернее сказать, изготовленном ГСУ питерского главка МВД, которое в феврале начал рассматривать Приморский районный суд Санкт-Петербурга, 282 млн рублей ущерба и 221 лицо, признанное следствием потерпевшим: никаких миллиардов и десятков тысяч потерпевших.
Министр и его Волк публично солгали – на основе информации, переданной замначальника ГСУ руководителем следственной группы полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, фактически даже руководившей СГ его заместительницей майором, а затем подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой по материалам, состряпанным опером УЭБиПК питерского главка МВД майором полиции А.Ю. Машевским, при попустительстве (или соучастии?) начальника ГСУ Негрозова и замначальника Следственного департамента федерального министерства Вохмянина. Полковник и подполковник с примерно пятого-шестого уровня иерархии МВД виляет генералом полиции Российской Федерации, постоянным членом Совета безопасности России – это позор для государства.
Так называемые потерпевшие и реально пострадавшие
Большинство «потерпевших» на суде заявляют суммы около 1–2 млн рублей, при этом в ходе судебного следствия выясняется, что они, как правило, получали немалый доход, причем, они еще и налоговые/валютные преступники, так как этот доход не декларировали. Среди «потерпевших» есть граждане, заявляющие смехотворные суммы в 50–70 тыс., то есть количество потерпевших специально накручивалось следствием. И даже с этим накручиванием удалось набрать так мало – учитывая, что у «Гермеса», по данным самого же следствия, более 200 тыс. клиентов в России, а в кооперативе «Бест Вей» – около 20 тыс. пайщиков.
То есть большинство и клиентов «Гермеса», и пайщиков кооператива не считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности этих организаций.
Судя по тысячам обращений во все инстанции, нескольким волнам митингов, прокатившихся по России, они считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности органов внутренних дел.
Ведь именно завербованный питерским УЭБиПК сисадмин российской платежной системы «Гермеса» Набойченко заблокирован и разгромил в феврале 2022 года эту платежную систему, повесив на сайте дисклеймер: «Обращайтесь в правоохранительные органы», что на месяцы прекратило вывод средств. Именно действия правоохранительных органов в отношении компании до и после затруднили вывод средств. Дело в том, что для вывода средств многими использовался механизм p2p, позволяющий не платить комиссию, то есть для вывода средств нужно, чтобы кто-то вносил средства (что, понятно, резко сократилось из-за уголовного дела) и происходил обмен. Однако этот способ не единственный, вывод средств так или иначе осуществляется.
Тысячи пайщиков кооператива тем более не считают себя потерпевшими от его деятельности – потому что именно правоохранительные органы воспрепятствовали приобретению недвижимости с помощью кооператива, а она из-за более чем двухлетнего ареста его счетов, на которых около 4 млрд рублей, не может быть приобретена по прежней цене.
Именно правоохранительные органы прямо запрещают выплаты пайщикам кооператива, решившим забрать свой пай, – даже по исполнительным листам судов. И клиентам «Гермеса», и пайщикам кооператива правоохранительными органами нанесен колоссальный ущерб – и материальный, и моральный, который они намерены взыскать с государства.
«Следователи»-преступники должны сидеть в тюрьме
Весьма скромный результат следствия МВД был достигнут откровенно преступным путем.
1. Некоторые из преступлений следствия были фактически признаны судами. 1 декабря прошлого года Приморский районный суд города Санкт-Петербурга признал незаконным, нарушающим УПК фактический отказ кооперативу в ознакомлении с материалами уголовного дела.При рассмотрении дела в суде выяснилось, что следственная группа ГСУ питерского главка МВД, формально руководимая замначальника ГСУ полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, а фактически – подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой, подделала документы. Автор подделки – Сапетова – еще в феврале была уволена из ГСУ «по собственному желанию».
Уличенная адвокатами кооператива в нарушении УПК, следственная группа составила письмо об удовлетворении ходатайства задним числом и попыталась представить дело так, что кооператив не получил письмо по своей вине. Ложь была выявлена в том числе и с помощью системы электронного документооборота питерского главка МВД.
2. Подделка документов была вынужденным преступлением для сокрытия более серьезного: незаконного содержания под стражей. Следственная группа грубо нарушила права гражданских истцов и ответчиков, потому что без этого нарушения она не успела за 30 суток до истечения предельного срока содержания четверых обвиняемых под стражей начать ознакомление обвиняемых с материалами дела –а это было единственное основание продления им срока содержания под стражей свыше предельного.
Следственная группа из-за спешки даже толком не смогла завершить следственные действия, незаконно вела параллельное расследование по «резервному» делу, но позднее, отбросив стыд, из-за отсутствия материала для составления «нужного» обвинительного заключения, незаконно продолжила расследование «основного» дела, в том числе проводила следственные действия, которые, согласно УПК, невозможны после начала ознакомления обвиняемых с материалами дела. Все эти ухищрения были необходимы для того, чтобы ни в коем случае не выпускать обвиняемых и продолжать держать их в заложниках.
3. Де-факто происходит уголовное наказание неосужденных людей – четверо подсудимых уже второй год сидят в тюрьме. При этом наказываются явно ни в чем неповинные люди – технические сотрудники «Лайф-из-Гуд»: даже если предположить, что действительно работала пирамида – что опровергается показаниями свидетелей самого обвинения, которые сообщают суду, что компания «Гермес» хорошо работала, они были довольны получаемым доходом, и проблемы начались после того, как российская платежная система компании была обрушена завербованным полицией петербургским сисадмином компании Набойченко. Все подсудимые – технические сотрудники компании «Лайф-из-Гуд» и ни к каким управленческим решениям отношения никогда не имели. Их взяли в заложники для того, чтобы они дали показания на руководство компании.
4. Еще одно преступление – заведомо подложное постановление руководителя следственной группы А.Н. Винокурова о привлечении кооператива «Бест Вей» в качестве гражданского ответчика на 16 млрд рублей, тогда как сумма ущерба в уголовном деле –282 млн, и в деле нет ни одного искового заявления – даже на 100 рублей.
5. Следствие стимулировало двух особенно активных так называемых потерпевших написать заявления о моральном ущербе на миллиард (!) рублей каждое – исключительно для ложного обоснования ареста активов кооператива, но понятно, что это ничтожные документы, так как моральный ущерб во всех случаях, не связанных с причинением смерти, присуждается российскими судами в размере не более десятков тысяч рублей.
6. Ни один из «потерпевших» не доказал обоснованность своих претензий в гражданском суде. При этом арестованы активы кооператива почти на 4 млрд рублей и активы частных лиц на такую же сумму. Это не что иное, как попытка захвата активов при участии органов внутренних дел некой заинтересованной группой клиентов «Гермеса» – необязательно из числа «потерпевших», то есть коррупционное преступление, которое упорно игнорирует ГУСБ МВД.
Механизм для такого захвата есть – это передача средств под управление Федерального общественно-государственного фонда по защите прав вкладчиков и акционеров. Понятно, почему не ограничиваются активами подсудимых и обвиняемых: этого недостаточно для удовлетворения аппетитов тех, кто стоит за заказным уголовным делом. И понятно, почему одно юридическое лицо – кооператив «Бест Вей» – незаконно пытаются привлечь к ответственности за другое – компанию «Гермес»: активы «Гермеса» – за рубежом.
7. Следствие, а теперь и прокуратура совершают еще одно преступление: незаконно удерживает средства пайщиков кооператива, отказываясь их вернуть, то есть совершают хищение.
Министр, управляемый мафией
Итак, Колокольцев публично солгал Совету Федерации, выдумав пирамиду, выдумав многомиллиардный ущерб и десятки тысяч пострадавших, он – некомпетентный руководитель, абсолютно ведомый своей камарильей, стремящейся создавать громкие пиар-истории на пустом месте и с коррупционной выгодой для себя. Он вызвал социальный протест десятков тысяч пайщиков кооператива «Бест Вей» и клиентов компании «Гермес» и членов их семей – в большинстве своем представителей социально незащищенных слоев населения, на годы лишенных возможности пользоваться своими деньгами и приобрести недвижимость, на которую они собрали средства, – в том числе десятков участников СВО. Министр вредит в тылу тем, кто защищает страну на фронте.
Глава МВД находится под влиянием или даже контролем давно ставшей притчей во языцех питерской полицейской мафии. Ликвидация этой мафии, как и ликвидация преступной, коррупционной, вредящей социально-политической стабильности системы управления МВД, со стороны Колокольцева является важнейшей государственной задачей.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
you are in reality a excellent webmaster. The website
loading velocity is amazing. It kind of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick.
Furthermore, The contents are masterwork. you’ve done a fantastic job in this subject!
Звон Колокольцева
[url=https://compromat.group/main/investigations/130259-zvon-kolokolceva.html]Гермес[/url]
Поздравляем вас, гражданин министр, соврамши!
Выступая прошлой осенью в Совете Федерации, министр внутренних дел Владимир Колокольцев рассказывал, о так называемом уголовном деле «Лайф-из-Гуд» – «Гермес» – «Бест Вей», обещал миллиарды рублей ущерба и десятки тысяч потерпевших. Пресс-служба МВД под руководством его боевой подруги Ирины Волк заявила о том, что вскрыта деятельность крупнейшей в истории России финансовой пирамиды.
Однако в уголовном деле, расследованном или, вернее сказать, изготовленном ГСУ питерского главка МВД, которое в феврале начал рассматривать Приморский районный суд Санкт-Петербурга, 282 млн рублей ущерба и 221 лицо, признанное следствием потерпевшим: никаких миллиардов и десятков тысяч потерпевших.
Министр и его Волк публично солгали – на основе информации, переданной замначальника ГСУ руководителем следственной группы полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, фактически даже руководившей СГ его заместительницей майором, а затем подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой по материалам, состряпанным опером УЭБиПК питерского главка МВД майором полиции А.Ю. Машевским, при попустительстве (или соучастии?) начальника ГСУ Негрозова и замначальника Следственного департамента федерального министерства Вохмянина. Полковник и подполковник с примерно пятого-шестого уровня иерархии МВД виляет генералом полиции Российской Федерации, постоянным членом Совета безопасности России – это позор для государства.
Так называемые потерпевшие и реально пострадавшие
Большинство «потерпевших» на суде заявляют суммы около 1–2 млн рублей, при этом в ходе судебного следствия выясняется, что они, как правило, получали немалый доход, причем, они еще и налоговые/валютные преступники, так как этот доход не декларировали. Среди «потерпевших» есть граждане, заявляющие смехотворные суммы в 50–70 тыс., то есть количество потерпевших специально накручивалось следствием. И даже с этим накручиванием удалось набрать так мало – учитывая, что у «Гермеса», по данным самого же следствия, более 200 тыс. клиентов в России, а в кооперативе «Бест Вей» – около 20 тыс. пайщиков.
То есть большинство и клиентов «Гермеса», и пайщиков кооператива не считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности этих организаций.
Судя по тысячам обращений во все инстанции, нескольким волнам митингов, прокатившихся по России, они считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности органов внутренних дел.
Ведь именно завербованный питерским УЭБиПК сисадмин российской платежной системы «Гермеса» Набойченко заблокирован и разгромил в феврале 2022 года эту платежную систему, повесив на сайте дисклеймер: «Обращайтесь в правоохранительные органы», что на месяцы прекратило вывод средств. Именно действия правоохранительных органов в отношении компании до и после затруднили вывод средств. Дело в том, что для вывода средств многими использовался механизм p2p, позволяющий не платить комиссию, то есть для вывода средств нужно, чтобы кто-то вносил средства (что, понятно, резко сократилось из-за уголовного дела) и происходил обмен. Однако этот способ не единственный, вывод средств так или иначе осуществляется.
Тысячи пайщиков кооператива тем более не считают себя потерпевшими от его деятельности – потому что именно правоохранительные органы воспрепятствовали приобретению недвижимости с помощью кооператива, а она из-за более чем двухлетнего ареста его счетов, на которых около 4 млрд рублей, не может быть приобретена по прежней цене.
Именно правоохранительные органы прямо запрещают выплаты пайщикам кооператива, решившим забрать свой пай, – даже по исполнительным листам судов. И клиентам «Гермеса», и пайщикам кооператива правоохранительными органами нанесен колоссальный ущерб – и материальный, и моральный, который они намерены взыскать с государства.
«Следователи»-преступники должны сидеть в тюрьме
Весьма скромный результат следствия МВД был достигнут откровенно преступным путем.
1. Некоторые из преступлений следствия были фактически признаны судами. 1 декабря прошлого года Приморский районный суд города Санкт-Петербурга признал незаконным, нарушающим УПК фактический отказ кооперативу в ознакомлении с материалами уголовного дела.При рассмотрении дела в суде выяснилось, что следственная группа ГСУ питерского главка МВД, формально руководимая замначальника ГСУ полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, а фактически – подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой, подделала документы. Автор подделки – Сапетова – еще в феврале была уволена из ГСУ «по собственному желанию».
Уличенная адвокатами кооператива в нарушении УПК, следственная группа составила письмо об удовлетворении ходатайства задним числом и попыталась представить дело так, что кооператив не получил письмо по своей вине. Ложь была выявлена в том числе и с помощью системы электронного документооборота питерского главка МВД.
2. Подделка документов была вынужденным преступлением для сокрытия более серьезного: незаконного содержания под стражей. Следственная группа грубо нарушила права гражданских истцов и ответчиков, потому что без этого нарушения она не успела за 30 суток до истечения предельного срока содержания четверых обвиняемых под стражей начать ознакомление обвиняемых с материалами дела –а это было единственное основание продления им срока содержания под стражей свыше предельного.
Следственная группа из-за спешки даже толком не смогла завершить следственные действия, незаконно вела параллельное расследование по «резервному» делу, но позднее, отбросив стыд, из-за отсутствия материала для составления «нужного» обвинительного заключения, незаконно продолжила расследование «основного» дела, в том числе проводила следственные действия, которые, согласно УПК, невозможны после начала ознакомления обвиняемых с материалами дела. Все эти ухищрения были необходимы для того, чтобы ни в коем случае не выпускать обвиняемых и продолжать держать их в заложниках.
3. Де-факто происходит уголовное наказание неосужденных людей – четверо подсудимых уже второй год сидят в тюрьме. При этом наказываются явно ни в чем неповинные люди – технические сотрудники «Лайф-из-Гуд»: даже если предположить, что действительно работала пирамида – что опровергается показаниями свидетелей самого обвинения, которые сообщают суду, что компания «Гермес» хорошо работала, они были довольны получаемым доходом, и проблемы начались после того, как российская платежная система компании была обрушена завербованным полицией петербургским сисадмином компании Набойченко. Все подсудимые – технические сотрудники компании «Лайф-из-Гуд» и ни к каким управленческим решениям отношения никогда не имели. Их взяли в заложники для того, чтобы они дали показания на руководство компании.
4. Еще одно преступление – заведомо подложное постановление руководителя следственной группы А.Н. Винокурова о привлечении кооператива «Бест Вей» в качестве гражданского ответчика на 16 млрд рублей, тогда как сумма ущерба в уголовном деле –282 млн, и в деле нет ни одного искового заявления – даже на 100 рублей.
5. Следствие стимулировало двух особенно активных так называемых потерпевших написать заявления о моральном ущербе на миллиард (!) рублей каждое – исключительно для ложного обоснования ареста активов кооператива, но понятно, что это ничтожные документы, так как моральный ущерб во всех случаях, не связанных с причинением смерти, присуждается российскими судами в размере не более десятков тысяч рублей.
6. Ни один из «потерпевших» не доказал обоснованность своих претензий в гражданском суде. При этом арестованы активы кооператива почти на 4 млрд рублей и активы частных лиц на такую же сумму. Это не что иное, как попытка захвата активов при участии органов внутренних дел некой заинтересованной группой клиентов «Гермеса» – необязательно из числа «потерпевших», то есть коррупционное преступление, которое упорно игнорирует ГУСБ МВД.
Механизм для такого захвата есть – это передача средств под управление Федерального общественно-государственного фонда по защите прав вкладчиков и акционеров. Понятно, почему не ограничиваются активами подсудимых и обвиняемых: этого недостаточно для удовлетворения аппетитов тех, кто стоит за заказным уголовным делом. И понятно, почему одно юридическое лицо – кооператив «Бест Вей» – незаконно пытаются привлечь к ответственности за другое – компанию «Гермес»: активы «Гермеса» – за рубежом.
7. Следствие, а теперь и прокуратура совершают еще одно преступление: незаконно удерживает средства пайщиков кооператива, отказываясь их вернуть, то есть совершают хищение.
Министр, управляемый мафией
Итак, Колокольцев публично солгал Совету Федерации, выдумав пирамиду, выдумав многомиллиардный ущерб и десятки тысяч пострадавших, он – некомпетентный руководитель, абсолютно ведомый своей камарильей, стремящейся создавать громкие пиар-истории на пустом месте и с коррупционной выгодой для себя. Он вызвал социальный протест десятков тысяч пайщиков кооператива «Бест Вей» и клиентов компании «Гермес» и членов их семей – в большинстве своем представителей социально незащищенных слоев населения, на годы лишенных возможности пользоваться своими деньгами и приобрести недвижимость, на которую они собрали средства, – в том числе десятков участников СВО. Министр вредит в тылу тем, кто защищает страну на фронте.
Глава МВД находится под влиянием или даже контролем давно ставшей притчей во языцех питерской полицейской мафии. Ликвидация этой мафии, как и ликвидация преступной, коррупционной, вредящей социально-политической стабильности системы управления МВД, со стороны Колокольцева является важнейшей государственной задачей.
Dedicated to the brave players!!
MCW Casino represents reliability and convenience. Registration is simple, bonuses are generous, and withdrawals are fast. With the dependable working mirror, playing and winning is a pleasure. I recommend it to all gambling enthusiasts!
Mega Casino World offers superb bonuses for newcomers. Registration was a breeze, with an always-accessible mirror. I relish playing and winning here; withdrawals are swift and seamless. I wholeheartedly recommend it!
Catch the site where everything is in the best shape! – [url=https://cwrmobility.com]MCW Casino[/url]
MCW Casino company
aviator game MCW Casino
MCW Casino download client
MCW Casino mirror for today download
Mega Casino World official site
Good profits!
Мы с гордостью предлагаем великолепную коллекцию качественных игровых слотов в нашей букмекерской конторе 7к казино, чтобы удовлетворить самые изысканные предпочтения игроков – [url=https://consmos.ru/]работающее зеркало сайта 7к казино[/url]
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Казино 7k casino обеспечивает честность и надежность всех игровых процессов – [url=https://depo-krasoty.ru/]р7 казино зеркало[/url]
В казино 7k casino доступны игры с прогрессивными джекпотами – [url=https://pasha-korchemkin.ru/]зеркало страницы r7 casino[/url]
Незаконные действия мошенников онлайн могут повлиять на Игровой аппарат – [url=https://lexithymiapro.ru/]рабочее зеркало 7к казино[/url]
Промокод для бонуса при регистрации доступен – [url=https://alex979.ru/]игровые автоматы 7k casino регистрация[/url]
Бренд казино 7k casino, основанный в 2023 году, немедленно привлек азартных игроков своим качеством и разнообразием услуг, стремясь к вершинам рейтинга – [url=https://sauna-beluga.ru/]рабочий сайт[/url]
На главной странице сайта casino размещена ссылка на Марафонбет, где можно ознакомиться с подробной информацией – [url=https://71pk.ru/]работающее зеркало сайта БК Марафон[/url]
Здравствуйте!
Моя жена давно мечтает о новой кухне, но покупка такой мебели обходится слишком дорого. Мы решили попробовать сделать кухню своими руками, чтобы сэкономить.
Я нашёл пост, в котором описан метод создания мебели своими силами. Автор утверждает, что его метод позволяет существенно сэкономить и избавиться от головной боли. Вот ссылка на этот пост: https://dzen.ru/a/Zo-hWHOX_FmaBP7S
Суть метода в том, чтобы заказать комплектующие для мебели, собрать их самостоятельно и таким образом сэкономить деньги. Однако у меня остаются сомнения: насколько это реально?
Я пересмотрел множество сайтов, где можно заказать распиловку деталей и фасады для кухни. Но сомнения всё ещё остаются. Может быть, кто-то из вас уже делал кухонную мебель своими руками и может оценить описанную методику?
Я уверен, что у меня получится, так как я умею работать руками и владею компьютером. Пожалуйста, помогите мне принять решение: вдохните в меня уверенность или отговорите от этой затеи.
[url=https://dzen.ru/a/Zo-hWHOX_FmaBP7S]уютная кухня своими руками[/url]
проектирование кухни самостоятельно
как сделать кровать своими руками в домашних условиях из дерева
кровать своими руками
Спасибо!
7к казино обеспечивает надежную защиту от незаконных действий и мошенничества в онлайн-сфере, создавая безопасную игровую среду для своих пользователей – [url=https://greenmasteron.ru/]официальный автоматы р7 казино[/url]
В казино 7k casino предлагается широкий выбор игр от ведущих разработчиков игрового софта – [url=https://energywish.ru/]зеркало сайта r7 casino[/url]
Букмекерская контора 7к казино обеспечивает надежную защиту от незаконных действий и мошенников в онлайн-сфере – [url=https://lux-vanna.ru/]7к казино работающее страницы[/url]
Одно из главных преимуществ Mediaget
– его кроссплатформенность.
Программа доступна не только для Windows, но и для других операционных систем.
медиа гет Более
того, веб-интерфейс Mediaget позволяет управлять загрузками с
любого устройства, имеющего доступ к
интернету. Это обеспечивает непревзойденную гибкость и удобство использования.
медиагет скачать бесплатно
скачать mediaget на пк
медиагет скачать
Hello Gamers !
Welcome to Limelight Stream, where endless entertainment awaits you. Explore our diverse array of content, including movies, TV series, documentaries, and exclusive shows available only on Limelight Stream. Our high-definition streaming technology ensures a superior viewing experience, making every moment more enjoyable. Navigate through our platform with ease using our user-friendly interface, designed to help you find your favorite content quickly. Stream anytime, anywhere, on any device, whether it’s your TV, laptop, tablet, or smartphone. Personalized recommendations based on your viewing habits make discovering new shows effortless. Join https://www.limelight-stream.com today and dive into a world of premium content, where the best in entertainment is always just a click away.
Game streaming with 4K resolution
Limelight third-party clients
Limelight graphics quality
Best free game streaming tools
Stream Steam games Limelight
Good luck!
На главной странице сайта казино имеется ссылка на 7к казино, где можно ознакомиться с подробной информацией – [url=https://otdelka80.ru/]рабочее зеркало 7k casino[/url]
Экосистема Mediaget включает в себя не только сам клиент, но и ряд дополнительных сервисов.
Например, мобильное приложение позволяет управлять загрузками на ходу, а облачное хранилище обеспечивает доступ к вашим
файлам из любой точки мира.
скачать mediaget на пк Интеграция с популярными облачными сервисами и медиаплеерами делает Mediaget
универсальным решением для работы с цифровым контентом.
медиагет
медиа джет скачать
медиа гет скачать
Созданный в 2023 году, бренд казино 7k casino мгновенно завоевал популярность среди азартных игроков своим качеством и разнообразием услуг, что может привести его к занятию верхних строчек в рейтинге лучших казино – [url=https://olgalintsova.ru/]7k casino официальный сайт регистрация[/url]
Добрый день!
Моя жена давно мечтает о новой кухне, но покупка такой мебели обходится слишком дорого. Мы решили попробовать сделать кухню своими руками, чтобы сэкономить.
Я нашёл пост, в котором описан метод создания мебели своими силами. Автор утверждает, что его метод позволяет существенно сэкономить и избавиться от головной боли. Вот ссылка на этот пост: https://dzen.ru/a/Zo-hWHOX_FmaBP7S
Суть метода в том, чтобы заказать комплектующие для мебели, собрать их самостоятельно и таким образом сэкономить деньги. Однако у меня остаются сомнения: насколько это реально?
Я пересмотрел множество сайтов, где можно заказать распиловку деталей и фасады для кухни. Но сомнения всё ещё остаются. Может быть, кто-то из вас уже делал кухонную мебель своими руками и может оценить описанную методику?
Я уверен, что у меня получится, так как я умею работать руками и владею компьютером. Пожалуйста, помогите мне принять решение: вдохните в меня уверенность или отговорите от этой затеи.
[url=https://dzen.ru/a/Zo-hWHOX_FmaBP7S]комод своими руками[/url]
шкаф своими руками
как сделать кровать своими руками в домашних условиях из дерева
деревянная кухня своими руками фото
Спасибо!
Вывод средств из Казино Риобет осуществляется без задержек в течение суток – [url=https://bespokemsk.ru/]официальное зеркало сайта Риобет[/url]
Казино Riobet обеспечивает защиту от мошенничества и аферистов – [url=https://premier-veneers.ru/]Riobet бонус за регистрацию[/url]
Казино Riobet проводит регулярные проверки честности и надежности своих игр – [url=https://irav-stars.ru/]Риобет зеркало[/url]
무료 슬롯 게임
해외 정세는 2경 13도보다 한없이 복잡하다.
Tributes flood in for BBC sport commentator whose wife and daughters were killed in suspected crossbow attack
[url=https://alfainvestor.ru/chto-ne-tak-s-investicionnoj-kompaniej-life-is-good/]смотреть гей порно[/url]
Figures from across the United Kingdom have offered their condolences to a BBC sport commentator, after his wife and two daughters were killed by an alleged crossbow attacker, in deaths that again drew attention to the epidemic of violence against women.
Carol Hunt, 61, wife of BBC horse racing commentator, John Hunt, and their daughters, Hannah Hunt, 28, and Louise Hunt, 25, died from injuries sustained in an attack in Bushey, just northwest of London, on Tuesday, according to police and Britain’s public broadcaster.
A 26-year-old suspect wanted in connection with the killings, and named as Kyle Clifford, was found by British police in Enfield, north London, on Wednesday, following a sprawling manhunt. There were no previous reports to the force over Clifford, who is in serious condition in hospital and is yet to speak with officers, Hertfordshire Police said in a statement.
A crossbow was recovered as part of the investigation, which police believe was used in a “targeted incident.”
Epidemic of violence against women
The killings of the three women rocked Britain, where mass murders are infrequent but violence against women and girls has been officially labeled as a national threat.
A woman is killed by a man every three days in the UK and one in four women will experience domestic violence in her lifetime, the United Nations’ special rapporteur on violence against women and girls, Reem Alsalem, said earlier this year.
Charities and human rights organizations have subsequently reiterated urgent demands to tackle femicide in the UK.
Воины-пайщики оказались без защиты в тылу
Пайщики «Бест Вей» — участники СВО готовы защищать свой кооператив
[url=https://svpressa.ru/society/article/421904]Андрей Белоусов[/url]
Многие пайщики кооператива «Бест Вей» и те, в чьих интересах приобретаются квартиры в кооперативе, — участники СВО. И они сами, и их родственники возмущены событиями, происходящими вокруг кооператива. Ведь защищая интересы страны на фронте, в тылу они не защищены от того, что не могут приобрести недвижимость из-за того, что счета кооператива с почти 4 млрд рублей уже более двух лет находятся под арестом — притом, что сумма ущерба по уголовному делу, рассматриваемому Приморским районным судом Санкт-Петербурга, согласно обвинительному заключению, составляет 282 млн рублей.
«Надеемся, новое руководство Министерства обороны поможет урегулировать ситуацию»
Наталья Пригаро, мать пайщика кооператива — участника СВО из Нефтеюганска Даниила Пригаро:
— Сын расплатился за однокомнатную квартиру, приобретенную с помощью кооператива, еще два года назад, подал пакет документов на оформление квартиры в собственность в Росреестр в начале сентября 2022 года — и все это время не может зарегистрировать собственность на нее из-за того, что в Росреестре она значится как арестованная. В конце сентября 2022 года он был мобилизован. Сын брал кредит, чтобы расплатиться за квартиру с кооперативом. Планировал продать эту квартиру и взять квартиру побольше в ипотеку. Однако неоднократно накладывался арест на недвижимость кооператива, несмотря на то что сейчас ареста нет — последний арест, накладывавшийся осенью 2023 года, 19 февраля истек, ходатайства о новом аресте дважды отклонены судом, по Росреестру арест с квартиры до сих пор не снят. В результате кредит приходится платить, квартира в собственность до сих пор не оформлена.
У сына нет никакой физической и финансовой возможности выяснять отношения с Росреестром — в административном или судебном порядке, он приезжает в отпуска на неделю-полторы, ему не до сутяжничества. Я нахожусь в Анапе, приобрела квартиру с помощью кооператива — сын не имеет возможности сделать на меня генеральную доверенность, а я не могу из Анапы приехать в Нефтеюганск и решать вопросы в Росреестре — кроме поезда, сейчас, сами понимаете, ничего не ходит (конец цитаты).
«На безобразие, которое происходит с кооперативом, мы пишем жалобы во все инстанции, — говорит она. — Надеемся, новое руководство Министерства обороны поможет урегулировать ситуацию».
«Надежда, что все разрешится, остается — не может же все быть коррумпировано»
Елена Бойко — пайщик кооператива из Новосибирска и мать солдата, воющего в СВО, для которого она собиралась приобрести одну из двух квартир в кооперативе. «Я стала пайщиком кооператива в 2021 году. В январе 2021 года подала заявление на покупку двух квартир с помощью кооператива по накопительной программе. У меня двое детей — сын и дочь, им нужно жилье. В 2020 году взяли в ипотеку загородный дом — причем оформили на сына как единственного, кому ее могли одобрить, а в 2021 году он ушел в армию как призывник, а потом подписал контракт. Его относительно недавно отправили „за ленточку“. Думали, что поживем в ипотечном доме, и тут как раз подойдет очередь приобретать квартиры с помощью кооператива. Мы останемся жить в частном доме, а дети въедут в кооперативные квартиры».
«Ипотека — это разорительно, — подчеркивает Елена, — мы взяли 2,5 млн, а за 30 лет отдадим 6 млн. Когда появился кооператив, для нас это была возможность предоставить каждому из детей жилье: за 10 лет или раньше они расплатятся с кооперативом, причем с минимальной по сравнению ипотекой переплатой, и у них будет собственное жилье. Из-за репрессий в отношении кооператива мы можем быть этой возможности лишены».
«Я всем сердцем переживаю за ситуацию с кооперативом, заявление о выходе из кооператива пока не пишу — надеюсь, что его деятельность „разморозится“, — говорит Елена. — Обращаемся во все инстанции, в прокуратуру — приходят отписки. Смысл происходящего я понимаю хорошо — когда-то занималась кредитным потребительским кооперативом: нас тогда закрыл Центральный банк. Нашел формальный повод. Но настоящая причина была в том, что мы мешали банкам обирать клиентов. Но надежда на то, что все разрешится, остается — не может же быть все коррумпировано».
«Больше всего в нашей ситуации возмущает то, что наши воины стоят на стороне государства на фронте, а здесь, в тылу, их интересы нарушаются государственными структурами. Такого быть не должно!»
«Для многих кооператив — единственная возможность приобрести квартиру»
Лариса Зискинд — пайщица «Бест Вей», переехавшая с помощью кооператива с семьей — с дочерью, зятем и маленьким внуком - с Дальнего Востока в Белгородскую область. Ее зять, живущий в кооперативной квартире, находится на фронте СВО. «С помощью кооператива я приобрела квартиру в двухэтажном доме в селе Пушкарное Белгородской области — мы с дочерью переехали сюда. Мы уже два года расплачиваемся за него с кооперативом. Не до конца сделали ремонт, кухни фактически нет: моем посуду в ванной. Финансовых средств не хватает, так как зять уже год на СВО, пока ни разу не был в отпуске, и перевести деньги с его карты в ВТБ сейчас непросто, потому что карта — в расположении, до ближайшего банка ехать далеко, а он сам — на линии фронта. Мы фактически живем с выплат на ребенка, на мне кредиты — у меня полпенсии уходит на их оплату. Квартира по Росреестру находится под арестом, хотя арест по квартирам кооператива арест истек — а я боюсь ехать в Белгород, чтобы решать по ней вопрос. Я с ребенком на улицу гулять не выхожу в нынешней военной обстановке — сирены воздушной тревоги постоянные. Побыстрее бы наши войска создали санитарную зону в Харьковской области!»
По поводу покупки квартиры Лариса сообщает, что «ипотека точно никак не светила. Кооператив — это 14 тыс. в месяц и всего лишь 10 лет. В кооперативе даже студентка может приобрести квартиру, почти не переплачивая. При покупке через банк придется заплатить еще как минимум за одну квартиру».
«Среди пайщиков кооператива очень много пенсионеров, социально незащищенных людей, это была их единственная возможность приобрести квартиру, — говорит Лариса. — Из-за репрессий против кооператива мы можем лишиться единственного жилья. Мы куда только не писали в защиту кооператива. Но, видимо, слишком большой куш. Кооперативу не дают даже платить налоги. Надеемся, что отношение к кооперативу в результате справедливого разбирательства изменится в лучшую сторону».
«Мы очень устали. Но боремся»
Людмила Гарина — пайщица кооператива из Саратова, зять которой, проживающий вместе с ней в кооперативной квартире, участвует в СВО. «Я проживаю в кооперативной квартире почти три года вместе с дочерью и внуком, вносим ежемесячные платежи через госуслуги».
«Возможности взять ипотеку не было, — говорит Людмила. — Фактически у нас один работающий человек — дочь, зять мобилизован, внук — студент, внучке — четыре года. Мы с мужем пенсионеры».
«У нас с кооперативом проблем не было никаких, — говорит она, — но сейчас уверенности в завтрашнем дне нет. Пишем во все возможные инстанции, в том числе в Администрацию президента, ходили на прием к Володину. Пока ничего не помогает. Вся надежда на то, что суд разберется».
«Хотелось, чтобы вопрос о возобновлении работы кооператива быстрее решился, — говорит она, — тогда стало бы проще. Когда кооператив заработает, будет совершенно иная ситуация. Мы очень устали. Но боремся».
«20 тыс. пайщиков кооператива не так просто остановить»
Алла Яровая — пайщик кооператива из Пятигорска и представитель пайщицы Людмилы Дворцовой, сын которой, Игорь Дворцов, находился на СВО, а теперь служит внутри страны. «Людмила приобрела с помощью кооператива в Пятигорске квартиру для своего сына. Вступила в кооператив она в 2017 году, сначала находилась в накопительной программе — накапливала на первоначальный паевый взнос, накопила, потом стояла в очереди на приобретение жилье, приобрела с помощью кооператива однокомнатную квартиру за 1450 тыс. рублей. Потом приобрела квартиру и постепенно полностью за нее расплатилась. Работала для этого на двух работах, в том числе санитаркой в инфекционном отделении».
Но оформить квартиру в собственность не удалось, так как она оказалась под арестом, поясняет Алла. И хотя арест 19 февраля истек и больше не накладывался, суд первой инстанции в Пятигорске этот арест подтвердил. «По вопросу получения права собственности и снятия ареста мы обратились в Пятигорский городской суд, где судья очень предвзято отнесся к решению вопроса и мы получили отказ, — говорит Алла, — Хотя аналогичный вопрос рассматривался в Минераловодском суде и там судья вынесла положительное решение и в настоящий момент пайщик получил право собственности на свою квартиру. Предстоит рассмотрение в апелляционной инстанции — несмотря на то, что рассматривать нечего: ареста на недвижимость кооператива сейчас нет. А на квартиру Людмилы Дворцовой — почему-то есть».
«Кооператив — единственная возможность для людей со средним достатком получить жилье, — говорит Алла, — Нерешенный вопрос — налоги. Мы вынуждены платить налоги с юридических лиц, но мы же физические лица. К депутатам — с нас берут налог как с юрлица. Почему мы должны оплачивать — мы же физлица? Во многих регионах это сделано. Надеемся добиться того, чтобы это было сделано по всей стране».
«20 тыс. пайщиков кооператива не так просто остановить, — подчеркивает пайщица. — Это наши деньги, и мы за них боремся. Обязательно отстоим наш кооператив!»
«Активно участвую в защите кооператива»
У пайщицы кооператива, жительницы из Ленинградской области Татьяны Власенко старший сын находится на СВО с сентября 2022 года. «Три месяца проходил обучение, а потом оказался „за ленточкой“, — говорит Татьяна. — Мы должны были в конце лета 2022 года купить квартиру с помощью кооператива — квартиру планировали большую. Но работа кооператива оказалась заблокирована, и кооператив не может ничего купить уже более двух лет, так как и его счета, и его деятельность заблокированы. Деньги пайщиков, собранные для приобретения квартир, при этом обесцениваются».
«Я активно участвую в защите нашего кооператива, — говорит Татьяна. — Езжу на все суды в Санкт-Петербурге, хотя живу в деревне — ехать два с половиной, а то и три часа, мне 64 года, а путь неблизкий. И сын в этом поддерживает меня».
«Вот уже более двух лет работа кооператива заблокирована, деньги обесцениваются»
У пайщицы из Хабаровска Натальи Ромашко на СВО было два племянника — один, к сожалению, погиб. Планировалась покупка большой квартиры в Хабаровске, Наталья состояла в накопительной программе. «Вот уже более двух лет работа кооператива заблокирована, деньги обесцениваются, — говорит Наталья. — Я участвую в защите кооператива, пишу письма в прокуратуру, в высшие государственные инстанции, потому что нарушаются наши права, нас лишают возможности приобрести квартиру вне ипотечной системы. Пока приходят одни отписки, но борьбу мы продолжаем!»
«Ситуация — как на СВО»
Пайщица Светлана Иванова из Новосибирска, волонтер СВО, планировала приобрести с помощью кооператива две квартиры — для себя и для сына, который воюет на СВО добровольцем. «До этого я продала квартиру и сейчас вообще без собственного жилья, — говорит она. — Вступила в кооператив по накопительной программе, рассматривали для приобретения квартиры Крым и Новосибирск. В СВО участвую как волонтер — не остаюсь в стороне, когда Родине нужна помощь».
«От ситуации с кооперативом очень многие люди пострадали, — говорит Светлана. — Ситуация — как на СВО. И еще больше пострадают, если реализуется плохой сценарий. Хочется надеяться на то, что все образуется, правда восторжествует. Заявление о выходе из кооператива и возврате паевых средств я не подавала. Готова продолжить участие в нем, готова приобрести недвижимость с его помощью: это самый лучший вариант покупки квартиры».
«Сдаваться в планах нет»
Пайщица Марина Янковская родом из Хабаровска, она переехала в Новороссийск, ее супруг погиб на СВО. «У нас уже подходила очередь на покупку квартиры в Новороссийске для нашей семьи, мы должны были подбирать объект, — рассказывает она. — Но два года назад все остановилось. Хотели приобрести двухкомнатную квартиру в Новороссийске. Деньги лежат на арестованных счетах кооператива — а недвижимость за это время подорожала. Надеемся хоть что-то приобрести после того, как счета разблокируют».
«Мы всячески поддерживаем кооператив, — говорит Марина. — Записывали видео, что мы не обманутые, а вполне довольные пайщики, объясняли, что это никакая не пирамида, а организация, созданная в помощь людям. Ждем, когда снимут эти аресты. Сдаваться в планах нет».
Воины-пайщики оказались без защиты в тылу
Пайщики «Бест Вей» — участники СВО готовы защищать свой кооператив
[url=https://svpressa.ru/society/article/421904]ЖК Бествей[/url]
Многие пайщики кооператива «Бест Вей» и те, в чьих интересах приобретаются квартиры в кооперативе, — участники СВО. И они сами, и их родственники возмущены событиями, происходящими вокруг кооператива. Ведь защищая интересы страны на фронте, в тылу они не защищены от того, что не могут приобрести недвижимость из-за того, что счета кооператива с почти 4 млрд рублей уже более двух лет находятся под арестом — притом, что сумма ущерба по уголовному делу, рассматриваемому Приморским районным судом Санкт-Петербурга, согласно обвинительному заключению, составляет 282 млн рублей.
«Надеемся, новое руководство Министерства обороны поможет урегулировать ситуацию»
Наталья Пригаро, мать пайщика кооператива — участника СВО из Нефтеюганска Даниила Пригаро:
— Сын расплатился за однокомнатную квартиру, приобретенную с помощью кооператива, еще два года назад, подал пакет документов на оформление квартиры в собственность в Росреестр в начале сентября 2022 года — и все это время не может зарегистрировать собственность на нее из-за того, что в Росреестре она значится как арестованная. В конце сентября 2022 года он был мобилизован. Сын брал кредит, чтобы расплатиться за квартиру с кооперативом. Планировал продать эту квартиру и взять квартиру побольше в ипотеку. Однако неоднократно накладывался арест на недвижимость кооператива, несмотря на то что сейчас ареста нет — последний арест, накладывавшийся осенью 2023 года, 19 февраля истек, ходатайства о новом аресте дважды отклонены судом, по Росреестру арест с квартиры до сих пор не снят. В результате кредит приходится платить, квартира в собственность до сих пор не оформлена.
У сына нет никакой физической и финансовой возможности выяснять отношения с Росреестром — в административном или судебном порядке, он приезжает в отпуска на неделю-полторы, ему не до сутяжничества. Я нахожусь в Анапе, приобрела квартиру с помощью кооператива — сын не имеет возможности сделать на меня генеральную доверенность, а я не могу из Анапы приехать в Нефтеюганск и решать вопросы в Росреестре — кроме поезда, сейчас, сами понимаете, ничего не ходит (конец цитаты).
«На безобразие, которое происходит с кооперативом, мы пишем жалобы во все инстанции, — говорит она. — Надеемся, новое руководство Министерства обороны поможет урегулировать ситуацию».
«Надежда, что все разрешится, остается — не может же все быть коррумпировано»
Елена Бойко — пайщик кооператива из Новосибирска и мать солдата, воющего в СВО, для которого она собиралась приобрести одну из двух квартир в кооперативе. «Я стала пайщиком кооператива в 2021 году. В январе 2021 года подала заявление на покупку двух квартир с помощью кооператива по накопительной программе. У меня двое детей — сын и дочь, им нужно жилье. В 2020 году взяли в ипотеку загородный дом — причем оформили на сына как единственного, кому ее могли одобрить, а в 2021 году он ушел в армию как призывник, а потом подписал контракт. Его относительно недавно отправили „за ленточку“. Думали, что поживем в ипотечном доме, и тут как раз подойдет очередь приобретать квартиры с помощью кооператива. Мы останемся жить в частном доме, а дети въедут в кооперативные квартиры».
«Ипотека — это разорительно, — подчеркивает Елена, — мы взяли 2,5 млн, а за 30 лет отдадим 6 млн. Когда появился кооператив, для нас это была возможность предоставить каждому из детей жилье: за 10 лет или раньше они расплатятся с кооперативом, причем с минимальной по сравнению ипотекой переплатой, и у них будет собственное жилье. Из-за репрессий в отношении кооператива мы можем быть этой возможности лишены».
«Я всем сердцем переживаю за ситуацию с кооперативом, заявление о выходе из кооператива пока не пишу — надеюсь, что его деятельность „разморозится“, — говорит Елена. — Обращаемся во все инстанции, в прокуратуру — приходят отписки. Смысл происходящего я понимаю хорошо — когда-то занималась кредитным потребительским кооперативом: нас тогда закрыл Центральный банк. Нашел формальный повод. Но настоящая причина была в том, что мы мешали банкам обирать клиентов. Но надежда на то, что все разрешится, остается — не может же быть все коррумпировано».
«Больше всего в нашей ситуации возмущает то, что наши воины стоят на стороне государства на фронте, а здесь, в тылу, их интересы нарушаются государственными структурами. Такого быть не должно!»
«Для многих кооператив — единственная возможность приобрести квартиру»
Лариса Зискинд — пайщица «Бест Вей», переехавшая с помощью кооператива с семьей — с дочерью, зятем и маленьким внуком - с Дальнего Востока в Белгородскую область. Ее зять, живущий в кооперативной квартире, находится на фронте СВО. «С помощью кооператива я приобрела квартиру в двухэтажном доме в селе Пушкарное Белгородской области — мы с дочерью переехали сюда. Мы уже два года расплачиваемся за него с кооперативом. Не до конца сделали ремонт, кухни фактически нет: моем посуду в ванной. Финансовых средств не хватает, так как зять уже год на СВО, пока ни разу не был в отпуске, и перевести деньги с его карты в ВТБ сейчас непросто, потому что карта — в расположении, до ближайшего банка ехать далеко, а он сам — на линии фронта. Мы фактически живем с выплат на ребенка, на мне кредиты — у меня полпенсии уходит на их оплату. Квартира по Росреестру находится под арестом, хотя арест по квартирам кооператива арест истек — а я боюсь ехать в Белгород, чтобы решать по ней вопрос. Я с ребенком на улицу гулять не выхожу в нынешней военной обстановке — сирены воздушной тревоги постоянные. Побыстрее бы наши войска создали санитарную зону в Харьковской области!»
По поводу покупки квартиры Лариса сообщает, что «ипотека точно никак не светила. Кооператив — это 14 тыс. в месяц и всего лишь 10 лет. В кооперативе даже студентка может приобрести квартиру, почти не переплачивая. При покупке через банк придется заплатить еще как минимум за одну квартиру».
«Среди пайщиков кооператива очень много пенсионеров, социально незащищенных людей, это была их единственная возможность приобрести квартиру, — говорит Лариса. — Из-за репрессий против кооператива мы можем лишиться единственного жилья. Мы куда только не писали в защиту кооператива. Но, видимо, слишком большой куш. Кооперативу не дают даже платить налоги. Надеемся, что отношение к кооперативу в результате справедливого разбирательства изменится в лучшую сторону».
«Мы очень устали. Но боремся»
Людмила Гарина — пайщица кооператива из Саратова, зять которой, проживающий вместе с ней в кооперативной квартире, участвует в СВО. «Я проживаю в кооперативной квартире почти три года вместе с дочерью и внуком, вносим ежемесячные платежи через госуслуги».
«Возможности взять ипотеку не было, — говорит Людмила. — Фактически у нас один работающий человек — дочь, зять мобилизован, внук — студент, внучке — четыре года. Мы с мужем пенсионеры».
«У нас с кооперативом проблем не было никаких, — говорит она, — но сейчас уверенности в завтрашнем дне нет. Пишем во все возможные инстанции, в том числе в Администрацию президента, ходили на прием к Володину. Пока ничего не помогает. Вся надежда на то, что суд разберется».
«Хотелось, чтобы вопрос о возобновлении работы кооператива быстрее решился, — говорит она, — тогда стало бы проще. Когда кооператив заработает, будет совершенно иная ситуация. Мы очень устали. Но боремся».
«20 тыс. пайщиков кооператива не так просто остановить»
Алла Яровая — пайщик кооператива из Пятигорска и представитель пайщицы Людмилы Дворцовой, сын которой, Игорь Дворцов, находился на СВО, а теперь служит внутри страны. «Людмила приобрела с помощью кооператива в Пятигорске квартиру для своего сына. Вступила в кооператив она в 2017 году, сначала находилась в накопительной программе — накапливала на первоначальный паевый взнос, накопила, потом стояла в очереди на приобретение жилье, приобрела с помощью кооператива однокомнатную квартиру за 1450 тыс. рублей. Потом приобрела квартиру и постепенно полностью за нее расплатилась. Работала для этого на двух работах, в том числе санитаркой в инфекционном отделении».
Но оформить квартиру в собственность не удалось, так как она оказалась под арестом, поясняет Алла. И хотя арест 19 февраля истек и больше не накладывался, суд первой инстанции в Пятигорске этот арест подтвердил. «По вопросу получения права собственности и снятия ареста мы обратились в Пятигорский городской суд, где судья очень предвзято отнесся к решению вопроса и мы получили отказ, — говорит Алла, — Хотя аналогичный вопрос рассматривался в Минераловодском суде и там судья вынесла положительное решение и в настоящий момент пайщик получил право собственности на свою квартиру. Предстоит рассмотрение в апелляционной инстанции — несмотря на то, что рассматривать нечего: ареста на недвижимость кооператива сейчас нет. А на квартиру Людмилы Дворцовой — почему-то есть».
«Кооператив — единственная возможность для людей со средним достатком получить жилье, — говорит Алла, — Нерешенный вопрос — налоги. Мы вынуждены платить налоги с юридических лиц, но мы же физические лица. К депутатам — с нас берут налог как с юрлица. Почему мы должны оплачивать — мы же физлица? Во многих регионах это сделано. Надеемся добиться того, чтобы это было сделано по всей стране».
«20 тыс. пайщиков кооператива не так просто остановить, — подчеркивает пайщица. — Это наши деньги, и мы за них боремся. Обязательно отстоим наш кооператив!»
«Активно участвую в защите кооператива»
У пайщицы кооператива, жительницы из Ленинградской области Татьяны Власенко старший сын находится на СВО с сентября 2022 года. «Три месяца проходил обучение, а потом оказался „за ленточкой“, — говорит Татьяна. — Мы должны были в конце лета 2022 года купить квартиру с помощью кооператива — квартиру планировали большую. Но работа кооператива оказалась заблокирована, и кооператив не может ничего купить уже более двух лет, так как и его счета, и его деятельность заблокированы. Деньги пайщиков, собранные для приобретения квартир, при этом обесцениваются».
«Я активно участвую в защите нашего кооператива, — говорит Татьяна. — Езжу на все суды в Санкт-Петербурге, хотя живу в деревне — ехать два с половиной, а то и три часа, мне 64 года, а путь неблизкий. И сын в этом поддерживает меня».
«Вот уже более двух лет работа кооператива заблокирована, деньги обесцениваются»
У пайщицы из Хабаровска Натальи Ромашко на СВО было два племянника — один, к сожалению, погиб. Планировалась покупка большой квартиры в Хабаровске, Наталья состояла в накопительной программе. «Вот уже более двух лет работа кооператива заблокирована, деньги обесцениваются, — говорит Наталья. — Я участвую в защите кооператива, пишу письма в прокуратуру, в высшие государственные инстанции, потому что нарушаются наши права, нас лишают возможности приобрести квартиру вне ипотечной системы. Пока приходят одни отписки, но борьбу мы продолжаем!»
«Ситуация — как на СВО»
Пайщица Светлана Иванова из Новосибирска, волонтер СВО, планировала приобрести с помощью кооператива две квартиры — для себя и для сына, который воюет на СВО добровольцем. «До этого я продала квартиру и сейчас вообще без собственного жилья, — говорит она. — Вступила в кооператив по накопительной программе, рассматривали для приобретения квартиры Крым и Новосибирск. В СВО участвую как волонтер — не остаюсь в стороне, когда Родине нужна помощь».
«От ситуации с кооперативом очень многие люди пострадали, — говорит Светлана. — Ситуация — как на СВО. И еще больше пострадают, если реализуется плохой сценарий. Хочется надеяться на то, что все образуется, правда восторжествует. Заявление о выходе из кооператива и возврате паевых средств я не подавала. Готова продолжить участие в нем, готова приобрести недвижимость с его помощью: это самый лучший вариант покупки квартиры».
«Сдаваться в планах нет»
Пайщица Марина Янковская родом из Хабаровска, она переехала в Новороссийск, ее супруг погиб на СВО. «У нас уже подходила очередь на покупку квартиры в Новороссийске для нашей семьи, мы должны были подбирать объект, — рассказывает она. — Но два года назад все остановилось. Хотели приобрести двухкомнатную квартиру в Новороссийске. Деньги лежат на арестованных счетах кооператива — а недвижимость за это время подорожала. Надеемся хоть что-то приобрести после того, как счета разблокируют».
«Мы всячески поддерживаем кооператив, — говорит Марина. — Записывали видео, что мы не обманутые, а вполне довольные пайщики, объясняли, что это никакая не пирамида, а организация, созданная в помощь людям. Ждем, когда снимут эти аресты. Сдаваться в планах нет».
WELCOME TO PUGACHEV LUXURY CAR RENTALS EXCLUSIVE MOTORING LUXURY & EXOTIC RENTALS
Dive into the ultimate driving experience with Pugachev Luxury Car Rentals, your premier destination for luxury and exotic car rentals in Los Angeles. Whether you’re looking to impress at a corporate event, add a splash of glamour to your weekend, or simply enjoy the thrill of driving some of the world’s most sought-after vehicles, we’ve got you covered.
https://pugachev.la/
Our extensive fleet includes the pinnacle of automotive excellence from renowned brands such as Lamborghini, Rolls-Royce, Bentley, Ferrari, McLaren, and more. Indulge in the elegance of a Rolls-Royce Ghost, starting at $1,150 per day, or experience the exhilarating performance of a Lamborghini Huracan EVO, available from $875 per day. With options ranging from the powerful Ferrari GTB Red at $1,100 per day to the opulent Bentley Continental GT at $950 per day, our collection is meticulously curated to cater to the most discerning tastes and preferences.
Navigating the vibrant streets of Los Angeles or cruising along the scenic coastlines has never been more accessible or more stylish. At Pugachev Luxury Car Rentals, we make it easy and efficient for you to rent the luxury car of your dreams with straightforward daily and weekly rental options—like the versatile Mercedes-Benz AMG G63, which can be yours for $790 daily or $4,424 weekly.
Embrace the luxury, power, and finesse of our elite vehicles and elevate your next Los Angeles visit into a truly memorable journey. Whether you’re seeking an exotic sports car for that extra special thrill, a luxury sedan for sophisticated travel, or a sumptuous SUV for family comfort and safety, our fleet promises the perfect match for every occasion and desire.
OUR COLLECTION OF LUXURY CARS FOR DISCERNING DRIVERS
Elegant Sedans for Business Executives
At Pugachev Luxury Car Rentals, we understand the importance of a strong first impression. Our fleet of luxury sedans is designed to cater to business executives who demand sophistication and functionality. Each vehicle, such as the Rolls-Royce Ghost Anthracite, available at $1,100 per day, offers a sublime mix of comfort and prestige, ensuring you arrive at your business engagements in unparalleled style. For a slightly different but equally impressive experience, consider the Bentley Flying Spur at $1,000 daily, which combines classic elegance with cutting-edge technology.
exotic car rental los angeles
[url=https://pugachev.la/lamborghini-rental/]lamborghini rental in los angeles[/url]
Sumptuous SUVs for Family and Leisure
Our selection of high-end SUVs blends luxury with practicality, making them perfect for family trips or stylish outings with friends. The Bentley Bentayga, starting from $700 per day, offers spaciousness and state-of-the-art amenities that ensure comfort without compromise. For those seeking a bolder statement, the Rolls-Royce Cullinan Black Badge provides an imposing presence and unrivaled luxury for $1,300 daily, ensuring every journey is an event in itself.
Prestige Convertibles for Scenic Drives
Los Angeles is renowned for its beautiful landscapes and stunning coastlines, best enjoyed in one of our prestige convertibles. Feel the exhilarating freedom of the open road in a Ferrari Portofino Spyder, available for $850 daily. Its breathtaking performance and sleek design are perfect for scenic drives along the Pacific Coast Highway. Alternatively, the BMW M4 Competition Cabrio, at $390 per day, offers a more accessible but equally thrilling option for cruising under the Californian sun.
Our fleet at Pugachev Luxury Car Rentals is meticulously maintained and regularly updated to ensure that each car looks and performs like new. This commitment to quality and excellence reflects our dedication to providing only the best for our clients, who return time and again for the reliability and prestige our services offer. Each model in our fleet is more than just a vehicle; it’s a part of an exclusive lifestyle made accessible to our discerning clientele. Whether you are looking to impress at a corporate event or simply indulge in the pleasure of driving a luxury car, our collection is guaranteed to enhance your experience in Los Angeles.
luxury car rental los angeles
[url=https://pugachev.la/lamborghini-rental/]rent a lamborghini in los angeles[/url]
Для доступа к играм казино 7k casino на сегодняшний день можно использовать рабочее зеркало – [url=https://raminamir.ru/]7k casino работающее зеркало страницы[/url]
На текущий день актуальное рабочее зеркало официального сайта 7к казино доступно для использования – [url=https://supolovan.ru/]7k casino работающее зеркало[/url]
Казино 7k casino имеет все необходимые лицензии и регулируется соответствующими органами – [url=https://aismmacademy.ru/]r7 casino регистрация[/url]
Игроки могут соревноваться с другими игроками в рейтинговых турнирах – [url=https://osdata.ru/]р7 казино официальный играть[/url]
This really answered my problem, thank you!
I loved as much as youll receive carried out right here The sketch is tasteful your authored material stylish nonetheless you command get bought an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Hello Gamers !
Welcome to Limelight Stream, where endless entertainment awaits you. Explore our diverse array of content, including movies, TV series, documentaries, and exclusive shows available only on Limelight Stream. Our high-definition streaming technology ensures a superior viewing experience, making every moment more enjoyable. Navigate through our platform with ease using our user-friendly interface, designed to help you find your favorite content quickly. Stream anytime, anywhere, on any device, whether it’s your TV, laptop, tablet, or smartphone. Personalized recommendations based on your viewing habits make discovering new shows effortless. Join https://www.limelight-stream.com/ today and dive into a world of premium content, where the best in entertainment is always just a click away.
Best practices for game streaming
Stream VR games from PC
Game streaming performance optimization
Stream games from PC to laptop
Limelight contribution guide
Good luck!
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
신규 슬롯 사이트
그것을 먹고 나면 온 사람이 조금 더 활기차게 됩니다.
A fairly new player in the Russian darknet arena, [url=https://bs-gl-darknet.com]blacksprut[/url] Blacksprut has quickly gained attention for its interesting features and growing popularity. While some aspects raise questions, it has the potential to become a prominent figure in the darknet scene.
Features:
Blacksprut https://bs-gl-darknet.com offers an “Instant Transactions” feature, inspired by the success of similar systems on other platforms like Hydra. Couriers hide goods within the city and provide buyers with coordinates, adding an adventurous element to the purchasing process.
Смелым игрокам посвящается!
Регистрация с промокодом 1xbet – получайте бонусы на депозиты и бесплатные спины. Активируйте промокод и начните выигрывать прямо сейчас с дополнительными бонусами! [url=http://nirvanaplus.ru/articles/22/amlamaslozachemegoi.html]1xbet бонус промокод[/url]
Регистрация с промокодом 1xbet – это ваш шанс получить бонусы на депозиты и фриспины. Активируйте промокод и начните выигрывать прямо сейчас с дополнительными средствами!
Сайт с самой четкой информацией! – http://nirvanaplus.ru/articles/22/amlamaslozachemegoi.html
1хбет промокод при регистрации на сегодня
промокод 1хбет кз на сегодня
1xbet промокод на сегодня
Удачи!
Военный адвокат Запорожье. Бесплатная консультация
[url=https://meget.kiev.ua/yuristi/2951-2-voenniy-advokat-zaporozhye/]юрист по военным делам Запорожье[/url]
— это опытный специалист имеющий высшее юридическое образование, сдавший квалификационный государственный экзамен на право осуществления адвокатской деятельностью и специализирующийся в основном на военных делах
Вся правовая помощь военного адвоката осуществляется в индивидуальном порядке, грамотно, четко и в соответствии с действующими нормативно-правовыми актами.
Мы как военные юристы действуем не против органов Украины или министерства обороны, мы действуем во благо Украины — наших защитников и граждан Украины, которые попали в тяжелую жизненную ситуацию связанную с незнанием военного и действующего законодательства.
Поскольку, проявив патриотизм и чувство гражданской ответственности – став на защиту суверенитета страны, граждане участвующие и помогавшие в обороне после, становятся никому не нужными, особенно если военнослужащий стал инвалидом, потерял часть тела или конечность, и не может самостоятельно защитить свои права. Именно в таких ситуациях мы как военные адвокаты приходим на помощь, и добиваемся в установленном законом порядке справедливости, необходимых выплат, установление статуса, оформление пенсий, льгот и т.п.
Тоже касается, и получение отсрочки от мобилизации, когда например, безосновательно призывают сына у которого отец инвалид 2 группы, или мать прикованная из-за тяжелой болезни к постели, и требующая постороннего ухода. Это же относится и к военнослужащим, рапорта которых не регистрируются в канцелярии воинской части и полностью игнорируются, под прикрытием суеты боевых действий..
Именно в таких ситуациях, мы приходим на помощь и с помощью ЗАКОННЫХ методов правовой защиты, используя свой опыт полученный при ведении аналогичных военных дел добиваемся справедливости.
bursa görüntülü diafon en uygun fiyat garantisi
와이즈 토토
옆에있는 Wang Jianye가 앞으로 나아갔습니다. “아빠, 아빠, 괜찮으세요?”
You have noted very interesting points! ps decent website.
nazilli pidesi nazilli meşhur pidesi
Казино Гама казино обеспечивает быстрые и надежные транзакции при пополнении и выводе средств – [url=https://kurl.ru/gamacasinozerkalo]официальное зеркало Гама[/url]
Если вы ищете место, где смогут преобразить вас с головы до ног, рекомендую Салон красоты Фелиссимо. Этот салон предлагает широкий спектр услуг: от окрашивания и наращивания волос до маникюра. Мастера здесь настоящие профессионалы, использующие только качественные материалы. Посещение Felissimo — это гарантия того, что вы выйдете оттуда абсолютно довольными. Отличный сервис и приятная атмосфера гарантированы!
Медиагет предлагает уникальную функцию
категоризации контента, что значительно упрощает
поиск нужных файлов. На https://skachat-mediaget-fast.ru пользователи могут ознакомиться с подробным описанием
этой функции. Программа автоматически сортирует файлы по типам
(фильмы, музыка, игры, программы и т.д.),
что позволяет быстро находить интересующий контент.
Кроме того, Медиагет предлагает возможность
создания пользовательских категорий, что еще больше упрощает
организацию скачанных файлов.
Разбираю ситуацию вокруг “кооператива” Life is Good
[url=https://kaissachess.ru/280524/novosti-vasilenko-roman-poslednie-novosti/]смотреть жесткое порно[/url]
Я решил написать этот пост, чтоб пройтись по доводам тех, кто привлекает новых “пайщиков” в структуры г-на Василенко (на деле – оплачивающих существование пирамиды Life is Good). Понятно, что, в этом сообществе крутятся сотни тех, кто занимается привлечением и теперь ЦБ с прокуратурой их оставят не только без заработка, но, возможно, придется отвечать за свои действия в суде. А деньги уже, наверняка, потрачены. Также есть люди, которые уже живут в квартире от LIG или выплатили некую сумму, они верят до конца и отказываются принимать ситуацию, в которой надо признать, что они могут остаться и без денег, и без квартиры. В любом случае, даже если кто-то живет в квартире от LIG, она ему не принадлежит и, в отличие от банковского залога, урегулировать вопрос не получится (их просто выселят через суд при банкротстве LIG, хотя ситуация скандальная и возможно государство что-то предпримет, чтоб сгладить проблему).Теперь по сути, что такое LIG.
Компания LIG – «Лайф-из-гуд» заявляет два основных направления деятельности: инвестиционные счета «Виста» в компании Hermes Management Ltd. и жилищный кооператив «Бест-вей» — альтернатива ипотеке.
Если верить консультантам «Лайф-из-гуд», доходность счетов «Виста» в компании «Гермес-менеджмент» последние годы держится в районе 20% годовых в долларах. Это довольно много (Уоррен Баффет позавидовал бы такой доходности), при этом непонятно, за счет чего достигается такая доходность.
Деятельность «Гермес-менеджмента» непрозрачна, на сайте не видно полноценных отчетов, нет сведений о структуре компании и ее руководстве.
«Гермес-менеджмент» привлекает российских клиентов через компанию «Лайф-из-гуд», но у него нет лицензии Центрального банка России на брокерскую деятельность или доверительное управление.
«Гермес-менеджмент» зарегистрирован в Белизе, офшорной зоне в Центральной Америке. Там же расположен офис компании. Еще в документах упоминается компания Hermes M в Шотландии. В случае проблем придется разбираться с зарубежной компанией, что делает задачу бесперспективной. Более того, учитывая реалии мошеннических схем, бывшие пайщики столкнутся еще и с лже-юристами, обещающими вернуть им вложенные деньги и конечно, останутся в крайне бедственном положении, с кредитами, без жилья и перспектив (у кого-то могут опуститься руки со всеми вытекающими).
Компания платит за привлечение новых клиентов, открывающих инвестиционные счета «Виста» (по сути – ничем не обеспеченные цифры на сайте. Заведение средств происходит через перевод средств на счета частных лиц(!), выполняющих роль консультантов LIG (а это сразу нарушает законы РФ и привлекает внимание регулятора), вывод – через перепродажу воздуха других буратинам. После внесения LIG в черный список, чаты структуры полны объявлений о продажи токенов Виста, но покупателей почти нет)) и вступающих в жилищный кооператив «Бест-вей». Система комиссионных выглядит такой разветвленной и продуманной, что становится понятно, что именно в ней суть компании, а не в инвестициях или альтернативе ипотеке.
Сам по себе сетевой маркетинг — вполне законный способ привлечения новых клиентов. Но когда он выглядит как основной вид деятельности, а клиентам при этом рассказывают про инвестиции, пассивный доход и успех в жизни, это наводит на очевидные выводы.
Суть предложения «Гермеса» такая: инвесторы открывают счет и перечисляют компании доллары или евро, а взамен получают пассивный доход. Минимальная сумма инвестиционного контракта — 10 тысяч долларов или евро. При этом первый взнос может быть 1130 долларов или 1100 евро, а оставшуюся сумму можно довнести позже.
Чтобы открыть счет «Виста», надо заполнить регистрационную форму на сайте «Лайф-из-гуд». При регистрации сайт просит поставить галочку «Я ознакомился и принимаю условия указанные в публичной оферте» (пунктуация сохранена).
По ссылке открывается не оферта, а договор об оказании услуг. В договоре не указаны название и реквизиты компании, с которой заключается договор. Кроме того, речь в нем идет не об управлении активами, а только об «образовательных и консультационных услугах об инвестиционных механизмах и способах управления капиталом». Это не похоже на обещанный пассивный доход от слова совсем. Таким образом, зазывалы в пирамиду пытаются уйти от ответственности.
[url=https://kompromat-group.com/wiki/item/81522-roman-viktorovich-vasilenko-rossiyskiy-piramidschik]русский анальный секс[/url]
Чтобы открыть счет и пользоваться им, придется заплатить различные комиссии. Все они прописаны в договоре:
Комиссия за открытие счета: 100 евро или 130 долларов.
Ажио, или входная комиссия: 7% от суммы лицевого счета. На сайте есть пример расчета: при вложении 100 000 $ ажио составит 7000 $.
Комиссия за управление счетом: 1% в год от размера счета, взимается каждый месяц по 1/12.
Комиссия с прибыли: 20% от ежемесячной прибыли, «полученной от инвестиционных продуктов сторонних партнерских компаний или физических лиц, в результате рекомендаций и деятельности Исполнителя».
Итак, LIG состоит из двух основных компаний: Гермес, которая предлагает участникам инвестиционный доход (с идеей полученную прибыль направить на квартиру) и Бест-Вэй, являющаяся ЖНК. Что это такое?
Это Жилищный накопительный кооператив (общепринятое сокращение — ЖНК) — вид потребительского кооператива, сочетающий в себе качества финансового и жилищно-строительного кооператива. ЖНК работают в соответствии с № 215-ФЗ «О жилищных накопительных кооперативах». Целью деятельности жилищных накопительных кооперативов является удовлетворения потребностей членов кооператива в жилых помещениях путём объединения членами кооператива паевых взносов. Жилищный накопительный кооператив имеет право:
– привлекать и использовать денежные средства граждан на приобретение жилых помещений;
– вкладывать имеющиеся у него денежные средства в строительство жилых помещений (в том числе в многоквартирных домах), а также участвовать в строительстве жилых помещений в качестве застройщика или участника долевого строительства;
– приобретать жилые помещения;
– привлекать заёмные денежные средства, общая величина не должна превышать сорок процентов стоимости имущества кооператива.
Членами жилищного накопительного кооператива могут быть только граждане РФ. Жилищный накопительный кооператив создаётся по инициативе не менее чем пятидесяти человек и не более чем пяти тысяч человек. Контроль за деятельностью кооператива по привлечению и использованию денежных средств граждан на приобретение жилых помещений, а также за соблюдением кооперативом требований действующего законодательства Российской Федерации осуществляет Центральный банк Российской Федерации.
Уже отсюда понятно, что заявления заинтересованных лиц из структур LIG о том, что ЦБ не в праве вмешиваться в деятельность собственно LIG лишены оснований. Может и вмешался.
Если говорить о цифрах, то на 13 декабря 2021 года в LIG было свыше 19 000 пайщиков изо всех уголков РФ. LIG выкупил и передал в безвозмездное пользование пайщикам примерно 2 500 объектов недвижимости, из них по 247 пайщики полностью выплатили пай, оформив недвижимость в собственность. Интересная статистика – 19 000 вступили, заплатив членский взнос в 160 000 рублей, но лишь 8 часть из них накопила необходимые 35% для получения недвижимости при том, что фактически недвижимость их собственностью не является. Заявления о том, что получившие недвижимость прописаны в квартирах – это пережитки советского прошлого и, вероятно, сознательное введение остальных в заблуждение. В современной РФ не существует института прописки, есть регистрация, постоянная и временная. Есть найм жилья и есть собственность. Допускаю, что какая-то часть людей все еще проживает в государственных квартирах и не оформила их в собственность, но это – давно не норма, как это было в СССР (где собственность как раз была редким явлением).
По сути кооператив — посредник между покупателем и продавцом жилья, а это увеличивает риски. Приходится полагаться на то, что кооператив соблюдает закон и что он не закроется до того, как вы оформите квартиру на себя.
Даже если все по закону, риск потерять деньги остается. Если кооператив по каким-то причинам перестанет работать, его собственность распродадут. Сначала он рассчитается с кредиторами и только затем вернет деньги пайщикам — пропорционально их паевым взносам. Хватит ли у кооператива денег, чтобы вернуть все паевые взносы, неизвестно.
Военный адвокат Запорожье. Бесплатная консультация
[url=https://g.co/kgs/dbnSE2C]военный адвокат Харьков[/url]
— это опытный специалист имеющий высшее юридическое образование, сдавший квалификационный государственный экзамен на право осуществления адвокатской деятельностью и специализирующийся в основном на военных делах
Вся правовая помощь военного адвоката осуществляется в индивидуальном порядке, грамотно, четко и в соответствии с действующими нормативно-правовыми актами.
Мы как военные юристы действуем не против органов Украины или министерства обороны, мы действуем во благо Украины — наших защитников и граждан Украины, которые попали в тяжелую жизненную ситуацию связанную с незнанием военного и действующего законодательства.
Поскольку, проявив патриотизм и чувство гражданской ответственности – став на защиту суверенитета страны, граждане участвующие и помогавшие в обороне после, становятся никому не нужными, особенно если военнослужащий стал инвалидом, потерял часть тела или конечность, и не может самостоятельно защитить свои права. Именно в таких ситуациях мы как военные адвокаты приходим на помощь, и добиваемся в установленном законом порядке справедливости, необходимых выплат, установление статуса, оформление пенсий, льгот и т.п.
Тоже касается, и получение отсрочки от мобилизации, когда например, безосновательно призывают сына у которого отец инвалид 2 группы, или мать прикованная из-за тяжелой болезни к постели, и требующая постороннего ухода. Это же относится и к военнослужащим, рапорта которых не регистрируются в канцелярии воинской части и полностью игнорируются, под прикрытием суеты боевых действий..
Именно в таких ситуациях, мы приходим на помощь и с помощью ЗАКОННЫХ методов правовой защиты, используя свой опыт полученный при ведении аналогичных военных дел добиваемся справедливости.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Подборка лучших моделей лебедок для спортивной серии, которые подойдут для профессиональных тренировок.
Подберите подходящую лебедку для тренировок, и достигните новых результатов.
Какую лебедку выбрать для оптимальных результатов, для успешной тренировки и достижения своих целей.
Топовые марки спортивных лебедок, которые заслужили доверие спортсменов.
Советы по выбору оптимального размера лебедки для спортзала, для предотвращения травм и обеспечения комфорта.
Какие материалы используются при изготовлении спортивных лебедок, и какой материал выбрать для долговечности и удобства.
Как правильно заниматься с использованием лебедки для спорта, для достижения лучших результатов и безопасной тренировки.
Спортивная серия лебедок [url=https://goldenpower4x4.ru/lebedki/sportivnaya-seriya.html]https://goldenpower4x4.ru/lebedki/sportivnaya-seriya.html[/url] .
Hi my loved one I wish to say that this post is amazing nice written and include approximately all vital infos Id like to peer more posts like this
Риобет предлагает обширный выбор качественных игровых слотов в своей коллекции – [url=https://riobetcasino-ecy.top/]Riobet рабочее на сегодня[/url]
7к казино предлагает широкий выбор высококачественных игровых слотов, удовлетворяющих различные предпочтения игроков и обеспечивающих захватывающий игровой опыт – [url=https://r7casino-zrh.top/]r7 casino сегодня[/url]
Букмекерская контора 7к казино предлагает обширную коллекцию качественных игровых слотов, включая разнообразные тематики и захватывающий игровой опыт – [url=https://7kcasino-xvi.top/]7k casino зеркало[/url]
В букмекерской конторе 7к казино мы придаем большое значение безопасности игроков и обеспечиваем надежную защиту от незаконных действий и мошенничества – [url=https://7kcasino-lbk.top/]рабочий сайт[/url]
메이저 슬롯
한밤중이 되자 달은 밝고 별은 희박했으며 밤에는 안개가 자욱했습니다.
Wonderful beat I wish to apprentice while you amend your web site how could i subscribe for a blog web site The account aided me a acceptable deal I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear idea
О команде Экипировка Эксперт
[url=https://ekipirovka.shop/katalog/item/ryukzak_podavitel_dronov_garpiya_gw6_uav/]РЮКЗАК ПОДАВИТЕЛЬ ДРОНОВ – ГАРПИЯ GW6-UAV[/url]
Боец, Экипировка Эксперт — это розничный интернет-магазин при оптовом складе. Это значит, что при должном количестве товара мы дадим очень хорошие цены.
Название взяли независимо от того, что наша страна сейчас проводит Специальную Военную Операцию, хорошая снаряга и экипировка нужна всегда. Готовишься в бой, мобилизован, привык активно проводить время или решил подготовить тревожный чемоданчик, мы поможем тебе. Наши клиенты: фонды, медики, такие же как ты бойцы СВО и обычные неравнодушные граждане.
Тактические берцы LOWA MID
https://ekipirovka.shop/katalog/taktika/meditsina/
Самое главное, что нужно о нас знать, мы детально объясняем, что и как работает, чтобы ты сделал правильный выбор не переплачивая.
Обращаясь к нам, не удивляйся, если ты получишь честный и жесткий ответ – часто случается так, что мы знаем лучше, что именно нужно нашему гостю. Особенно это касается мобилизованных без опыта боевых действий. Здесь ты можешь полагаться на нашу экспертность.
Одна из наших основных целей предоставить тебе возможность удобной и безопасной покупки: хоть за наличку, хоть по карте, хоть по счету. Повторимся, если нужна оптовая поставка, согласуем и отгрузим.
Именно от того, как ты производишь оплату, зависит цена заказа. Для нас важно предоставить тебе качественную экипировку и снаряжение соблюдая при этом законы нашей страны.
Боец, помни, мы помогаем фондам, нуждающимся людям, подразделениям в зоне СВО. Отчеты об этом вскоре будут опубликованы как на сайте, так и на наших каналах в социальных сетях. На эту деятельность уходит значительная часть выручки. Делая покупки в нашем магазине, ты помогаешь людям и фронту. Уверен, что это найдет отзыв в твоем сердце.
У нашей команды есть набор ценностей: честность, справедливость, сопереживание, взаимопомощь, мужество, патриотичность. Уверены, ты их разделяешь, и мы легко найдем общий язык.
Ну а если что-то пойдет не так, не руби с плеча, объясни, где мы ошиблись и поверь, мы разберемся и исправим.
Наш девиз “In hostem omnia licita” – по отношению к врагу дозволено все. Возьми этот девиз, он поможет тебе принять правильное решение в трудной ситуации, с честью выполнить боевую задачу и вернуться домой живым и здоровым!
Отборное оборудование для спортивных лебедок, для эффективных тренировок.
Найдите идеальный вариант лебедки для своих целей, и улучшения своей физической формы.
Какие характеристики важны при выборе лебедки для спорта, чтобы избежать ошибок и добиться успеха.
Лучшие бренды и производители спортивных лебедок, привлекающие внимание профессиональных спортсменов.
Советы по выбору оптимального размера лебедки для спортзала, для предотвращения травм и обеспечения комфорта.
Основные виды материалов для производства лебедок для спорта, и какой материал предпочтителен для длительной эксплуатации и безопасности.
Как правильно заниматься с использованием лебедки для спорта, для максимальных результатов и предотвращения травм.
Спортивная серия лебедок [url=https://goldenpower4x4.ru/lebedki/sportivnaya-seriya.html]https://goldenpower4x4.ru/lebedki/sportivnaya-seriya.html[/url] .
Присоединившись к кооперативу “Бест Вей”, я не только приобрел жилье, но и обрел уверенность в завтрашнем дне для своей семьи. Роман Василенко предложил не просто квартиру, но и спокойствие и гарантии, которые так важны для семейных людей. Весь процесс от начала до конца был организован так, чтобы минимизировать стресс и упростить жизнь пайщикам. Я благодарен Роману за его преданность делу и за его стремление помогать людям, которые сталкиваются с жилищными проблемами. “Бест Вей” – это не просто дом, это место, где я могу чувствовать себя уверенно и защищенно.
[url=https://spasi-i-sohrani.com/novosti/item/76099-delo-layf-iz-gud-germes-best-vey-kto-takie-naboychenko-i-komarov]лайф из гуд[/url]
Title: Mejores estrategias para jugar en Spin Casino Brasil: Consejos de los profesionales
Description: Descubre estrategias expertas y consejos profesionales para optimizar tus juegos en Spin Casino Brasil. ?Aprende de los mejores!
[url=https://spincasino-brasil.com/]spin online[/url]
H1: Mejores estrategias para jugar en Spin Casino Brasil: Consejos de los profesionales
Bienvenidos al emocionante mundo de Spin Casino Brasil, donde la oportunidad de ganar se combina con el entretenimiento de primera clase. En este articulo, exploraremos estrategias efectivas y consejos profesionales que te ayudaran a maximizar tus experiencias de juego. Desde comprender la estructura del casino hasta aplicar tacticas especificas en tus juegos favoritos, te guiaremos paso a paso para mejorar tus habilidades y aumentar tus posibilidades de exito.
[img]http://1-x-bet.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/kandinsky-download-1712570944059-min.png[/img]
H2: Conociendo Spin Casino Brasil
Introduccion al Casino
Spin Casino Brasil se destaca en el mercado por ofrecer una experiencia de juego segura y dinamica. Con una licencia valida y un compromiso con la seguridad del jugador, este casino se presenta como una opcion confiable para los entusiastas de los juegos de azar en linea.
Variedad de Juegos
Explora la amplia gama de juegos que Spin Casino Brasil tiene para ofrecer. Desde tragamonedas clasicas hasta juegos de mesa sofisticados como el blackjack y la ruleta. Cada juego viene con una descripcion detallada de las reglas y los porcentajes de retorno al jugador (RTP), asegurando que los jugadores puedan elegir sabiamente segun sus preferencias.
Software y Tecnologia
Spin Casino Brasil utiliza software de los lideres de la industria, garantizando graficos de alta calidad y una interfaz de usuario fluida. Este apartado discutira como la tecnologia de Spin Casino Brasil mejora la experiencia del usuario y mantiene la integridad del juego.
Atencion al Cliente
El soporte al cliente es esencial en cualquier plataforma de juego en linea. Detalla como los jugadores pueden acceder al soporte 24/7 a traves de chat en vivo, correo electronico y telefono, asegurando que todas las consultas y problemas se resuelvan de manera eficiente.
H2: Estrategias generales de juego
Gestion del Bankroll
Un buen jugador sabe que la gestion del bankroll es crucial. Explica tecnicas para determinar cuanto dinero destinar al juego sin comprometer la estabilidad financiera personal. Se incluiran metodos para establecer limites de apuestas y la importancia de adherirse a estos limites.
Comprender las Probabilidades
El juego de casino no solo se trata de suerte; las matematicas juegan un papel crucial. Ofrece una explicacion sencilla de como entender las probabilidades y como pueden influir en las decisiones de juego. Este apartado demuestra como un conocimiento basico de estadisticas y probabilidad puede ayudar a tomar decisiones mas informadas.
Importancia de la Seleccion del Juego
No todos los juegos de casino ofrecen las mismas probabilidades de ganar. Discute como la eleccion del juego puede afectar las posibilidades de exito, destacando aquellos juegos que ofrecen mejores probabilidades y explicando por que algunos juegos son mas amigables con el jugador que otros.
Estrategias de Apuestas
Finalmente, se abordaran diversas estrategias de apuestas que los jugadores pueden emplear. Desde la estrategia conservadora hasta la mas arriesgada, cada estilo de apuesta sera discutido con ejemplos practicos, ayudando a los jugadores a entender cuando y como ajustar sus apuestas segun el flujo del juego.
H2: Estrategias especificas para juegos populares en Spin Casino Brasil
Este apartado se centra en las tacticas especializadas que los jugadores pueden emplear en algunos de los juegos mas populares disponibles en Spin Casino Brasil, asegurando que los jugadores de todos los niveles puedan optimizar sus oportunidades de ganar.
H3: Tragamonedas
Comprender la Varianza y el RTP
Inicia con una explicacion sobre la importancia del retorno al jugador (RTP) y la varianza de las tragamonedas. Describe como seleccionar maquinas con un RTP alto puede aumentar las posibilidades de ganancias a largo plazo y como la varianza afecta la frecuencia y cantidad de los pagos.
Estrategias de Apuestas
Detalla estrategias de apuestas eficaces para las tragamonedas, como ajustar el tamano de las apuestas basado en el ciclo de ganancias/perdidas y la importancia de maximizar las lineas de pago para aumentar las posibilidades de ganar en cada giro.
Aprovechar los Bonos
Explica como los jugadores pueden utilizar bonos y giros gratis ofrecidos por Spin Casino para maximizar sus jugadas sin aumentar el riesgo financiero, destacando la importancia de leer los terminos y condiciones asociados a estos bonos.
H3: Blackjack
Estrategia Basica
Proporciona una guia detallada sobre la estrategia basica de blackjack, incluyendo cuando pedir carta, plantarse, dividir o doblar la apuesta, basado en la mano del jugador y la carta visible del crupier.
Gestion del Riesgo
Discute la importancia de la gestion del riesgo y del bankroll especificamente para el blackjack, enfatizando como evitar las apuestas impulsivas y como adaptar el tamano de las apuestas en funcion de la situacion del juego.
Contar Cartas
Introduce conceptos basicos del conteo de cartas (donde legalmente sea aplicable), explicando como esta tecnica puede dar a los jugadores una ventaja estadistica sobre el casino y como practicar de manera efectiva sin infringir las reglas.
H3: Ruleta
Apuestas Exteriores vs. Interiores
Explica la diferencia entre apuestas exteriores e interiores, sus riesgos y beneficios, y por que las apuestas exteriores suelen ser una mejor opcion para aquellos que buscan minimizar riesgos.
Sistemas de Apuestas
Analiza varios sistemas de apuestas como el Martingala, Fibonacci y D’Alembert, evaluando su efectividad y como pueden ser aplicados en la ruleta para gestionar mejor las perdidas y potenciar las ganancias.
H3: Poker
Conocimientos Fundamentales de Poker
Detalla los conocimientos basicos del poker, como las reglas del Texas Hold’em, las clasificaciones de manos y la importancia de la posicion en la mesa.
Estrategias de Apuesta y Bluff
Describe estrategias avanzadas como el arte del bluff, saber leer a los oponentes, y la importancia de ajustar las apuestas basado en el estilo de juego de los contrincantes y la dinamica de la mesa.
Importancia del Control Emocional
Destaca la importancia de mantener el control emocional, como gestionar las ganancias y las perdidas, y por que un enfoque disciplinado y una mente clara son esenciales para el exito en el poker a largo plazo.
H2: Consejos de los profesionales
Aprender de la Experiencia
Introduccion a las lecciones aprendidas por jugadores experimentados, enfatizando la importancia de aprender tanto de los exitos como de los fracasos. Resalta como la experiencia es un recurso invaluable que puede ayudar a prever situaciones de juego y tomar decisiones mas informadas.
Adaptabilidad y Flexibilidad
Describe como los profesionales se adaptan a diferentes situaciones de juego, ajustando sus estrategias segun la dinamica del juego y las acciones de otros jugadores. Discute la importancia de ser flexible y no apegarse rigidamente a una sola estrategia.
Mantener la Disciplina
Enfatiza la necesidad de mantener la disciplina, especialmente en momentos de ganancias o perdidas significativas. Explica como la gestion efectiva del bankroll y el control emocional son cruciales para el exito a largo plazo en los juegos de casino.
H2: Maximizando bonificaciones y promociones
Entender los Tipos de Bonificaciones
Explica los diferentes tipos de bonificaciones que ofrece Spin Casino Brasil, como bonos sin deposito, bonos por deposito, y giros gratis. Detalla como cada tipo puede beneficiar a los jugadores dependiendo de su estilo de juego y objetivos.
Estrategias para Aprovechar Promociones
Ofrece estrategias especificas para aprovechar al maximo las promociones, como planificar depositos durante eventos de bonificacion y elegir promociones que complementen el estilo de juego del usuario. Discute la importancia de leer los terminos y condiciones para evitar sorpresas.
Cumpliendo con los Requisitos de Apuesta
Proporciona consejos practicos sobre como cumplir con los requisitos de apuesta sin comprometer el bankroll. Explora tecnicas para maximizar las oportunidades de ganancia mientras se juega a traves de los requisitos de apuesta de manera eficiente.
H2: Herramientas y recursos utiles
Software y Aplicaciones de Ayuda
Presenta software y aplicaciones que pueden ayudar a los jugadores a mejorar su juego, como calculadoras de probabilidades, diarios de juego, y herramientas de analisis de manos. Evalua como estas herramientas pueden proporcionar una ventaja competitiva.
Recursos Educativos
Recomienda libros, tutoriales en video y cursos que pueden proporcionar a los jugadores nuevos y experimentados conocimientos avanzados sobre estrategias de juego y psicologia del juego. Destaca recursos especificos que han sido bien recibidos por la comunidad de juego.
Foros y Comunidades
Alude a la importancia de participar en foros y comunidades en linea donde los jugadores pueden intercambiar estrategias, experiencias y consejos. Subraya como el aprendizaje colaborativo y el apoyo mutuo pueden mejorar la experiencia de juego y el desarrollo de habilidades.
Al aplicar las estrategias y consejos discutidos en este articulo, estaras bien equipado para afrontar los desafios que Spin Casino Brasil ofrece. Recuerda que la clave del exito en los juegos de casino reside no solo en conocer las reglas, sino en aplicar estrategias informadas y mantener una disciplina ferrea. Juega de manera responsable y dentro de tus limites para disfrutar de una experiencia tanto segura como emocionante. ?Buena suerte y que disfrutes de cada juego!
FAQ:
?Es seguro jugar en Spin Casino Brasil?
?Absolutamente! Spin Casino Brasil esta completamente regulado y ofrece un entorno seguro para todos sus jugadores. Disfruta de tu juego sin preocupaciones.
?Que juegos ofrecen las mejores probabilidades en Spin Casino Brasil?
Los juegos como el blackjack y el video poker generalmente ofrecen las mejores probabilidades, especialmente cuando aplicas las estrategias adecuadas.
?Puedo jugar en Spin Casino Brasil desde mi movil?
Si, Spin Casino Brasil ofrece una plataforma movil excelente que te permite jugar tus juegos favoritos desde cualquier lugar y en cualquier momento.
?Como puedo maximizar las bonificaciones ofrecidas por Spin Casino Brasil? Asegurate de leer los terminos y condiciones de las bonificaciones. Aprovecha los bonos de bienvenida, recargas y programas de fidelidad para obtener el maximo beneficio.
[url=https://xrumer.ru/]роблокс r34[/url]
[url=https://xrumer.xyz/]роблокс r34[/url]
[url=https://odiflucan.online/]buy diflucan online without prescription[/url]
I have learn several good stuff here. Certainly worth bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how so much effort you place to create this sort of wonderful informative website.
Обеспечьте конфиденциальность с резидентскими прокси, советуем этим инструментом.
Какие преимущества у резидентских прокси?, ознакомьтесь с подробностями.
Как выбрать лучший резидентский прокси, советы для пользователей.
Какие задачи решают резидентские прокси?, ознакомьтесь с возможностями.
Почему резидентские прокси безопасны?, анализ функций безопасности.
Какие риски может предотвратить резидентский прокси?, разберем важные аспекты.
Как резидентский прокси помогает повысить эффективность?, сравним основные плюсы.
Как быстрее работать в сети с резидентским прокси?, практические советы для оптимизации работы.
Каким образом ускорить процесс парсинга с помощью резидентского прокси, анализ возможностей для парсеров.
Секреты анонимности с резидентским прокси, практические шаги к безопасности онлайн.
Как расширить свои возможности в соцсетях с резидентским прокси?, рекомендации функционала.
Зачем арендовать резидентские прокси и какие бонусы?, проанализируем лучшие варианты.
Способы защиты от DDoS с помощью резидентского прокси, рассмотрим меры безопасности.
Какие преимущества привлекают пользователей к резидентским прокси?, подробно изучим основные факторы.
Какие прокси лучше: резидентские или дата-центры?, рекомендации для выбора.
качественные резидентские прокси [url=https://rezidentnieproksi.ru/]https://rezidentnieproksi.ru/[/url] .
Обеспечьте конфиденциальность с резидентскими прокси, советуем этим инструментом.
В чем особенность резидентских прокси?, узнайте подробностями.
Как выбрать лучший резидентский прокси, рекомендации для пользователей.
Для каких целей используют резидентские прокси?, подробнее ознакомьтесь с возможностями.
Почему резидентские прокси безопасны?, анализ функций безопасности.
Как резидентские прокси защищают от опасностей?, анализируем важные аспекты.
Зачем нужны резидентские прокси и какой их выигрыш?, проанализируем основные плюсы.
Как быстрее работать в сети с резидентским прокси?, советы для оптимизации работы.
Зачем использовать резидентский прокси для сбора информации?, обзор возможностей для парсеров.
Секреты анонимности с резидентским прокси, рекомендации к безопасности онлайн.
Как улучшить работу в социальных сетях с резидентским прокси, подробный обзор функционала.
Зачем арендовать резидентские прокси и какие бонусы?, сравним лучшие варианты.
Как избежать DDoS с резидентским прокси?, подробно изучим меры безопасности.
Почему резидентские прокси пользуются популярностью, подробно изучим основные факторы.
Сравнение резидентских и дата-центровых прокси, рекомендации для выбора.
где взять резидентский прокси [url=https://rezidentnieproksi.ru/]https://rezidentnieproksi.ru/[/url] .
Защитите свои данные с помощью резидентских прокси, воспользоваться этим инструментом.
В чем особенность резидентских прокси?, узнайте подробностями.
Советы по выбору резидентского прокси, советы для пользователей.
Какие задачи решают резидентские прокси?, узнайте возможностями.
Почему резидентские прокси безопасны?, обзор функций безопасности.
Какие риски может предотвратить резидентский прокси?, рассмотрим важные аспекты.
Как резидентский прокси помогает повысить эффективность?, сравним основные плюсы.
Как быстрее работать в сети с резидентским прокси?, советы для оптимизации работы.
Каким образом ускорить процесс парсинга с помощью резидентского прокси, анализ возможностей для парсеров.
Как оставаться анонимным в Интернете с резидентским прокси, рекомендации к безопасности онлайн.
Секреты эффективной работы в соцсетях с резидентским прокси, рекомендации функционала.
Как сэкономить время с помощью аренды резидентского прокси?, рассмотрим лучшие варианты.
Как избежать DDoS с резидентским прокси?, подробно изучим меры безопасности.
Почему резидентские прокси пользуются популярностью, проанализируем основные факторы.
Какие прокси лучше: резидентские или дата-центры?, рекомендации для выбора.
резидентные прокси купить [url=https://rezidentnieproksi.ru/]https://rezidentnieproksi.ru/[/url] .
Защитите свою конфиденциальность с резидентским прокси, использовать этим инструментом.
В чем особенность резидентских прокси?, ознакомьтесь с подробностями.
Какой резидентский прокси выбрать?, инструкция для пользователей.
Для каких целей используют резидентские прокси?, ознакомьтесь с возможностями.
В чем преимущество безопасности резидентских прокси?, обзор функций безопасности.
Какие риски может предотвратить резидентский прокси?, рассмотрим важные аспекты.
Как резидентский прокси помогает повысить эффективность?, сравним основные плюсы.
Секреты увеличения скорости с резидентским прокси, советы для оптимизации работы.
Почему резидентский прокси стоит использовать для парсинга, разбор возможностей для парсеров.
Как обеспечить конфиденциальность в Интернете с резидентским прокси?, шаги к безопасности онлайн.
Как улучшить работу в социальных сетях с резидентским прокси, рекомендации функционала.
Зачем арендовать резидентские прокси и какие бонусы?, проанализируем лучшие варианты.
Способы защиты от DDoS с помощью резидентского прокси, рассмотрим меры безопасности.
Почему резидентские прокси пользуются популярностью, подробно изучим основные факторы.
Какие прокси лучше: резидентские или дата-центры?, подсказки для выбора.
сервис резидентных прокси [url=https://rezidentnieproksi.ru/]https://rezidentnieproksi.ru/[/url] .
Охраняйте свою конфиденциальность с резидентскими прокси, для чего это нужно.
Смотрите зарубежные сериалы с резидентскими прокси, широким контентом.
Оптимизируйте работу сети благодаря резидентским прокси, как это работает.
Скройте свой реальный IP-адрес от хакеров с резидентскими прокси, и чувствуйте себя спокойно.
Защитите свою личную жизнь и данные с резидентскими прокси, и наслаждайтесь анонимностью.
Используйте резидентские прокси для безопасного серфинга в интернете, и не бойтесь за свою приватность.
резидентные прокси [url=https://rezidentnie-proksi.ru/]https://rezidentnie-proksi.ru/[/url] .
Защитите свои данные с помощью резидентских прокси, как это работает.
Обходите географические блокировки с резидентскими прокси, пользуйтесь контентом.
Получите быстрый и надежный интернет с резидентскими прокси, как это работает.
Защитите свои учетные данные и личную информацию с резидентскими прокси, и не беспокойтесь о своей безопасности.
Сделайте свои онлайн-активности невидимыми благодаря резидентским прокси, и наслаждайтесь анонимностью.
Скачивайте файлы анонимно через резидентские прокси, и не бойтесь за свою приватность.
сервис резидентных прокси [url=https://rezidentnie-proksi.ru/]https://rezidentnie-proksi.ru/[/url] .
Безопасность данных с резидентскими прокси, как это работает.
Получите доступ к контенту из других стран с резидентскими прокси, неограниченным контентом.
Получите быстрый и надежный интернет с резидентскими прокси, с чем связано.
Защитите свои учетные данные и личную информацию с резидентскими прокси, и будьте уверены в своей безопасности.
Защитите свою личную жизнь и данные с резидентскими прокси, и наслаждайтесь анонимностью.
Скачивайте файлы анонимно через резидентские прокси, и не тревожьтесь за свою приватность.
резидент прокси [url=https://rezidentnie-proksi.ru/]https://rezidentnie-proksi.ru/[/url] .
Защитите свои данные с помощью резидентских прокси, как это работает.
Смотрите зарубежные сериалы с резидентскими прокси, полномасштабным контентом.
Оптимизируйте работу сети благодаря резидентским прокси, с чем связано.
Обезопасьте свои онлайн-платежи с резидентскими прокси, и не беспокойтесь о своей безопасности.
Защитите свою личную жизнь и данные с резидентскими прокси, и наслаждайтесь анонимностью.
Скачивайте файлы анонимно через резидентские прокси, и не бойтесь за свою приватность.
сервис резидентных прокси [url=https://rezidentnie-proksi.ru/]https://rezidentnie-proksi.ru/[/url] .
Если все предыдущие шаги не помогли, попробуйте сбросить настройки Алисы и настроить голосовую активацию заново.
Иногда это помогает решить проблемы с
распознаванием голоса. Пошаговая инструкция по сбросу настроек и повторной настройке Алисы представлена на как сделать чтобы алиса включалась по голосу.
Помните, что после сброса вам придется заново настроить все персональные предпочтения.
Воины-пайщики оказались без защиты в тылу
Пайщики «Бест Вей» — участники СВО готовы защищать свой кооператив
Многие пайщики кооператива «Бест Вей» и те, в чьих интересах приобретаются квартиры в кооперативе, — участники СВО. И они сами, и их родственники возмущены событиями, происходящими вокруг кооператива. Ведь защищая интересы страны на фронте, в тылу они не защищены от того, что не могут приобрести недвижимость из-за того, что счета кооператива с почти 4 млрд рублей уже более двух лет находятся под арестом — притом, что сумма ущерба по уголовному делу, рассматриваемому Приморским районным судом Санкт-Петербурга, согласно обвинительному заключению, составляет 282 млн рублей.
«Надеемся, новое руководство Министерства обороны поможет урегулировать ситуацию»
Наталья Пригаро, мать пайщика кооператива — участника СВО из Нефтеюганска Даниила Пригаро:
— Сын расплатился за однокомнатную квартиру, приобретенную с помощью кооператива, еще два года назад, подал пакет документов на оформление квартиры в собственность в Росреестр в начале сентября 2022 года — и все это время не может зарегистрировать собственность на нее из-за того, что в Росреестре она значится как арестованная. В конце сентября 2022 года он был мобилизован. Сын брал кредит, чтобы расплатиться за квартиру с кооперативом. Планировал продать эту квартиру и взять квартиру побольше в ипотеку. Однако неоднократно накладывался арест на недвижимость кооператива, несмотря на то что сейчас ареста нет — последний арест, накладывавшийся осенью 2023 года, 19 февраля истек, ходатайства о новом аресте дважды отклонены судом, по Росреестру арест с квартиры до сих пор не снят. В результате кредит приходится платить, квартира в собственность до сих пор не оформлена.
У сына нет никакой физической и финансовой возможности выяснять отношения с Росреестром — в административном или судебном порядке, он приезжает в отпуска на неделю-полторы, ему не до сутяжничества. Я нахожусь в Анапе, приобрела квартиру с помощью кооператива — сын не имеет возможности сделать на меня генеральную доверенность, а я не могу из Анапы приехать в Нефтеюганск и решать вопросы в Росреестре — кроме поезда, сейчас, сами понимаете, ничего не ходит (конец цитаты).
«На безобразие, которое происходит с кооперативом, мы пишем жалобы во все инстанции, — говорит она. — Надеемся, новое руководство Министерства обороны поможет урегулировать ситуацию».
«Надежда, что все разрешится, остается — не может же все быть коррумпировано»
Елена Бойко — пайщик кооператива из Новосибирска и мать солдата, воющего в СВО, для которого она собиралась приобрести одну из двух квартир в кооперативе. «Я стала пайщиком кооператива в 2021 году. В январе 2021 года подала заявление на покупку двух квартир с помощью кооператива по накопительной программе. У меня двое детей — сын и дочь, им нужно жилье. В 2020 году взяли в ипотеку загородный дом — причем оформили на сына как единственного, кому ее могли одобрить, а в 2021 году он ушел в армию как призывник, а потом подписал контракт. Его относительно недавно отправили „за ленточку“. Думали, что поживем в ипотечном доме, и тут как раз подойдет очередь приобретать квартиры с помощью кооператива. Мы останемся жить в частном доме, а дети въедут в кооперативные квартиры».
«Ипотека — это разорительно, — подчеркивает Елена, — мы взяли 2,5 млн, а за 30 лет отдадим 6 млн. Когда появился кооператив, для нас это была возможность предоставить каждому из детей жилье: за 10 лет или раньше они расплатятся с кооперативом, причем с минимальной по сравнению ипотекой переплатой, и у них будет собственное жилье. Из-за репрессий в отношении кооператива мы можем быть этой возможности лишены».
«Я всем сердцем переживаю за ситуацию с кооперативом, заявление о выходе из кооператива пока не пишу — надеюсь, что его деятельность „разморозится“, — говорит Елена. — Обращаемся во все инстанции, в прокуратуру — приходят отписки. Смысл происходящего я понимаю хорошо — когда-то занималась кредитным потребительским кооперативом: нас тогда закрыл Центральный банк. Нашел формальный повод. Но настоящая причина была в том, что мы мешали банкам обирать клиентов. Но надежда на то, что все разрешится, остается — не может же быть все коррумпировано».
«Больше всего в нашей ситуации возмущает то, что наши воины стоят на стороне государства на фронте, а здесь, в тылу, их интересы нарушаются государственными структурами. Такого быть не должно!»
«Для многих кооператив — единственная возможность приобрести квартиру»
Лариса Зискинд — пайщица «Бест Вей», переехавшая с помощью кооператива с семьей — с дочерью, зятем и маленьким внуком - с Дальнего Востока в Белгородскую область. Ее зять, живущий в кооперативной квартире, находится на фронте СВО. «С помощью кооператива я приобрела квартиру в двухэтажном доме в селе Пушкарное Белгородской области — мы с дочерью переехали сюда. Мы уже два года расплачиваемся за него с кооперативом. Не до конца сделали ремонт, кухни фактически нет: моем посуду в ванной. Финансовых средств не хватает, так как зять уже год на СВО, пока ни разу не был в отпуске, и перевести деньги с его карты в ВТБ сейчас непросто, потому что карта — в расположении, до ближайшего банка ехать далеко, а он сам — на линии фронта. Мы фактически живем с выплат на ребенка, на мне кредиты — у меня полпенсии уходит на их оплату. Квартира по Росреестру находится под арестом, хотя арест по квартирам кооператива арест истек — а я боюсь ехать в Белгород, чтобы решать по ней вопрос. Я с ребенком на улицу гулять не выхожу в нынешней военной обстановке — сирены воздушной тревоги постоянные. Побыстрее бы наши войска создали санитарную зону в Харьковской области!»
По поводу покупки квартиры Лариса сообщает, что «ипотека точно никак не светила. Кооператив — это 14 тыс. в месяц и всего лишь 10 лет. В кооперативе даже студентка может приобрести квартиру, почти не переплачивая. При покупке через банк придется заплатить еще как минимум за одну квартиру».
«Среди пайщиков кооператива очень много пенсионеров, социально незащищенных людей, это была их единственная возможность приобрести квартиру, — говорит Лариса. — Из-за репрессий против кооператива мы можем лишиться единственного жилья. Мы куда только не писали в защиту кооператива. Но, видимо, слишком большой куш. Кооперативу не дают даже платить налоги. Надеемся, что отношение к кооперативу в результате справедливого разбирательства изменится в лучшую сторону».
«Мы очень устали. Но боремся»
Людмила Гарина — пайщица кооператива из Саратова, зять которой, проживающий вместе с ней в кооперативной квартире, участвует в СВО. «Я проживаю в кооперативной квартире почти три года вместе с дочерью и внуком, вносим ежемесячные платежи через госуслуги».
«Возможности взять ипотеку не было, — говорит Людмила. — Фактически у нас один работающий человек — дочь, зять мобилизован, внук — студент, внучке — четыре года. Мы с мужем пенсионеры».
«У нас с кооперативом проблем не было никаких, — говорит она, — но сейчас уверенности в завтрашнем дне нет. Пишем во все возможные инстанции, в том числе в Администрацию президента, ходили на прием к Володину. Пока ничего не помогает. Вся надежда на то, что суд разберется».
«Хотелось, чтобы вопрос о возобновлении работы кооператива быстрее решился, — говорит она, — тогда стало бы проще. Когда кооператив заработает, будет совершенно иная ситуация. Мы очень устали. Но боремся».
«20 тыс. пайщиков кооператива не так просто остановить»
Алла Яровая — пайщик кооператива из Пятигорска и представитель пайщицы Людмилы Дворцовой, сын которой, Игорь Дворцов, находился на СВО, а теперь служит внутри страны. «Людмила приобрела с помощью кооператива в Пятигорске квартиру для своего сына. Вступила в кооператив она в 2017 году, сначала находилась в накопительной программе — накапливала на первоначальный паевый взнос, накопила, потом стояла в очереди на приобретение жилье, приобрела с помощью кооператива однокомнатную квартиру за 1450 тыс. рублей. Потом приобрела квартиру и постепенно полностью за нее расплатилась. Работала для этого на двух работах, в том числе санитаркой в инфекционном отделении».
Но оформить квартиру в собственность не удалось, так как она оказалась под арестом, поясняет Алла. И хотя арест 19 февраля истек и больше не накладывался, суд первой инстанции в Пятигорске этот арест подтвердил. «По вопросу получения права собственности и снятия ареста мы обратились в Пятигорский городской суд, где судья очень предвзято отнесся к решению вопроса и мы получили отказ, — говорит Алла, — Хотя аналогичный вопрос рассматривался в Минераловодском суде и там судья вынесла положительное решение и в настоящий момент пайщик получил право собственности на свою квартиру. Предстоит рассмотрение в апелляционной инстанции — несмотря на то, что рассматривать нечего: ареста на недвижимость кооператива сейчас нет. А на квартиру Людмилы Дворцовой — почему-то есть».
«Кооператив — единственная возможность для людей со средним достатком получить жилье, — говорит Алла, — Нерешенный вопрос — налоги. Мы вынуждены платить налоги с юридических лиц, но мы же физические лица. К депутатам — с нас берут налог как с юрлица. Почему мы должны оплачивать — мы же физлица? Во многих регионах это сделано. Надеемся добиться того, чтобы это было сделано по всей стране».
«20 тыс. пайщиков кооператива не так просто остановить, — подчеркивает пайщица. — Это наши деньги, и мы за них боремся. Обязательно отстоим наш кооператив!»
«Активно участвую в защите кооператива»
У пайщицы кооператива, жительницы из Ленинградской области Татьяны Власенко старший сын находится на СВО с сентября 2022 года. «Три месяца проходил обучение, а потом оказался „за ленточкой“, — говорит Татьяна. — Мы должны были в конце лета 2022 года купить квартиру с помощью кооператива — квартиру планировали большую. Но работа кооператива оказалась заблокирована, и кооператив не может ничего купить уже более двух лет, так как и его счета, и его деятельность заблокированы. Деньги пайщиков, собранные для приобретения квартир, при этом обесцениваются».
«Я активно участвую в защите нашего кооператива, — говорит Татьяна. — Езжу на все суды в Санкт-Петербурге, хотя живу в деревне — ехать два с половиной, а то и три часа, мне 64 года, а путь неблизкий. И сын в этом поддерживает меня».
«Вот уже более двух лет работа кооператива заблокирована, деньги обесцениваются»
У пайщицы из Хабаровска Натальи Ромашко на СВО было два племянника — один, к сожалению, погиб. Планировалась покупка большой квартиры в Хабаровске, Наталья состояла в накопительной программе. «Вот уже более двух лет работа кооператива заблокирована, деньги обесцениваются, — говорит Наталья. — Я участвую в защите кооператива, пишу письма в прокуратуру, в высшие государственные инстанции, потому что нарушаются наши права, нас лишают возможности приобрести квартиру вне ипотечной системы. Пока приходят одни отписки, но борьбу мы продолжаем!»
«Ситуация — как на СВО»
Пайщица Светлана Иванова из Новосибирска, волонтер СВО, планировала приобрести с помощью кооператива две квартиры — для себя и для сына, который воюет на СВО добровольцем. «До этого я продала квартиру и сейчас вообще без собственного жилья, — говорит она. — Вступила в кооператив по накопительной программе, рассматривали для приобретения квартиры Крым и Новосибирск. В СВО участвую как волонтер — не остаюсь в стороне, когда Родине нужна помощь».
«От ситуации с кооперативом очень многие люди пострадали, — говорит Светлана. — Ситуация — как на СВО. И еще больше пострадают, если реализуется плохой сценарий. Хочется надеяться на то, что все образуется, правда восторжествует. Заявление о выходе из кооператива и возврате паевых средств я не подавала. Готова продолжить участие в нем, готова приобрести недвижимость с его помощью: это самый лучший вариант покупки квартиры».
«Сдаваться в планах нет»
Пайщица Марина Янковская родом из Хабаровска, она переехала в Новороссийск, ее супруг погиб на СВО. «У нас уже подходила очередь на покупку квартиры в Новороссийске для нашей семьи, мы должны были подбирать объект, — рассказывает она. — Но два года назад все остановилось. Хотели приобрести двухкомнатную квартиру в Новороссийске. Деньги лежат на арестованных счетах кооператива — а недвижимость за это время подорожала. Надеемся хоть что-то приобрести после того, как счета разблокируют».
«Мы всячески поддерживаем кооператив, — говорит Марина. — Записывали видео, что мы не обманутые, а вполне довольные пайщики, объясняли, что это никакая не пирамида, а организация, созданная в помощь людям. Ждем, когда снимут эти аресты. Сдаваться в планах нет».
Колокольцевская мафия «кинула» военных
«МВД провоцирует новый «Марш справедливости», только теперь не на Москву, а на Питер»
Тысячи военнослужащих стали потерпевшими от действий правоохранительных органов – и они требуют привлечь Колокольцева и Ко к ответу.
Деньги военных пытаются украсть лжеправоохранители
Приморский районный суд Санкт-Петербурга (судья Екатерина Богданова) сейчас рассматривает так называемое уголовное дело «Лайф-из-Гуд» – «Гермес» – «Бест Вей», в рамках этого дела два года почти непрерывно арестованы счета кооператива «Бест Вей», на которых около 4 млрд рублей. В уголовном деле речь идет прежде всего об обязательствах иностранной инвесткомпании «Гермес» перед более чем 200 клиентами этой компании.
Следствие ГУ МВД по Санкт-Петербургу и прокуратура города на Неве объявили кооператив, «Гермес» и «Лайф-из-Гуд» частью некоего единого холдинга, которого в природе никогда не существовало. Кооператив объявлен гражданским ответчиком по уголовному делу.
Общая сумма претензий потерпевших, согласно обвинительному заключению, 282 млн рублей – даже их (незаконное) изъятие для погашения долгов перед клиентами «Гермеса» никак бы не сказалось ни на операционной деятельности, ни на ликвидности кооператива. Но из раза в раз арестовываются абсолютно все средства на счетах, что полностью блокирует как покупку квартир кооперативом, так и возврат денег пайщикам, которые изъявили желание забрать свои паевые взносы.
Недвижимость, на которую претендовали пайщики, обесценивается, деньги обесцениваются – и этот беспредел продолжается уже более двух лет по ходатайствам ГСУ питерского главка МВД и Прокуратуры Санкт-Петербурга.
Кто-то влиятельный пытается наложить лапу именно на кооперативные 4 млрд – хотя это деньги пайщиков: физических лиц, рядовых граждан России, и как минимум соучастниками грабежа являются сотрудники правоохранительных органов.
Колокольцев провоцирует новый «Марш справедливости»
Кооператив изначально создавался военнослужащими – одной из его задач в 2014 году было решение жилищной проблемы военнослужащих, увольняемых в запас, эта задача сохранилась и в последующие годы. Из почти 20 тыс. его пайщиков – тысячи военнослужащих со всей России. Значительная часть из них – участники СВО.
Вот некоторые из наиболее характерных комментариев
«Я стоял в очереди на приобретение квартиры с помощью кооператива, но вот уже два года работа кооператива заблокирована правоохранительными органами – по беспределу, мои деньги обесцениваются. Я спрошу с каждого, кто в этом виноват!», – заявил один из военнослужащих, имеющий Орден Мужества.
«Я стоял в накопительной программе, – заявил участник одного из секретных подразделений, о котором рассказывал Первый канал. – Уже два года накапливать на квартиру на счете в кооперативе не могу, так как счета арестованы, забрать деньги я также не могу: правоохранительные органы незаконно отказываются возвращать средства. Это самый настоящий грабеж, за который нужно судить!»
«Купил квартиру с помощью кооператива, расплатился за нее с кооперативом, взяв кредит, – говорит пайщик К., кавалер ордена Суворова. –- Но так как недвижимость кооператива осенью прошлого года арестовывалась, Росреестр с моей квартиры арест не снял до сих пор, так как я не имею физической возможности на месяц или больше погрузиться в сутяжничество с ним, в хождение по судам, а жена сидит с маленьким ребенком. Квартиру я планировал продать, чтобы купить квартиру больше. Из-за действий лже-правоохранителей я вынужден и платить кредит, и не могу продать квартиру. Вернувшись, предъявлю ущерб питерским следователям, по ходатайству которых арестовывалась недвижимость кооператива (суд разобрался и арест снял)!»
«Кооперативом я очень доволен, – говорит пайщик С., замполит одного из подразделений. – Это покупка квартиры в рассрочку, переплата за квартиру минимальна, просто несопоставима с ипотекой. Кооператив вызывал полное доверие – в том числе и потому, что у руля стояли и стоят офицеры. Он помог тысячам людей – тысячам военным лишить квартирный вопрос. За попытками его уничтожить стоят банковские олигархи, чтобы не было альтернативы брать у них в ипотеку одну квартиру, а платить за две-три, а также нечистые на руку правоохранители. Подобные действия могут провоцировать новый «Марш справедливости», только теперь не на Москву, а на Питер!».
Сотни семей военнослужащих, в том числе участников СВО стали потерпевшими от действий правоохранительных органов.
Камарилья, которая устроила репрессии против кооператива – руководители следственной группы Сапетова и Винокуров, начальник ГСУ питерского главка МВД Негрозов и начальник этого главка Плугин, замминистра внутренних дел по следствию Лебедев, пресс-секретарь министра Волк, транслировавшая на всю страну ложь про десятки тысяч потерпевших от работы кооператива, сам министр внутренних дел Колокольцев.
Ищете качественную мебель для офиса? Рекомендую обратить внимание на мебель замм. Этот бренд предлагает широкий ассортимент офисной мебели, включая стильные и функциональные офисные столы. Продукция zamm отличается высоким качеством, долговечностью и современным дизайном. Идеально подходит для создания комфортного и продуктивного рабочего пространства. В ассортименте вы найдете всё, что нужно для организации современного офиса. Отличный выбор для тех, кто ценит надежность и стиль! С уважением, Zamm мебель.
Ищете качественную мебель для офиса? Рекомендую обратить внимание на мебель для офиса замм. Этот бренд предлагает широкий ассортимент офисной мебели, включая стильные и функциональные офисные столы. Продукция замм отличается высоким качеством, долговечностью и современным дизайном. Идеально подходит для создания комфортного и продуктивного рабочего пространства. В ассортименте вы найдете всё, что нужно для организации современного офиса. Отличный выбор для тех, кто ценит надежность и стиль! С уважением, Zamm мебель.
i-guru – Ремонт Iphone и другой техники Apple в Минске
[url=https://iphone-remont.by/remont-iphone]ремонт контроллера iphone[/url]
Профессиональный ремонт любых устройств из линейки Apple, без посредников
80% ремонтов iPhone занимает около 20 минут
Несложные ремонты делаются быстро, модульный ремонт в большинстве случаев занимает не более 20 минут.
Почему выбирают i-guru
Ремонт в тот же день
Даже большинство сложных ремонтов выполняем день в день.
Гарантировано низкие цены
Мы беремся за сложные задачи, не передавая их сторонним исполнителям, и зарабатываем не как посредники.
Честная гарантия
Предлагаем честную гарантию на выполненные работы до 12 месцев в зависимости от вида работ.
Ищете качественную мебель для офиса? Рекомендую обратить внимание на мебель для офиса замм. Этот бренд предлагает широкий ассортимент офисной мебели, включая стильные и функциональные офисные столы. Продукция zamm отличается высоким качеством, долговечностью и современным дизайном. Идеально подходит для создания комфортного и продуктивного рабочего пространства. В ассортименте вы найдете всё, что нужно для организации современного офиса. Отличный выбор для тех, кто ценит надежность и стиль! С уважением, Zamm мебель.
Ищете качественную мебель для офиса? Рекомендую обратить внимание на мебель для офиса замм. Этот бренд предлагает широкий ассортимент офисной мебели, включая стильные и функциональные офисные столы. Продукция замм отличается высоким качеством, долговечностью и современным дизайном. Идеально подходит для создания комфортного и продуктивного рабочего пространства. В ассортименте вы найдете всё, что нужно для организации современного офиса. Отличный выбор для тех, кто ценит надежность и стиль! С уважением, Zamm мебель.
Если вам нужны профессионалы в области продвижения сайтов и разработки, обратите внимание на Mihaylov Digital. Они предлагают полный спектр услуг: от SEO и SEM до работы с Яндекс.Директ. Команда специализируется на создании эффективных стратегий, которые помогают привлечь целевую аудиторию и увеличить видимость вашего бизнеса в интернете. Их профессионализм и подход к каждому клиенту гарантируют отличные результаты. Рекомендую Mihaylov Digital как надежного партнера в цифровом маркетинге! С уважением, Mihaylov Digital.
Для установки некоторых приложений может потребоваться обновление прошивки
Яндекс ТВ. Проверьте наличие обновлений в разделе
“Настройки” -> “Система” -> “Обновление системы”.
Если доступно обновление, установите его перед попыткой установки
приложения. Подробнее об обновлении системы: как установить приложение на яндекс тв
My brother suggested I might like this website. He used to be totally right. This publish actually made my day. You can not imagine just how much time I had spent for this info! Thank you!
Если вам нужны профессионалы в области продвижения сайтов и разработки, обратите внимание на Mihaylov Digital. Они предлагают полный спектр услуг: от SEO и SEM до работы с Яндекс.Директ. Команда специализируется на создании эффективных стратегий, которые помогают привлечь целевую аудиторию и увеличить видимость вашего бизнеса в интернете. Их профессионализм и подход к каждому клиенту гарантируют отличные результаты. Рекомендую Михайлов Дмитрий как надежного партнера в цифровом маркетинге! С уважением, Mihaylov Digital.
Если вам нужны профессионалы в области продвижения сайтов и разработки, обратите внимание на ООО”МД”. Они предлагают полный спектр услуг: от SEO и SEM до работы с Яндекс.Директ. Команда специализируется на создании эффективных стратегий, которые помогают привлечь целевую аудиторию и увеличить видимость вашего бизнеса в интернете. Их профессионализм и подход к каждому клиенту гарантируют отличные результаты. Рекомендую Михайлов Дмитрий как надежного партнера в цифровом маркетинге! С уважением, Mihaylov Digital.
Если вам нужны профессионалы в области продвижения сайтов и разработки, обратите внимание на ООО”МД”. Они предлагают полный спектр услуг: от SEO и SEM до работы с Яндекс.Директ. Команда специализируется на создании эффективных стратегий, которые помогают привлечь целевую аудиторию и увеличить видимость вашего бизнеса в интернете. Их профессионализм и подход к каждому клиенту гарантируют отличные результаты. Рекомендую Михайлов Дмитрий как надежного партнера в цифровом маркетинге! С уважением, Mihaylov Digital.
With Tezfiles Premium, enjoy numerous benefits for a low cost. This option not only boosts the service’s capabilities and introduces additional benefits that free account users can also enjoy.
[url=https://tezfiles.cc/]Tezfiles[/url]
Компания Септик-Нара-[url=https://septik-nara.ru/]купить септик для частного дома[/url]
занимается продажей, установкой и обслуживанием септиков в Наро-Фоминске Наро-Фоминском районе. Основное направление деятельности нашей компании именно установка под ключ септиков любых видов и размеров. С момента основания нашей компании, мы произвели монтаж более 1000 септиков по Московской и Калужской области. Благодаря этому у нас огромный опыт работы с любыми станциями, представленными в нашем регионе!
Если Вы решили купить септик для дома или дачи, мы с радостью поможем Вам с выбором модели, доставим и установим септик на вашем участке в кратчайшие сроки.
Мы занимаемся продажей септиков таких марок: Топас Юнилос Астра Евролос Тверь Аквалос Дочиста Фекалов Волгарь Удача. Мы работаем напрямую с производителями септиков, поэтому Вы можете быть уверены, что не переплачиваете ни копейки. Вся продукция в нашей компании имеет соответствующие сертификаты и лицензии. Время выезда на осмотр, установки или привоза оборудования согласовывается с клиентами и выполняется в срок. Мы заботимся о своей репутации, поэтому выполняем работу надежно и быстро.
Если Вы не знаете, какой септик больше всего Вам подходит, мы предоставим консультацию и выезд специалиста на Ваш участок абсолютно бесплатно!
Благодаря приобретению качественных септиков в нашей компании, каждый клиент получает большое количество преимуществ:
» компактные размеры и небольшой вес устройства;
» доступная стоимость очистной установки;
» быстрый и простой монтаж;
» невысокая стоимость эксплуатации;
» отсутствие неприятных запахов;
» высокая производительность;
» длительный срок эксплуатации;
» высокая степень очистки;
» практически полностью автономный режим работы.
Попробуйте свою удачу на Вавада казино, огромный выбор игр, Вавада казино – мир азарта и выигрышей, Получите адреналин от игры на Вавада казино, Станьте богаче с Вавада казино, крупные призы ждут вас, Играйте на Вавада казино и выигрывайте круглосуточно, Шанс на выигрыш в Вавада казино, выгодные предложения для игроков, заработайте крупный выигрыш, Побеждайте вместе с Вавада казино, играйте и становитесь богаче, получайте максимум азарта, играйте и выигрывайте в онлайн казино
[url=https://www.baby-country.ru/forum/topic.php?forum=29&topic=719] казино онлайн vavada [/url]
Если у вас есть ключ от домофона,
но вы хотите узнать код для гостей, попробуйте найти инструкцию
к вашей модели домофона. В некоторых моделях есть
функция отображения кода на дисплее при определенной
комбинации клавиш. Инструкции по использованию различных моделей домофонов доступны на как узнать код домофона в своем подъезде.
Ищете переводчик, который не подведет в критический момент?
На странице https://teletype.in/@golosai/kakoi-perevodchik-rabotaet-bez-interneta вы
найдете обзор приложений,
работающих без интернета.
Будьте готовы к любым языковым ситуациям!
A fairly new player in the Russian darknet arena, [url=https://bs-gl-darknet.com]blacksprut[/url] Blacksprut has quickly gained attention for its interesting features and growing popularity. While some aspects raise questions, it has the potential to become a prominent figure in the darknet scene.
Features:
Blacksprut https://bs-gl-darknet.com offers an “Instant Transactions” feature, inspired by the success of similar systems on other platforms like Hydra. Couriers hide goods within the city and provide buyers with coordinates, adding an adventurous element to the purchasing process.
슬롯 쿠폰
어린왕자 보르지진 바투멩케부터…
하바네로 슬롯
가재는 특히 장시와 같은 환경에서 먹이기 쉽습니다.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Привет всем!
Штампы для медицинских страховых компаний
Медицинские страховые компании часто нуждаются в специальных штампах для оформления страховой документации и отчетов. Мы предлагаем изготовление штампов для медицинских страховых компаний, которые помогут вам быстро и эффективно оформлять документы и отметки. Наши штампы изготавливаются из качественных материалов и обеспечивают чёткие оттиски, что упрощает работу и повышает эффективность документооборота. Обеспечьте порядок и организацию работы вашей медицинской страховой компании с нашими штампами!
Более подробно на сайте – https://www.moipechati.ru/pechati-i-shtampi/latunnye/
купить экслибрис
заказать печать ип
печати на заказ москва
изготовление печатей рядом со мной
печати цветные
[url=https://www.moipechati.ru/]изготовление печати[/url]
Удачи!
I¦ll right away seize your rss feed as I can not to find your e-mail subscription link or newsletter service. Do you have any? Please let me recognize in order that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
nazilli apart otel
맥심 슬롯
물론 이것은 단지 세부 사항 일 뿐이며 모두가 갑자기 마음 속으로 깨달았습니다.
Hi Neat post Theres an issue together with your web site in internet explorer may test this IE still is the marketplace chief and a good component of people will pass over your fantastic writing due to this problem
МОСКВА, 7 мая — РИА Новости. Правительство России, возглавляемое Михаилом Мишустиным, уйдет в отставку во вторник.
Сразу после инаугурации президента Владимира Путина нынешний кабинет министров сложит полномочия перед вступившим в должность главой государства.
[url=https://xrumer.us/]Прогон по комментария[/url]
Звон Колокольцева. Питерская полицейская мафия виляет Министерством внутренних дел
[url=https://compromat-base.com/kriminal/item/454419-zvon-kolokoltseva-piterskaya-politsejskaya-mafiya-vilyaet-ministerstvom-vnutrennikh-del]Кооператив Бествей[/url]
Поздравляем вас, гражданин министр, соврамши!
Выступая прошлой осенью в Совете Федерации, министр внутренних дел Владимир Колокольцев рассказывал, о так называемом уголовном деле «Лайф-из-Гуд» – «Гермес» – «Бест Вей», обещал миллиарды рублей ущерба и десятки тысяч потерпевших. Пресс-служба МВД под руководством его боевой подруги Ирины Волк заявила о том, что вскрыта деятельность крупнейшей в истории России финансовой пирамиды.
Однако в уголовном деле, расследованном или, вернее сказать, изготовленном ГСУ питерского главка МВД, которое в феврале начал рассматривать Приморский районный суд Санкт-Петербурга, 282 млн рублей ущерба и 221 лицо, признанное следствием потерпевшим: никаких миллиардов и десятков тысяч потерпевших.
Министр и его Волк публично солгали – на основе информации, переданной замначальника ГСУ руководителем следственной группы полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, фактически даже руководившей СГ его заместительницей майором, а затем подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой по материалам, состряпанным опером УЭБиПК питерского главка МВД майором полиции А.Ю. Машевским, при попустительстве (или соучастии?) начальника ГСУ Негрозова и замначальника Следственного департамента федерального министерства Вохмянина. Полковник и подполковник с примерно пятого-шестого уровня иерархии МВД виляет генералом полиции Российской Федерации, постоянным членом Совета безопасности России – это позор для государства.
Так называемые потерпевшие и реально пострадавшие
Большинство «потерпевших» на суде заявляют суммы около 1–2 млн рублей, при этом в ходе судебного следствия выясняется, что они, как правило, получали немалый доход, причем, они еще и налоговые/валютные преступники, так как этот доход не декларировали. Среди «потерпевших» есть граждане, заявляющие смехотворные суммы в 50–70 тыс., то есть количество потерпевших специально накручивалось следствием. И даже с этим накручиванием удалось набрать так мало – учитывая, что у «Гермеса», по данным самого же следствия, более 200 тыс. клиентов в России, а в кооперативе «Бест Вей» – около 20 тыс. пайщиков.
То есть большинство и клиентов «Гермеса», и пайщиков кооператива не считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности этих организаций.
Судя по тысячам обращений во все инстанции, нескольким волнам митингов, прокатившихся по России, они считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности органов внутренних дел.
Ведь именно завербованный питерским УЭБиПК сисадмин российской платежной системы «Гермеса» Набойченко заблокирован и разгромил в феврале 2022 года эту платежную систему, повесив на сайте дисклеймер: «Обращайтесь в правоохранительные органы», что на месяцы прекратило вывод средств. Именно действия правоохранительных органов в отношении компании до и после затруднили вывод средств. Дело в том, что для вывода средств многими использовался механизм p2p, позволяющий не платить комиссию, то есть для вывода средств нужно, чтобы кто-то вносил средства (что, понятно, резко сократилось из-за уголовного дела) и происходил обмен. Однако этот способ не единственный, вывод средств так или иначе осуществляется.
Тысячи пайщиков кооператива тем более не считают себя потерпевшими от его деятельности – потому что именно правоохранительные органы воспрепятствовали приобретению недвижимости с помощью кооператива, а она из-за более чем двухлетнего ареста его счетов, на которых около 4 млрд рублей, не может быть приобретена по прежней цене.
Именно правоохранительные органы прямо запрещают выплаты пайщикам кооператива, решившим забрать свой пай, – даже по исполнительным листам судов. И клиентам «Гермеса», и пайщикам кооператива правоохранительными органами нанесен колоссальный ущерб – и материальный, и моральный, который они намерены взыскать с государства.
«Следователи»-преступники должны сидеть в тюрьме
Весьма скромный результат следствия МВД был достигнут откровенно преступным путем.
[url=https://compromat-base.com/kriminal/item/454419-zvon-kolokoltseva-piterskaya-politsejskaya-mafiya-vilyaet-ministerstvom-vnutrennikh-del]Что с судом Гермес[/url]
1. Некоторые из преступлений следствия были фактически признаны судами. 1 декабря прошлого года Приморский районный суд города Санкт-Петербурга признал незаконным, нарушающим УПК фактический отказ кооперативу в ознакомлении с материалами уголовного дела.При рассмотрении дела в суде выяснилось, что следственная группа ГСУ питерского главка МВД, формально руководимая замначальника ГСУ полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, а фактически – подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой, подделала документы. Автор подделки – Сапетова – еще в феврале была уволена из ГСУ «по собственному желанию».
Уличенная адвокатами кооператива в нарушении УПК, следственная группа составила письмо об удовлетворении ходатайства задним числом и попыталась представить дело так, что кооператив не получил письмо по своей вине. Ложь была выявлена в том числе и с помощью системы электронного документооборота питерского главка МВД.
2. Подделка документов была вынужденным преступлением для сокрытия более серьезного: незаконного содержания под стражей. Следственная группа грубо нарушила права гражданских истцов и ответчиков, потому что без этого нарушения она не успела за 30 суток до истечения предельного срока содержания четверых обвиняемых под стражей начать ознакомление обвиняемых с материалами дела –а это было единственное основание продления им срока содержания под стражей свыше предельного.
Следственная группа из-за спешки даже толком не смогла завершить следственные действия, незаконно вела параллельное расследование по «резервному» делу, но позднее, отбросив стыд, из-за отсутствия материала для составления «нужного» обвинительного заключения, незаконно продолжила расследование «основного» дела, в том числе проводила следственные действия, которые, согласно УПК, невозможны после начала ознакомления обвиняемых с материалами дела. Все эти ухищрения были необходимы для того, чтобы ни в коем случае не выпускать обвиняемых и продолжать держать их в заложниках.
3. Де-факто происходит уголовное наказание неосужденных людей – четверо подсудимых уже второй год сидят в тюрьме. При этом наказываются явно ни в чем неповинные люди – технические сотрудники «Лайф-из-Гуд»: даже если предположить, что действительно работала пирамида – что опровергается показаниями свидетелей самого обвинения, которые сообщают суду, что компания «Гермес» хорошо работала, они были довольны получаемым доходом, и проблемы начались после того, как российская платежная система компании была обрушена завербованным полицией петербургским сисадмином компании Набойченко. Все подсудимые – технические сотрудники компании «Лайф-из-Гуд» и ни к каким управленческим решениям отношения никогда не имели. Их взяли в заложники для того, чтобы они дали показания на руководство компании.
4. Еще одно преступление – заведомо подложное постановление руководителя следственной группы А.Н. Винокурова о привлечении кооператива «Бест Вей» в качестве гражданского ответчика на 16 млрд рублей, тогда как сумма ущерба в уголовном деле –282 млн, и в деле нет ни одного искового заявления – даже на 100 рублей.
5. Следствие стимулировало двух особенно активных так называемых потерпевших написать заявления о моральном ущербе на миллиард (!) рублей каждое – исключительно для ложного обоснования ареста активов кооператива, но понятно, что это ничтожные документы, так как моральный ущерб во всех случаях, не связанных с причинением смерти, присуждается российскими судами в размере не более десятков тысяч рублей.
6. Ни один из «потерпевших» не доказал обоснованность своих претензий в гражданском суде. При этом арестованы активы кооператива почти на 4 млрд рублей и активы частных лиц на такую же сумму. Это не что иное, как попытка захвата активов при участии органов внутренних дел некой заинтересованной группой клиентов «Гермеса» – необязательно из числа «потерпевших», то есть коррупционное преступление, которое упорно игнорирует ГУСБ МВД.
Механизм для такого захвата есть – это передача средств под управление Федерального общественно-государственного фонда по защите прав вкладчиков и акционеров. Понятно, почему не ограничиваются активами подсудимых и обвиняемых: этого недостаточно для удовлетворения аппетитов тех, кто стоит за заказным уголовным делом. И понятно, почему одно юридическое лицо – кооператив «Бест Вей» – незаконно пытаются привлечь к ответственности за другое – компанию «Гермес»: активы «Гермеса» – за рубежом.
7. Следствие, а теперь и прокуратура совершают еще одно преступление: незаконно удерживает средства пайщиков кооператива, отказываясь их вернуть, то есть совершают хищение.
Звон Колокольцева. Питерская полицейская мафия виляет Министерством внутренних дел
[url=https://compromat-base.com/kriminal/item/454419-zvon-kolokoltseva-piterskaya-politsejskaya-mafiya-vilyaet-ministerstvom-vnutrennikh-del]Ситуация с ПК Бествей[/url]
Поздравляем вас, гражданин министр, соврамши!
Выступая прошлой осенью в Совете Федерации, министр внутренних дел Владимир Колокольцев рассказывал, о так называемом уголовном деле «Лайф-из-Гуд» – «Гермес» – «Бест Вей», обещал миллиарды рублей ущерба и десятки тысяч потерпевших. Пресс-служба МВД под руководством его боевой подруги Ирины Волк заявила о том, что вскрыта деятельность крупнейшей в истории России финансовой пирамиды.
Однако в уголовном деле, расследованном или, вернее сказать, изготовленном ГСУ питерского главка МВД, которое в феврале начал рассматривать Приморский районный суд Санкт-Петербурга, 282 млн рублей ущерба и 221 лицо, признанное следствием потерпевшим: никаких миллиардов и десятков тысяч потерпевших.
Министр и его Волк публично солгали – на основе информации, переданной замначальника ГСУ руководителем следственной группы полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, фактически даже руководившей СГ его заместительницей майором, а затем подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой по материалам, состряпанным опером УЭБиПК питерского главка МВД майором полиции А.Ю. Машевским, при попустительстве (или соучастии?) начальника ГСУ Негрозова и замначальника Следственного департамента федерального министерства Вохмянина. Полковник и подполковник с примерно пятого-шестого уровня иерархии МВД виляет генералом полиции Российской Федерации, постоянным членом Совета безопасности России – это позор для государства.
Так называемые потерпевшие и реально пострадавшие
Большинство «потерпевших» на суде заявляют суммы около 1–2 млн рублей, при этом в ходе судебного следствия выясняется, что они, как правило, получали немалый доход, причем, они еще и налоговые/валютные преступники, так как этот доход не декларировали. Среди «потерпевших» есть граждане, заявляющие смехотворные суммы в 50–70 тыс., то есть количество потерпевших специально накручивалось следствием. И даже с этим накручиванием удалось набрать так мало – учитывая, что у «Гермеса», по данным самого же следствия, более 200 тыс. клиентов в России, а в кооперативе «Бест Вей» – около 20 тыс. пайщиков.
То есть большинство и клиентов «Гермеса», и пайщиков кооператива не считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности этих организаций.
Судя по тысячам обращений во все инстанции, нескольким волнам митингов, прокатившихся по России, они считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности органов внутренних дел.
Ведь именно завербованный питерским УЭБиПК сисадмин российской платежной системы «Гермеса» Набойченко заблокирован и разгромил в феврале 2022 года эту платежную систему, повесив на сайте дисклеймер: «Обращайтесь в правоохранительные органы», что на месяцы прекратило вывод средств. Именно действия правоохранительных органов в отношении компании до и после затруднили вывод средств. Дело в том, что для вывода средств многими использовался механизм p2p, позволяющий не платить комиссию, то есть для вывода средств нужно, чтобы кто-то вносил средства (что, понятно, резко сократилось из-за уголовного дела) и происходил обмен. Однако этот способ не единственный, вывод средств так или иначе осуществляется.
Тысячи пайщиков кооператива тем более не считают себя потерпевшими от его деятельности – потому что именно правоохранительные органы воспрепятствовали приобретению недвижимости с помощью кооператива, а она из-за более чем двухлетнего ареста его счетов, на которых около 4 млрд рублей, не может быть приобретена по прежней цене.
Именно правоохранительные органы прямо запрещают выплаты пайщикам кооператива, решившим забрать свой пай, – даже по исполнительным листам судов. И клиентам «Гермеса», и пайщикам кооператива правоохранительными органами нанесен колоссальный ущерб – и материальный, и моральный, который они намерены взыскать с государства.
«Следователи»-преступники должны сидеть в тюрьме
Весьма скромный результат следствия МВД был достигнут откровенно преступным путем.
[url=https://compromat-base.com/kriminal/item/454419-zvon-kolokoltseva-piterskaya-politsejskaya-mafiya-vilyaet-ministerstvom-vnutrennikh-del]ЖК Бествей[/url]
1. Некоторые из преступлений следствия были фактически признаны судами. 1 декабря прошлого года Приморский районный суд города Санкт-Петербурга признал незаконным, нарушающим УПК фактический отказ кооперативу в ознакомлении с материалами уголовного дела.При рассмотрении дела в суде выяснилось, что следственная группа ГСУ питерского главка МВД, формально руководимая замначальника ГСУ полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, а фактически – подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой, подделала документы. Автор подделки – Сапетова – еще в феврале была уволена из ГСУ «по собственному желанию».
Уличенная адвокатами кооператива в нарушении УПК, следственная группа составила письмо об удовлетворении ходатайства задним числом и попыталась представить дело так, что кооператив не получил письмо по своей вине. Ложь была выявлена в том числе и с помощью системы электронного документооборота питерского главка МВД.
2. Подделка документов была вынужденным преступлением для сокрытия более серьезного: незаконного содержания под стражей. Следственная группа грубо нарушила права гражданских истцов и ответчиков, потому что без этого нарушения она не успела за 30 суток до истечения предельного срока содержания четверых обвиняемых под стражей начать ознакомление обвиняемых с материалами дела –а это было единственное основание продления им срока содержания под стражей свыше предельного.
Следственная группа из-за спешки даже толком не смогла завершить следственные действия, незаконно вела параллельное расследование по «резервному» делу, но позднее, отбросив стыд, из-за отсутствия материала для составления «нужного» обвинительного заключения, незаконно продолжила расследование «основного» дела, в том числе проводила следственные действия, которые, согласно УПК, невозможны после начала ознакомления обвиняемых с материалами дела. Все эти ухищрения были необходимы для того, чтобы ни в коем случае не выпускать обвиняемых и продолжать держать их в заложниках.
3. Де-факто происходит уголовное наказание неосужденных людей – четверо подсудимых уже второй год сидят в тюрьме. При этом наказываются явно ни в чем неповинные люди – технические сотрудники «Лайф-из-Гуд»: даже если предположить, что действительно работала пирамида – что опровергается показаниями свидетелей самого обвинения, которые сообщают суду, что компания «Гермес» хорошо работала, они были довольны получаемым доходом, и проблемы начались после того, как российская платежная система компании была обрушена завербованным полицией петербургским сисадмином компании Набойченко. Все подсудимые – технические сотрудники компании «Лайф-из-Гуд» и ни к каким управленческим решениям отношения никогда не имели. Их взяли в заложники для того, чтобы они дали показания на руководство компании.
4. Еще одно преступление – заведомо подложное постановление руководителя следственной группы А.Н. Винокурова о привлечении кооператива «Бест Вей» в качестве гражданского ответчика на 16 млрд рублей, тогда как сумма ущерба в уголовном деле –282 млн, и в деле нет ни одного искового заявления – даже на 100 рублей.
5. Следствие стимулировало двух особенно активных так называемых потерпевших написать заявления о моральном ущербе на миллиард (!) рублей каждое – исключительно для ложного обоснования ареста активов кооператива, но понятно, что это ничтожные документы, так как моральный ущерб во всех случаях, не связанных с причинением смерти, присуждается российскими судами в размере не более десятков тысяч рублей.
6. Ни один из «потерпевших» не доказал обоснованность своих претензий в гражданском суде. При этом арестованы активы кооператива почти на 4 млрд рублей и активы частных лиц на такую же сумму. Это не что иное, как попытка захвата активов при участии органов внутренних дел некой заинтересованной группой клиентов «Гермеса» – необязательно из числа «потерпевших», то есть коррупционное преступление, которое упорно игнорирует ГУСБ МВД.
Механизм для такого захвата есть – это передача средств под управление Федерального общественно-государственного фонда по защите прав вкладчиков и акционеров. Понятно, почему не ограничиваются активами подсудимых и обвиняемых: этого недостаточно для удовлетворения аппетитов тех, кто стоит за заказным уголовным делом. И понятно, почему одно юридическое лицо – кооператив «Бест Вей» – незаконно пытаются привлечь к ответственности за другое – компанию «Гермес»: активы «Гермеса» – за рубежом.
7. Следствие, а теперь и прокуратура совершают еще одно преступление: незаконно удерживает средства пайщиков кооператива, отказываясь их вернуть, то есть совершают хищение.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Paketi Skype: By_uMuT@KRaLBenim.Com -_- live:by_umut
Greetings to the romantics and casino lovers!!
Glory Casino offers quality and reliability. There are bonuses for new players, high betting odds, and fast withdrawals. The working mirror is always available. I play and win with pleasure. I recommend trying it!
Glory Casino is the place where you win. I bet on sports and play in the casino with pleasure. The working mirror is always available, and withdrawals are fast. The official site is convenient and reliable. I recommend it to everyone!
Catch the site where everything is in the best shape! – [url=https://prpelizz.blogspot.com/2024/06/glory-casino-your-destination-for-fish.html]Glory Casino[/url]
Glory Casino official bookmaker
Glory Casino bookmaker’s office mirror
does Glory Casino withdraw money
Glory Casino official website mirror
Glory Casino slots
Good profits!